Changes in insulin resistance and inflammatory factors in cataract patients with glaucoma after phacoemulsification and trabeculectomy: a self-controlled trial
2019-10-12JianFengZhaoYuGengQianBoChenJingHuiYangYanLi
Jian-Feng Zhao, Yu Geng, Qian-Bo Chen, Jing-Hui Yang, Yan Li
Department of Ophthalmology, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, Yunnan Province, China
Abstract
Key words:cataract; cinterleukin; C-reactive protein; glaucoma; insulin resistance; insulin sensitivity index; orneal endothelial cells; phacoemulsification; trabeculectomy; tumor necrosis factor-α
INTRODUCTION
Background
Cataract is an ophthalmic disease characterized by opacity of the lens as the main pathological change, and is an important cause of blindness.1-4Glaucoma is characterized by atrophy of the optic papilla, depression, and decreased vision, and can cause blindness in humans.5,6The concurrent occurrence of glaucoma and cataract can adversely affect visual acuity and corneal endothelial cells in patients, and severely reduce their quality of life.7-10Therefore, effective early diagnosis of glaucoma with cataract is needed.
Phacoemulsification plays an increasingly important role in the treatment of cataract.11-14Trabeculectomy allows drainage of aqueous humor from within the eye to underneath the conjunctiva where it is absorbed.15Insulin resistance is a decrease in the body's sensitivity to insulin, and contributes to the pathological progression of various ophthalmic diseases.16,17Inflammatory factors such as interleukin and C-reactive proteinare the main mediators of the inflammatory response and are strongly associated with the pathogenesis of ocular diseases such as cataract.18,19However, there are few reports on the changes in inflammatory factors and insulin resistance in patients with cataract and glaucoma treated with phacoemulsification combined with trabeculectomy.
The first author retrieved PubMed papers published from 2017 to 2018 using the search terms “cataract,” “glaucoma” and “interleukin.” The three latest clinical studies on inflammatory factor changes in cataract and/or glaucoma patients in China were screened (Table 1).20-22
Objective
In this planned trial, we will examine insulin resistance and the efficacy of phacoemulsification combined with trabeculectomy in cataract patients with glaucoma to provide a rational basis for clinical treatment.
PARTICIPANTS/METHODS
Design
Prospective, single-center, open-label, self-controlled clinical trial.
Setting
Department of Ophthalmology, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, China.
Investigator qualification
All physicians performing phacoemulsification and trabeculectomy in this study will receive professional medical training and will be skilled surgeons. They will be associate chief physician, and have more than 10 years of clinical experience in the Department of Ophthalmology.
Participants
Recruitment
Before publishing the recruitment information, the protocol and the content of the recruitment announcement will be approved by the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University.
A research recruitment notice will be sent to patients and their family members in the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University to recruit patients who are interested in participating in the trial.
Patients and their family members who receive the leaflet will read the leaflet carefully. If they decide to participate in the trial, they can contact the investigator by telephone. After undergoing screening procedures and providing written informed consent, eligible individuals will be included in the trial.
Patients will be given the latest treatment information in information sessions before beginning the clinical trial, and will receive close follow-up from the professional medical team of our hospital for free. The laboratory examination and registration fees will be waived during follow-up.
Inclusion criteria
- Diagnosis of glaucoma combined with cataract in accordance with the criteria formulated by the Ophthalmological Branch of the Chinese Medical Association23
- Effective drug treatment cannot be carried out, confirmed by ophthalmologists in the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University (no significant improvement in the best corrected visual acuity after treatment)
- Age range, 35-65 years, irrespective of sex
- Irrespective of disease in the left or right eye
- Provision of written informed consent
- Primary angle-closure glaucoma
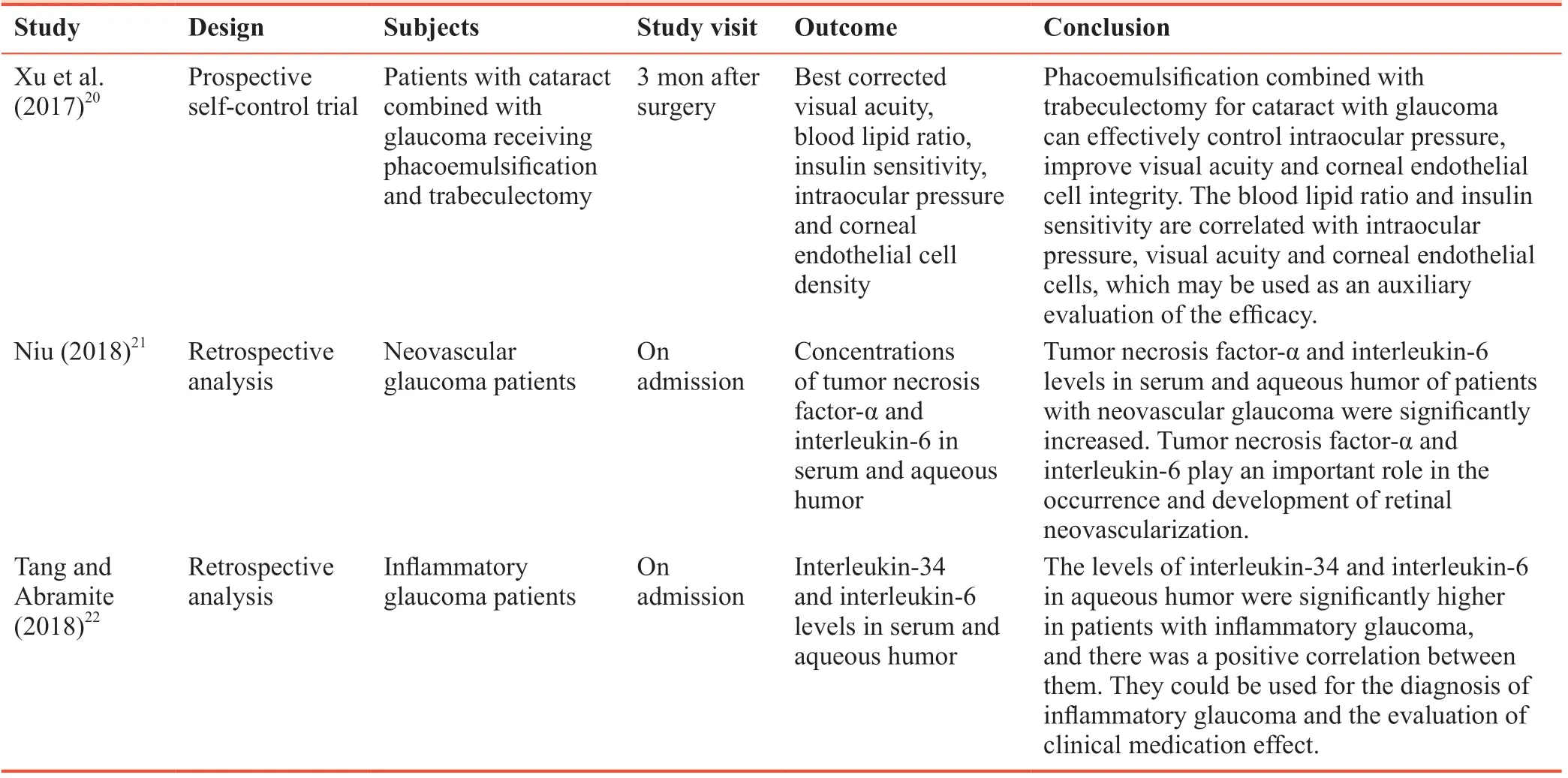
Table 1: Three Chinese most representative clinical trials addressing inflammatory factor changes in cataract and/or glaucoma patients from 2017 to 2018
Exclusion criteria
- Concurrently participating in other ophthalmic treatments
- High myopia
- Keratitis
- Diabetes
- Nervous system diseases
- Cardiac or renal dysfunction
Provision of insurance
Participants who participate in this clinical trial will be required to have inpatient medical insurance, and the majority of medical expenses during hospitalization will be paid by the insurance company in proportion to the medical insurance contract.
Interventions
Preoperative preparation
All patients will be treated with intraocular pressure control before phacoemulsification combined with trabeculectomy. Pilocarpine (Anhui Shuangke Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China; GYZZ H20058062, 5 mL:25 mg, one drop every 5-10 minutes for 3-6 times, then every 1-3 hours, until the intraocular pressure is reduced) will be used to ensure intraocular pressure of no more than 30 mmHg.
Phacoemulsification
Phacoemulsification will be performed after mydriasis and anesthesia, and ensuring that the angle of the ocular chamber is below 180°. Appropriate intraocular lens implantation will be selected for trabeculectomy. Intraocular lens (Alcon Laboratories Incorporated; GXZJ20153221306; three-piece/posterior chamber, foldable, modified C-shaped loop) will be used. The optical part is made of acrylate and methacrylate materials containing ultraviolet absorbent, and the loops are made of PMMA materials; spherical, single focal; ethylene oxide sterilization, disposable. It is suitable for the replacement of human lens and the implantation of lens after extracapsular cataract surgery or phacoemulsification in adults. The brief procedure of trabeculectomy is as follows: (1) Eyelid opening and eyeball fixation; (2) conjunctival flaps: fornix is the basal conjunctival flap; corneal limbus as the basal conjunctival flaps; (3) scleral flaps: scleral plate separation; (4) trabecular removal; (5) iris removal; (6) stratified suture of sclerae and conjunctival flaps; and (7) anterior chamber forming.
Postoperative treatment
The patients will be treated with routine Tobradex eye ointment (S.A. Alcon Couvreur N.V., Puurs, Belgium; approval No. H20160337; three or four times a day, applying 1.0-1.5 cm long ointment to conjunctival sac each time) and routine anti-infective therapy using tobramycin-dexamethasone eye drops (Shanghai Xinyi Jinzhu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China; GYZZ H20067439; 1-2 drops every 5 hours; for serious cases, every 3 hours). Antihypertensive drugs (pilocarpine; Anhui Shuangke Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; GYZZ H20058062, 5 mL:25 mg, one drop every 5-10 minutes for 3-6 times, then every 1-3 hours) will be used to control intraocular pressure below 21 mmHg.
Follow-up
All patients will be followed up at 5 days, and at 1 and 3 months by telephone by the outpatient department. Detailed data of laboratory tests will be recorded during follow-up, and the occurrence of adverse events during follow-up will be carefully observed.
Outcome measures
Primary outcome measure
Serum interleukin-2 levels, used to assess the inflammatory response, 3 months after surgery. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) will be used to measure serum interleukin-2 levels using the RT-6000 microplate reader (Rayto Ltd., Shenzhen, China) and reagents purchased from R&D Systems, Oxon, UK.
Secondary outcome measures
- Interleukin-2 level before and 5 days and 1 month after surgery, measured by ELISA, as described above.
- Levels of interleukin-1β, interleukin-10, C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor-α before and 5 days, and 1 and 3 months after surgery, measured by ELISA, as described above.
- Best corrected visual acuity, endothelial cell density, mean cell area, coefficient of variation before and 5 days, and 1 and 3 months after surgery: The best corrected visual acuity is the corrected naked vision. Corneal endothelial cells will be photographed using a corneal endothelial microscope. The corneal endothelial cell density, mean cell area and coefficient of variation of cell area will be measured with the non-contact corneal endothelial microscope. Corneal endothelial cells are generally responsible for the nutrient metabolism and material transport of the cornea. The decrease in the number of corneal endothelial cells indicates the improvement of corneal function.
- Insulin sensitivity index before and 5 days, and 1 and 3 months after surgery. Insulin sensitivity index = 1/(fasting insulin × fasting blood glucose). Insulin sensitivity index describes the degree of insulin resistance. The lower the insulin sensitivity, the weaker the effect of insulin per unit, and the lower the degree of sugar decomposition.
- Intraocular pressure before and 5 days, and 1 and 3 months after surgery. Intraocular pressure refers to the pressure of the intraocular fluid in the eyeball, measured with a manometer (Huaian Antel Instrument Factory, Huaian, China).
- Incidence of adverse reactions at 5 days and 1 and 3 months after surgery: Adverse reactions will be monitored after surgery in the two groups. Incidence of adverse reactions = (number of patients with adverse reactions during followup/total number of patients) × 100%.
The schedule for primary and secondary outcome measures is given in Table 2.
Sample size
Based on the number of hospitalized patients with cataract and glaucoma in recent years in the Department of Ophthalmology, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University (approximately 180 cases per year), we anticipate recruiting atleast 150 patients during the recruitment period (2019-12-30 to 2020-12-30). Assuming a patient loss rate of 5%, an initial sample size ofn= 160 will be used, approximately twice the size of the small sample test.
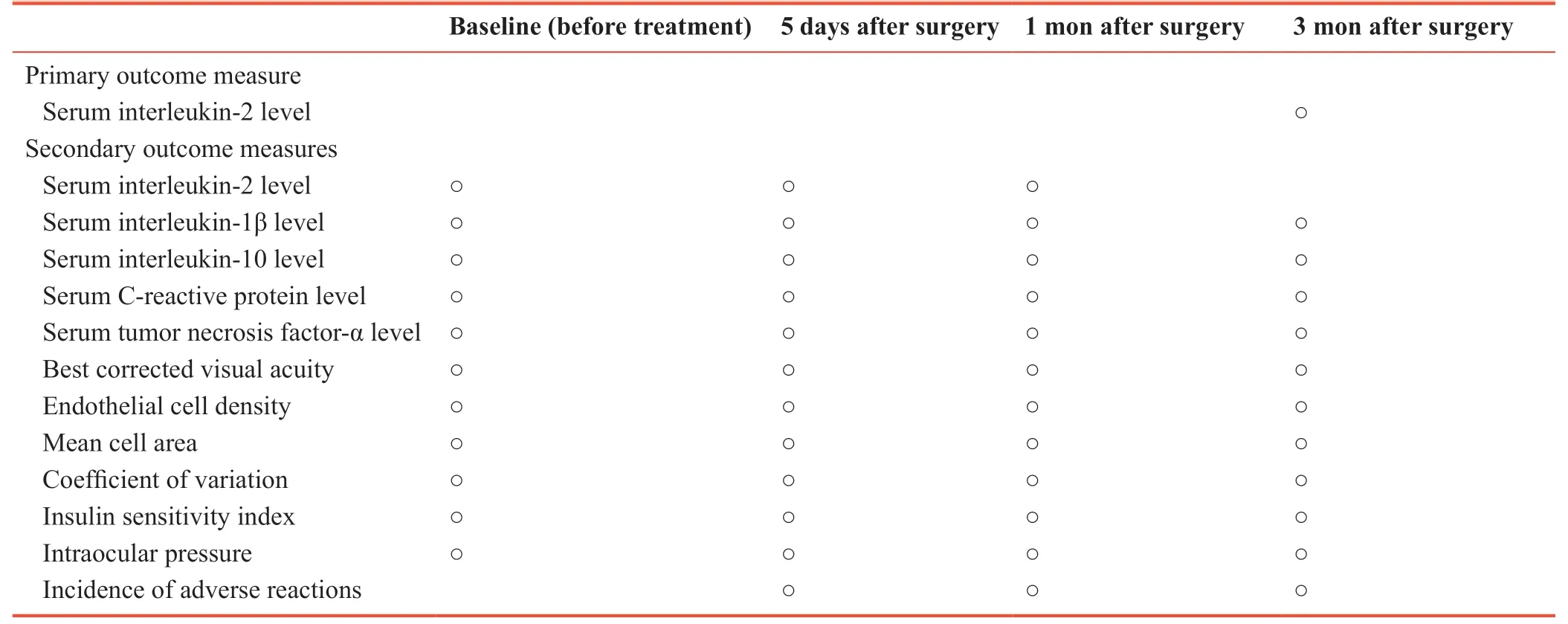
Table 2: Timing of primary and secondary outcome measures
Randomization
Randomized grouping will not be used in this trial.
Blinding method
The assessors will be unaware of the test plan, and the blind method will be used.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Com-mittee, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, China on December 15, 2013 (approval No. 20131215085; Additional file 1). This study will be performed in accordance with the principles of theDeclaration of Helsinki. Study protocol version is 1.0. The writing and editing of the article will be performed in accordance with the Transparent Reporting of Evaluations with Nonrandomized Designs (TREND) (Additional file 2).
Informed consent
Patients and their family members will participate in the trial voluntarily. All patients will sign the informed consent on the premise of fully understanding the treatment plan (Additional file 3).
Statistical analysis
All data will be statistically analyzed using SPSS 24.0 software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Measurement data will be expressed as mean; standard deviation; median, minimum, and maximum values; and upper and lower quartiles. Count data will be expressed as number and percentage.
Serum levels of interleukin-2, interleukin-1β, interleukin-10, C-reactive protein and tumor necrosis factor-α, best corrected visual acuity, endothelial cell density, mean cell area, coefficient of variation, insulin sensitivity index and intraocular pressure at various time points will be compared using repeated-measures analysis of variance and least significant difference test. Incidence of adverse reactions will be compared using Pearson's chi-square test in both groups. Pearson linear correlation analysis will be used to analyze the correlation between inflammatory factors and insulin sensitivity index. The significance level (two-sided) will beα= 0.05.
All included patients will be assigned to the per-protocol set.
RESULTS
Flow chart
The study flow chart is shown in Figure 1.
Patients intended to be recruited into the trial
We anticipate that 160 patients will be recruited from December 30, 2019 to December 30, 2020.
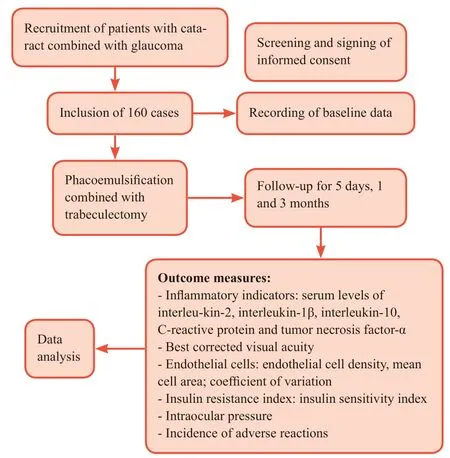
Figure 1: Trial flow chart.
Baseline requirements for prospective recruits
The patient baseline data, including age, sex, side of the affected eye and duration of illness, will be recorded in detail before surgery.
Expected outcome measures
Serum levels of interleukin-2, interleukin-1β, interleukin-10, C-reactive protein and tumor necrosis factor-α, best corrected visual acuity, endothelial cell density, mean cell area, coefficient of variation, insulin sensitivity index, intraocular pressure and incidence of adverse reactions during follow-up will be recorded in detail.
Expected possible adverse reactions
The main adverse reactions expected to be observed during the trial are intraocular and corneal edema, anterior chamber hemorrhage, conjunctival superficial dehiscence and anterior chamber exudation.
Adverse event report stipulates that if adverse events occur after phacoemulsification combined with trabeculectomy, the report time limit is 24 hours. Irrespective of the treatment a subject receives, any adverse events that occur will be treated immediately.
If serious adverse events such as bleeding, coma or shock, prolonged hospitalization, continuous functional loss and lifethreatening caused by unforeseen factors occur, the clinician will report the serious adverse event(s) to the project manager within 1 hour and take corresponding emergency treatment measures.
Small-sample-size study results
Baseline data
The small sample included 80 patients (95 eyes) with cataract combined with glaucoma undergoing phacoemulsification combined with trabeculectomy in the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2014 to June 2017. The patients included 43 males (24 affected in the left eye and 28 affected in the right eye) and 37 females (20 affected in the left eye and 23 affected in the right eye), with a mean age of 47.5 ± 11.4 years.
Postoperative follow-up results analysis
After phacoemulsification combined with trabeculectomy, the best corrected visual acuity was significantly improved, endothelial cell density was significantly decreased (P< 0.05), while mean cell area and coefficient of variation were significantly increased (P< 0.05; Table 3).
After phacoemulsification combined with trabeculectomy, insulin sensitivity index was significantly increased and intraocular pressure was significantly decreased (P< 0.05; Table 4).
After phacoemulsification combined with trabeculectomy, the levels of interleukin-1β, interleukin-2, interleukin-10, Creactive protein and tumor necrosis factor-α were significantly decreased (P< 0.05; Table 5).
Analysis of adverse reactions
No significant adverse reactions occurred during the treatment in any subject.
DISCUSSION
Study limitations
The study does not include a control group, or randomized or blind grouping. The long-term efficacy (beyond 1 year) will not be explored. It is a self-controlled trial. The limitations might affect the reliability of the test results. The team will use multi-center, large-sample, randomized controlled trials in future studies to more rigorously verify the effectiveness of the treatment method.
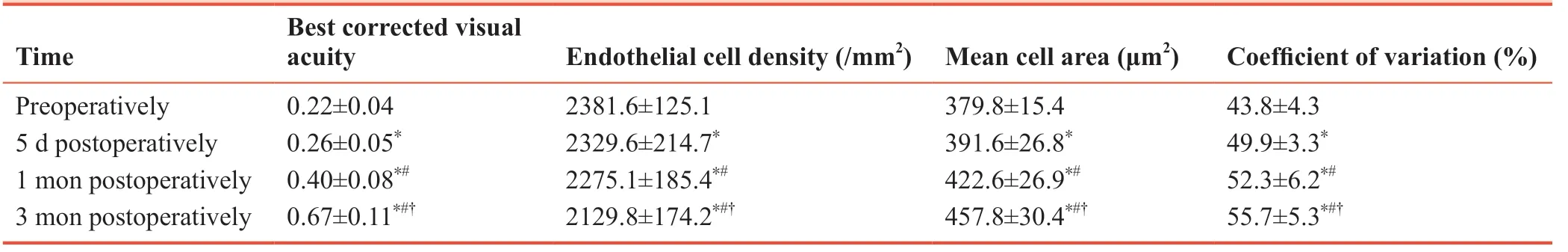
Table 3: Analysis of best corrected visual acuity and changes of corneal endothelial cells after phacoemulsification combined with trabeculectomy

Table 4: Changes of insulin sensitivity index and intraocular pressure after phacoemulsification combined with trabeculectomy
Generalizability
The findings should confirm whether phacoemulsification and trabeculectomy is an effective method for the treatment of cataract combined with glaucoma. The results should also clarify whether the therapeutic effect is associated with the regulation of insulin sensitivity index, corneal endothelial cells and inflammatory factors. This trial will provide a rational basis for the clinical treatment of cataract combined with glaucoma using phacoemulsification and trabeculectomy.

Table 5: Changes in inflammatory factors (ng/mL) after phacoemulsification combined with trabeculectomy
Explanation
The completed small-sample trial showed that the best corrected visual acuity was significantly improved, endothelial cell density, intraocular pressure and interleukin-2 and interleukin-10 levels were significantly decreased, and the mean cell area, coefficient of variation and insulin sensitivity index were significantly increased after surgery. These results suggest that phacoemulsification combined with trabeculectomy is an effective therapeutic strategy for cataract combined with glaucoma.
Interleukin is strongly associated with the pathogenesis and treatment of cataract and glaucoma. However, many other inflammatory factors may contribute to disease. Therefore, in future studies, numerous additional inflammatory factors will be analyzed to provide a more comprehensive evaluation of the inflammatory response in the pathogenesis and treatment of cataract and glaucoma.
DATA AUTHENTICITY MANAGEMENT
Data collection
All data from patients with cataract combined with glaucoma will be collected and recorded in case report forms, signed and dated, and finally entered into an electronic version of the document saved on the computer.
Data management
After collecting the experimental data, they will be input by an investigator using Epi-Data 3.0 software using the double entry method. The accuracy of the data will be checked item by item to ensure the authenticity and credibility of the data.
Data quality control
The data monitoring committee will include ophthalmologists, and clinical trial management, statistics and ethics experts. The research will be carried out under the supervision of the responsible representative with corresponding qualifications. The data will be checked regularly.
Modification of the research plan
Participating researchers may not modify the content of the protocol during the trial without the permission of the research leader (such as enrollment criteria for cataract patients with glaucoma and postoperative follow-up outcome data).
Audits
Clinical monitors will check the trial records and case report forms of all cataract patients with glaucoma after phacoemulsification combined with trabeculectomy during and after the study. The data monitoring committee will report the progress of the trial to the Ethics Committee of the hospital every other month.
Confidentiality
Personal information of all cataract patients with glaucoma after phacoemulsification combined with trabeculectomy will be kept strictly confidential by our hospital, and a confidentiality agreement will be signed before the trial.
Declaration of interest
None declared.
Data sharing statement
Individual participant data that underlie the results reported in this article, after deidentification (text, tables, figures, and appendices). Data will be available immediately following publication, with no end date. Anonymized trial data will be available indefinitely at www.figshare.com.
Result release
Results will be disseminated through presentations at scientific meetings and/or by publication in a peer-reviewed journal.
TRIAL STATUS
Registration time:September 10, 2019.
Recruitment time:December 30, 2019-December 30, 2020 .
Study completed:June 30, 2021.
Trial status:Preparation for recruitment.
Additional files
Additional file 1: Hospital Ethics Approval (Chinese).
Additional file 2: TREND checklist.
Additional file 3: Informed Consent Form (Chinese).
Author contributions
Study design: JJZ; recruitment, data collection and analysis: JJZ, YG, QBC, JHY, and YL. All authors approved the final version of the paper.
Conflicts of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Financial support
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81560159 (to YG); the Health Science and Technology Project of Yunnan Province of China, No. 2016NS063 (to JFZ). The funding sources had no role in study conception and design, data analysis or interpretation, paper writing or deciding to submit this paper for publication.
Institutional review board statement
This study will be performed in strict accordance with theDeclaration of Helsinkiformulated by the World Medical Association. This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee, First AffiliatedHospital of Kunming Medical University, China on December 15, 2013 (approval No. 20131215085).
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they will obtain all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form, the patients will give their consent for their images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Reporting statement
The writing and editing of the article was performed in accordance with the Transparent Reporting of Evaluations with Nonrandomized Designs (TREND) statement.
Biostatistics statement
The statistical methods of this study were reviewed by the biostatistician of First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, China.
Copyright license agreement
The Copyright License Agreement has been signed by all authors before publication.
Data sharing statement
Individual participant data that underlie the results reported in this article, after deidentification (text, tables, figures, and appendices). Data will be available immediately following publication, with no end date. Results will be disseminated through presentations at scientific meetings and/or by publication in a peer-reviewed journal. Anonymized trial data will be available indefinitely at www.figshare.com.
Plagiarism check
Checked twice by iThenticate.
Peer review
Externally peer reviewed.
Open access statement
This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
杂志排行
Clinical Trials in Degenerative Diseases的其它文章
- A study protocol on effectiveness of theory-based intervention on self-care and glycated hemoglobin among type 2 diabetes patients in National Center for Diabetes in Yemen
- Effects of electroanalgesia on knee osteoarthritis: study protocol for a randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- Comparison of efficacy of continuous and intermittent walking exercise on blood pressure and renal function in elderly hypertensive subjects: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
