Inhibition Effects of Salvianolic Acid M and Rosmarinic Acid in Salvia deserta Schang on Human Aldose Reductase
2019-09-19,3*
,3*
1. College of Pharmacy, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011; 2.Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medical Hospital, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011; 3. Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, State Key Laboratory Basis of Xinjiang Indigenous Medicinal Plants Resource Utilization, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Urumqi 830011, China
Abstract [Objectives]This study aimed to investigate the inhibition effects of two chemical constituents in Salvia deserta Schang on human aldose reductase (AR). [Methods]The isolated salvianolic acid M and rosmarinic acid were prepared into different concentrations of solutions for in vitro enzyme kinetics experiments. [Results]Salvianolic acid M and rosmarinic acid had the strongest inhibition effects at the concentration of 1 g/L. [Conclusions]Salvianolic acid M and rosmarinic acid have inhibition effects on human aldose reductase. The IC50 of salvianolic acid M is 0.79 μg/mL, and that of rosmarinic acid is 1.13 μg/mL.
Key words Salvia deserta Schang, Aldose reductase, Salvianolic acid M, Rosmarinic acid
1 Introduction
SalviadesertaSchang (Lamiaceae:Salvia) is entirely used as medicine in folks, with effects of clearing away heat, detoxifying, relieving cough, eliminating phlegm, reducing swelling and promoting diuresis[1]. It belongs to the same genus asSalviamiltiorhizaBunge included in thePharmacopoeiaofthePeople’sRepublicofChina. As a blood stasis-removing drug,S.miltiorhizahas long been used in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular and gynecological diseases. Recent studies have shown thatS.miltiorhizahas a certain inhibition effect on tumors and diabetes, and it shows a good activity especially in the prevention and treatment of diabetic chronic complications (DCCs)[2]. The pharmacological effects of the species belonging to the same genus asS.miltiorhizahave attracted more and more people’s interest and attention.
DCCs caused by hyperglycemia such as mental disorders, nephropathy, retinopathy and cataracts greatly increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, blindness, amputation and kidney failure[3]. Modern medical research has proven that DCCs are associated with polyol pathway. The key rate-limiting enzyme of this pathway, aldose reductase (AR), is activated during hyperglycemia, catalyzing the massive conversion of glucose into sorbitol that does not penetrate the cell membrane, causing cell osmotic damage, leading to DCCs[4]. The use of AR inhibitors has become a key factor in delaying and preventing DCCs. In order to find effective and low-toxicity AR inhibitors, using theinvitroenzyme kinetics experimental method, the inhibition effects of salvianolic acid M and rosmarinic acid inS.desertaon AR were analyzed.
2 Materials and methods
2.1MaterialsThe used drugs and reagents included UV-2401 PC ultraviolet spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Japan), NADPH (sigma, purity > 98%), DL-glyceraldehyde (ICN Biomedicals), human AR (Japan WAKO Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., human muscle), quercetin (National Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products of China). The rest of the reagents produced by China were analytically pure. TheS.desertaspecimens were identified and stored by the Medical Teaching and Research Section of Xinjiang Medical University.
2.2ExtractionandseparationS.desertawas extracted three times with water, and the water extract was extracted with n-butanol. After repeated column chromatography (AB-8 macroporous adsorption resin, Sephadex LH-20) and elution (acetonitrile: H2O), salvianolic acid M and rosmarinic acid were obtained. After freeze-dried, the constituents were prepared into solutions of 1, 0.75, 0.50 and 0.25 g/L, respectively with DMSO.
2.3MethodsThe reaction system was composed of 700 μL of 0.2 mol/L phosphate buffer (pH 6.2), 100 μL of 1.5 mmol/L NADPH, 100 μL of 100 mmol/L DL-glyceraldehyde, 3 μL of 3×10-2U/L human AR and 97 μL of buffer. After placed at 25℃ for 20 s, the mixture was stood for 180 s. Finally, the absorbance of the mixture at 340 nm was measured. The decrease in the absorbance (ΔA) indicates the activity of human AR. The inhibition of various parts ofS.desertaon human AR refers to the reduction of enzyme activity after adding 3 μL of sample to the above reaction system. For blank determination, the sample was replaced by DMSO solvent, and human AR was replaced by buffer. For control determination, the sample was replaced by DMSO solvent. The positive control was quercetin (1 mg/mL), which is currently recognized as a positive control for the measuring the effects of other AR inhibitors.
Human AR inhibition rate (%)=[1-(ΔAsample-ΔAblank)/(ΔAcontrol-ΔAblank)]×100%[5].
3 Results and analysis
The inhibition effects of salvianolic acid M and rosmarinic acid isolated fromS.desertaon human AR are shown in Table 1. As shown in Table 1, salvianolic acid M and rosmarinic acid both have inhibition effects on human AR. At the concentration of 3 μg/L, their inhibition effects were stronger. As the concentration decreased, the inhibition rate also declined accordingly. TheIC50of salvianolic acid M was 0.79 μg/mL, and that of rosmarinic acid was 1.13 μg/mL.
Table1IntensityofinhibitioneffectsofthetwocompoundsonhumanARatdifferentconcentrations(μg/mL,n=3)
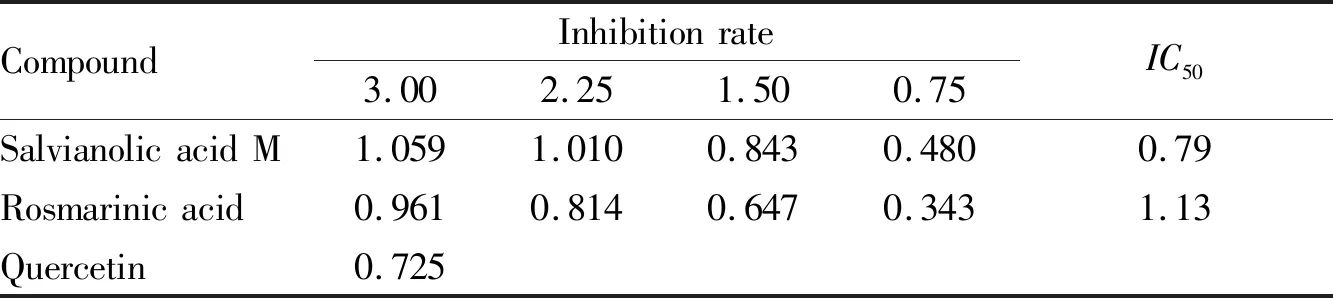
CompoundInhibitionrate3.002.251.500.75IC50SalvianolicacidM1.0591.0100.8430.4800.79Rosmarinicacid0.9610.8140.6470.3431.13Quercetin0.725
4 Discussion
Many scholars at home and abroad are working hard to find powerful AR inhibitors. Traditional Chinese medicine has a history of thousands of years in the treatment of DCCs, and it is an important advantage to find strong AR inhibitors from traditional Chinese medicines. In this study, the inhibition activity of two chemical constituents inS.deserta, salvianolic acid M and rosmarinic acid, on AR was studied; and human AR was used as the enzyme source for drug screening, so the experimental results are highly reliable. In the future, animal’s overall test will be carried out for verification.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Difference of Regional Benefits after Linking Newly-added Cropland Quotas with Amount of Land Used for Construction Based on Targeted Poverty Alleviation: A Case Study of Xinjiang
- Variation Diagnosis and Regional Comparison of Different Intensity of Rainfalls and Their Contribution to Total Rainfall in China in the Context of Global Warming
- Study on the Poverty Alleviation Model of Internet+Agricultural Industry: Taking Anhua Dark Tea Industry as an Example
- Ecological Compensation-assisted Relocation in Extreme Poverty-stricken Counties in China’s Ecologically Vulnerable Areas: Taking Dongchuan District of Yunnan Province as an Example
- Outdoor Domestication Cultivation and Survival Mechanism for Tissue Culture Seedlings of Paeonia suffruticosa
- Effects of Microbial Pesticides on Prevention and Control of Cucumber Downy Mildew
