Effects of Microbial Pesticides on Prevention and Control of Cucumber Downy Mildew
2019-09-19*
*
1. Plant Science College, Tibet Agriculture & Animal Husbandry University, Nyingchi 860000, China; 2. Shouguang Green Control Agricultural Technology Co., Ltd., Shouguang 262700, China
Abstract This experiment was carried out to explore the effects of microbial pesticides on prevention and control of cucumber downy mildew. Three kinds of microbial pesticides (Recharge, Dynamic F, and 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS) were used and clean water was taken as the control (CK). The experiment showed that Recharge and 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS had better control effect on cucumber downy mildew. After the first application, the average control effect of Recharge and 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS was higher than 50%. After the third application, the average control effect of Recharge and 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS was higher than 20%. The control effect of Dynamic F on cucumber downy mildew was relatively poor, and the average control effect after the first application was 38.34%, and the average control effect after the third application was only 15.64%. According to the experimental results, the average control effect of three pesticides after application showed a gradual decline trend.
Key words Cucumber, Downy mildew, Microbial pesticide
1 Introduction
Cucumis sativus Linn belongs to Cucurbitaceae vegetables and takes up a large proportion in greenhouse vegetables of China. Cucumbers are green in surface, also known as green cucumbers. The earliest cucumber varieties were imported from foreign countries. In ancient times, foreigners were called "Hu people", so cucumbers were also called "Hu melon". Cucumber surface has white thorns, the fruit is green or dark green, the flesh is crisp and juicy, and the taste is fresh. It is one of the most popular vegetables. The yield of cucumber is high, but the disease occurrence is also very serious during the planting process, especially the cucumber downy mildew, which occurs almost in every planting area of all cucumber varieties. So far, no cucumber varieties resistant to downy mildew have been found.
Cucumber downy mildew is caused by the infection of the Mastigomycotina, Oomycetes, Peronosporaceae, Pseudoperonospora cubensis[1], it is commonly called "black hair" and is vulnerable to temperature and humidity. When the cucumber is in the environment of low temperature (15-24℃) and high humidity (up to 80%), it is most vulnerable to infection of the downy mildew. The downy mildew of cucumber is closely connected with the temperature and humidity. However, when planting cucumber, the temperature and humidity in the planting area can be used to inhibit the occurrence of cucumber downy mildew. When the temperature in the planting area exceeds 28℃, or if it falls below 15℃[2], and the humidity is kept below 80%, it will exert a certain influence on the occurrence of cucumber downy mildew. Summer is the season with the highest rainfall in the whole year. High rainfall causes the humidity in the cucumber planting area to increase sharply, which provides favorable conditions for the infection of downy mildew. The pathogens mainly rely on airflow and rainwater[3], resulting in the reduction of the disease resistance of cucumber and causing a large outbreak of the downy mildew. The comprehensive control method of downy mildew includes using 20 kg of slaked lime powder in the agricultural control method[4]; adopting varieties with strong disease resistance, such as: Jinchun No.3, Jinchun No.4, Zhongnong No.4, Zhongnong No.5,etc.[5]; warm water soaking of seeds[6]; strengthening the cultivation management[7], as well as the smoke method in the chemical control method[8]and high-temperature sterilization by mulching solarization in the physical control method[9]. Microbial pesticide, as a kind of biological pesticides, refers to microorganisms and their metabolites, and processed substances that have the activity of killing, sterilizing, weeding or regulating plant growth[10]. The development of microbial pesticides in China has shown a rising trend and has become an important means of biological control. In recent years, biological pesticides such asBacillusthuringiensis,Bacillussubtilis,Bacilluscereus, Validamycin,Beauveriabassiana, and avermectin have been rapidly developed and widely applied in the prevention and control of pests and diseases. For example,Bacillusthuringiensis, as the most widely used microbial pesticide in the world, has good control effects on agricultural pests such as maize borer, cotton bollworm and cabbage caterpillar;Beauveriabassianahas good control effects onLeguminivoraglycinivorella,Plutellaxylostella, andHolotrichiadiomphalia, and has been favored by users in recent years; avermectin is a kind of macrolide antibiotics and has been widely applied in the control of pesticides such as mites,PhyllocnistiscitrellaandPlutellaxylostella, and the control effect is remarkable[11].
2 Control effect experiment
2.1 Experimental materials
2.1.1Test agents. The agent used in the experiment and the dilution times are shown in Table 1.
2.1.2Test varieties. Zhongnong No.106 cucumber, medium-maturing variety, strong growth potential, moderate branch, dark green skin, dense thorns, crisp and sweet taste.
2.2 Experimental siteThe experiment was carried out in the experiment base No.9 greenhouse of Weifang University of Science and Technology. The experimental area was 300 m2. Within the experimental greenhouse, the soil conditions were suitable and the fertility and water condition management was consistent.
Table 1 Statistics of test agents

CommoditynameManufacturerEffectivecomponentDilutiontimesRechargeRussell,UK-500DynamicFRussell,UK-500BaicleanBeijingMultigrassFormulationCo.,Ltd3.0%amino-oligosaccharinAS750
2.3 Experiment design
2.3.1Experiment treatment. This experiment was designed with 4 treatments and 3 repetitions, namely: Recharge WP 500 times solution; Dynamic F WP 500 times solution; 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS 750 times solution; clean water control (CK).
2.3.2Experimental method. Recharge, Dynamic F, 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS, and clean water control (CK) were randomly arranged in each repetition. An isolation belt was placed between every two repetitions for the purpose of observation.
Spraying can be carried out when there is a disease spot on the cucumber leaves. Cloudy weather, outdoor temperature between -2-5℃, and greenhouse temperature 8-22℃, appropriate humidity, are conducive to the maximum effect of the pesticide. The pesticide was sprayed three times every 7 days. The cucumber plants were sprayed with 1 200-15 000 kg/ha of pesticide by Qingfeng 3WD-20 electric sprayer. In addition to spraying and survey records, the daily management of the cucumber plants in the experimental greenhouse were handled by the staff of the experiment base. The management of the fertilizer and water in the three replicate test areas should be consistent with each other. In case of any problem, the staff of the base should promptly communicate with our team.
2.4 Experiment survey and data statisticsThe random sampling method is the main method in this experiment. The specific operation is as follows: take three points in each zone, take three cucumber plants per point, and survey the disease spot of all the cucumber leaves, and check them four times. It should be specially noted that survey of cucumber leaf spot should be carried out before the first application, with each survey interval of 7 days. Table 2 lists the grading standard of cucumber downy mildew.
The calculation formula for the pesticide effect:
Some of the bits she stuffed in empty cans of tuna fish. Other bits she stuffed in the middle of over-ripe watermelons. And other bits she hid inside old smelly socks.
Table 2 Grading standard of cucumber downy mildew

DiseasegradeDiseasedegreeGrade0NodiseasespotGrade1Thediseasespotaccountsforlessthan5%ofthewholeleafareaGrade3Thediseasespotaccountsfor6%-10%ofthewholeleafareaGrade5Thediseasespotaccountsfor11%-25%ofthewholeleafareaGrade7Thediseasespotaccountsfor26%-50%ofthewholeleafareaGrade9Thediseasespotaccountsformorethan50%ofthewholeleafarea
Disease index=[∑ (Number of leaves of each grade × Relative grade)]/[(Total number of survey × 9)]×100
Control effect (%)=[1-(CK0×PT1)/(CK1×PT0)]×100
whereCK0denotes the disease index of the control area before pesticide application,CK1denotes the disease index of the control area after pesticide application,PT0denotes the disease index of the treatment area before pesticide application, andPT1denotes the disease index of the treatment area after pesticide application.
During the investigation, we should also observe the growth of cucumbers in each area, check whether there is any external wound,etc., and make a record of them.
3 Experimental results and analysis
3.1 Results of the control effect experiment of three pesticides on cucumber downy mildewThe survey was started before the onset of cucumber downy mildew, and the later investigation was carried out after the seventh day of each time of pesticide application. The disease spot on the leaves of the same plant were observed and compared with the results of the previous investigation to see if there was any change and evaluate the disease grade. According to the calculation formula, we calculated the disease index and control effect, and the results are listed in Table 3.
3.2 Experimental analysisFrom Table 3 and Table 4, we can clearly see the control effects and differences of the three biological agents in this experiment. Compared with the control group, after comparing the experimental results, it was found that after spraying three kinds of biological agents, all three kinds of agents produced the control effects on cucumber downy mildew, and the best control effect was the microbial pesticide Recharge. From Table 3, it can be seen that the control effects were 66.19%, 50.4% and 57.82% measured seven days after the first application of cucumber with Recharge, the control effects were 47.58%, 40.34%, 44.09% measured seven days after the second application of cucumber with Recharge, and the control effects were 23.70%, 25.27%, 26.34% measured seven days after the third application of cucumber with Recharge. The control effects of Dynamic F were 38.43%, 35.52% and 41.07% measured seven days after the first application of cucumber with Dynamic F, the control effects were 28.61%, 27.03%, 31.14% measured seven days after the second application of cucumber with Dynamic F, and the control effects were 13.40%, 15.41%, 18.13% measured seven days after the third application of cucumber with Dynamic F. Finally, the control effects of 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS were 52.38%, 57.02% and 51.90% measured seven days after the first application of cucumber with 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS, the control effects were 39.08%, 47.40%, 41.23%measured seven days after the second application of cucumber with 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS, and the control effects were 20.13%, 25.28%, 22.57% measured seven days after the third application of cucumber with 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS. In view of the control effects of the three kinds of microbial pesticides on the cucumber downy mildew after three times of application, the microbial pesticide Recharge and 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS had little difference in the control effects measured seven days after the first application, all were higher than 50%. However, compared with the other two kinds of microbial pesticides, Dynamic F had weaker control effects after the first time of application, and its control effect on the cucumber downy mildew was lower than 40%. After the first time of application, the control effects of three kinds of microbial pesticides on the cucumber downy mildew was Dynamic F, 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS, and Recharge from weak to strong. In terms of the control effects seven days after the second time of application, Dynamic F was still the weakest in the three kinds of microbial pesticides, Recharge had the best control effects, and 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS ranked the second. In terms of the control effects seven days after the third time of application, there was little difference between Recharge and 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS, Recharge had slightly higher control effects, while Dynamic F still ranked third in the three kinds of microbial pesticides.
Table 3 Control effects of three kinds of microbial pesticides on cucumber downy mildew
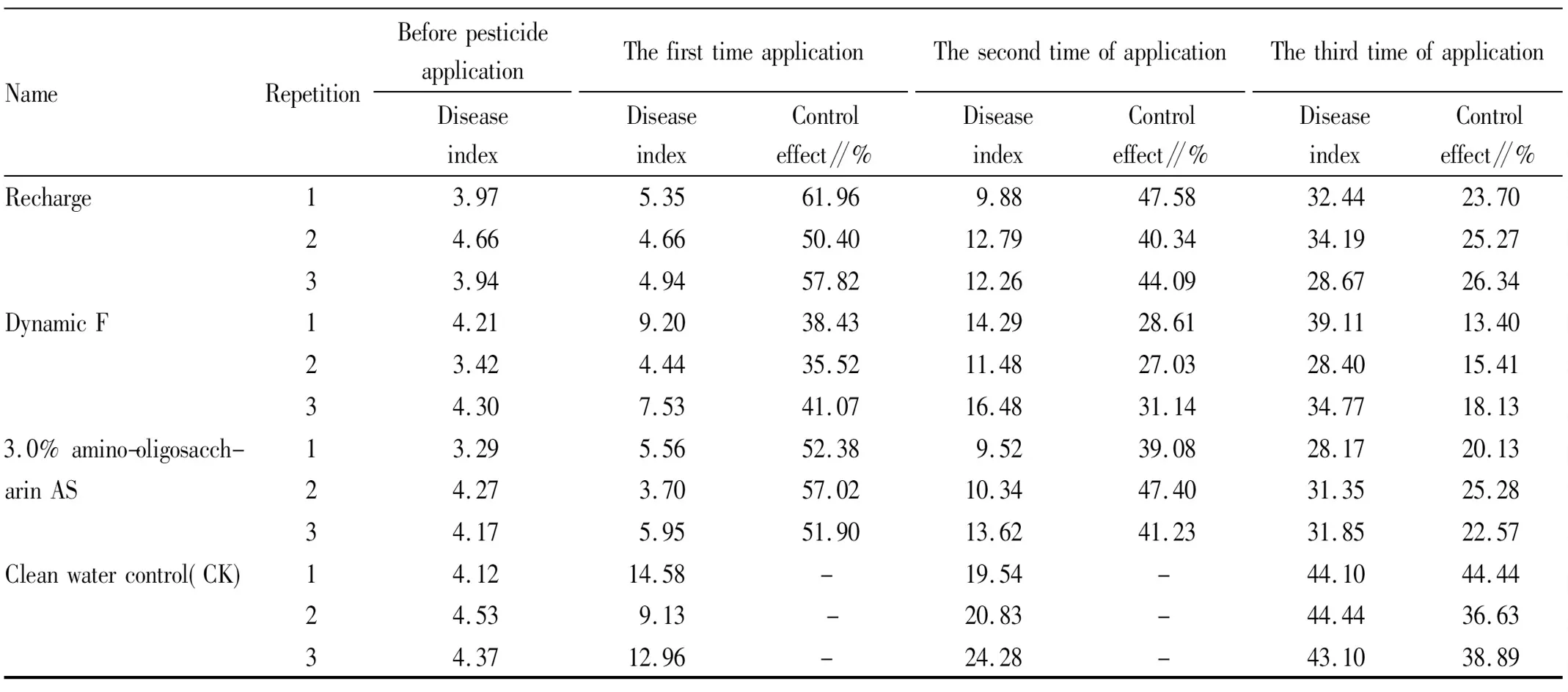
NameRepetitionBeforepesticideapplicationDiseaseindexThefirsttimeapplicationDiseaseindexControleffect∥%ThesecondtimeofapplicationDiseaseindexControleffect∥%ThethirdtimeofapplicationDiseaseindexControleffect∥%Recharge13.975.3561.969.8847.5832.4423.7024.664.6650.4012.7940.3434.1925.2733.944.9457.8212.2644.0928.6726.34DynamicF14.219.2038.4314.2928.6139.1113.4023.424.4435.5211.4827.0328.4015.4134.307.5341.0716.4831.1434.7718.133.0%amino-oligosacch-13.295.5652.389.5239.0828.1720.13arinAS24.273.7057.0210.3447.4031.3525.2834.175.9551.9013.6241.2331.8522.57Cleanwatercontrol(CK)14.1214.58-19.54-44.1044.4424.539.13-20.83-44.4436.6334.3712.96-24.28-43.1038.89
Table 4 Average control effects after three times of pesticide application on cucumber downy mildew%
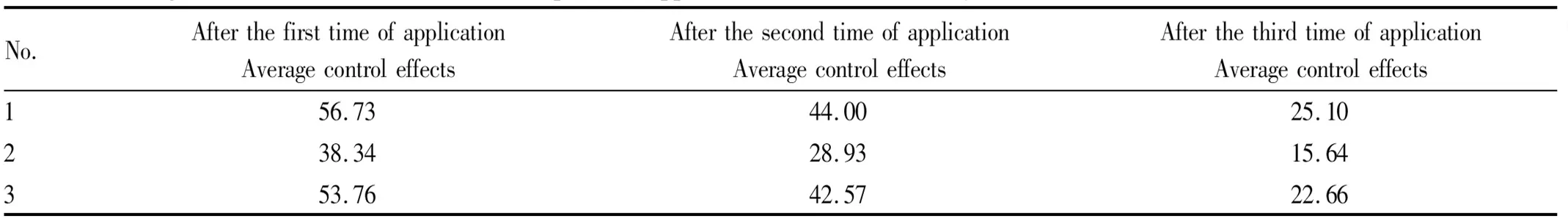
No.AfterthefirsttimeofapplicationAveragecontroleffectsAfterthesecondtimeofapplicationAveragecontroleffectsAfterthethirdtimeofapplicationAveragecontroleffects156.7344.0025.10238.3428.9315.64353.7642.5722.66
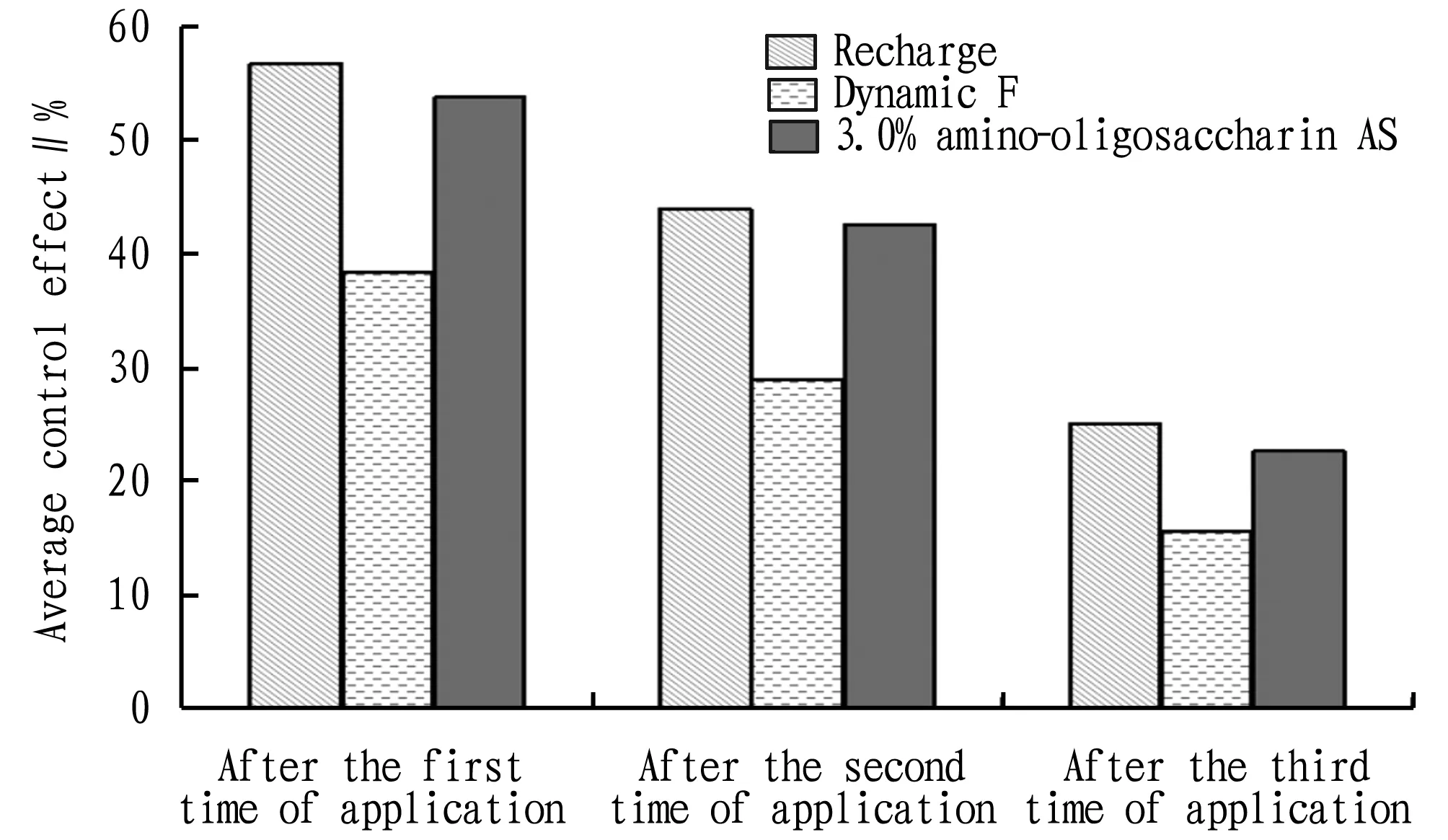
Fig.1 Average control effects after three times of pesticide application on cucumber downy mildew
From Fig.1, the average control effect of microbial pesticide Recharge seven days after the first time of application was 12.73% higher than that after the second time of application, the average control effect of Recharge seven days after the third time of application was 31.63% lower than that of the first time of application, and 18.9% lower than that of the second time of application. For the microbial pesticide Dynamic F, the average control effect seven days after the first time of application was 9.41% higher than that of the second time of application, the average control effect seven days after the third time of application was 22.70% lower than that of the first time of application, and 13.29% lower than that of the second time of application. For the 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS, the average control effect seven days after the first time of application was 11.19% higher than that after the second time of application, the average control effect seven days after the third time of application was 31.10% lower than that of the first time of application, and 19.91% lower than that of the second time of application.
According to the above results, we can reach the following conclusions. After the application of the microbial pesticide Recharge, the control effects on cucumber downy mildew is better than Dynamic F and 3.0% amino-oligosaccharin AS. The control effects of Recharge on cucumber downy mildew is gradually reducing, but it is because Recharge is a kind of microbial pesticide, different from the principle of chemical pesticides to control crop diseases. The former is to prevent and cure cucumber resistance and immunity, while the latter is to kill the pathogens to control crop diseases. In practice, the application of the pesticide always occurs after the symptoms of the cucumber downy mildew, thus the above effects are gradually reduced. It can be concluded that Recharge is suitable for application before the occurrence of the disease, and its control effect is remarkable. If the downy mildew outbreaks on a large scale, the control effect of Recharge will be greatly reduced.
3.3 Recommended method of use of the microbial pesticide RechargeWhen using Recharge to control cucumber downy mildew, it is recommended to apply Recharge before the occurrence of cucumber downy mildew. The control method can be root irrigation or leaf spraying. It should be noted that the application time should be carried out on the morning or afternoon of sunny days. After the first time of application, the pesticide can be applied once every half month or twenty days, the application of the pesticide can effectively increase the content of probiotics in the soil, improve the disease resistance of cucumber, so as to lay a certain foundation for the high yield of cucumber.
3.4 Investigation on the phytotoxicity of cucumber in greenhouse after the pesticide applicationAt the same time of the investigation of the disease index and control effects on cucumber downy mildew, we also investigated the growth of cucumber and the phytotoxicity in the planting area after the pesticide application. The investigation found that the cucumbers after application showed good growth, especially in areas where Recharge was applied. There were no abnormal changes except for the wilt of some leaves. In addition, compared with the clean water control group (CK), the cucumbers after spraying Recharge grew vigorously, the stems was thick, the cucumber shape and color were normal, while the cucumbers in the control group not only grew weak, but also the leaves appeared wilting, and some cucumber plants showed deformation. By observation and comparison, it can be concluded that the spraying of Recharge not only does not cause phytotoxicity of cucumber, but also improves the quality and yield of cucumber.
4 Conclusions and discussions
4.1 ConclusionsFrom the experimental results and data analysis, the three kinds of microbial pesticide used in this experiment have certain control effects on cucumber downy mildew, and the microbial pesticide Recharge has the best control effect, and the 3.0% amino oligosaccharin AS has slightly lower control effect than Recharge, Dynamic F has the lowest control effect on cucumber downy mildew, so when using Dynamic F, it should be considered. The experiment confirmed that the microbial pesticide Recharge can be used as a control agent for cucumber downy mildew, but it is recommended that Dynamic F be used as appropriate.
4.2 DiscussionsThe use of chemical pesticides will inevitably have certain impact on crops and ecological environment, while the use of microbial pesticides will become the key to solve this problem. According to the experimental data, the control effects of Recharge are gradually reduced, mainly because the main synthetic substance is the probiotic bacteria. The superiority of its control is mainly reflected before the occurrence of the crop disease, the application of this pesticide can improve the crop immunity and resistance. In our experiment, the pesticide is applied after the occurrence of the downy mildew, so there is the reduction of the control effects. Therefore, to bring into the best control effects of the Recharge, it is recommended to apply it before the occurrence of the cucumber downy mildew.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Effects of Water-Soluble Fertilizer on Yield and Quality of Asparagus in Greenhouse under Chemical Fertilizer Reduction
- The Model of Health Poverty Alleviation in Poor Mountainous Areas in Southwest China: A Case Study of "5+5" Model of Health Poverty Alleviation in Xundian County
- Difference of Regional Benefits after Linking Newly-added Cropland Quotas with Amount of Land Used for Construction Based on Targeted Poverty Alleviation: A Case Study of Xinjiang
- Inhibition Effects of Salvianolic Acid M and Rosmarinic Acid in Salvia deserta Schang on Human Aldose Reductase
- Outdoor Domestication Cultivation and Survival Mechanism for Tissue Culture Seedlings of Paeonia suffruticosa
- Ecological Compensation-assisted Relocation in Extreme Poverty-stricken Counties in China’s Ecologically Vulnerable Areas: Taking Dongchuan District of Yunnan Province as an Example
