稳定型圆锥角膜患者植入新型Phakic角膜接触镜的视觉效果分析
2019-07-25作者单位59599伊朗德黑兰ShahidBeheshti医科大学Negah眼科研究中心59599伊朗德黑兰ShahidBeheshti医学科学与卫生服务大学59599伊朗德黑兰伊朗医学与健康服务大学59599伊朗西阿塞拜疆Urmia医科大学公共卫生系
(作者单位:59599伊朗德黑兰Shahid Beheshti医科大学,Negah眼科研究中心;59599伊朗德黑兰,Shahid Beheshti医学科学与卫生服务大学;59599伊朗德黑兰,伊朗医学与健康服务大学;59599伊朗西阿塞拜疆,Urmia医科大学公共卫生系)
INTRODUCTION
Keratoconus is a non-inflammatory,progressive ectatic disorder related to irregular astigmatism and decrease corneal thickness[1].Treatment of keratoconus relies upon the condition of the cornea ectasia and the degree of irregular astigmatism.In view of the biomechanical adjustments of the corneal collagen compound,it has been recommended to utilize collagen cross-linking(CXL)to end the progression of keratoconus,when progress is approved[2].Soft contact lenses or glasses can be utilized in mild type and when the astigmatism increments and corneal distortion occurs,rigid gas permeable(RGP)lenses,intra-stromal ring sections or keratoplasty may be utilized to enhance the visual acuity[2-4].The results of other treatment strategies like laser in situ keratomileusis(LASIK)appear to be capricious,as they may outcome in the furtherdiminishing ofthe cornea and remainder refractive error[5-6].Numerous studies[7-10]have utilized the Phakic intraocular lenses(pIOLs)containing posterior chamber pIOLs to rectify refractive errors related to keratoconus,proposing a promising option.At present,it is one of the prosperous pIOLs,the implantable Phakic contact lens(Toric IPCL,Care Group India).The IPCL is similar to the soft contact lens,single piece posterior chamber Phakic IOL,which can be inserted into eye through 2.8 mm incision.Sulcus placed posterior chamber Phakic intraocular lens(IOL)which is made from reinforced hybrid acrylic material.Another type oflens thathas a longer history is the implantable collamer lens(ICL)(STAAR Surgical Inc.).However,the potential reactions of this method remain to be explored.This examination expected to evaluate the efficacy,safety,stability and predictability of the Toric implantable Phakic contact lens in patients with stable keratoconus amid a 6mo follow up.As far as we know,this is the first study to examine the behavior of this posterior Phakic IOL model.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
This prospective study was conducted the clinical outcomes of the implantable Phakic contact lens to correct refractive error were researched in 28 keratoconic eyes of 14 consecutive patients(Table 1).
Patients who were over 23 years old were viewed as qualified to experience implantation of the Toric IPCL,intolerant to spectacles and contact lenses,had a steady refraction for at least one year and were happy with their vision when wearing glasses.Patients had no other general pathology and ocular and no more than stage Ш keratoconus pursuant to the Amsler-Krumeich classification[11].
Inclusion CriteriaAccompanied corrected distance visual acuity(CDVA)of+0.4 Logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution(LogMAR) of 5/10 decimal or better,clear cornea,intraocular pressure(IOP) <20 mmHg,normal ACD of at least 3 mm to the endothelium,a pupil diameter of less than 6.25 mm,width of angle greater than 30°and a presurgery endothelial cell count in association with age.Contact lens utilization was ceased for at least more than 3wk for RGP and one week for soft contact lens prior to any intervention.

Table 1 Preoperative and postoperative demographic and clinical data of patients underwent Toric IPCL
Exclusion Criteriacontained introduction of autoimmune diseases and other ophthalmic issues,with the exception of keratoconus, for example, corneal opacification or scar,cataract,uveitis,diabetic retinopathy,glaucoma ,central endothelial cell count of less than 2000 cells/mm2by specular microscopy(SP-8800;Konan,Nishinomiya,Japan),focal corneal thickness of under 450 mm[estimated by optical pachymetry(Pentacam-HR,Oculus Optikgerate,Wetzlar,Germany)]and ACD less than 3 mm from the endothelium to the anterior capsule measured by Orbscan IIZ(Orbscan,Bausch and Lomb,Rochester,New York,USA).
ImplantableIPCLInsertionProcedureIn this examination,the current V2 IPCL configuration was implanted.When started with topical anesthesia,dilating specialists were directed.For the Toric IPCL implantation,the surgeon(FD)denoted the zero horizontal axis amid slitlamp examination while the patient was lying upright to avoid cyclotorsion.IPCL,unlike the ICL,does not require a specific set.IPCL cartridge needs a 2.8 mm incision,marked to ensure proper orientation in the eye as it unfolds,observe the IPCL for proper orientation in the cartridge,open the cartridge and injector fill the Cartridge with saline and HPMC,open the IPCL Container,gently hold the IPCL with McPherson Forceps near haptics,check the orientation of IPCL,Place the IPCL in the Cartridge,put the Cartridge in injector.
In a temporal approach,after injection of vasculosis,a small incision of the cornea was made at 2.8 mm,and the IPCL was injected through the incision into the anterior chamber and got slowly opened.
After injection of the Toric IPCL into the anterior chamber,theproper motion was accomplished with gentle posterior pressure and calm rotation of one or more clock hour.This move was rehashed for each of the four footplates,situating them under the iris plane.In the event that any change of the Toric IPCL was fundamental,it was expert with a gentle movement contacting the IPCL at the intersection of the optic and haptic.Aspiration and irrigation of the viscoelastic materials were accomplished.An intraocular miotic(acetylcholine) was utilized to diminish the pupil size.The arrangement of the Toric IPCL was assessed by slitlamp examination at all visits postoperatively.

Table 2 Manifest refraction,the Toric implantable Phakic contact lens
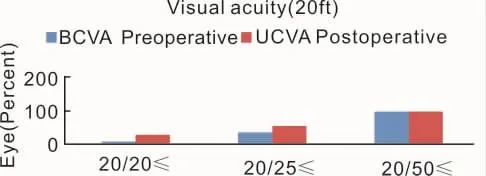
Figure 1 A comparison of preoperative best corrected visual acuity and postoperative uncorrected distance visual acuity 6m after Toric IPCL.
Study Outcomes and Patients Follow-upPostoperative examinations were directed at a consistent follow-up program(baseline and in 1,2,4 and 6mo).The primary results parameters for this examination were cycloplegic refractions and manifest,uncorrected distance visual acuity(UCDVA)and CDVA.We assessed the accompanying:anterior and posterior segments assessment with dilated fundus evaluation,pre- and postoperative inconveniences,endothelial cell count estimated on the central piece of the cornea by specular microscopy(SP-8800,IOP with Goldman applanation tonometry and non-contact tonometer Topcon CT-1P.Vault heightwasestimated objectively with ultrasound biomicroscope(UBM, Sonomed, New York, USA) and subjectively(slit-lamp examination).
Contrast sensitivity test got accomplished under mesopic(3 cd/m2)and photopic(85 cd/m2)conditions utilizing the CVS1000 contrast sensitivity test(VectorVision,Greenville,SC).The tests were accomplished with the best glasses correction before the surgery and without correction after the surgery,utilizing a light level of 3 cd/m2after 10min of dark adaptation at a distance of 3 m.Testing was accomplished at 1,3,5,6,12 and 18 cycles for every degree(c/d).The defocus curve additionally gotten to assess the scope of utilitarian vision.
Statistical AnalysisTo statistically analyze the results,we utilized the SPSS programming(SPSS Statistics for Windows,V.23.0,2013;IBM).The non-parametric Wilcoxon marked rank test was connected to decide the significant differences between the target outcomes before and after the implantation of Toric IPCL,for example,contrast sensitivity and the LogMAR visual acuity, defocus curve.Given that these variables had ordinary dispersion,we reported the mean and SD to them.Ordinary factors were accounted for as mean and SD,and we sat the middle if circulations were skewed.We considered 5%level to discover the statistically significant differences in our analysis.
RESULTS
Patient PopulationTable 1 illustrates patient's demographics in summary.The mean spherical error was -4.89±3.96 D(range:-1.50 to -12.00 D),and the astigmatism was -4.24±1.42 D(range: -1.75 to -8.00 D).Toric IPCL was accomplished at the clinical investigational site from October 2017 to May 2018 in this group.Patients were followed up seven times after surgery at 1,2,4 and 6mo.All patients had a preoperative UCDVA worse than 20/40 with 95%having uncorrected acuity limited to counting of fingers.In 6mo,post-surgically UCDVA was better than or equal to pre -surgically CDVA in 85%(24/28)of eyes,and UCDVA was incremented by≥byrement,a 22 eyes(Table 2).
The preoperative CDVA and postoperative UCVA 6mo after Toric IPCL operation is compared in Figure 1.
Six months after postoperative,71.42%of eyes were within ±0.50 D,and 96.42%were within ± 1.0 D of endeavored correction.At the end of the follow-up,the mean vault height was 603±54.33(range:510-701) μm,and the IOP was 11.32±2.28 mmHg.
Safety LogMARCDVA was 0.06±0.11,0.04±0.15,0.05±0.15 and 0.05±0.15 in 1,2,4 and 6mo after surgery with the IPCL,respectively.We found a significant difference between preoperative CDVA IPCL and all other follow-up(P<0.05,Wilcoxon signed-rank test).The safety index(mean postoperative CDVA/mean preoperative CDVA)was 1.09,1.15,1.11 and 1.11 at 1,2,3 and 6mo after operation with the IPCL,respectively.
Treatment EffectivenessUncorrected distance visual acuity 6mo after postoperative for the entire subjects was≥20/20 in 46.42% of eyes and ≥ 20/40 in 100% of eyes.The uncorrected visual outcomes in this‘all eyes’group must be interpreted in the context:only 50%of these eyes had CDVA of≥ 20/20 at the baseline.6mo after postoperative,UCDVA was equal to or better than preoperative CDVA in 78.57%(22/28)of eyes.
PredictabilityofManifestRefraction(attemptedvsachieved) The following outcomes are relied upon to give a more exactappraisalofrefraction exactness than the postoperative mean refractive spherical equivalent(MRSE)results.Six months after postoperative,71.42%of eyes were inside ± 0.50 D,and 96.42%were inside ± 1.0 D of endeavored correction.The differences in SE,cylinder and sphere were statistically significant between preoperative and 1mo postoperatively.These differences remained stable for 6mo and 2,4 and 6mo after operation(Figure 2).
Even though emmetropia wasthe targeted postoperative refraction in allpatients,smallhyperopic and myopic deviations were found after IPCL implantation.
Defocus CurveFigure 3 demonstrates the LogMAR visual acuity under defocus curve of+2,+1,0,-1,-2,and -3 D in postoperative and preoperative periods in a noncycloplegic situation.The contrasts between the estimations of binocular distance corrected defocus bend in the examination showed significant differences in LogMAR visual acuity at the defocus bend levels of+1,0 and-1 D,yet no significant differences were seen at the defocus bend levels of+2,-2,and -3 D.
Contrast SensitivityFigure 4 demonstrates the mesopic contrast sensitivity outcomes,which exhibit no loss of contrast at any spatial frequency and a measurably noteworthy change conversely an incentive at 3 and 1.5 for each degree.Furthermore,photopic contrast sensitivity exhibited a critical change,interestingly,an incentive at 3 for each degree incomparable mesopic conditions.
Vaulting the IPCLFigure 5 shows the adjustment in vault between successive estimations in various times.Objective and subjective vaults were steady after IPCL implantation in 2mo.
DISCUSSION
This examination exhibited the visual results of Toric IPCL implantation in stable keratoconus with a 6-month follow-up.This examination assessed efficacy,predictability,safety and stability of this system in patients with stable keratoconus.These discoveries in conjunction with excellent outcomes for refractive signs that influence the quality of life 12 empower Toric ICL to be the primary suggested Phakic IOL approved in the USA for patients younger than 60 years[13].Posterior chamber Phakic IOLs can be viewed as a safe procedure to treat refractive errors in keratoconic patients with better restorative results,due to position of the IOL behind the iris[12,14-15].

Figure 2 Postoperative spherical equivalent during follow-up(3 and 6mo).

Figure 3 LogMAR(Logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution)visual acuity defocus curve of+2,+1,0,-1,-2,and-3 D in a non-cycloplegic condition in the preoperative and postoperative.

Figure 4 A:contrast sensitivity under mesopic illumination(3 cd/m2)(statistically significantly different at a level of 0.05);B:contrast sensitivity under photopic illumination(85 cd/m2).
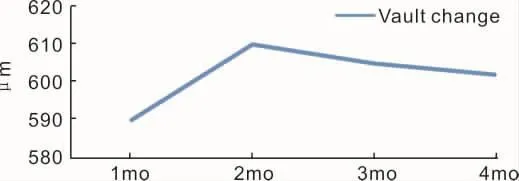
Figure 5 Vault change during follow-up.
Toric IPCL is accessible with spherical powers from+15.0 to-30.0 D for adjustment of refractive error and an astigmatism power to 10.00 D that wide range is viewed as an awesome benefit at show.The visual acuity test is bitten by bit turning into the gold standard level for the appraisal of vision,giving exclusively a confined amount of information under artificial conditions(Table 2).Contrastsensitivity exhibited an assortmentofvisualperformance information underreal conditions.This inspired us to gain ground around there of medicine.To the best of our knowledge(Web of Science and PubMed),this is the first investigation of Toric IPCL in patients with stable keratoconus that focuses on visual function(contrastsensitivity, visualacuity, defocuscurve and refraction).No decrease in contrast sensitivity was seen at any spatial frequency.Photopic and mesopic contrast sensitivity demonstrated a statistically significant betterment in value at 3 per degree.There is no totally consummate test for contrast sensitivity[16].We picked this strategy,since it is easy to understand,time-saving and accessible,and it diminishes the examiners'mistake.Notwithstanding, in spite of the considerable number of contemplations,the test result was impacted by numerous different components that enhanced contrast sensitivity,other than refractive correction of auxiliary system,one-time CXL with riboflavin and UVA,enhance aberrations and contrastsensitivity[17-18].We had three patients with pre-surgery astigmatism more noteworthy than six(Table 2).A few subjects of s would do well to resilience to myopic defocus curve(- 1),which appears to be identified with the remaining refraction in these subjects.
The chiefpossibly complications afterIPCL and ICL implantation are cataract formation,15 intense increments in IOP and night vision disorder[19].Anterior segment anatomy assessment with new propelled advances and consideration of the surgeon to notice signs before operation permits the choice of the best possible size and diminishes likely complications[20].We believe that before operation,patients with shallower ACD and older patients and larger White to Whiteoughttobemademindfulofthelikelihood of complication after this technique[21].Cataract surgery in keratoconus prompts resurgence of visual acuity,particularly by various means,for example,Toric multifocal lenses[22].Conceivable hazard factors for night vision unsettling influences after ICL are White to White measurement of the cornea,distinction between the optic zone width and the mesopic pupil size,corona and toricity of the ICL and glare[23]but fortunately,the new lenses make it possible to orderlenses with largeroptics,which minimizes the possibility of light transmission and glare in large pupils.The pre-surgery and postoperative are comprised of a complete ophthalmic examination.
The IPCL implantation is a plausible manage with less infringement in visual function since it doesn't change the curvature ratios between the front and backcorneas[24].In this regard,albeit a few methodologies may demonstrate slightly better results for UCVA and refractive consistency,Toric IPCL implantation indicated dependable outcomes like those of bioptics.A single-step method with IPCL implantation may maintain a strategic distance from the potential complications for elective second surgeries.A pattern toward reduction of corneal transplantation for keratoconus looking at two changed periods was accounted for by some studies[25].It is a guarantee that appears to be identified with contemporary administration modalities in prior recognition of movement and medications of keratoconus.
The clinical results of the present examination exhibit the efficacy,safety and predictability of Toric implantable Phakic contact lens in patients with stable keratoconus.One of the limitations of this study was a small number of patients and a short follow-up period that required further studies and a large number of patients in future studies.
