急性细菌性痢疾患儿采用阿奇霉素口服与头孢地嗪静滴治疗的临床效果
2019-10-06赵宏艳
赵宏艳
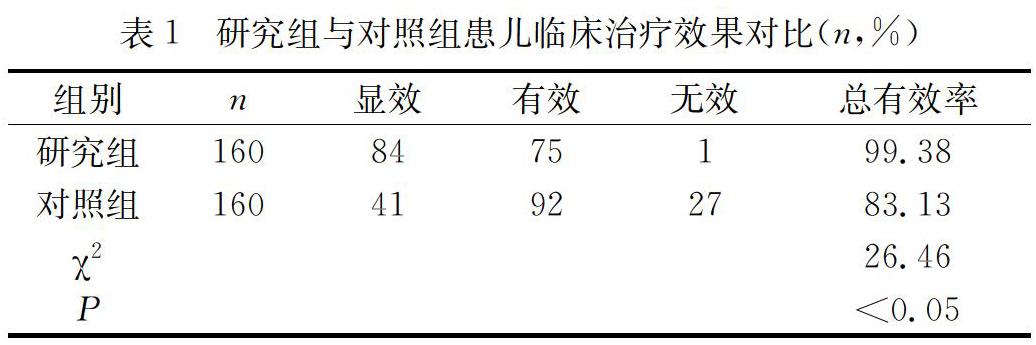

【摘 要】 目的:分析阿奇霉素口服与头孢地嗪静滴联合疗法应用于小儿急性细菌痢疾的效果。方法:以2016年2月至2018年2月本院儿科收治的320例急性细菌型痢疾患儿为研究对象,随机分为研究组与对照组各160例。所有患儿给予饮食调理、纠酸、补液、平衡电解质等常规治疗。在此基础上,对照组患儿给予头孢曲松鈉针静滴进行抗感染治疗;研究组给予阿奇霉素口服联合头孢地嗪静脉滴注治疗。对比两组患儿临床治疗效果,观察两组退热、止泻及大便培养转阴等状况。结果:治疗后,研究组患儿治疗总有效率(99.38%)显著高于对照组(83.13%)(P<0.05);研究组退热时间、止泻时间等指标均优于对照组(P<0.05)。结论:将“阿奇霉素口服+头孢地嗪静滴联合方案”应用于临床小儿急性细菌型痢疾的治疗具有操作简易、效果显著、安全可靠等优点。
【关键词】 小儿急性细菌型痢疾;阿奇霉素;头孢地嗪
Clinical effect of azithromycin oral and cefodizime intravenous drip in children with acute bacillary dysentery
Zhao Hongyan
Jingbian County Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Yulin, Shaanxi 718500
[Abstract] Objective:To analyze the effect of azithromycin oral combined with Cefodizime intravenous drip in the treatment of acute bacillary dysentery in children. Methods: 320 children with acute bacillary dysentery admitted to our hospital from February 2016 to February 2018 were randomly divided into study group and control group (160 cases each). The children in the control group were given dietary conditioning, acid rectification, fluid replacement, balanced electrolyte, and corresponding drug treatment for diarrhea and other diseases. On this basis, the study group was given azithromycin orally plus cefodizime intravenous drip for anti-infective treatment. The control group received intravenous drip of ceftriaxone sodium for anti-infection treatment. The effect of clinical treatment was compared between the two groups, and the antipyretic, antidiarrheal and negative change of stool culture were observed in the two groups.Results: After treatment, the total effective rate (99.38%) in the study group was significantly higher than that in the control group (83.13%) with statistical significance (P<0.05). The indexes of antipyretic time and antidiarrheal time in the study group were better than those in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion: Azithromycin oral plus cephaladizine intravenous drip combined regimen is simple, effective, safe and reliable in the treatment of acute bacterial dysentery in children.
[Key words]Acute bacillary dysentery in children; Azithromycin; Ceftazidime
小儿急性细菌性痢疾是一种临床常见的肠道传染性疾病,又称为“菌痢”[1],多发于3岁以上儿童,尤其在夏秋季节发病率较高。临床主要伴有发热、便血、腹泻等症状,若未进行及时有效的治疗,病情会迅速发展。临床常规方法治疗时间较长且并发症较多,不利于患儿病情发展。基于此,本文联用阿奇霉素口服与头孢地嗪静滴,探讨联合疗法应用于临床小儿急性细菌痢疾的效果。现将报道整理如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
以2016年2月至2018年2月本院儿科收治的320例急性细菌性痢疾患儿为研究对象,经临床检查所有患儿均符合《实用儿科学》中关于菌痢的诊断标准[2],且病程<5d;临床主要表现以腹痛、腹泻、脓血便、黏液便为主;培养粪便可见痢疾杆菌滋长。排除肛裂、肠道息肉、肠套叠等外科疾病及食物过敏、克隆病、结肠炎等内科疾病。以随机方式分为研究组与对照组各160例。研究组男性81例,女性79例;对照组男性76例,女性84例。两组患儿一般资料对比,差异没有统计学意义(P>0.05)。
