Effects of Different Herbicides on the Control of Malachium aquaticum L. and Poa annua L.
2019-06-27
College of Agriculture and Biotechnology, Hunan University of Humanities, Science and Technology, Loudi 417000, China
Abstract In this experiment, the effects of 13 kinds of herbicides (or mixtures) on the control of two kinds of weeds were studied by pot cultivation with the broadleaf weed Malachium aquaticum L. and Gramineae weed Poa annua L. as the materials. The results showed that the herbicide MCPA-Na had the best and fastest control effect on M. aquaticum L., and all the M. aquaticum L. died 7 d after treatment; it was followed by the other four herbicides including MCPA-Na+ clethodim, MCPA-Na+ quizalofop-p-ethyl, bentazon and nicosulfuron·atrazine, and all the M. aquaticum L. died 14 d after treatment. Atrazine was the best herbicide to control Gramineae weeds, followed by nicosulfuron·atrazine, and mesotrione·nicosulfuron·atrazine. The study on the application of field herbicide found that four herbicides including atrazine, mesotrione·nicosulfuron·atrazine, nicosulfuron·atrazine and bentazon had better control effect on weeds. The best herbicide for flax field was MCPA-Na+clethodim, followed by MCPA-Na and MCPA-Na+quizalofop-p-ethyl. The optimized herbicides and combinations had no harmful effects on the growth of corn and flax.
Key words Herbicides, Weeds, Malachium aquaticum L., Poa annua L., Control effect
1 Introduction
Corn plays a more and more important role in food security in China, and it has become an important cash crop to ensure food security. Weed damage in corn field has become the main factor affecting the stable yield, high yield and good quality of corn[1-2]. At present, the research on weed control in corn field is mainly focused on the comparison of herbicide control effect[3-5], and the effect of herbicide mixture[6], tillage method, planting density and variety on weed occurrence[7-9]and so on. However, most of these studies are focused on corn planting areas in the north, and there are few studies on weed control in corn fields in the south. Flax is one of the three largest fiber crops and one of the five major oil crops in the world, and China is the second largest producer in the world after Russia. The damage of flax weeds in winter in southern China is one of the main factors limiting its stable and high yield. At present, there are many studies on weed identification, distribution characteristics, occurrence features and integrated control in northern flax field[10-12], but few on weeds in southern flax field[13]. For this reason, in view of the harm of the broadleaf weedMalachiumaquaticumL. and Gramineae weedPoaannuaL. to the northern flax and corn field, the pot cultivation method was used to study the control effects of 13 kinds of herbicides on the two kinds of weeds. In this paper, the control effect of herbicide on weeds in corn field and flax field and the effect on growth safety of corn and flax were studied in order to find out the best herbicide in corn field and flax field. The purpose of this study is to provide a theoretical scientific basis for controlling weeds in corn and flax fields and promoting stable and high-yield cultivation of corn and flax in southern China.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Test site and timeThe pot experiment was conducted in the school base from November 2017 to March 2018, the corn field experiment was conducted in April-August 2018, and the flax field experiment was conducted in the school base from October 2018 to March 2019.
2.2 Test Materials
2.2.1Potted weeds.M.aquaticumL. andP.annuaL.
2.2.2Weeds in the corn fields.VeronicadidymaTenor,M.aquaticumL.,ApludamuticaL.,P.annuaL.
2.2.3Weeds in the flax field.M.aquaticumL.,PoaannuaL.,AlopecurusaequalisSobol.,CardaminehirsutaL. and so on.
2.2.4Herbicides. 56% MCPA-Na powder produced by Shandong Vicome Greenland Chemical Co., Ltd.; clethodim produced by Shandong Kqiao Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; 10.8% high efficiency haloxyfop EC produced by Beijing Zhonglin Jiacheng Technology Co., Ltd.; 5% refined quinoline EC produced by Jiangsu Bailing Agrochemical Co., Ltd.; 100 g/L mesotrione suspending agent produced by Anhui Huaxing Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.; 38% atrazine produced by Jinan Kesai Agrochem Co., Ltd.; 4% nicosulfuron produced by Chengdu Huangting Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; bentazon produced by Jiangsu Sword Chemical Co., Ltd.; mesotrione·nicosulfuron·atrazine produced by Shandong Ao Kun Biological Co., Ltd.; nicosulfuron·atrazine produced by Shandong Dehao Chemical Co., Ltd.
2.3 Experimental design
2.3.1Pot experiment. The tested soil was loam, and the diameter of the plastic test pot was 12 cm, and each pot was filled with soil for 1 kg. When the seeds of budding weeds were sown to the stage of 3 to 4 leaves, the herbicides were sprayed according to the conventional concentration and dose. The tested herbicides were mesotrione, atrazine, nicosulfuron, bentazon, MCPA-Na, clethodim, haloxyfop, quizalofop-p-ethyl and their mixtures. 6 pots were replicated for each treatment, repeated 3 times, using a randomized block design.
2.3.2Weeding and safety test in the corn field. When the corn grew to 3-4 leaf stage, the pesticide was applied. Seedlings were thinned out one day before pesticide application, the area of the plot was 8 m2, repeated three times, using a randomized block design. The herbicides tested were mesotrione, atrazine, nicosulfuron, mesotrione·nicosulfuron·atrazine, nicosulfuron·atrazine and bentazon. The application was the same as that in pot experiment. The effects of pesticide application on the growth of weeds and corn were observed 15 d after application.
2.3.3Weeding and safety test in the flax field. 30 d after the emergence of flax, most of the weeds in the field were sprayed with herbicides and auxiliaries at the stage of 3 to 4 true leaves. The herbicides tested were MCPA-Na, clethodim, haloxyfop and quizalofop-p-ethyl, and the application was the same as that in the pot experiment. With spraying water as control, random block design was used, each treatment was repeated 3 times, and the plot area was 10 m2. The effects of pesticide application on the growth of weeds and flax plants in the field were observed 20 d after application.
2.3.4Determination of drug damage. "-": no drug damage, normal growth of leaves and plants; "+": 1% to 20% of the leaf area withered; "++": 21% to 35% of the leaf area withered; "+++": 36% to 50% of the leaf area withered; "++++": 51% to 75% of the leaf area withered; "+++++": 76% to 100% of the leaf area withered.
2.4 Control effect investigation and statistical analysis
2.4.1Pot experiment. On the 7th and 14th day after treatment, the number of weeds and the control effect on fresh weight were investigated in 3 pots per treatment.
2.4.2Corn fields. On the 14th day after treatment, 10 representative corn plants were selected from each plot, the plant height and fresh weight were measured, and the control effects on plant height and fresh weight were calculated. At the same time, the number of weeds, fresh weight and herbicide damage to corn plants were investigated.
2.4.3Flax fields. 14 days after treatment, 15 representative flax plants were selected from each plot, the plant height and fresh weight were measured, and the control effects on plant height and fresh weight were calculated. And the herbicide damage to corn plants was investigated. At the same time, the number and fresh weight of weeds in each plot were investigated.
2.4.4Control effect and inhibition rate. Control effect(%)=[Control weed number (fresh weight)-Treated weed number (fresh weight)]-Control weed number (fresh weight)×100;
Plant height (fresh weight) inhibition rate(%)=[Control plant height (fresh weight)-Treated plant height (fresh weight)]-Control plant height (fresh weight)×100.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Effect of herbicide on the control of weedM.aquaticumL.Table 1 showed the effects of different herbicides on the control of broadleaf weedM.aquaticumL. From this table, it can be seen that 7 d after treatment, MCPA-Na had the best control effect on weedM.aquaticumL., and both the plant control effect and fresh weight inhibition rate were up to 100%. The control effect of other herbicides was 0, and the inhibition rate of fresh weight was 0-45.2%, respectively. The inhibition rate of fresh weight of MCPA-Na+quizalofop-p-ethyl was the highest, followed by that of MCPA-Na+clethodim (43.8%). 14 d after treatment, the control effect of five treatments (MCPA-Na, MCPA-Na+clethodim, MCPA-Na+quizalofop-p-ethyl, bentazon and nicosulfuron·atrazine) was the best, with the fresh weight inhibition rate and plant control effect reaching 100%, followed by that of three herbicide treatments (atrazine, mesotrione·nicosulfuron·atrazine and mesotrione), with the control effect of 66.7%-83.3%, and the fresh weight inhibition rate of 66.2% and 86.5%. The control effect of other herbicides was still 0, and the inhibition rate of fresh weight was only 1.4%-24.7%. The above analysis showed that there were differences in the control effects of different herbicides and their combinations on broadleaf weedM.aquaticumL., and the effect of MCPA-Na was the fastest and the best after application. All the weeds died on the 7th day after treatment. On the 14th day after treatment, allM.aquaticumL. died under four treatments (MCPA-Na+clethodim, MCPA-Na+quizalofop-p-ethyl, bentazon and nicosulfuron·atrazine). The results showed that the five treatments had good control effect on weedM.aquaticumL.
3.2 Effects of herbicide on control of weedPoaannuaL.The effects of different herbicides on the control ofP.annuaL., a weed of Gramineae, are shown in Table 2. It can be seen from the table that 7 days after treatment, the treatment of 13 herbicides (or mixtures) had little effect on the weedP.annuaL., and the plant control effect was 0. The inhibition rate of fresh weight was only 3.6%-8.4% for MCPA-Na and its combination and nicosulfuron treatment. Atrazine treatment had the best effect 14 days after treatment, and the plant control effect and inhibition rate fresh weight reached 100%, followed by that of nicosulfuron·atrazine and mesotrione·nicosulfuron·atrazine, with the control effect of 66.7%, and the fresh weight inhibition rate of 74.8%-78.6%, respectively. The treatments of nicosulfuron, mesotrione, MCPA-Na+haloxyfop, MCPA-Na, clethodim, haloxyfop and quizalofop-p-ethyl had little effect onP.annuaL. The control effect on the plant was 0, and the inhibition rate of fresh weight was 0-20.7%, respectively. The results showed that different herbicides and their combinations had little effect on the control ofP.annuaL. at the early stage after treatment (7 days after treatment), and the plant control effect and fresh weight inhibition rate was low or zero. However, the control effect of atrazine was the best on the 14th day after treatment, followed by that of nicosulfuron·atrazine and mesotrione·nicosulfuron·atrazine, and the control effect of the other treatments was not satisfactory.
Table 1 Differences in control effects of different herbicides onMalachiumaquaticumL.
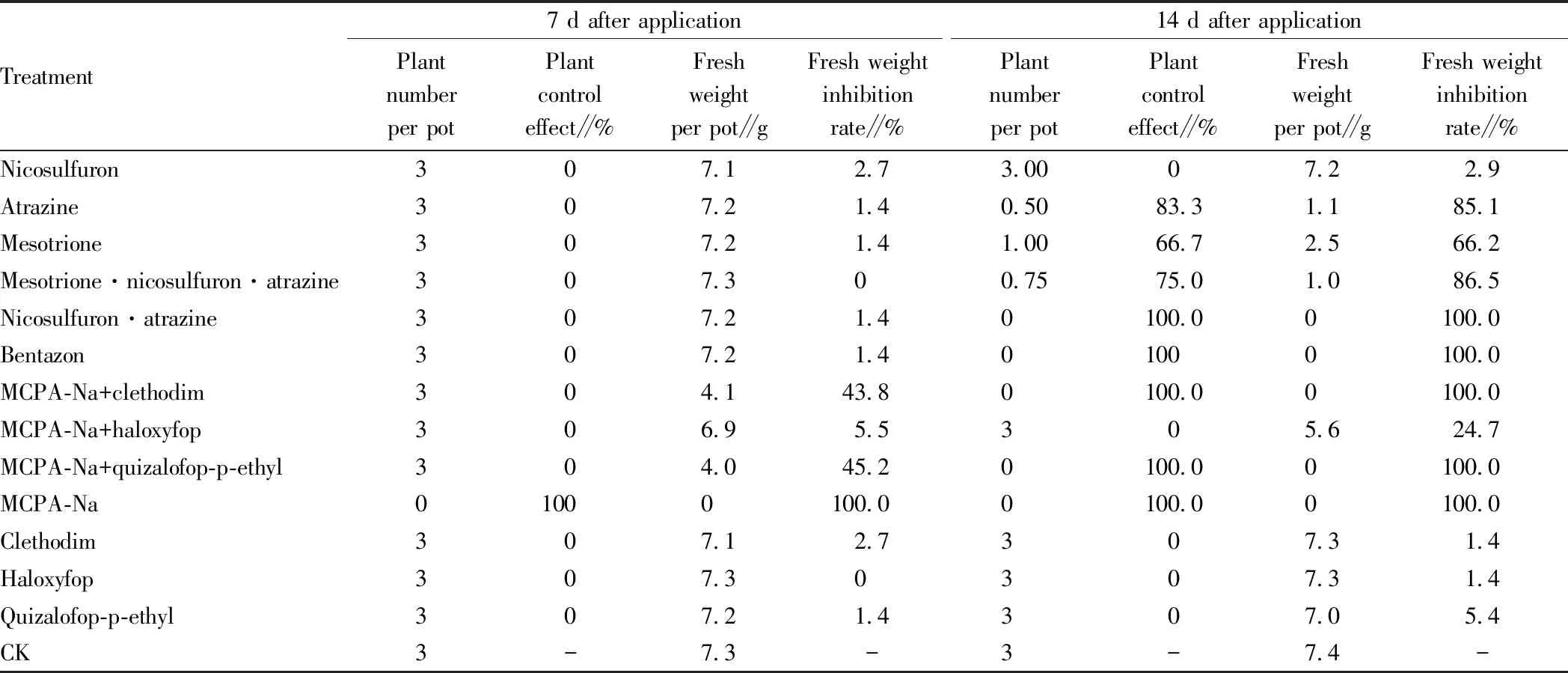
Treatment7 d after applicationPlantnumberper potPlantcontroleffect∥%Freshweightper pot∥gFresh weightinhibitionrate∥%14 d after applicationPlantnumberper potPlantcontroleffect∥%Freshweightper pot∥gFresh weightinhibitionrate∥%Nicosulfuron307.12.73.0007.22.9Atrazine307.21.40.5083.31.185.1Mesotrione307.21.41.0066.72.566.2Mesotrione·nicosulfuron·atrazine307.300.7575.01.086.5Nicosulfuron·atrazine307.21.40100.00100.0Bentazon307.21.401000100.0MCPA-Na+clethodim304.143.80100.00100.0MCPA-Na+haloxyfop306.95.5305.624.7MCPA-Na+quizalofop-p-ethyl304.045.20100.00100.0MCPA-Na01000100.00100.00100.0Clethodim307.12.7307.31.4Haloxyfop307.30307.31.4Quizalofop-p-ethyl307.21.4307.05.4CK3-7.3-3-7.4-
Table 2 Differences in control effects of different herbicides onPoaannuaL.
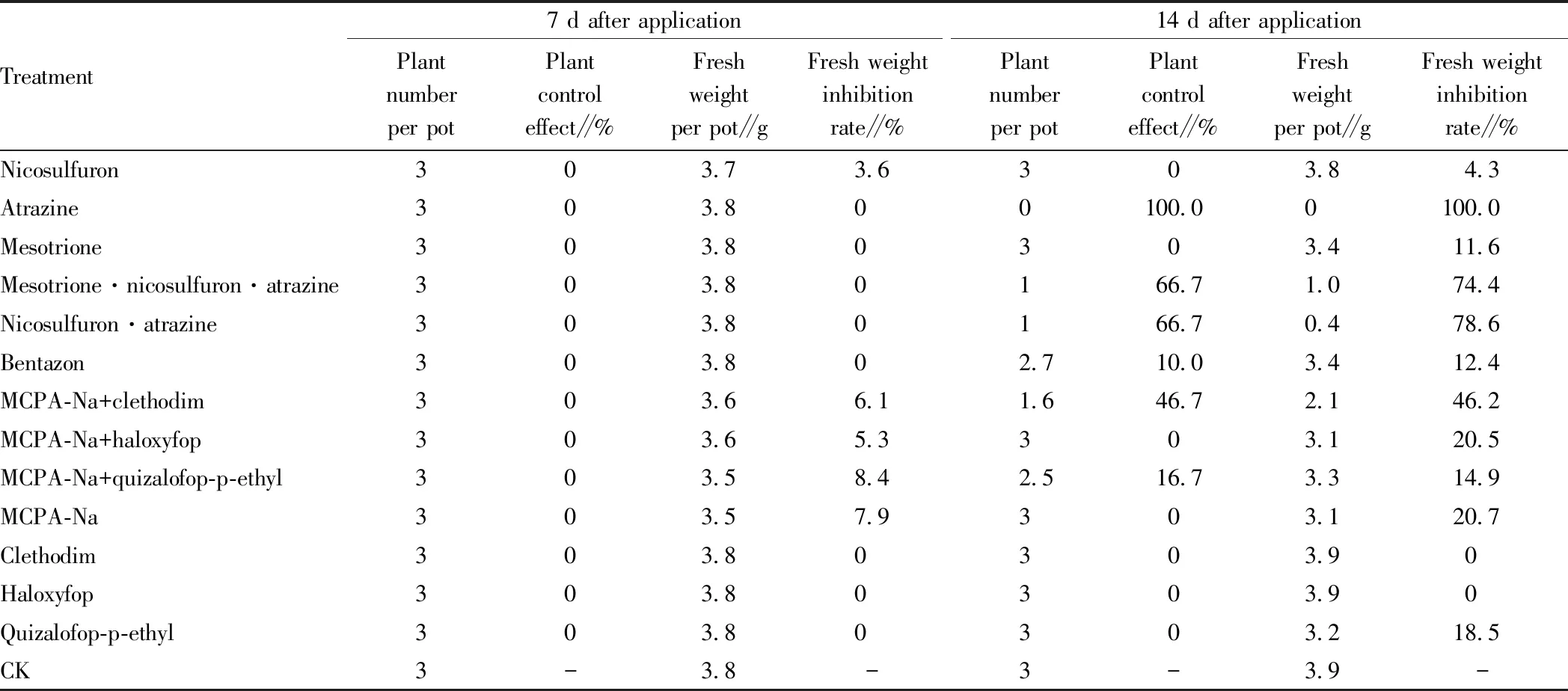
Treatment7 d after applicationPlantnumberper potPlantcontroleffect∥%Freshweightper pot∥gFresh weightinhibitionrate∥%14 d after applicationPlantnumberper potPlantcontroleffect∥%Freshweightper pot∥gFresh weightinhibitionrate∥%Nicosulfuron303.73.6303.84.3Atrazine303.800100.00100.0Mesotrione303.80303.411.6Mesotrione·nicosulfuron·atrazine303.80166.71.074.4Nicosulfuron·atrazine303.80166.70.478.6Bentazon303.802.710.03.412.4MCPA-Na+clethodim303.66.11.646.72.146.2MCPA-Na+haloxyfop303.65.3303.120.5MCPA-Na+quizalofop-p-ethyl303.58.42.516.73.314.9MCPA-Na303.57.9303.120.7Clethodim303.80303.90Haloxyfop303.80303.90Quizalofop-p-ethyl303.80303.218.5CK3-3.8-3-3.9-
3.3 Effects of herbicides on weed control in the corn field and seedling growth of cornThe effects of different herbicides on weed control and seedling growth of corn are shown in Table 3. From this table, it can be seen that there were some differences in the control of weeds in corn field among the six herbicides, the variation of plant control effect was 42.33%-91.61%, and the inhibition rate of fresh weight was 47.68%-93.57%, respectively. Four treatments (nicosulfuron·atrazine, mesotrione·nicosulfuron·atrazine, atrazine and bentazon) showed better performance, the control effect on the plant was higher than 83.59%, and the inhibition rate of fresh weight was higher than 86.43%. Each herbicide treatment (except for mesotrione·nicosulfuron·atrazine) had little inhibitory effect on plant height and fresh weight. The inhibition rate of plant height and fresh weight were 0.17%-2.79%, 0-3.87%, respectively. This showed that spraying herbicides had a certain effect on plant height and fresh weight of corn, but it was not obvious. Thus it can be seen that after taking into account the control effect of herbicides on weeds in the corn field and the inhibition rate of corn plants, the application effect of four herbicides (atrazine, mesotrione·nicosulfuron·atrazine, nicosulfuron·atrazine and bentazon) was good in the corn field, with high weed plant control effect, little inhibitory effect on corn plants and no herbicide damage.
Table 3 Effects of different herbicides on weeds and seedling growth of corn
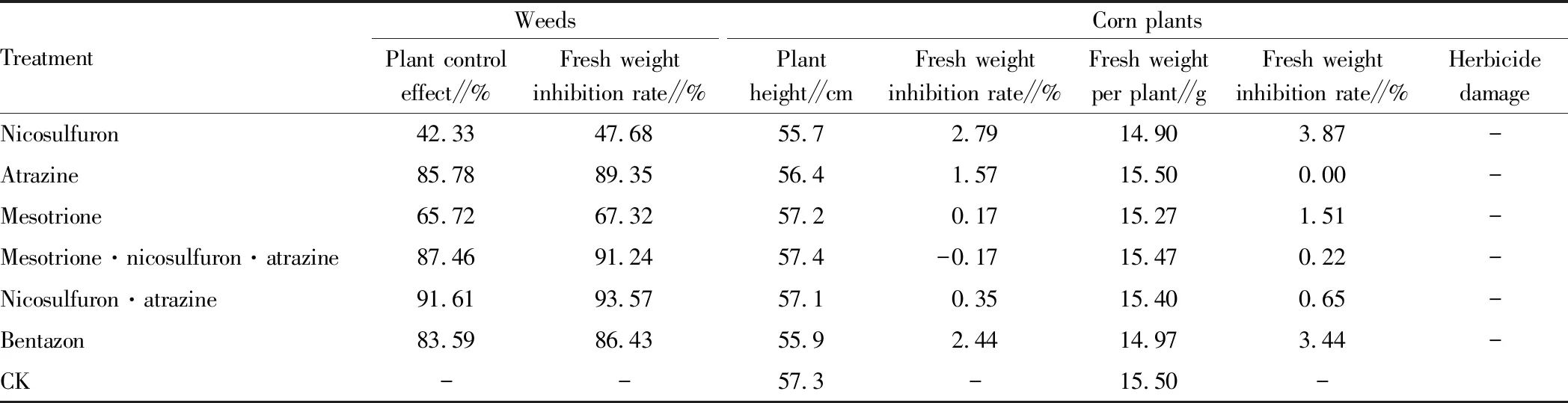
TreatmentWeedsPlant controleffect∥%Fresh weightinhibition rate∥%Corn plantsPlantheight∥cmFresh weightinhibition rate∥%Fresh weightper plant∥gFresh weightinhibition rate∥%HerbicidedamageNicosulfuron42.3347.6855.72.7914.903.87-Atrazine85.7889.3556.41.5715.500.00-Mesotrione65.7267.3257.20.1715.271.51-Mesotrione·nicosulfuron·atrazine87.4691.2457.4-0.1715.470.22-Nicosulfuron·atrazine91.6193.5757.10.3515.400.65-Bentazon83.5986.4355.92.4414.973.44-CK--57.3-15.50-
3.4 Effects of herbicides on weed control and flax seedling growth in the flax fieldTable 4 showed the effects of different herbicides on the control of weeds in the flax field and on the growth of flax at seedling stage. From this table, it can be seen that there were some differences in the control of weeds in the flax field among 7 kinds of herbicides (or mixtures). The control effect on plant was 10.25%-81.53%, and the inhibition rate of fresh weight was 6.89%-77.29%, respectively. The control effect of MCPA-Na+clethodim was the best, followed by that of MCPA-Na and MCPA-Na+quizalofop-p-ethyl, and the control effect of the other treatments was poor. All herbicide treatments had little inhibitory effect on plant height and fresh weight of flax (except for the plant height in haloxyfop treatment and the fresh weight in the clethodim treatment). The inhibition rates of plant height and fresh weight were 0.43%-4.26%, 0.99%-4.95%, respectively. All of them had no obvious herbicide damage to flax plants, indicating that spraying herbicides had little effect on the growth and development of flax. The above results showed that the treatment of MCPA-Na+clethodim had the best weed control effect and had no chemical effect on the growth of flax, followed by that of MCPA-Na and MCPA-Na+quizalofop-p-ethyl.
Table 4 Effects of herbicides on weed control and flax seedling growth in the flax field
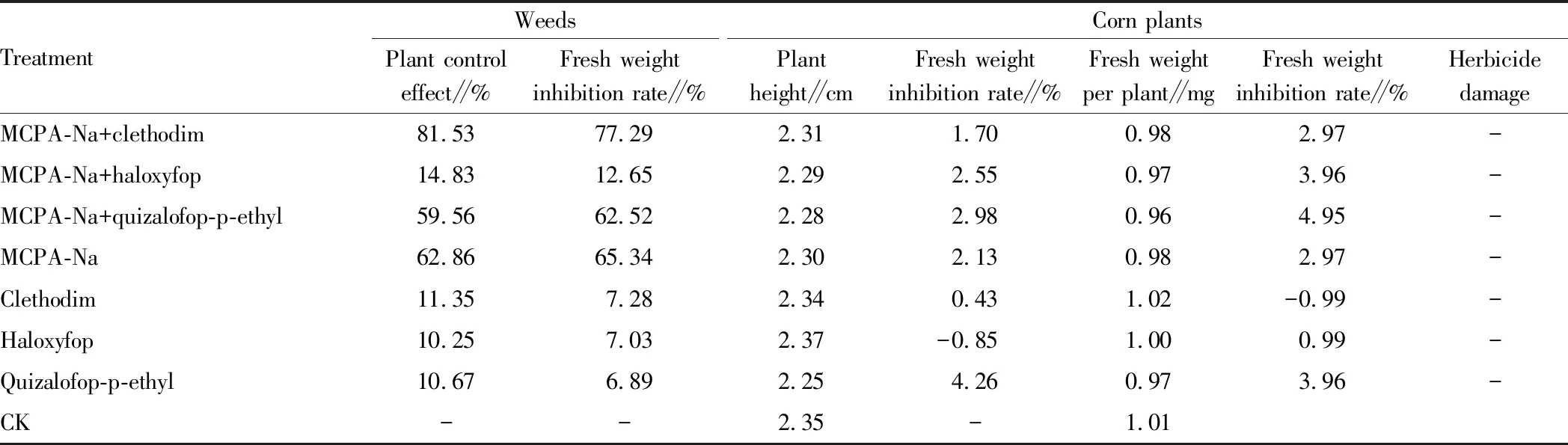
TreatmentWeedsPlant controleffect∥%Fresh weightinhibition rate∥%Corn plantsPlantheight∥cmFresh weightinhibition rate∥%Fresh weightper plant∥mgFresh weightinhibition rate∥%HerbicidedamageMCPA-Na+clethodim81.5377.292.311.700.982.97-MCPA-Na+haloxyfop14.8312.652.292.550.973.96-MCPA-Na+quizalofop-p-ethyl59.5662.522.282.980.964.95-MCPA-Na62.8665.342.302.130.982.97-Clethodim11.357.282.340.431.02-0.99-Haloxyfop10.257.032.37-0.851.000.99-Quizalofop-p-ethyl10.676.892.254.260.973.96-CK--2.35-1.01
4 Conclusion
The pot experiment showed that there were differences in the control effects of different herbicides and their combinations on the broadleaf weedM.aquaticumL. and Gramineae weedP.annuaL. As far as the control effect onM.aquaticumL. is concerned, the control effect of MCPA-Na was the best and also the fastest. 7 days after treatment, the control effect and fresh weight inhibition rate of weeds were up to 100%. After four treatments (MCPA-Na+clethodim, MCPA-Na+quizalofop-p-ethyl, bentazon and nicosulfuron·atrazine), the effect was slightly slow, but the control effect was very good. 14 days after the treatment, all the weeds ofM.aquaticumL. died. The results showed that the five treatments had good control effects on weeds. According to the control effect on Gramineae weedP.annuaL., the effect of 13 herbicides was slow, and the effect was not obvious 7 d after treatment. 14 days after treatment, the effect of herbicide atrazine was the best, and all the weeds died. It was followed by nicosulfuron·atrazine and mesotrione·nicosulfuron·atrazine, with the plant control effect of 66.7% and the fresh weight inhibition rate of 74.8%-78.6%, respectively. The study on the application effect of herbicide in the field showed that four treatments (nicosulfuron·atrazine, mesotrione·nicosulfuron·atrazine, atrazine and bentazon) in the corn field showed ideal performance, the control effect on the plant was more than 83.59%, and the inhibition rate of fresh weight was higher than 86.43%. Moreover, it had little inhibitory effect on plant height and fresh weight of corn, and there was no obvious herbicide damage. The treatment of MCPA-Na+clethodim had the best weed control effect in the flax field, and the plant control effect and inhibition rates of fresh weight were 81.53% and 77.29%, respectively, followed by that of MCPA-Na and MCPA-Na+quizalofop-p-ethyl. These treatments were less harmful to flax plants.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Career Planning Education Paths for Students of Aquatic Animal Medicine Discipline in the Context of the Belt and Road Initiative: A Case Study of Construction Achievement of Guangdong Ocean University
- Screening and Simple Identification of Drought-resistant Lines in Sugarcane Breeding
- Optimization of Technology for Increasing Total Ester Content of Jujube Wine by Adding Nutrients
- Comprehensive Risk Prevention of "Ice Silk Road" Construction in the Context of Global Warming
- Childcare, Elderly Caring and Off-farm Employment of Rural Couples in China
- Regional Advantages of Green Feed Production in China: Based on Panel Data of 31 Provinces in China from 2014 to 2016
