Effect of Curing Temperature on the Morphology and Hydration of MgO Expansive Material in Paste
2019-09-25ENGTianZiWANGFuPENGHailongYANGWeiboGAOPeiwei
ENG Tian Zi,WANG Fu,PENG Hailong,YANG Weibo,GAO Peiwei*
1.Department of Civil Engineering,Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,Nanjing 210016,P.R.China;
2.Communication Plan Survey and Design Institute of Shanxi Province,Taiyuan 030012,P.R.China
Abstract: The morphologies and hydration properties of MgO expansive material at different curing temperatures were investigated. When the curing temperature varies from 25 ℃to 50 ℃,the conductivity of MgO rises from 40 to 80 μs/cm,the hydration product of MgO expansive material curing in water for 28 days is from 1.5—2 mm to 2—2.5 μm in length through SEM observation,and the expansion of pastes with 5% of the magnesium oxide is from 0.36% up to 1.01%,it is increased by 2.78 times. When the content of cement paste increases to 95% and cured in water for 90 days,the brucite forms as hexaflaggy-shaped crystal,which is less than 0.1 μm and tends to aggregates.The effect of curing temperature on the hydration of MgO expansive material is obvious.
Key words: MgO expansive material;hydration;curing temperature;morphology;expansion
0 Introduction
Considering the hydration heat of cement,the adiabatic temperature rises of volume concrete are generally 20—30 ℃,and the temperatures in concrete are above 50 ℃[1-3]. It is convenient and effective to use the MgO expansive material to compensate the shrinkage of hydraulic concrete[4-5]. Previous studies on the hydration activity of magnesium oxide have generally been conducted at a curing temperature of 25 ℃instead of 50 ℃,which is different from the practical conditions. In general,the hydration activity of magnesium oxide is very low. The crystal morphologies of brucite are globosity,blocky or fibrous,depending on environmental conditions,such as crystal size,curing temperature,forming method and reaction time[6-9]. The crystal length of brucites formed at room temperature are usually 1.5—3 μm,and a length of 1.5 μm will be formed at 70 ℃of water curing[10-11].
The hydration rate,degree,size and morphology of brucite in specimens are different at the curing temperature of 25 ℃and 50 ℃. The brucite crystals formed by the hydration of magnesium oxide are irregularly blocky,which adhere to and develop around the surface of magnesium oxide,as well as produce local stresses and cracks in concretes[12-14].In this paper,the conductivity,morphology,and expansion of magnesium oxide at different curing temperatures were investigated,which can be used to compensate the shrinkage of concrete and improve the serviceability and durability of the concrete dam.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Materials
MgO expansive material is prepared from magnesite calcined in an electric furnace in a laboratory at 1 050—1 200 ℃for one hour,followed by cooling in the air and pulverization into powder. The chemical compositions of the expansive materials are listed in Table 1. The 42.5 MPa Portland cement and grade I fly ash are used.

Table 1 Chemical composition of materials %
1.2 Methods
The conductivity of MgO solution is measured at 25 ℃and 50 ℃with a conductometer type DDS-307 with DJS-1 pole under the agitation rate of 300 rad/min,after the instrument has been corrected with 0.01 mol/l KCl. 0.2 g magnesium oxide was added to 100 ml distilled water in the conduction pool,and then the first reading was taken at once[15]. The sampling interval is 1 min at the beginning of 15 min,followed by 5 min until 30 min from the beginning.
The SEM images of hydrated MgO expansive material with and without cement were analyzed.The ratio of water to cement was 0.28. The paste was cured in water for different temperature and age,placed in absolute alcohol to stop hydration,and then dried in an oven(60 ℃)for 48 h before SEM observation.
In accordance with the China National Standard JC476—2001, the expansion tests of the pastes with 5% of the magnesium oxide were performed. Three paste specimens were 10 mm×10 mm×40 mm,and the ratio of water to cement was 0.28. The paste specimens were cured in a fog room for one day and demolded. Their initial lengths L0were measured,and then the specimens were cured in 50 ℃water for different curing time.The lengths L were measured and the expansions were calculated by(L-L0)×100% / L0.
2 Results and Discussion
2.1 Effect of curing temperature on the conductivity of MgO expansive material
Fig.1 shows the effect of curing temperature(25 ℃and 50 ℃)on the conductivity of MgO expansive material.
Under the same hydration conditions,the hydration conductivity of MgO increases rapidly in the first five minutes and then slowly in the later age.
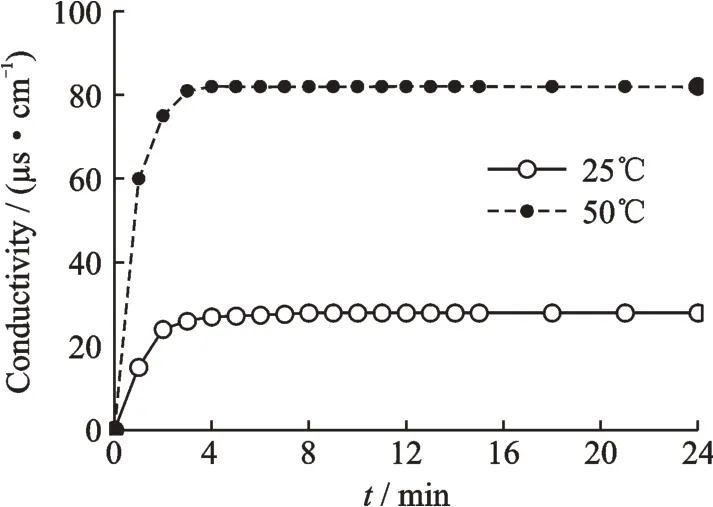
Fig.1 Influence of curing temperature (25 ℃& 50 ℃) on conductivity of MgO suspended solutions
When the curing temperature of the magnesium oxide in 25 min rose from 25 ℃up to 50 ℃,the conductivity increased from 40 μs/cm up to 80 μs/cm.
The results show that curing temperature influences the conductivity of magnesium oxide. The conductivity of magnesium oxide changes with the hydration activity,and the hydration activity of magnesium oxide is related to the curing temperature.Different curing temperature leads to a difference in hydration of magnesium oxide and growth of brucite crystal,so do the effects on the conductivity. After the curing period,magnesia hydration is rare,and the change of conductivity is small.
2.2 Effect of curing temperature on the morphology of MgO expansive material
The SEM images of magnesium oxide hydrated to Mg(OH)2under the different curing temperatures(25 ℃& 50 ℃water)for one day are shown in Fig.2.
When MgO expansive material is cured at 25 ℃for one day,the brucites could be found at the edge(refer to Fig.2(a)). After curing in water at 50 ℃for one day,a significant increase in the size of brucite crystals can clearly be observed,the larger brucite crystals formed around the MgO expansive material are up to 1—1.5 μm in length and 0.5 μm in width(Fig.2(b)),which are stick-shaped. The results show that the hydration rate of MgO expansive material and the size of brucite crystals increased when the curing water temperature changed from 25 ℃to 50 ℃.
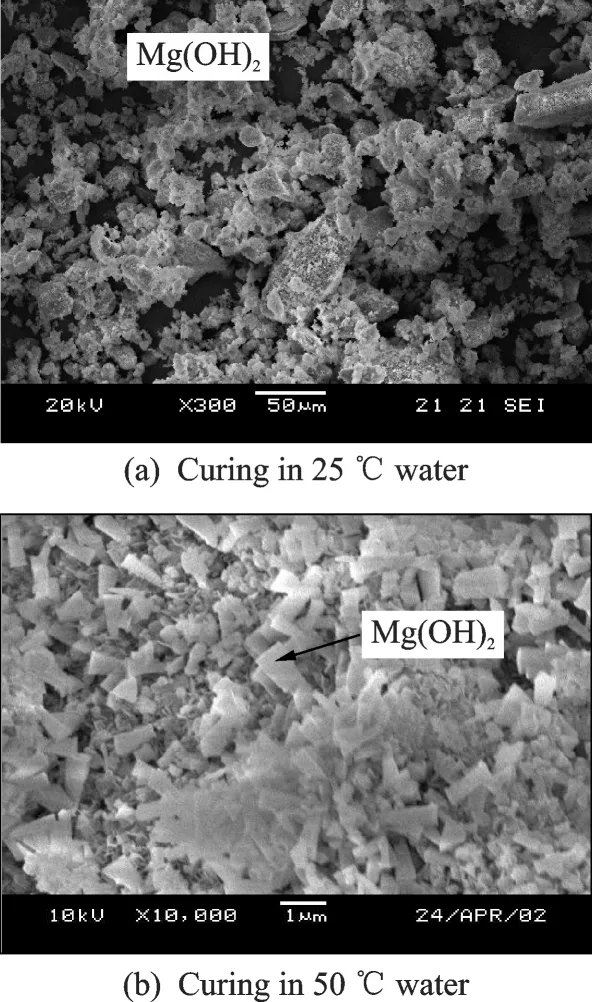

Fig.2 SEM images of hydrated MgO expansive material curing in water for 1 d
The SEM images of magnesium oxide curing in 25 ℃and 50 ℃water for 28 d are shown in Fig.3.
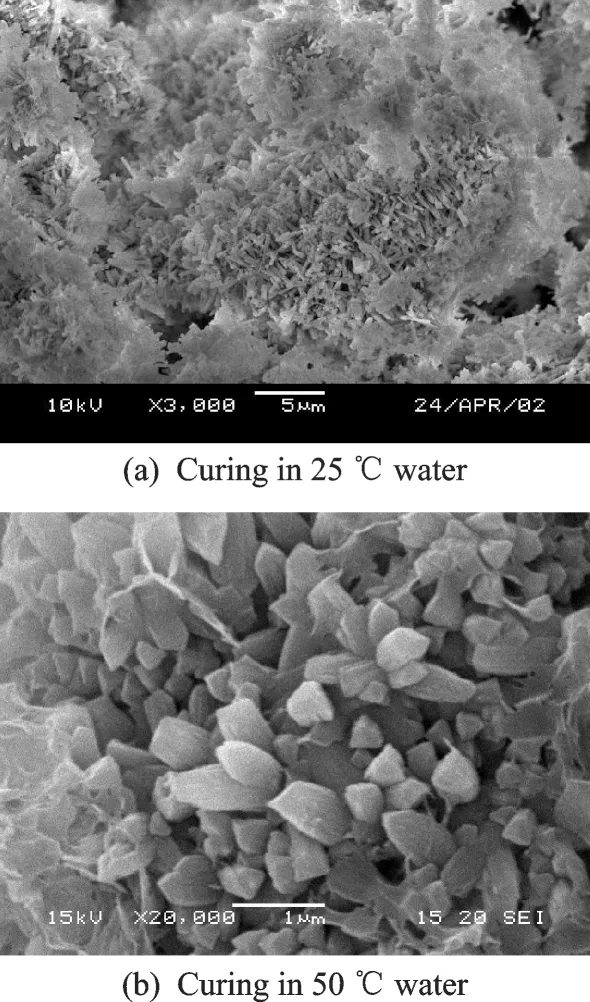

Fig.3 SEM images of hydrated MgO expansive material curing in water for 28 d
When magnesium oxide is cured in water at 25 ℃for 28 d,the hydration products of MgO are fibrous crystals and formed on the surface of MgO expansive material. The larger brucite crystals are about 1.5—2 μm in length. When magnesium oxide is cured in 50 ℃,the brucite crystals are fibrous and stacked with each other,few of MgO expansive material can be observed. The larger brucite crystals are 2—2.5 μm in length,and they are not much change in width.
The results show that the amount and size of brucite increased with the curing temperature and age. Magnesium oxide with low activity will hydrate slowly,and the length and width of the brucite crystals curing in 25 ℃water and early age is little. As the curing temperature and age increase,both the activity of magnesium oxide and the size of brucite crystal increase.
2.3 Effect of curing temperature on expansion of pastes with MgO expansive material
Fig.4 shows the influence of curing temperature on the expansion of paste with 5% MgO expansive material. The specimens were cured in 25 ℃and 50 ℃of water for different periods.
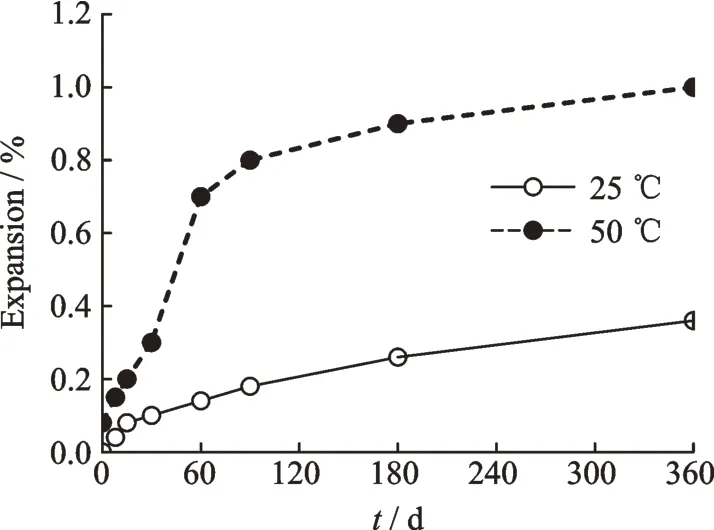
Fig.4 Expansion of pastes with 5% MgO expansive material curing in different condition
When the curing temperature increased from 25 ℃to 50 ℃in a year,the expansion of paste with 5% MgO expansive material increased from 0.36%to 1.01%,that is,by 2.78 times. It indicates that curing temperature plays an important role in the hydration reaction of MgO in pastes. The higher the curing temperature,the more the expansion of paste. When the curing temperatures increase,the molecules move faster,and more magnesium oxides react with water,so the conductivities of MgO expansive material and expansion contents of pastes increase. The results show that when the curing temperature is increased from 25 ℃to 50 ℃,the hydration rate of MgO and the size of brucite crystal increase,but the shape of brucite crystal does not change.
2.4 SEM images of paste with MgO expansive material
The SEM images of hydrated MgO expansive material in pastes with 10% and 95% cement(by weight)cured in 80 ℃water for 90 d are shown in-Fig.5.
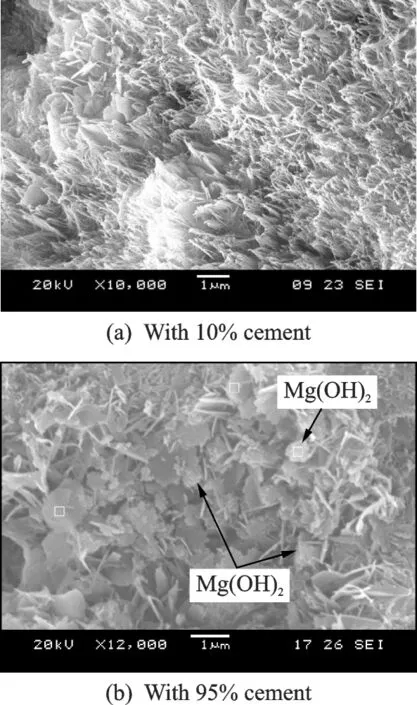

Fig.5 SEM images of hydrated MgO expansive material in paste curing in 80 ℃water for 90 d
When the specimens with 90% MgO expansive material and 10% cement were cured in 80 ℃water for 90 d,the size and shape of brucite crystals(Fig. 5(a))are different from those cured in water.The crystals are needle-shaped and the sizes decrease. The lengths of brucite crystals are about 0.5—1 μm,and spread evenly in the pores of paste.
When the specimens with 5% MgO expansive material and 95% cement cured in 80 ℃water for 90 d,the size,shape,and distribution of brucite crystals(Fig.5(b))are different from those of brucite for 90% MgO expansive material and 10% cement(Fig.5(a)). The crystals of Mg(OH)2are hexaflaggy-shaped and less than 0.1 μm in length,and aggregate in the pore edge of paste,which can produce an expansive stress and cause local cracks in the constructions with magnesium oxide.
3 Conclusions
Based on the experimental results,when the curing temperature rises from 25 ℃to 50 ℃,the experimental materials will produce the following changes:
(1)The conductivity of the magnesium oxide increases from 40 μs/cm to 80 μs/cm,and the reaction activity also increased. While the larger brucite crystals formed around the magnesium oxide are 1—1.5 μm in length. Besides,the larger brucite crystals of magnesium oxide are increased from 1.5—2 μm to 2—2.5 μm in length,which are fibrous and stacked with each other. The expansion of paste with 5% MgO expansive material increases from 0.36% to 1.01%,and it increases by 2.78 times,which plays an important role in the hydration reaction of the magnesium oxide in pastes.
(2)When MgO expansive material in pastes with a low amount of cement is cured in water for 90 d,the brucite crystals are needle-shaped with 0.5—1 μm in length,it is spread and develop evenly in pastes. If the cement content in pastes increased to 95%,the brucite crystal becomes the hexaflaggyshaped crystals,which is less than 0.1 μm and tends to aggregate.
杂志排行
Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics的其它文章
- Performance Analysis and Power Allocation for Cooperative SSK System with Receive Correlation in Rayleigh Fading Channel
- Retro-reflective Beamforming Technique with Applications in Wireless Power Transmission
- A 60 GHz Phased Array System Analysis and Its Phase Shifter in a 40 nm CMOS Technology
- Design of Power Amplifier for mmWave 5G and Beyond
- MoM-PO/SBR Algorithm Based on Collaborative Platform and Mixed Model
- Low-Complexity DOA Estimation of Noncircular Signals for Coprime Sensor Arrays
