Risk Assessment and Service Benefit Evaluation of Forestry Meteorological Disasters in Guangxi
2019-05-24ShuyanHUANG1YanjunLI2YouhuaLI1ShanGAO1WeiLI
Shuyan HUANG1*, Yanjun LI2, Youhua LI1, Shan GAO1, Wei LI
1. Guangxi Meteorological Service Center, Nanning 530022, China; 2. Guangxi Climate Center, Nanning 530022, China; 3. Guangxi Meteorological Bureau, Nanning 530022, China
Abstract In order to strengthen the construction of forestry meteorological service capacity and improve the quality of forestry meteorological services, the national forestry meteorological disaster risk survey and service benefit assessment were carried out from November 2016 to May 2017. A total of 196 risk sites in Guangxi were collected by means of questionnaire survey, expert evaluation and field survey. The results showed that fire, pest and wind hazards are the main types of risk points in Guangxi. The survey showed that there were 77 monitoring stations around the disaster risk sites belonging to the Forestry Sector, which mainly monitor fire hazards, while other disasters had no monitoring point yet. Early warning facilities were still constantly improving. The meteorological disasters that affecting forestry production were drought, gale, and heavy rainfall, and the main meteorological hazard factors were temperature, wind speed, and precipitation. Forest fire prevention, forestry resources development and utilization, forestation and tending demand for meteorological services were relatively large. It was hoped that forestry meteorological service products would be obtained through telephone, SMS and early warning systems. In addition, experts objectivly evaluated the contribution rate of meteorological services in Guangxi. The contribution rate of forest meteorological services in the whole region was 8.41%. The scale of Guangxi’s total forestry output value was 31.478 billion yuan in 2016. According to the calculation of this value, the service benefit value had reached 2.647 billion yuan. In conclusion, strengthening the cooperation in forestry meteorological monitoring, technology development, and emergency response, and further improving forestry meteorological services and effective reducing forestry disaster losses are the top priorities of the meteorological department.
Key words Forestry, Risk census, Meteorological service, Benefit evaluation
1 Introduction
In order to implement theFrameworkAgreementonDeepeningComprehensiveStrategicCooperationissued by the China Meteorological Administration and the National Forestry Administration, in accordance with the requirements ofNoticeonDoingaGoodJobinForestryMeteorologicalDisasterRiskInvestigationandServiceBenefitEvaluationissued by Office of Emergency Disaster Reduction and Public Service of China Meteorological Administration and Office of National Forest Fire Prevention Command, we carried out the forestry meteorological disaster risk survey and service benefit evaluation in Guangxi. The purpose is to find out and understand the forestry meteorological disaster risks and service demand in Guangxi, evaluate and understand meteorological service benefits, and determine relevant indicators; the survey is demand-oriented and aims at strengthening Guangxi forestry meteorological service capacity construction, and improving the quality of forestry meteorological services. The survey items include the location and coverage area of the forest farms or townships and villages where the meteorological disasters are situated, the types of dominant tree species, the types of meteorological disasters, the distribution of disaster seasons, the arrangement of disaster monitoring and early warning facilities,etc. The survey also includes the demands for meteorological services in key areas such as forest fire prevention, forestry pest control, afforestation and tending, forest resources development and utilization, as well as the contribution of meteorological services to forestry-related production.
2 Materials and methods
We carried out the questionnaire survey, expert evaluation and field survey, and analyzed the survey data by using Delphi method and comparative analysis method[1]. The specific implementation plan[2]is illustrated in Fig.1.
The survey objects include Guangxi Forest Fire Prevention Command, Control and Quarantine Station, Forest Management Department, Seedling Station and its jurisdictional units and forest farms, involving forest fire prevention, forestry pest control, afforestation and tending, forestry resources development and utilization. The survey includes 37 experts in leadership, technology, management and finance who focus on the production line (Table 1). We selected five typical units including Baise Yachang Forest Farm, Beihai Protective Forest Farm, Fangchenggang Central Nursery, Nanning Forestry Bureau and Laibin Weidu Forest Farm to carry out forestry meteorological service benefit evaluation.
Table 1 Proportion of survey expert types

Expert typeNumber of peoplePercentage∥%Leadership924.3Technical2054.1Management616.2Financial25.4
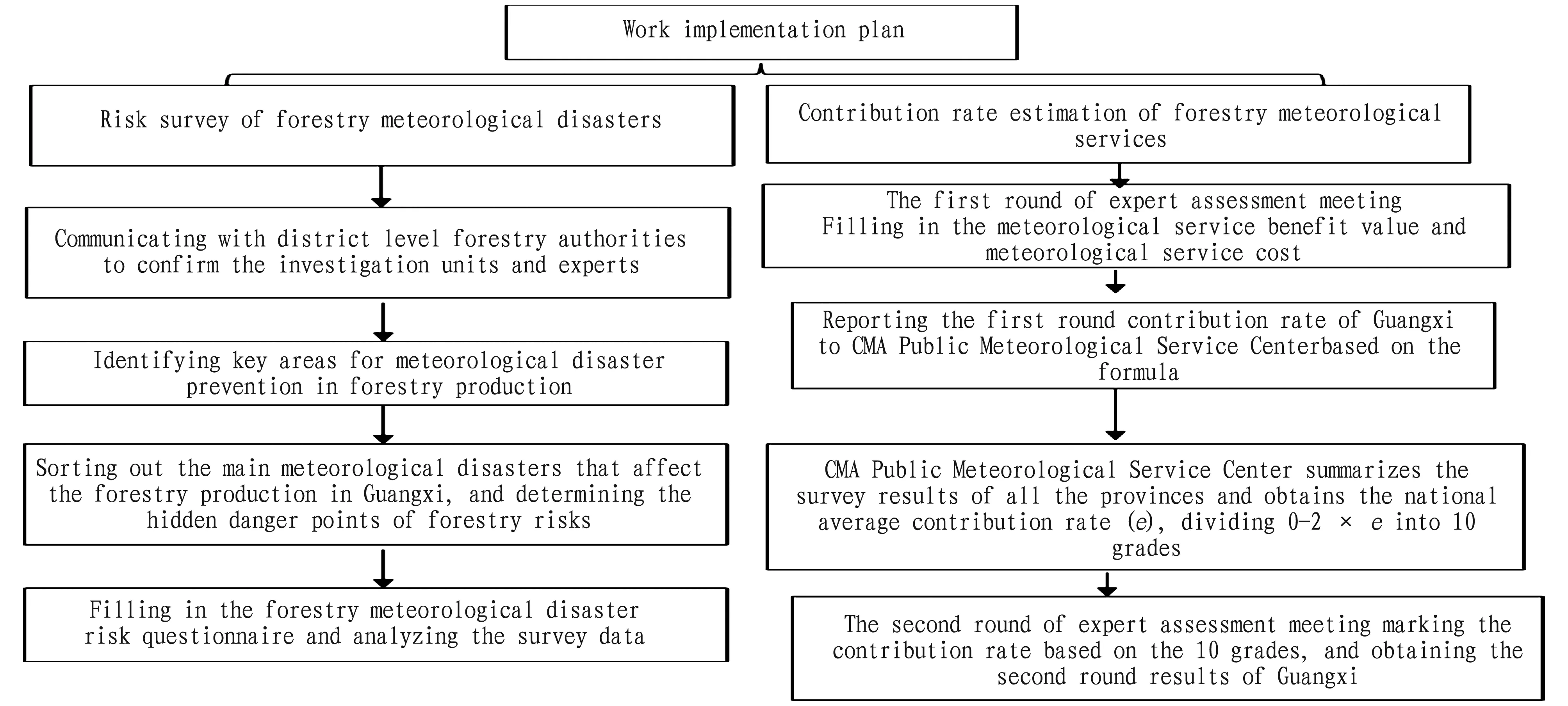
Fig.1 Implementation plan for risk general survey and service benefit evaluation of forestry meteorological disasters in Guangxi
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Distribution of risk points of forestry meteorological disasters in GuangxiWe collected a total of 196 risk hazard related points, the specific distribution is shown in Fig.2.
Fig.2 Distribution of forestry hidden danger points in Guangxi
3.2 Basic characteristics of Guangxi risk pointsThrough further analysis, it can be known that fires, plant diseases and insect pests, and wind disasters[3-4]are the main types of forestry risks in Guangxi, accounting for 50.40%, 19.90% and 15.50%, respectively (Fig.3); the main dominant species are conifer, evergreen and softwood, accounting for 34.20%, 33.20% and 14.80%, respectively (Fig.4); the main dominant tree species were eucalyptus,Pinusmassoniana, pine, and cedar, accounting for 29.89%, 17.93%, 15.76% and 13.04%, respectively (Fig.5).
3.3 Distribution characteristics of disaster risks in Guangxi
According to the risk point survey data, we analyzed the distribution characteristics of Guangxi risk points from three aspects: city, altitude and area. The survey results show that the risk points below 100 m above sea level and 300-500 m above sea level mainly exist in Guigang City, and the risk point area is 6.831 5×106m2and 5×106m2, respectively. In Laibin City, the risk point area with an altitude range of 100-300 m is 1.273 9 ×107m2. The risk points with altitude above 500 m are mainly distributed in Baise City, up to 4.384 53×106m2(Fig.6).
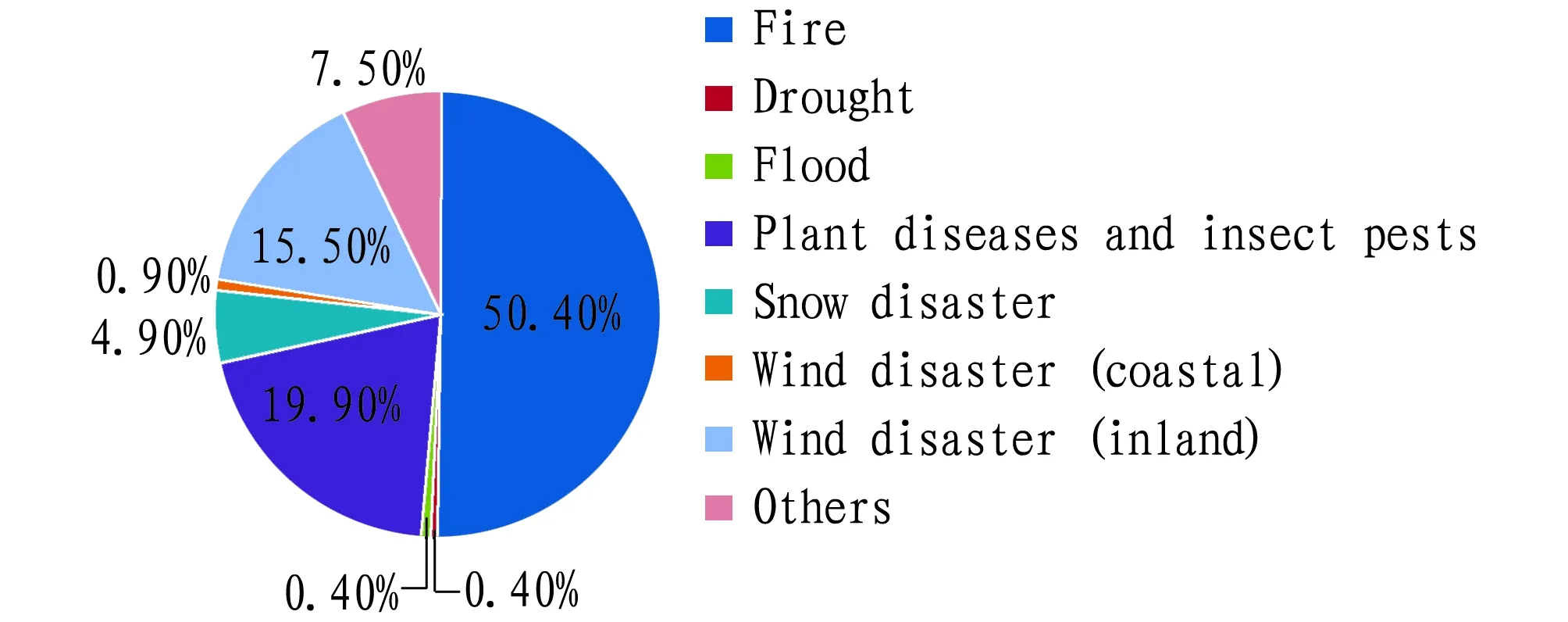
Fig.3 Types of disaster risk points
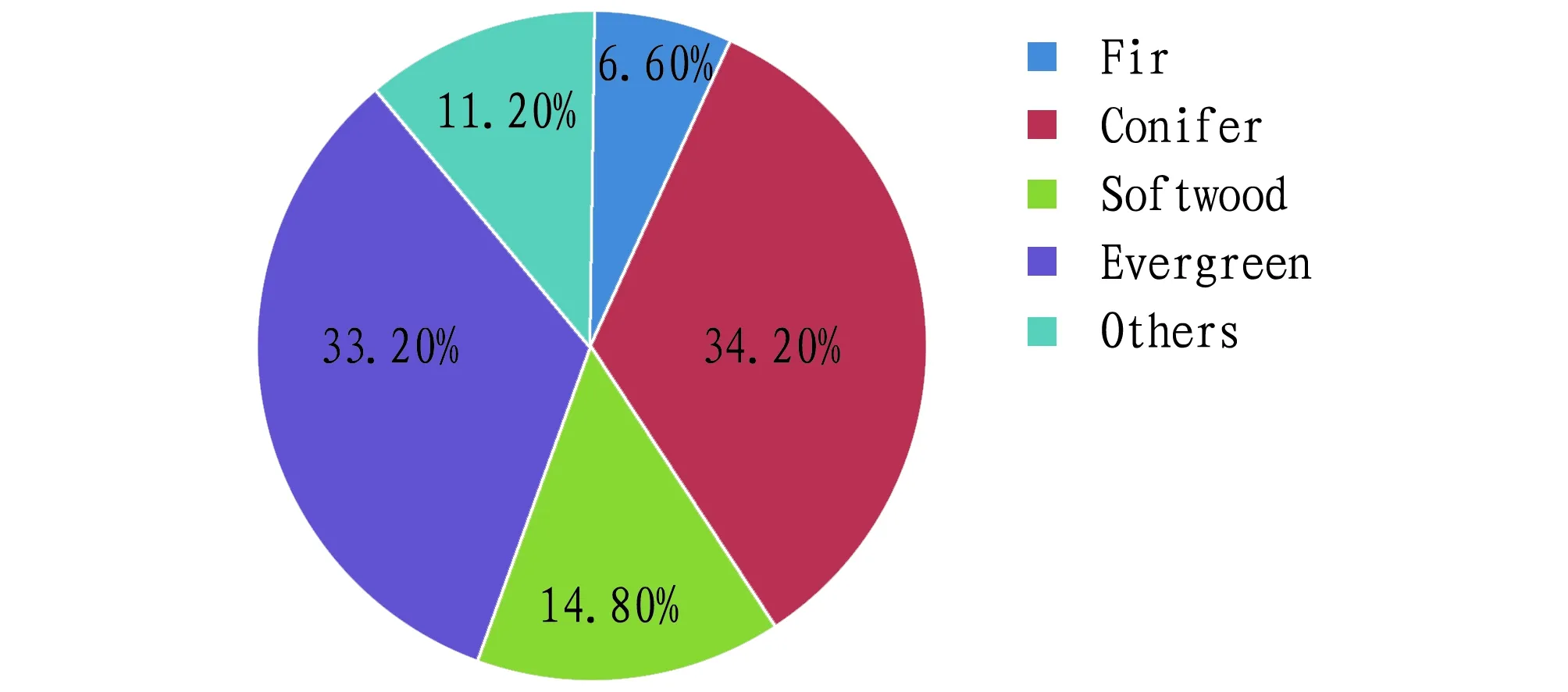
Fig.4 Classification of dominant tree species
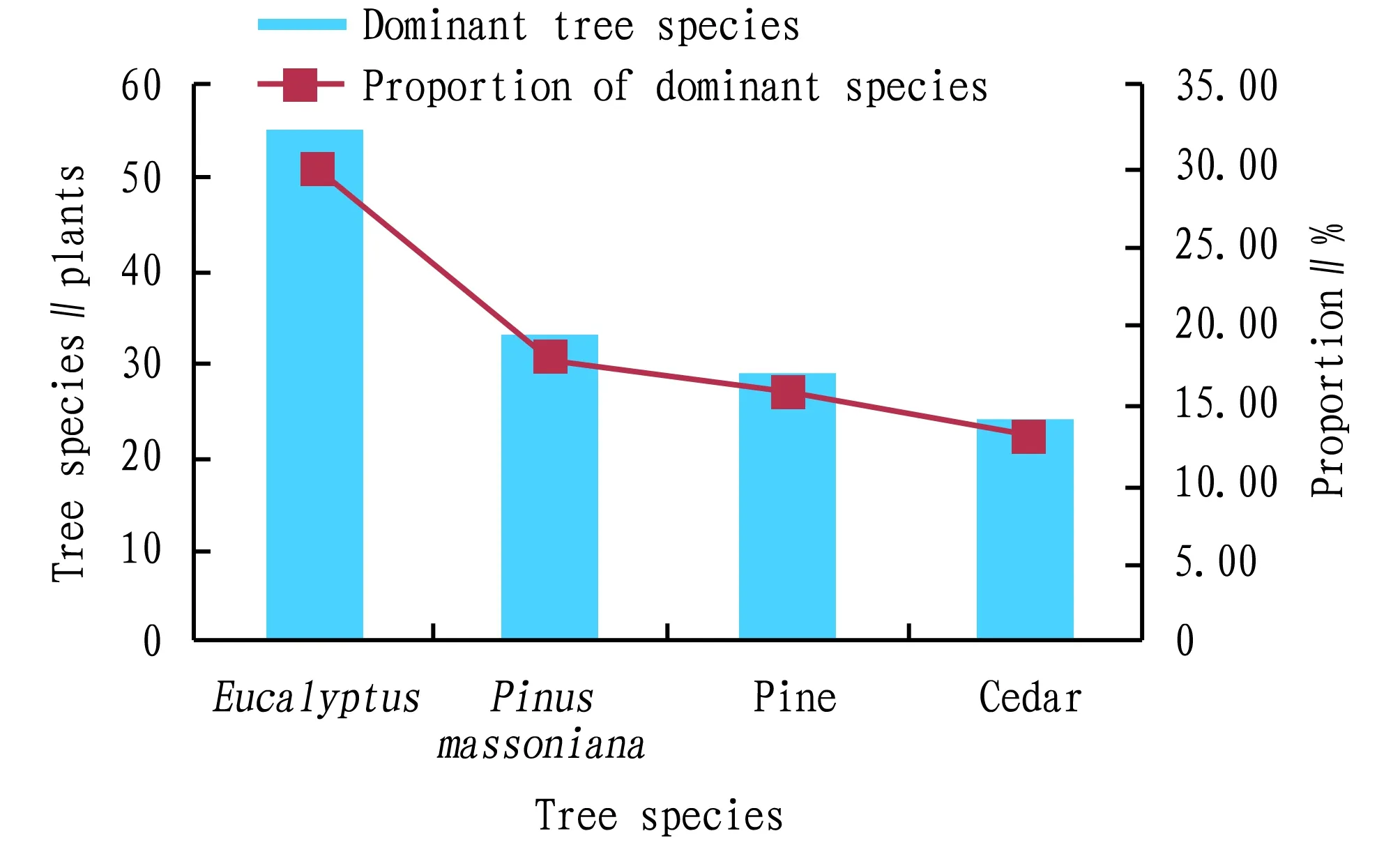
Fig.5 Distribution of dominant tree species
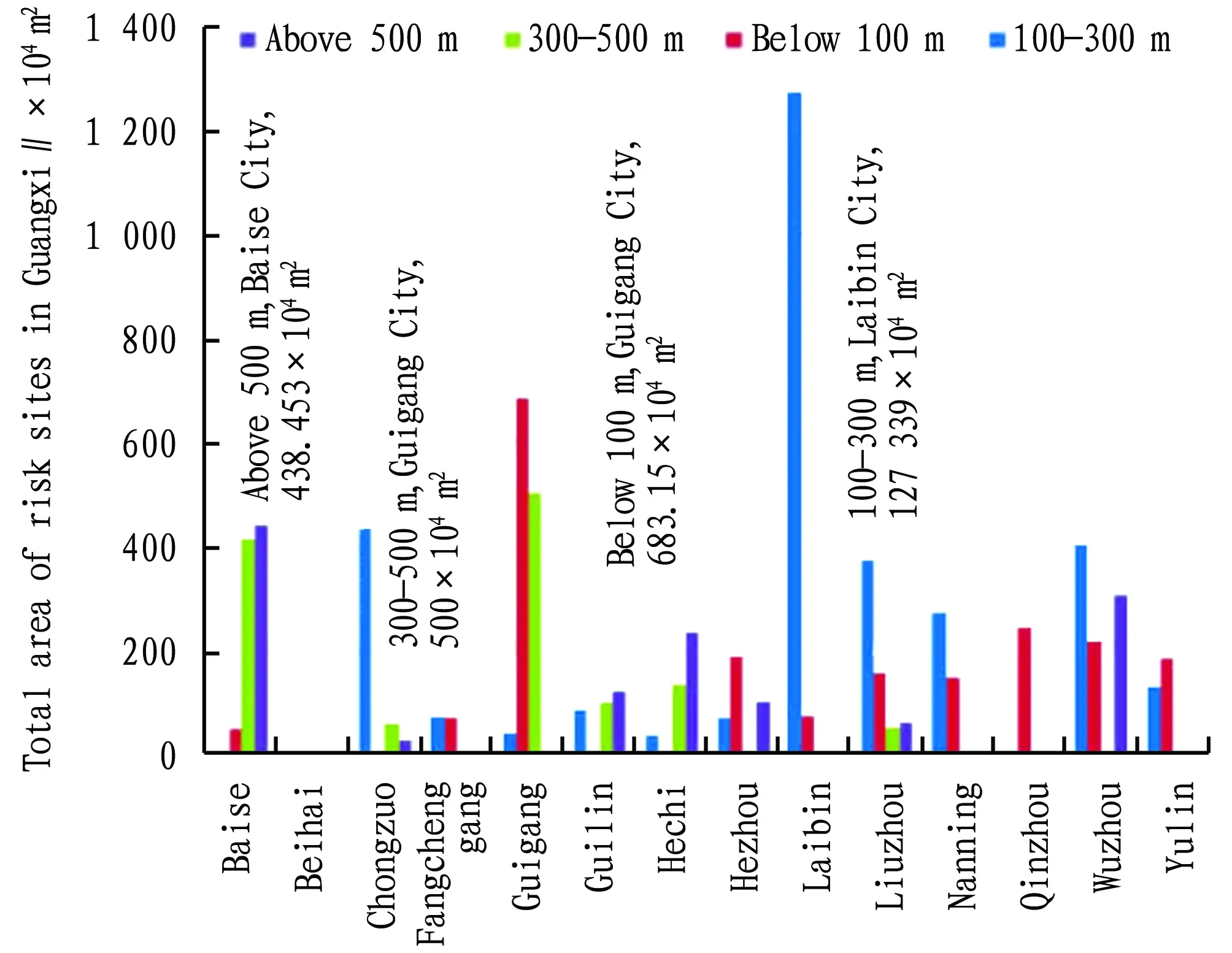
Fig.6 Distribution of risk points, altitude and area of cities in Guangxi
3.4.1Types of major meteorological disasters and disaster-causing factors. According to the survey, the main types of meteorological disasters in Guangxi include drought (40.00%), high temperature (39.73%), gale (inland) (12.33%), and heavy rainfall (3.01%) (Fig.7); the main disaster-causing factors are temperature (42.14%), humidity (33.49%), wind speed (12.07%), precipitation (10.93%), snow (1.37%),etc. (Fig.8). This is consistent with the geographical environment of Guangxi.
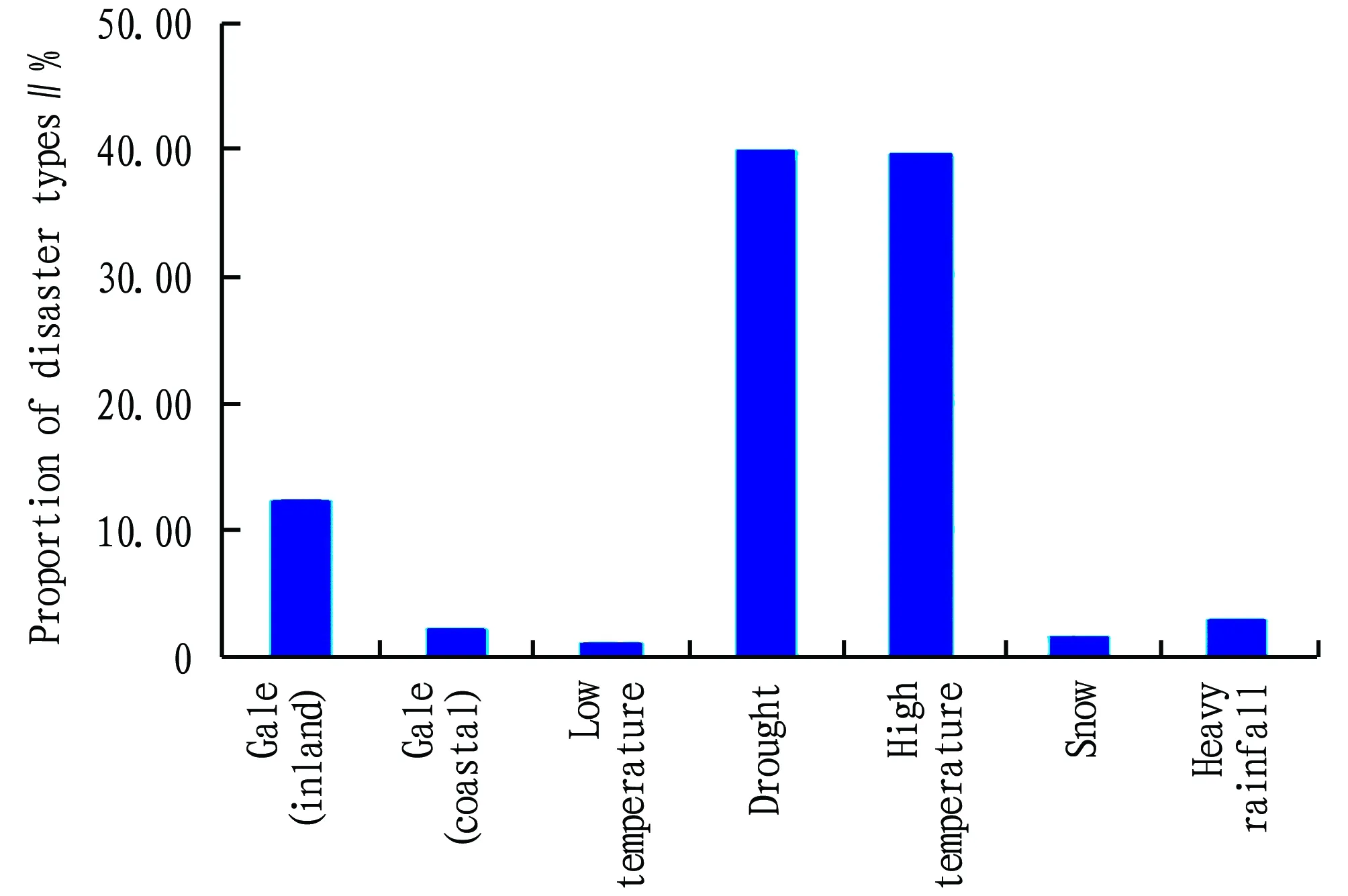
Fig.7 Types of meteorological disasters in Guangxi
According to the survey, meteorological factors affecting fires include high temperature and drought[5-7]. The fire is prone to occur from March to April and September to November. High temperatures lasting for 2-3 or more consecutive days are liable to fire, the fire area is related to the wind speed and wind direction at that time; plant diseases and insect pests are related to temperature and humidity, long-term high temperature weather will cause seedling pests and diseases; afforestation tending is sensitive to wind, rain, snow and low temperature. Precipitation above the level of heavy rain, gale above eight scale will cause the seedlings to overturn, 3-5 consecutive days of rainy weather, freezing below 0℃ or low temperature between 5-6℃ up to five consecutive days or more is likely to cause rotten seedlings, which will adversely affect the afforestation and tending.
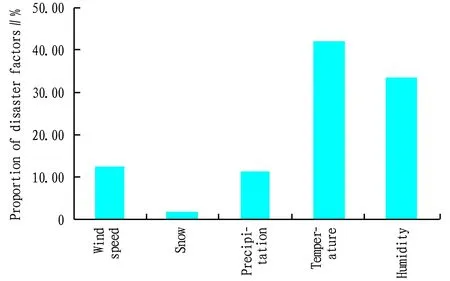
Fig.8 Main disaster-causing factors in Guangxi
3.4.2Accidents caused by disasters. According to the survey data, there were 16 natural disasters in Guangxi from 2011 to 2015, mainly caused by high temperature and drought (31.25%), gale (31.25%), and heavy rainfall (25%), resulting in economic losses of 6.84 million yuan. In 2016, nine accidents happened.
3.5 Monitoring and early warning of risk points of meteorological disasters in Guangxi
3.5.1Monitoring station distribution. Taking the risk points as the center, there are 163 stations with a monitoring range of 5 km around the risk point, of which 77 belong to the forestry department, mainly for fire hazards, however there is still no monitoring point for other disasters.
3.5.2Types and characteristics of monitoring stations. The types of monitoring stations in Guangxi include regional automatic stations, general stations, basic stations,etc. The departments are mainly meteorological and forestry departments, and their corresponding relationships are indicated in Table 2.
But what a strange assembly it was! Each monarch travelled in the way he thought most impressive; and some came borne in litters, others had carriages of every shape and kind, while the rest were mounted on elephants, tigers, and even upon eagles. So splendid a wedding had never been seen before; and when it was over the king announced that it was to be followed by a coronation, for he and the queen were tired of reigning50, and the young couple must take their place. The rejoicings lasted for three whole months, then the new sovereigns settled down to govern their kingdom, and made themselves so much beloved by their subjects, that when they died, a hundred years later, each man mourned them as his own father and mother.
Table 2 Statistics of monitoring stations and their departments in Guangxi
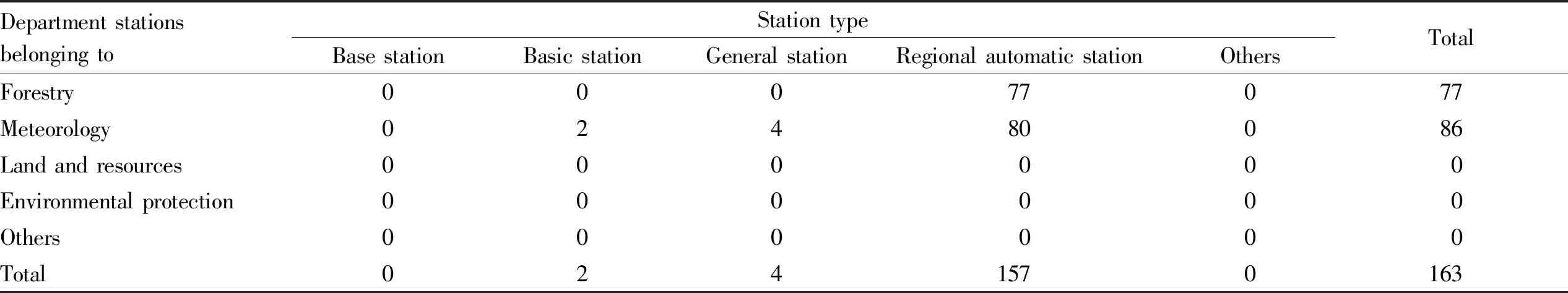
Department stationsbelonging toStation typeBase stationBasic stationGeneral stationRegional automatic stationOthersTotalForestry00077077Meteorology02480086Land and resources000000Environmental protection000000Others000000Total0241570163
3.5.3Monitoring data management. According to the survey data, the main factors influencing the meteorological disasters are humidity, temperature, precipitation, and wind speed[3-4]. At present, the monitoring stations have not realized the sharing and exchange of data.
3.6 Early warning and prevention facilities of forestry meteorological disasters in Guangxi
3.6.1Early warning facility distribution. At present, the forestry department mainly gets to know the occurrence and changes of fires through observation stations, and there are few electronic displays (information boards). Others facilities such as mobile early warning clients, mobile TV, radio, telephone fax, and network WiFi have not been deployed yet.
3.6.2Types and characteristics of early warning facilities. According to the survey, the early warning facilities are still not perfect and are mainly distributed in Hengxian County and Wuming County of Nanning City, with an average annual warning frequency of 36 times.
3.6.3Early warning facility management. At present, the management of early warning facilities is mainly undertaken by the forestry department, and the existing facilities are used normally. The early warning products are forest fire hazard monitoring and forecasting.
3.6.4Preventive measures. In the aspect of preventive measures, the main engineering measures to prevent fire hazards include setting up isolation belts and reinforcement arrangements. In addition, other temporary preventive measures include: straightening the trees overturned by wind, extinguishing fire, evacuating personnel, repairing roads, repairing seedling sheds, and transferring seedlings, and so on.
3.7 Meteorological service benefit evaluation of the forestry in Guangxi
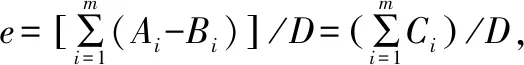
Table 3 Contribution rate level (1-10) and corresponding range of meteorological services in Guangxi[1]

Contribution rateLevelRange∥%LinkForest firepreventionPrevention and controlof forestry pestsAfforestationand tendingDevelopment andutilization of forestry resourcesTotal10-1.40000021.5-2.80000032.9-4.30000044.4-5.70010155.8-7.10000067.2-8.51000178.6-9.900112810.0-11.301001911.4-12.8000001012.9-14.200000Total11215
3.7.2Forestry meteorological service benefit value. According to the survey, the GDP (G) of Guangxi’s forestry in 2016 was 31.784 billion yuan, the contribution rate of forestry meteorological services (E) was 8.41%, and the benefit value of forestry meteorological services in the whole region (P=E×G) was 2.647 billion yuan.
3.8 Analysis on current situations of forestry meteorological services in Guangxi
3.8.1Basic conditions of the forestry meteorological service products. According to the survey, the most widely used forestry meteorological service products in Guangxi include: forecasting and early warning of forest fire risk, monitoring and forecasting of forest drought, monitoring (process monitoring) of forest fire points, special networked services, monitoring and forecasting of forest growth, and forecasting of forestry diseases and pests,etc.
3.8.2Main types of the forestry meteorological service products. Main types of the forestry meteorological service products in Guangxi include monitoring and forecasting of forest drought (forest drought meteorological index), monitoring (process monitoring) of forest fire points, forecasting and early warning of forest fire risk, forecasting of forestry diseases and pests, monitoring and evaluation of forest growth, and the first three types have high demands accounting for 29.29%, 22.78% and 22.78%, respectively (Fig.9).
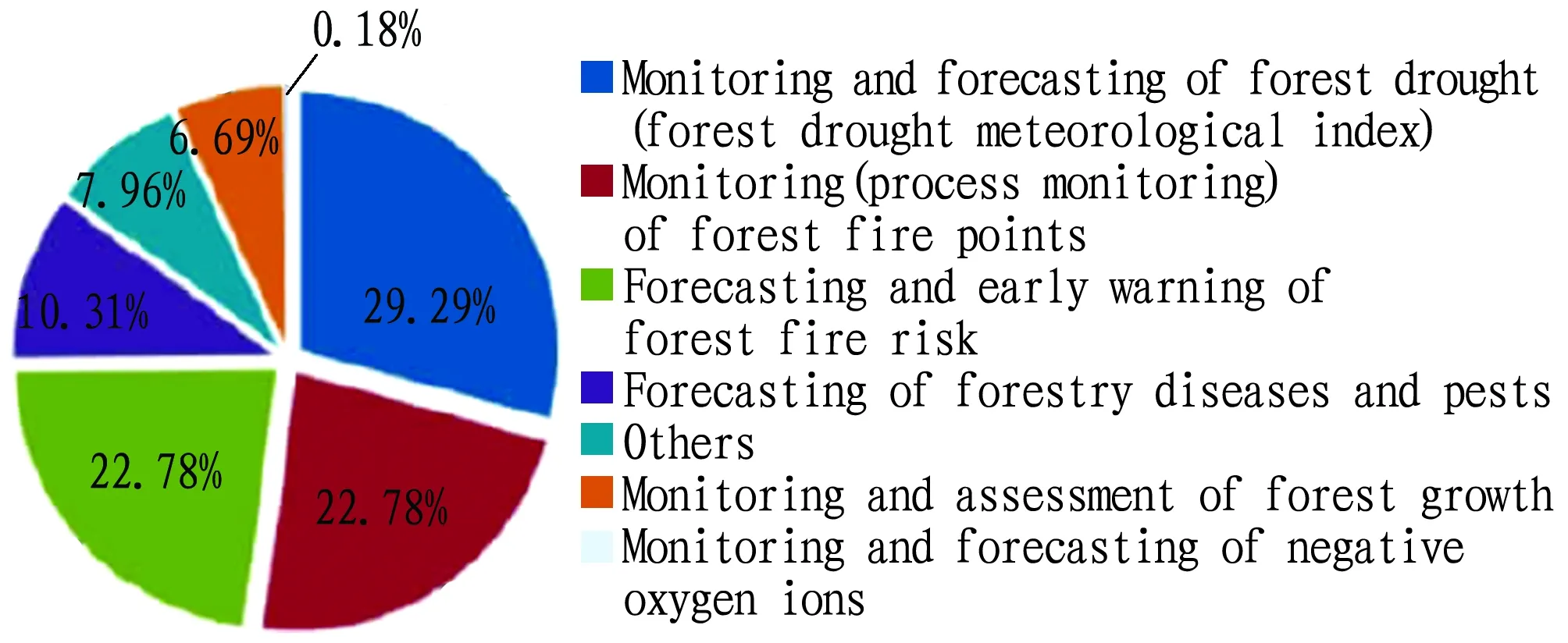
Fig.9 Distribution of the demands for forestry meteorological service products in Guangxi
3.8.3Forms of the forestry meteorological service products. From Fig.10, it can be seen that the demands for forestry meteorological service products in Guangxi are forest fire prevention (65.96%), afforestation and tending (24.82%) and forestry pest control (9.22%), while there is no relevant and targeted demand for the development and utilization of forestry resources.
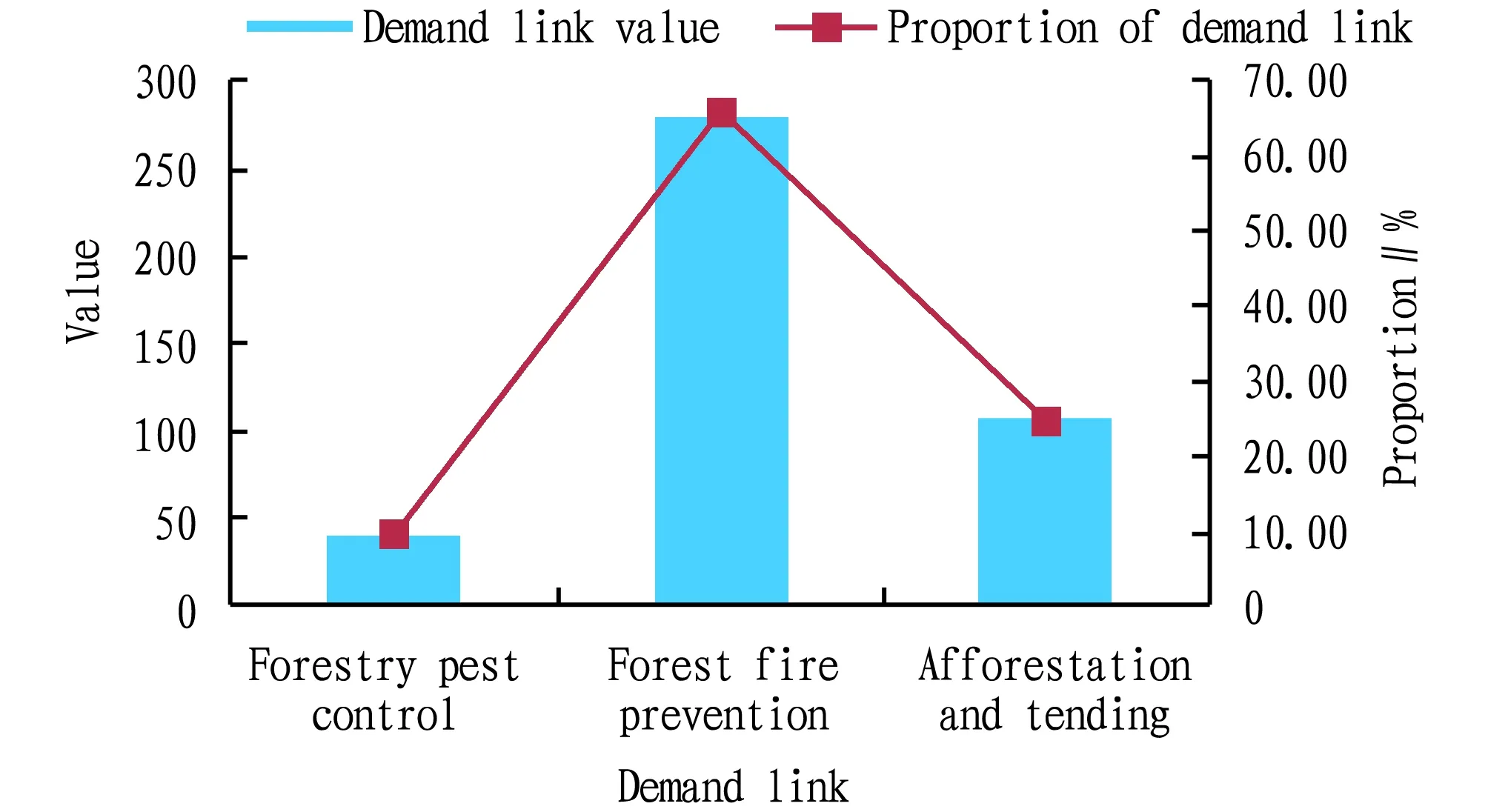
Fig.10 Demands for meteorological services in forestry production of Guangxi
3.9 Analysis on the demands for forestry meteorological service products in Guangxi
3.9.1Basic conditions of the demand products for forestry meteorological services in Guangxi. The demand products for forestry meteorological service in Guangxi mainly include long-term, medium-term, and short-term high temperature weather forecast for forest fires; weather trend forecast of pests and diseases; and forecasting of meteorological factors such as temperature, rainfall, and strong winds affecting afforestation[5-7].
3.9.2Main types of the demand products for forestry meteorological services. Main types of the demand products for forestry meteorological services in Guangxi include monitoring (process monitoring) of forest fire points, forecasting and early warning of forest fire risk, and monitoring and forecasting of forest drought, accounting for 27.50%, 25.50% and 23.50%, respectively (Fig.11).
3.9.3Forms of the demand products for forestry meteorological services. According to the survey data, forest fire prevention and development and utilization of forestry resources have higher demands for meteorological services, accounting for 68.8% and 18.8% respectively.
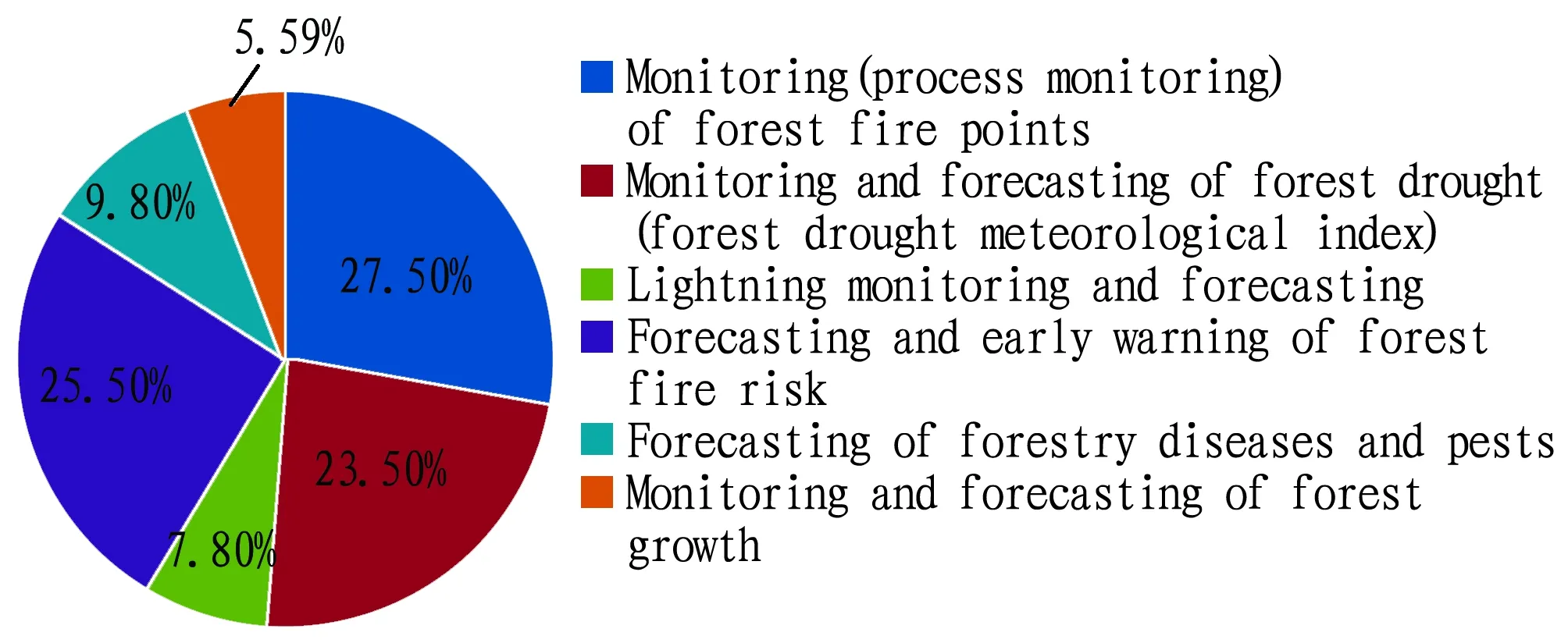
Fig.11 Main types of the demand products for forestry meteorological services
3.9.4Communication channels for forestry meteorological service demand products in Guangxi. According to the survey, telephone, SMS, and early-warning system are main communication channels for forestry meteorological service demand products in Guangxi, accounting for 29.40%, 29.40% and 17.60%, respectively (Fig.12).
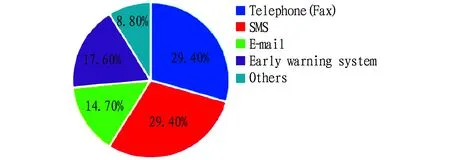
Fig.12 Communication channels for forestry meteorological service demand products in Guangxi
3.9.5Comparative analysis on the demands for forestry meteorological service products in Guangxi. According to the survey[8-10], forest fire prevention, forestry pest prevention and control, afforestation and tending, development and utilization of forestry resources are closely connected with the meteorological services. Apart from needing the provision of forecasting and early warning of forest fire risk and monitoring (process monitoring) of forest fire points, monitoring and forecasting of forest drought, the lightning, and forest growth, as well as special networked services (such as fire risk level publication, wind power, wind direction, rainfall, temperature, humidity and other factors) are also needed. In addition, services are needed to provide through television and the Internet, and early warning and forecast information are needed in a timely manner through telephone, SMS and early warning systems.
For a long time, Guangxi meteorological and forestry departments have maintained a good cooperative relationship, established a major forestry meteorological disaster early warning and release mechanism, and provided meteorological actual information and service information in a timely manner by various means. Main services include 24 h forest fire risk level through television and forecasting and warning of the high forest fire weather process in Guangxi. The professional meteorological services provided by network mainly include seasonal forest fire risk short-term climate prediction monthly forest fire risk short-term climate prediction, 10 d precipitation days and 10 d forest fire risk level, as well as 5 d rolling fire risk level and high fire risk prediction. In other words, when there is a continuous high temperature, drought and high fire risk in a local area for more than 10 d, the forest fire risk level, temperature and high fire risk weather duration are predicted for this area, but the service product is not refined, and there is still a gap in the demand for forestry meteorological service products.
4 Conclusions
According to the results of this risk census and service benefit evaluation, the types of forestry disasters in Guangxi are mainly fire, plant diseases and insect pests, and the types of meteorological disasters influencing forestry production mainly include drought, gale and heavy rainfall. The main meteorological factors include temperature, wind speed, and rainfall. At present, only the fire risk points are arranged with monitoring points, other disasters have no monitoring point yet, and early warning facilities are still constantly improving. Forest fire prevention, development and utilization of forestry resources, forestation and tending have high demands for meteorological services. The demand products for forestry meteorological service in Guangxi mainly include long-term, medium-term, and short-term weather high temperature forecast for forest fires, weather trend forecast of pests and diseases and forecasting of meteorological factors such as temperature, rainfall, and strong winds affecting afforestation and tending. Besides, it is expected that forestry meteorological service products would be obtained through telephone, SMS and early warning systems. The contribution rate of forest meteorological services in the whole region was 8.41%. The scale of Guangxi’s total forestry output value was 31.478 billion yuan in 2016. According to the calculation of this value, the service benefit value had reached 2.647 billion yuan.
Based on above results, we came up with the following recommendations. (i) it is recommended to strengthen the construction of forestry meteorological observation stations to achieve full sharing of various observational data such as forestry observation stations, forest resource basic data, forestry pest and disease data, meteorological observation stations, and meteorological satellite clouds. (ii) It is recommended to improve the timeliness and accuracy of forest fire risk meteorological level forecasting, jointly implement forestry industry and ecological meteorological services, jointly conduct meteorological level prediction of forestry pests and diseases, and use satellite remote sensing technology to jointly implement dynamic evaluation such as afforestation and forestry resource development and utilization. (iii) It is recommended to jointly strengthen and standardize the release of forest forecasting and early warning information, and further expand the information release channel. The meteorological department should take advantage of the national emergency warning information release platform to make information release faster, more efficient and more instructive. (iv) It is recommended to take advantage of the forest farm special management, to jointly build a forestry ecological observation station, improve visibility, illumination hours, lightning monitoring and negative oxygen ion concentration monitoring, so as to meet the needs of modern forestry for ecotourism.
AboutKIT
The Royal Tropical Institute (KIT) in Amsterdam is an independent centre of knowledge and expertise in the areas of international and intercultural cooperation, operating at the interface between theory and practice and between policy and implementation. The Institute contributes to sustainable development, poverty alleviation and cultural preservation and exchange.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Ridge Covering High-yield Cultivation Techniques of Jinhong Apple in Cold Region
- Different Fertilization Modes of Sugarcane in Latosolic Red Soil of Guangxi
- Effects of Seaweed Extracts on Promoting Growth and Improving Stress Resistance in Sugarcane
- Rules of Changes in Soil Nutrients and Enzyme Activities of Larix principis-rupprechtii in Different Forest Ages
- Cultivation Countermeasures of Farmers’ Ecological Consciousness and Behavior in Eco-civilization Construction——A Case Study of Agricultural Waste Recycling
- Survey on Factors Influencing the Decline in Chicken Consumption of Urban Residents in Liaoning Province
