n-6和n-3多不饱和脂肪酸对心肌缺血/再灌注损伤炎症因子TNF-α和IL-1释放的影响
2019-07-11吕珩鲍丽刚
吕珩 鲍丽刚

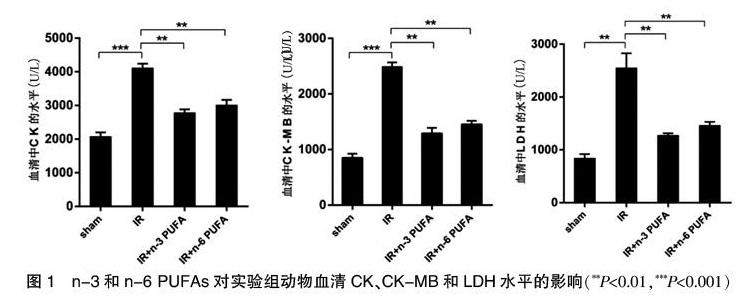
[摘要] 目的 探讨n-6和n-3多不饱和脂肪酸对心肌缺血/再灌注损伤炎症因子TNF-α和IL-1释放的抑制作用及其抗炎作用机制。 方法 构建健康成年SD大鼠4组模型(sham、IR、n-3 PUFA+IR和n-6 PUFA+IR),通过肌酸激酶(CK)、肌酸激酶同工酶(CK-MB)和乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)活性检测缺血/再灌注的损伤程度;通过酶联免疫吸附测定促炎细胞因子TNF-α、IL-1的表达水平;通过qPCR和Western blot检测TLR4/NF-κB的表达水平。 结果 与IR组相比,n-3 PUFA+IR和n-6 PUFA+IR组的CK、CK-MB和LDH显著降低,心肌梗死面积减少,心肌组织形态学结构改善;ELISA检测发现n-6和n-3 PUFAs处理组,TNF-α、IL-1的表达水平显著降低;TLR4、NF-κB的mRNA和蛋白的表达也显著降低。 结论 n-3 PUFA和n-6 PUFA通过TLR4/NF-κB途径抑制促炎因子TNF-α和IL-1的表达,从而保护心肌缺血/再灌注损伤,TLR4介导的NF-κB信号传导途径可能成为心肌缺血/再灌注损伤的新策略。
[关键词] 心肌缺血/再灌注损伤;n-3和n-6多不饱和脂肪酸;炎症因子;TLR4 /NF-κB
[中图分类号] R285 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2019)14-0031-06
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the inhibitory effects of n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the release of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1 in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and its anti-inflammatory mechanism. Methods Four sets of models of healthy adult SD rats(sham, IR, n-3 PUFA+IR, and n-6 PUFA+IR) were constructed. The degree of ischemia-reperfusion injury was measured by activity of creatine kinase(CK), creatine kinase isoenzyme (CK-MB) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH); The expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1 were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The expression levels of TLR4/NF-κB were detected by qPCR and Western blot. Results Compared with the IR group, CK, CK-MB and LDH were significantly lower in the n-3 PUFA+IR and n-6 PUFA+IR groups, the myocardial infarct size was reduced, and the myocardial histomorphology was improved. ELISA showed that the expression levels of TNF-α and IL-1 in n-6 and n-3 PUFAs groups were significantly decreased; the mRNA and protein expression of TLR4 and NF-κB were also significantly decreased. Conclusion n-3 PUFA and n-6 PUFA inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-1 through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway, thereby protecting myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. TLR4-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway may be a new strategy for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.
[Key words] Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury; n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids; Inflammatory factors; TLR4/NF-κB
目前,缺血性心臟病的最佳治疗策略为心肌再灌注,它可以通过逆转心肌缺血和限制梗死面积来保持心肌的活力和功能[1-2]。然而,随后出现的缺血/再灌注(I/R)损伤可能会降低治疗效果[3]。心肌I/R是一个复杂的病理生理过程,涉及各种因素和途径[4],炎症反应被认为是I/R诱导的组织损伤的主要原因[5],有实验及临床证据表明抗炎作用可以减轻I/R损伤[6]。
Toll样受体4(TLR4)作为模式识别受体的成员,通过识别外源性病原体相关分子模式和内源性配体,在诱导炎症反应中发挥重要作用[7-8]。TLR4的激活与几种细胞类型中促炎细胞因子的表达和NF-κB信号传导途径的激活有关[9-10]。有研究表明,与野生型相比,缺血/再灌注后TLR4敲除和TLR4突变小鼠均表现出较少的心肌损伤和炎症[11-12],还发现TLR4表达与心肌I/R大鼠模型中的肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)和白细胞介素-1(IL-1)水平呈正相关[13]。
