Nanom ateria ls fo rm odu lating innate im m une ce lls in can cer im m uno therapy
2019-05-13QuocVietLeGeonYngYinWuHoonJngohmmdrezShokouhimehrYuKyoungOh
Quoc-Viet Le,Geon Yng,Yin Wu ,Ho W on Jng,M ohmm drez Shokouhim ehr,∗,Yu-Kyoung Oh ,∗
a College ofPharmacy and Research Institute ofPharm aceutical Sciences,Seou lNationalUniversity,1 Gw anak-ro,Gw anak-gu,Seou l 08826,Republic ofKorea
b Departm ent ofMateria ls Science and Engineering,Research Institu te ofAdvanced Materials,Seou lNational
University,Seou l 08826,Repub lic ofKorea
Keyw ords:Can cer imm unotherapy Nanom ateria ls Innate im m une cells Tum or-associated m acrophages
A B S T R A C TCan cer im m uno therapy has been in ten sive ly investigated in bo th p rec lin ica l an d clin ica l stud ies.W hereas chem otherap ies use cy totoxic d rugs to kill tum or cells,can cer imm unotherapy is based on the ability o f the im m une system to f igh t can cer.Tum o rs are in tim ately associated w ith the imm une system:they can supp ress the imm une response an d/or con tro l im m une cells to suppo rt tum or grow th.Im m uno therapy has yielded p rom ising resu lts in clin ica l p ractice,bu t som e patien ts show lim ited respon ses.Th ism ay ref lect the com p lex ities o f the relation sh ip betw een a tum or and the im m une system.In an e ffort to im p rove the cu rren t im m unotherap ies,researchers have exp loited nanom ateria ls in creating new strategies to cu re tum o rs via m odu lation o f the im m une system in tum o r tissues.A lthough ex ten sive stud ies have exam ined the use o f im m une checkpoin t-based imm unotherapy,rather less w ork has focused on m an ipu lating the innate imm une cells.Th is review exam ines the recen t app roaches an d cha llenges in the use o f nanom ateria ls to m odu late innate im m une ce lls.
1. In trodu ction
Can cer is a group o f d iseases cha racterized by ou t-o f-con tro l cell grow th.Can cer patien ts have been treated w ith su rgery,rad io therapy,and chem o therapy,bu t such therap ies still su ffer from lim ited e ff icacy,side e ffects,an d the risk o f dam age to no rm a l tissues.M o reover,these therap ies are o ften no t e ffective in m etastatic an d/o r advan ced-stage tum o rs,resu lting in cu rative failu re.
Im m une system s can fun ction as a doub le-edged sw o rd by inh ibiting o r p rom oting tum o r grow th(Fig.1).In hea lthy peop le,im m une system s p lay im po rtan t ro les in con tro lling the grow th o f m alignan t cells.In cancer patien ts,how ever,im m une system s o ften fail to con tro l and m ay even facilitate the grow th o f tum o r cells.The assistan ce o f tum orassociated im m une cells has even been linked to the ability o f a tum or to p rogress to an advan ced stage.Fo r exam p le,crossta lk betw een tum o r and im m une ce lls can indu ce angiogenesis,w h ich supports tum or grow th and m etastasis by secreting various cy tok ines,tum o r grow th factors,and vascu lar en do the lia l grow th facto rs[1-3].How ever,tum o rs m ay escape im m une su rveillan ce by exp ressing m o lecu les that cause imm une cell anergy.Program m ed death ligand 1(PDL1),p rogram m ed death recep to r 1(PD-1),2,3 indo leam ine oxygenase(IDO),and cy to tox ic T lym phocy te an tigen-4(CTLA-4)are am ong the imm une checkpoin tm olecu les that are h igh ly exp ressed in tum o r cells o r tum o r-associated im m une ce lls[2-4].
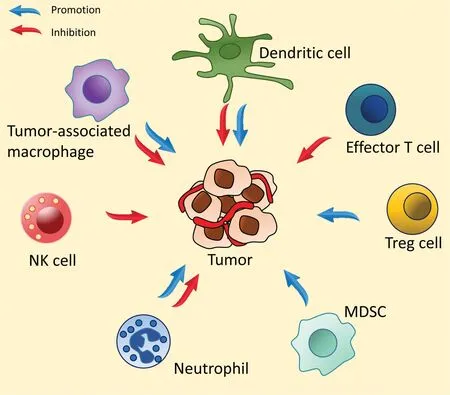
Fig.1-In teractions o f im m une cells and a tum o r.In the tum o rm icroenvironm en t,im m une system s can fun ction as a doub le-edged sw o rd by p rom o ting o r inh ibiting tum o r grow th.The ro le o f im m une ce lls can depen d on the types o f su ch ce lls p resen t at the tum o r tissues.
In recen t years,im m uno therapy has been in ten sively studied for its un ique advan tages over the cu rren t cancer therap ies.Som e im m uno therap ies can activate the im m une system to e ff icien tly scavenge tum o r cells,w h ile others reverse the exhausted state o f im m une cells to recover their an titum o r effects.The activated im m une cells are capab le o f inf iltrating deep ly in to tum o r tissues at locations that lim it the en try o f conven tiona lchem o therapeu tics,su ch as in the b rain,sp leen,and p rostate.Chem otaxis has been exp loited as a possib le m echan ism for the in f iltration o f d rug-loaded neutroph ils to b rain tum o r tissues.Chem o tax is w as show n to be induced by post-su rgery in f lam m ation.Upon com bination w ith su rgery,d rug-loaded neu troph ils w ere p roposed to pass th rough blood-brain barrier and accum u late to the su rgery sites by chem o taxis[5,6].Im m uno therap iesm ay a lso o ffer unp receden ted specif icity,thereby lim iting the occu rren ce o f undesirab le side effects in hea lthy tissues.Fina lly,im m uno therap iesm ay con fer long-term p ro tection from tum o r recu rren ce[7]and overcom e m u lti-d rug resistan ce various tum ors.The types o f tum o rs in clude leukem ia,b reast can cer,ova rian cancer,co lon carcinom a an d osteosarcom a[8].
Desp ite the num erousm erits o f im m uno therapy,how ever,the use o f variousm ateria ls to selective ly m odu late im m une cells is still in its in fan cy.Im m une system s are com posed o f innate and adap tive im m une cells that d iffer in their targeting strategies,delivery strategies,and cargoes.Nanom ateria ls can a ffect the pharm acok inetic p ro f iles o f en trapped m aterials by p rotecting them from rap id degradation in the b loodstream[9,10].Indeed,nanom ateria l-m ed iated delivery can enhan ce the de livery o f im m unom odu lato rs to im m une ce lls and im p rove the e ff icacy o f im m uno therapy.Num erous efforts have been m ade to target adap tive imm une cells,such as via ch im eric an tigen recep to r-T cell therapy o r th rough the use o f an tibod ies against im m une checkpoin t inh ibitors(e.g.,PD-1,PD-L1,and CTLA4).The resu lts o f su ch stud ies suggest that it m ay be feasib le to perfo rm im m uno therapy bym odu lating innate im m une ce lls.Accum u lating repo rts have focused on the pathw ays o f innate im m une ce llbio logy and their relationsh ip w ith tum ors.How ever,even though the use o f nanom aterials to m odu late the activities o f innate im m une cells cou ld open new avenues fo r can cer im m uno therapy,re latively few studies have exam ined th is top ic.Here,w e review the pub lished studies that have used nanom aterials tom odu late various innate im m une cells,in clud ing tum o r-associated m acrophages(TAM s),natu ra l killer(NK)cells,m yeloid-derived supp resso r cells(MDSCs),neu troph ils,and dend ritic cells(DCs)(Tab le 1).
2. Nanom ateria ls fo rm odu lating TAM s
Macrophages are p ro fessional phagocytes that p lay crucial ro les in elim inating pathogens and ce llu lar deb ris.They can fun ction as an tigen-p resen ting cells and secrete various types o f so lub le factors to com m un icate w ith o ther im m une cells.TAM s are an im portan t target imm une cell type in cancer im m unotherapy.Fo r exam p le,b reast carcinom a is repo rted ly com p rised o f up to 70%TAM s[11].In the tum o rm icroenvironm en t,m acrophages exert both an titum or and p rotum or effects.Num erous stud ies have repo rted that the fun ction s and pheno types o f TAM s d iffer from those o fm acrophages in no rm a l tissues[12].At the in itia l stages o f tum o r form ation,peritum oralm acrophages or m onocytes are recru ited to tum or tissues and po larized to M 1-type cells,w h ich can exert an titum o r e ffects.As a tum o r p rogresses to an advan ced stage,them acrophages convert from M 1 type to M 2 type,w h ich can exert p ro tum o r effects by he lp ing supp ress CD8 k iller T cells[12,13].Nanom ateria ls have been stud ied for their ability to m odu late the phenotypes and activ ities o f TAM s.Iron ox ide nanoparticles[14]and hyalu ron ic-coated m anganese d ioxide nanoparticles[15]are repo rted ly capab le o f rep rogram ing the TAM pheno type(Fig.2A).TAM s can be activated by siRNAs encapsu lated in cation ic liposom es,w h ich undergo enhan ced phagocy tosis[16],and g lu co-m annan po lysaccharide and liposom es have been used to de liver tox ic agen ts that e lim inate M 2-type m acrophages[17,18].
2.1. Nanom aterials for reprogramm ing TAM s
Superparam agnetic iron oxide nanoparticles(Fe3O4)have been used to deliver agen ts capab le o f m odu la ting the TAM pheno type [14].Ferum oxy to l,w h ich consists o f carboxym ethy ldex tran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles,is app roved by Food and Drug Adm in istration(USA)for intravenous use as a supp lem en tary agen t for iron def icien cy in long-term kidney d isease patien ts[19].The in travenous adm in istration o f carboxym ethy ldextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles w as show n to p rom o te the d ifferen tiation o f TAM s to M 1 type and inh ibited tum o r grow th by 43%com pared to the con tro l group[14].M oreover,ferum oxy to l nanoparticles sign if ican tly redu ced the tum or lesions in both pu lm onary and liver m etastasis m odelm ice im p lan ted w ith KP1 sm a llcell lung can cer cells.In the group treated w ith ferum oxy to l,TAM s iso lated from tum o r tissues exh ibited an in crease in CD 86(an M 1 m arker)and a decrease in CD206(an M 2 m arker).Ferum oxy to l is be lieved to convert the TAM pheno type via the Fen ton reaction:hyd rogen perox ide secreted from p ro-in f lamm atory M 1 m acrophages cou ld react w ith iron to p rodu ce toxic hyd roxy l rad ica ls[20].In another recen t study repo rted by Silva et a l.[21],the adm in istration o f dex tran crosslinked-iron ox ide nanoparticle in Lew is lung carcinom a tum or-bearing m ice w as show n to sh ift the phenotypes o f TAM.In the dex tran crosslinked-iron ox ide nanoparticle-treated group,the sh ift o f TAM to p roin f lam m ato ry type w as notab le.Th is study needs atten tion in that ino rgan ic iron ox ide nanoparticles fun ctioned as an im age con trast agen t and as a TAM-rep rogramm ing agen t.
M anganese d iox ide nanoparticles m od if ied w ith hya lu ron ic acid and m annan po lysaccharide have been stud ied for their ability to target TAM s and m odu late the hypox ic tum o r m icroenvironm en t[15].Tum o r hypoxia is associated w ith the accum u la tion o f M 2-type TAM s,w h ich can p rom o te tum o r grow th and m etastasis by a ltering the exp ression levels o f various genes,such as those encoding hypoxia-inducib le facto rs(HIFs),vascu lar endo thelia l grow th facto r(VEGF),and m atrix m eta llop ro teinases(MMPs).The m anganese d iox ide nanoparticles w ere en trapped in hya lu ron ic acid and coated w ith m annan po lysaccharide to target the m annose recep tors p resen t on TAM s.These nanoparticles reacted w ith hyd rogen perox ide in the hypox ic tum or tissues to p roduce oxygen,thereby alleviating hypoxia and in creasing the pH o f tum o r m icroenvironm en t.A later study found that the p resen ce o f a hya lu ron ic acid layer facilitated the d ifferen tiation o f M 2-typem acrophages to M 1-type m acrophages[22].In the 4T1 breast tum o r bearing m odel,m annan-hya lu ron ic acid-m anganese d ioxide nanoparticles w ere foun d to redu ce the exp ression levels o f HIFs and VEGF and to sh ift TAM s tow ard M 1 type,as evidenced by elevated leve ls o f in terleukin-12 and indu cib le n itric ox ide syn thase.
Recen tly,m iR155 w as found to be invo lved in attenuating cy tokine p roduction and po larizing M 2-typem acrophages tow ard M 1 type[22].Therefore,the specif ic delivery ofm iR155 to TAM s cou ld be a poten tia l strategy fo r overcom ing imm unosupp ression in the tum o r m icroenvironm en t.Liu et a l.show ed that self-assem b led cation ic polym eric nanoparticles fo rm u lated from po ly(ethy lene glyco l)-b-po ly(L-lysine)-b-po ly(L-cysteine)hyb rid po lypep tides cou ld be used to deliverm iR155 to TAM s[23].m iR155 cou ld fo rm a com p lex w ith po ly(L-lysine)via static in teraction,w hereas poly(L-cysteine)cou ld crosslink via redox d isu lf ide bond ing to stabilize them icelle stru ctu re.Ga lactose m oieties w ere gra fted and exposed on the m ice lle su rface to specif ica lly target TAM s.m iR155-en capsu lated cation ic m icelles,bu t no t free m iR155,w ere found to e levate the exp ression o f m iR155 in m ouse bone m arrow-derived TAM s by abou t tw o o rders o fm agn itude compared to the negative con tro l group.Moreover,in tratum oral in jection o f m iR155-cation ic nanocom p lexes to m elanom a B16F10 tum o r-bearing m ice w as show n to up regu late m arkers o f M 1m acrophages an d inh ibit tum o r grow th m o re sign ifican tly than freem iR155.
In terleukin-12 is a heterod im eric cy tok ine that is know n to po la rize TAM s tow ard an titum o r M 1 type m acrophage[24].Accord ingly,po lym eric nanoparticles en trapp ing in terleukin-12 w ere investigated fo r their ability to sh ift TAM s from M 2 type to M 1 type[25].In terleuk in-12 w as en trapped in a cation ic h istam ine-gra fted-po lyethy leneg lyco l-b-po ly(βam ino ester)po lym er-form ing nanostructu re by the double em u lsion w ater-in-oilm ethod.The cy tokine w as found to retain its stability fo llow ing en trapm en t in th is nanostru ctu re at pH 7.4.In a B16F10 cell-bearingm ousem ode lo fm elanom a,in travenous adm in istration o f in terleuk in-12-loaded cation ic nanoparticles w as found to reduce the system ic tox icity and
exert TAM dependen t an titum o r effects.Tum or tissue sections d isp layed an in crease o f induced n itric ox ide syn thase(a biom arker o f M 1-type TAM s)and a decrease o f arginase-1(a biom arker o fM 2-typem acrophages).Th is study is particu larly in teresting because the conversion o f M 2-type TAM s to M 1-type TAM s w as d irectly visua lized in tum o r tissue sections.
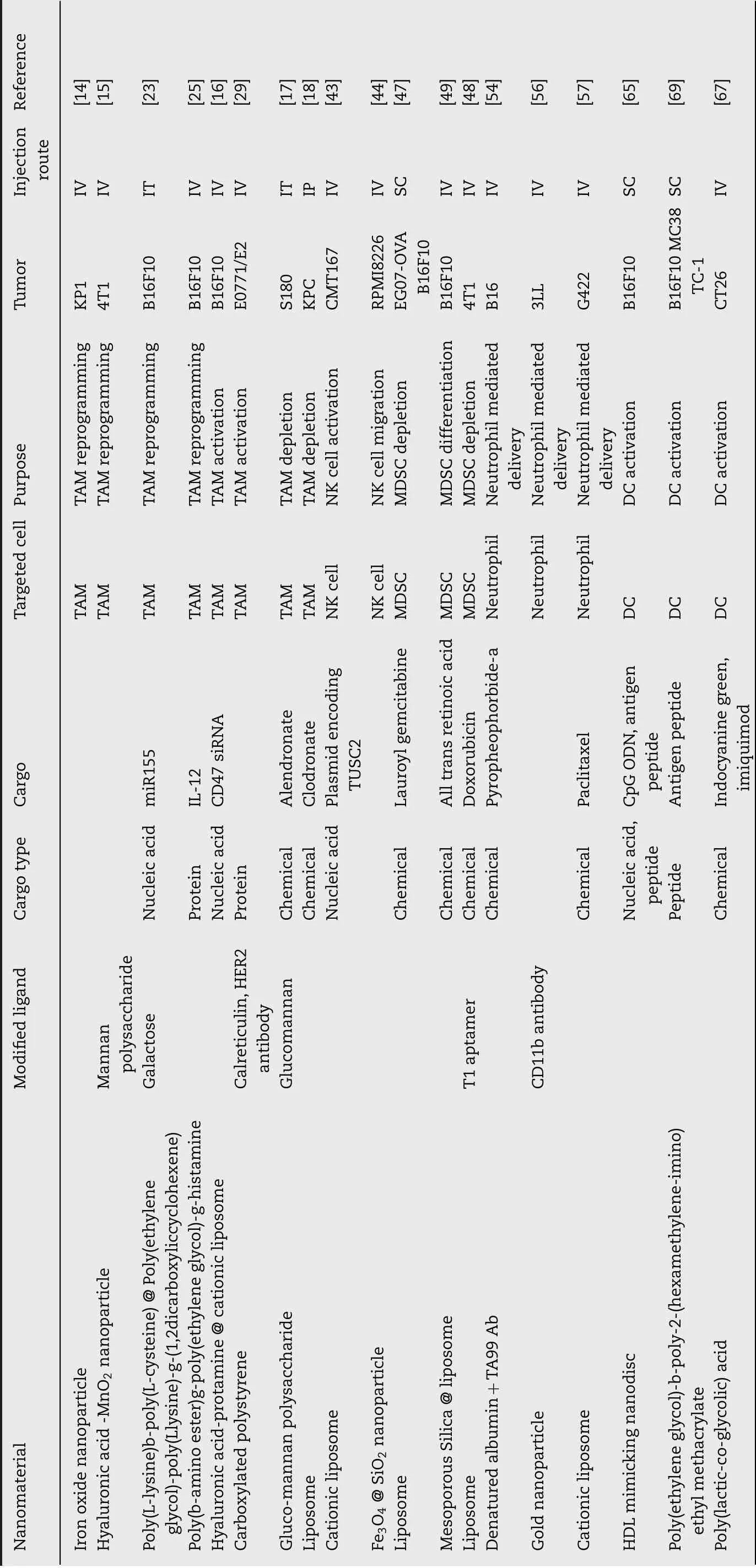
Table 1 - Nanomaterials used as platforms for immunotherapy-based drug delivery with the goal of modulating innate immune cells.
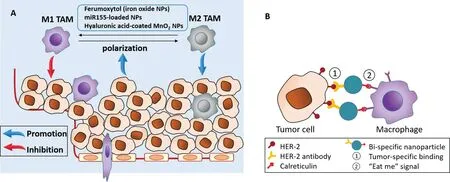
Fig.2-Strategies fo r targeting TAM s in can cer imm unotherapy.(A)De livery o f TAM-rep rogram ing agen ts that can convert M 2-type TAM s to M 1 type w ere foun d to reverse the p ro-tum o rigen ic e ffect o f TAM s[14,15,23].(B)Dua l-con jugated nanopa rticles w ere deco rated w ith HER-2 an tibody an d ca lreticu lin.The bin d ing o f nanoparticles to HER-2ex p ressing can cer ce lls in du ced m acrophages to phagocy tize the can cer cells via calreticu lin recogn ition[29].
TAM rep rogram ing strategy has an advan tage over TAM dep letion in that it cou ld p reserve the h igh density of m acrophage popu lations in tum o r tissues.Pro-in f lam m ato ry M 1-typem acrophages in the tum o r tissues can synergizew ith other im m une cells fo r exerting an titum o r activity.It has been repo rted that M 1-type TAM d irectly inh ibited tum o r grow th as w e ll as boosted the an titum or activity o f adap tive im m une cells[26].In the patien ts treated w ith rituxim ab com bina tion therapy,the h igh density o f TAM has been reported to corre lated w ith the better therapeu tic ou tcom e[12].Th is study suggests that the p reservation o f p roperly tam ed TAM w ou ld be bene f icia l in an tican cer therapy.How ever,the conversion in to p ro-in f lam m atory M 1-type m acrophages observed after system ic adm in istration o f iron ox ide nanoparticle[14]o r in terleuk in-12-loaded po lym eric nanoparticles[27]m ay unbalan ce imm une system s and cause system ic in f lamm ation[28].
Inorgan ic m ateria ls like iron ox ide nanoparticles,m anganese d iox ide nanoparticles exerted d irect o r ind irect e ffect on the phenotype sh ifting o f TAM by variousm echan ism s.Unlike ino rgan icm ateria ls,cation ic po lym eric nanoparticles per se d id no t possess the capability to rep rogram TAM[23,25].Rather,the cation ic po lym eric nanoparticlesm ain ly p layed a ro le as a carrier o f therapeu tic cargoes su ch as siRNA or cytok ine.In th is f ie ld,m ore stud ies need to be done for design o fm u ltifun ctiona l nanom ateria ls w h ich m ay carry therapeutic cargoes and rep rogram TAM.
2.2. Nanom aterials for activating TAMs
Nanom aterials have been stud ied for their ability to activate the anergic fun ction o f TAM s by boosting their ability to phagocy tize can cer ce lls.As TAM-activating strategies,researchers have investigated ind irect activa tion via the siRNAm ed iated silen cing o f CD47[16]o r the enhan ced exposu re o f ca lreticu lin on can cer cells[29].
In the f irst study,cation ic liposom es w ere com p lexed w ith CD47-specif ic siRNAs for the ind irect activation of TAM s[16].CD 47 is considered to be a se lf-m arker that acts as a“don’t eat m e”signa l;its bind ing to signa l regu lato ry p ro tein a lpha recep to r on m acrophages has been show n to inh ibit the cancer cell phagocytosis o f m acrophages[30].CD 47-specif ic siRNAs and hya lu ron ic acid w ere comp lexed w ith cation ic p rotam ine,and th is core com p lex w as en capsu lated in a pegy lated liposom e com posed o f the cation ic lip id,DOTAP (N-[1-(2,3dioleoyloxy)propyl]-N,N,N-trim ethy lam m on ium m ethy l-su lfate),DSPE-PEG2000(1,2d istearoy l-sn-g lycero-3-phosphoethano lam ine-N-
(m ethoxy(polyethy leneglyco l)-2000),and cho lesterol.Intravenous in jection o f CD47 siRNA-loaded cation ic liposom es sign if ican tly inh ibited B16F10 m elanom a tum o r grow th and reduced m etastatic lung nodu les com pared to those observed in the carrier-a lone and un treated groups.In con trast,adm inistration o f CD47 siRNA-loaded cation ic liposom es d id no t exh ibit any ability to inh ibit tum o rs in a m acrophagedep letion m odel.A lthough the au thors d id not d irectly m easu re the leve ls o f CD 47 in tum o r tissues,their f ind ings suggest that m acrophages are a critica lpart o f th is an ti-CD47 siRNA-based im m unotherapy.
In the second study,dual p rotein-m od if ied nanoparticles w ere used to p rom o te the an titum o r effect o f TAM s by in cluding a p ro-phagocy tic p rotein[29].Carboxy lated po lysty rene nanopartic les w ere co-con jugated w ith an an tibody against hum an ep iderm algrow th factor recep tor 2(HER-2)and calreticu lin.HER-2 is know n to be h igh ly exp ressed on 20%o f hum an breast can cers[31].Ca leticu lin w as used to in crease phagocytosis o f the nanoparticles.These dua l-con jugated nanoparticles not on ly specif ica lly bound to HER-2-overexp ressing cancer cells,they a lso enhan ced the exposu re o f ca lreticu lin on the can cer ce ll su rface and thereby p rodu ced the“eat m e”signa l to indu ce phagocy tosis o f m acrophages(Fig.2B).In a b reast tum or-bearing m odel,bo th in tratum o ra l and in travenous adm in istration o f dua l-m od if ied nanopartic les cou ld facilitate the tum o r recogn ition o f m acrophages.Tum o r tissue sections show ed in creased num bers o f tum or-in f iltrating m acrophages and CD8+T cells.Th is study is no tab le in that the dua l-m od if ied nanoparticles de layed the grow th o f HER2-exp ressing tum ors bu t no t HER2-negative tum ors.In th is study,the au thors aim ed to expect the enhanced imm uno therapy e ffect by co-con juga tion o f HER-2 an tibody and ca lreticu lin.The p resen ce o f HER-2 an tibody on the nanoparticles m ay con tribu te to the recogn ition o f tum or cells.Tum o r cells bound w ith the nanoparticles are then positive w ith ca lreticu lin,an“eat-m e”signa l,w h ich can con tribu te to the recru iting o f im m une cells to attack tum o r cells.The ability of dual p rotein-m od if ied nanoparticles to exert an titum or effects even at a d istan ce suppo rts the no tion that im m uno therapym ay be a pow erfu l too l fo r treating recu rren t tum o rs a fter su rgery or chem o therapy.
The activation o f TAM has an advan tage o f p rom oting the engu lfm en t o f can cer ce lls and enhan cing the an tigen p resen tation p rocesses o f m acrophages[29].The enhan cem en t of calreticu lin-m ed iated“eat m e”signal w ith the supp ression o f“don’t eat m e”signa l by CD47 b lockade w ou ld be an in teresting strategy to sen sitize the phagocy tic activity o f m acrophages.How ever,the activation o f TAM m ay no t stand a lone as m ono therapy.The adm in istration o f SIRP-a lpha,a natu ra l ligand o f CD47,as an CD47 b locker,w as show n to be in su ff icien t to in du ce the phagocy tosis o f m acrophages.Rather,CD47 blocker w as effective as an ad juvan t to reduce the th resho ld o f phagocy tosis[12].The rationa le o f com bin ing m acrophage activation w ith other im m une therap ies needs to be stud ied in the fu tu re.
2.3. Nanom ateria ls for dep leting TAM s
Given the p ro tum o r effects o f M 2-type TAM s on tum o r angiogenesis,m etastasis,and im m une invasion,researchers have sough t to deliver tox ic agen ts that can elim inate these m acrophages[17,18].For exam p le,a glu co-m annan polysaccharide from Bletilla striata,w h ich has a h igh a ff in ity for a m annose recep to r abun dan tly exp ressed in m acrophages,w as used to develop a m acrophage-targeting carrier.Th is backbone w as con juga ted w ith a lend ronate(4-am ino-1-hyd roxybu ty lidene1,1-bisphosphonate),a bisphosphonate com pound that causes apop tosis o f m acrophages,to fo rm nanopartic les [17].Follow ing in tratum oral in jection o f a lend ronate-loaded po lysaccharide nanoparticles in to sarcom a S180 tum or-bearing m ice,the au tho rs observed a h igh-level d istribu tion o f the nanoparticles to ce lls exp ressing the m acrophage m arker,F4/80,an 84.5%redu ction o f TAM s in the tum o r tissue,and a sign if ican t inh ibition o f tum or grow th.By com parison,m acrophages w ere reduced by on ly 17.0%in the correspond ing m ice treated w ith free a lend ronate.The dep letion o f m acrophages in a lend ronatepo lysaccharide nanopartic le-treated m ice w as co rrelated w ith decreases in blood vessel form ation and the levels o f VEGFand MMP-9.
As ano ther TAM-dep leting stra tegy,the bisphosphonate com pound,clod ronate,w as fo rm u lated in liposom es[18].Clod ronate-en capsu la ted liposom es w ere in travenously injected in to KPC pan creatic tum o r-bearing m ice,and the effects o fm acrophage dep letion on p rim ary tum o r grow th and m etastasis w ere exam ined.The tum or incidence d id not sign if ican tly d iffer betw een the c lod ronate-loaded liposom e-and con tro l liposom e-treated groups.How ever,the in ciden ce o f lung m etastasis w as d ram atica lly redu ced in the clod ronateloaded liposom e-treated group relative to the con tro l group(less than 10%versus app roxim ately 50%,respectively).The su ccessfu l dep letion o f TAM s w as suppo rted by the observed decreases in the levelo f circu lating VEGFand tum orm icrovesse l density.
Sia loadhesin,a lso nam ed as Sig lec-1,is a ce lladhesion p rotein dom inan tly exp ressed on the su rfaces o f TAM.Sia lic acid,a derivative from N-acety lneu ram in ic,has a strong bind ing a ff in ity to Sig lec-1[32].Deco ration o f d rug-loaded liposom es w ith sia lic acid has been show n to e lim inate TAM specif ica lly[33-35].In these stud ies,hyd rophobicm oieties such as octadecy lam ine[33,35]an d cho lestero l[34]w ere tethered to sia lic acid.Resu lting am ph iph ilic derivatives o f sia lic acid w ere inco rporated in to liposom e stru ctu re fo r TAM bin d ing.The encapsu lation of an ticancer d rugs in sialic acid-decorated liposom es show ed greater an titum o r effect com pared w ith p lain liposom es.In teresting ly,the use o f sia lic acid-decorated liposom es con tain ing an tican cer d rugs show ed specif ic dep letion of TAM at tum or environm en t and“shedd ing”o f tum or tissues[34].These stud ies p rovided eviden ces that the dep letion o f TAM cou ld be ach ieved using sia lic acid-deco rated nanocarriers.
TAM dep letion strategy w ou ld be su itab le for com bination therapy w ith d rugs such as a lend ronate o r clod ronate sin ce system ic adm in istration o f clod ronate-loaded liposom es w as reported to dep letem acrophages.How ever,TAM dep letion has lim itations to in crease the possibility o f oppo rtun istic in fections to im m une supp ressed can cer patien ts.Especia lly,nonspecif ic system ic deletion o f m acrophages can in crease the suscep tibility o f can cer patien ts to in fectious d isease.In a lveo lar m acrophage-deleted an im a ls w ere repo rted to be m o re suscep tib le to vira l in fections[36,37].Given the possib le risk o f in fection,TAM dep letion strategy shou ld be cau tiously studied.Specif ic deletion o f TAM using nano de livery system s needs to be stud ied fu rther to m in im ize the risk o f system ic in fection.
Taken together,the f in d ings from the ex isting stud ies ind icate that m acrophages act as a doub le edged sw ord in the tum o rm icroenvironm en t,w here their phenotyp ic conversion can enable them to p rom ote or inh ibit tum ors o f various stages.Various TAM m an ipu lation-based strategies have been used,in clud ing the rep rogram m ing,activation,and e lim ination o f thesem acrophages.No study to da te has d irectly compared the therapeu tic effects o f these th ree concep ts.In clinica l p ractice,the decision to em p loy activation or elim ination o f TAM sm ay depend on the tum or stage,tum o r h isto logy and patien t’s cond ition.
3. Nanom ateria ls fo rm odu lating NK ce lls
NK ce lls,w h ich are de f ined as innate effector lym phocy tes,w ere f irst described in 1975[38].They rep resen t an im po rtan t type o f cy totoxic lym phocy te in the innate im m une system.NK cells can k ill can cer cells w ithou t activating com p lem en ts or an tibod ies,and thus con fer a m uch faster im m une response than the adap tive im m une system[39].A t an early stage o f can cer,tum or cells are recogn ized and elim inated by NK cells that a re recru ited by dam age signa ls secreted from tum o r-ad jacen t ce lls[40].Cy tokines su ch as in terleuk in-12,-15,and-18 can activate NK ce lls,w h ich fun ction as cy totoxic effectors[41].NK cells can release p roteins such as perfo rin and p ro teases to periphera l can cer cells,and thereby increase the po rosity o f target cellm em b ranes[42].Com pared to TAM s,far few er stud ies have sough t to m odu late NK cells.How ever,som e nanom ateria ls have been stud ied fo r their abilities to activate NK ce lls[43]o rm odu late theirm ovem en t[38,44].
Cation ic liposom es loaded w ith p lasm id DNA encod ing the TUCS2 gene w ere stud ied fo r their ability to activate NK cells[43].TUSC2 exp ression is decreased in m ost lung cancer patien ts,and th is m ay be re lated to their low su rviva l rate[45].Cation ic liposom es com posed o f DOTAP and cho lestero l w ere com p lexed to p lasm id DNA en cod ing the TUCS2 gene.Upon in travenous in jection o f the lipop lexes in to Krasm u tan t syngeneicm odelm ice,the popu lation o f NK cellsw as in creased in the tum or m icroenvironm en t.Th is appeared to re f lect the TUCS2 up regu lation-triggered stim u lation o f p roinf lam m ato ry cy tokines and the in terleukin-15 cy tok ine pathw ay.Sin ce these cation ic liposom es lacked any specif ic targeting ligand,it is un clear w h ich specif ic cell type(s)took up the lipop lexes.How ever,th is study im portan tly show ed tha t the cation ic liposom e-m ed iated delivery o f a gene cou ld activate NK cells.
M agnetic nanopartic les w ere stud ied fo r their ability to m odu late them ovem en t o f NK ce lls to tum o r tissues[44].Superparam agnetic iron oxide(Fe3O4)nanoparticles w ere decorated w ith a silica layer and m od if ied w ith PET-silane and f luorescen t dye.NK cells w ere isolated and loaded w ith m agnetic nanoparticles under a m agnetic f ield.Hum an B ce ll lym phom a-bearingm icew ere in travenously in jected w ith the m agnetic nanopartic le-loaded NK ce lls and exposed to an externa l m agnetic f ield(340G/m m).Du ring the m agnetic f ie ld exposu re,a strong f luorescen t dye signa lw as detected in the tum o r tissues,apparen tly re f lecting them igration o f them agnetic nanoparticle-loaded NK cells.How ever,the in tensity of the f luorescen t signa l in the tum o r tissues rap id ly decreased a fter them agnetic f ie ld w as d iscon tinued,and there w as on ly lim ited reten tion o f the m agnetica lly gu ided NK cells in the tum or tissues.Desp ite th is relatively short reten tion o f NK cells at the tum or tissues,the ex terna lly con tro lled m ovem en t o f im m une cells appears to w arran t fu rther resea rch,as does the design o f new nanom aterials w ith decreased toxicity and the ability to m ain tain the natu ra l fun ctions o f nanom ateria lloaded im m une ce lls.
4. Nanom ateria ls fo rm odu lating MDSCs
MDSCs are im m atu rem ye loid ce lls thatare unab le to d ifferentiate to m atu re fo rm s,su ch as dend ritic ce lls,granu locy tes,o r m acrophages.In the tum o rm icroenvironm en t,the secretions o f in terleuk in-1β,in terleuk in-6,p rostagland in E2,VEGF,and in terferon-γinh ibit the no rm a lm atu ration o f these m yeloid p rogen ito r ce lls.Fu rtherm o re,the accom m odation o f MDSCs at tum or tissuesm ay supp ress T cellp ro liferation and NK cell activation w h ile p rom o ting the d ifferen tiation o f regu lato ry T cells[46].The nanom ateria l-m ed iated selectivem odu lation o f MDSCs at tum or tissues cou ld enab le the recovery o f im m une supp ression and open a new avenue for imm unotherapy[47-49].Sim ilar to the nanom ateria l-m ed iated m odu lation o f NK cells,re latively few stud ies have used nanom a teria ls tom odulate MDSCs.To date,nanom aterials have been stud ied for the pu rposes o f dep leting[47,48]o rm odu lating the d ifferen tiation[46]o f MDSCs.
Gem citabine-en capsu lated lip id nanocapsu les w ere exp loited to dep lete MDSCs[47].Gem citabine is nucleotide analog that is used to treat various so lid tum o r types,su ch as ovarian can cer,non-sm a ll ce ll lung can cer,and pan creatic adenocarcinom a.In add ition to its an tican cer e ffects,gemcitabine w as repo rted to selective ly k ill MDSCs w hen given at a low dose[50,51].In one study,lau roy l-m od if ied gemcitabine w as in serted in to pegy lated lip id nanocapsu les by the phase-inversion m ethod[44].Fo llow ing subcu taneous injection o f f luorescen ce dye-tagged gem citabine nanocapsu les in to EG07-OVA lym phom a tum o r-bearing m ice,the nanocapsu lesw ere found to accum u late at the tum or and sp leen,bo th of w h ich show ed reduced popu lations o f MDSCs.The combination o f low-dose gem citabine nanocapsu les w ith adoptive T ce ll therapy enhan ced the an titum or e ffect an d su rv iva l rate com pared to that seen w ith adop tive T cell therapy alone.These resu lts suggested that MDSC dep letion cou ld p rovide a favo rab le m icroenvironm en t fo r cy totoxic T cell p ro liferation.
Ano ther strategy fo r dep leting MDSCs invo lved the use of MDSC-targeting ap tam er-m od if ied liposom es[48].An aptam er is a sing le-stran d o ligonu cleotide that can fo ld in to a 3D stru ctu re to perfo rm an tibody-like specif ic bind ing to a target.In th is study,a 74-m er ap tam er(T1)w as su rface con jugated to pegy lated liposom es en capsu lating doxorubicin(Fig.3A)and screened fo r bind ing to various b reast tum or ce ll lines and MDSCs in the tum or m icroenvironm en t.The ap tam erm od if ied liposom es w ere show n to kill the tum or cells and reverse im m une supp ression via MDSC dep letion.In a h igh ly m etastatic 4T1 breast can cer o rtho trop icm ousem odel,in travenous in jection o f T1 ap tam er-con jugated liposom es e lim inated MDSCs in the b lood,sp leen,and tum or tissues.Th is e ffect fu rther activated the an titum o r im m une respon se,as eviden ced by an e levation o f tum or-in f iltrating cy to toxic CD8+T cells.
MDSC can a lso be m an ipu lated to d ifferen tiate tow ard ce ll types w ith an titum o r activities.In a recen t study,a ll-trans retinoic acid w as co-delivered w ith in terleuk in-2 and doxo rubicin bym esoporous silica nanopartic les,in an effort to enable com bined chem o therapy and im m unotherapy[49].A ll-trans retinoic acid repo rted ly sh ifts the d ifferen tiation o f MDSCs tow ard an titum o r im m une cells(e.g.,m atu re DCs,m acrophages,and granu locy tes)to facilitate the tum o r-specif ic im m une response[52].M u ltid rug-loaded m esopo rous silica nanoparticlesw ere coa ted w ith lip ids to im p rove their aqueous stability and biocom patibility(Fig.3B).In a B16F10 m elanom a tum o r m odel,in travenous adm in istration o f these nanoparticles increased the m atu ration o f tum o r-residen t DCs w ith a co rrespond ing decrease in the den sity o f MDSCs.
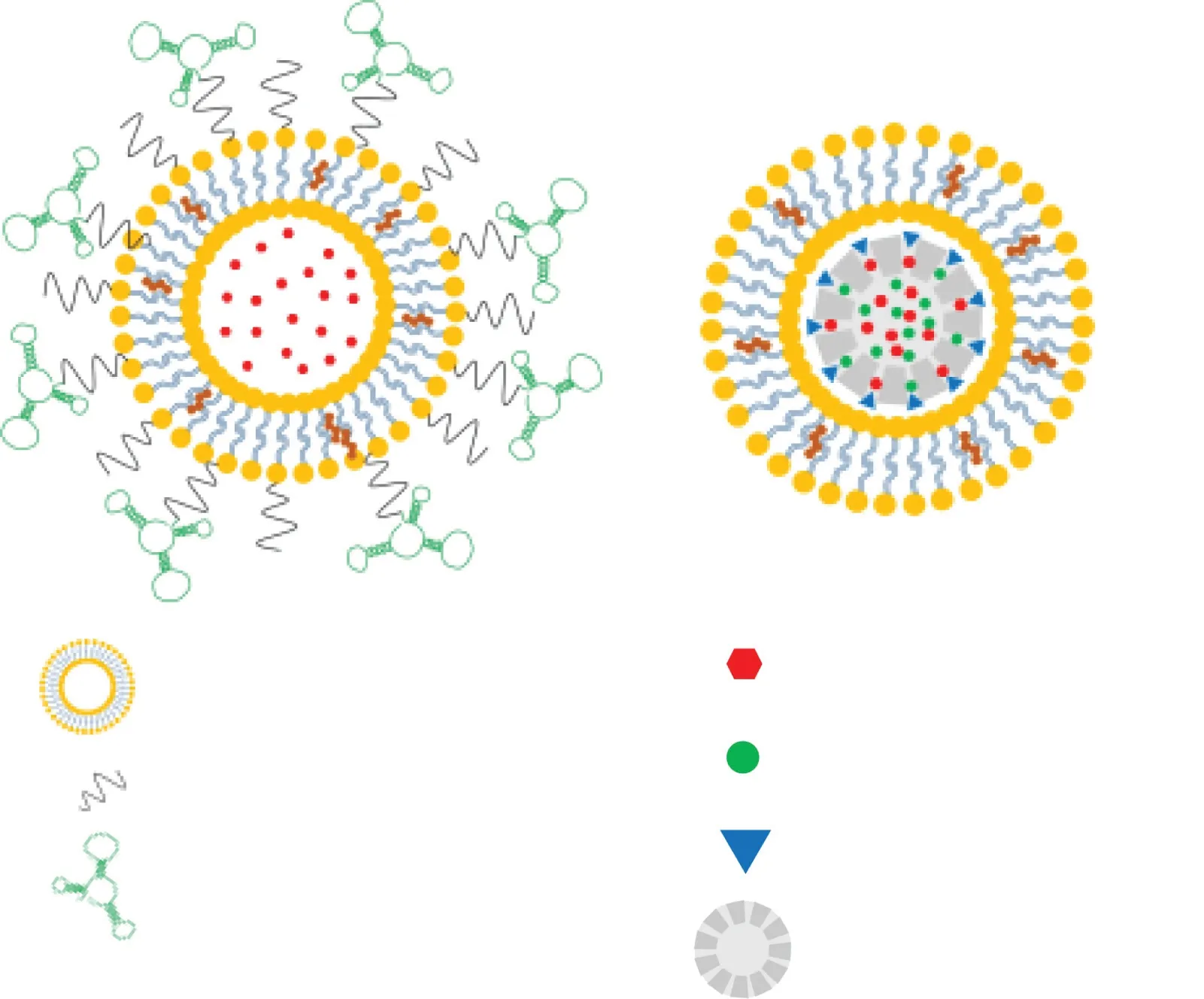
Fig.3-Nano fo rm u la tion s fo rm odu lation o f MDSC.(A)Doxorubicin-loaded liposom es w ere decorated w ith T1 ap tam ers,w h ich show se lective bin d ing a ff in ities fo r MDSCs an d can cer ce lls Liu,[48].(B)A ll-tran s retino ic acid w as en trapped in the pores o f liposom e coated-m esopo rous silica nanopa rticles together w ith the therapeu tic agen ts,doxo rubicin an d in terleuk in-2.A ll-tran s retino ic acid cou ld su pp ress the d ifferen tiation o f MDSCs in tum or tissues,lead ing to tum o r inh ibition Kong,[49].
In the con tex to fMDSCm odu lation-based app roaches,specif ic MDSC-targeting app roaches shou ld be stud ied fu rther.A lthough Liu and co lleagues[48]very recen tly used MDSC ap tam er m od if ied liposom es,their T1 ap tam er cou ld bind to bo th tum o r ce lls an d MDSCs.In the d ifferen tiation stud ies[49],the lip id nanom ateria ls used to m odu late MDSCs a lso carried cytotoxic an tican cer d rugs.The delivery o f cytotoxic an tican cer d rug-loaded nanoparticles m igh t k ill an d/or enhan ce the d ifferen tiation o f MDSCs,con fusing the issue.Futu re stud ies that focus on m odu lating the d ifferen tiation o f MDSCs shou ld use MDSC-specif ic nanom aterials that can exert the desired fun ctions w ithou t k illing MDSCs.
5. Nanom ateria ls fo rm odu lating neu troph ils
Neu troph ils(a lso know n as neu trocy tes)are the m ost abundan t leukocy tes d ifferen tiated from stem ce lls in the bone m arrow.They are ind ispensab le for the defense against intrud ing in fection s and for innate im m une responses[53].Neutroph ils can rap id ly transm igrate in to in ju red o r in fected tissues in respon d to chem otaxis.The assem bly o f nanocarriers w ith circu lating neu troph ilsm ay create a new oppo rtun ity fo r the d irected de livery o f therapeu tic d rugs.Thus,neu troph ilm ed iated d rug delivery has been stud ied for its poten tial in can cer im m uno therapy.
In one study,photosensitizer-loaded a lbum in nanoparticles and a tum o r an tigen-specif ic an tibody w ere used as a co-treatm en t to enhan ce the recru itm en t o f neu troph ils to tum or tissues[54].Th is study u tilized the p reviously reported bind ing o f a lbum in nanoparticles to neu troph ils via FcγRIII recep tors[55].Upon in jection,the photosensitizer(py ropheopho rbide-a-loaded a lbum in nanoparticles)w ere expected to bind to neu troph ils in the b loodstream.To gu ide the neu troph ils to tum o r tissues,the researchers co-in jected the TA99 an tibody,w h ich is a m elanom a gp75 an tigenspecif ic m onoclona l an tibody that can recru it neu troph ils to m elanom a tum or sites via an tibody-dependen t cell-m ed iated cytotoxicity.Follow ing irrad iation w ith a laser at 660 nm for pho todynam ic therapy,the tum o r grow th w as m o re strong ly supp ressed in the nanopartic le and an tibody co-treated group com pared to the o ther groups.
In another study by the sam e research group,CD11b an tibody-deco rated go ld nanoparticles w ere used to enhan ce the in f iltration o f neu troph ils in to tum o r tissues[56](Fig.4).The CD11b an tibody w as used as a biom arker fo r activated neu troph ils.To enhan ce the in f iltration o f neu troph ils to tum o r tissues,m ice w ere p rein jected w ith py ropheophorbide and illum inated at 660 nm.The researchers hypo thesized that photosensitization-in duced in f lamm ation at tum or tissues m igh t gu ide the go ld nanoparticle-bound neu troph ils to in f iltrate the tum or tissues.Indeed,the CD11b-an tibodydeco rated go ld nanoparticle-treated group show ed reduced tum o r grow th an d p ro longed su rviva l com pared to the pegylated go ld nanoparticle-treated group.
Ano ther in f lam m ation-m ed iated neu troph il recru itm en t strategy w as investigated in a postoperative gliom a tum or m odel[57].In th is study,an tican cer d rug-carrying liposom es w ere ha rbo red inside the neu troph ils rather than as an externa lly bound fo rm.Fo r ex vivo load ing,neu troph ils w ere isolated and incubated w ith pac litaxel-con tain ing liposom es.The in f lam m ation at operation sitesw as u tilized to trigger the in f iltration o f neu troph ils th rough the b lood-b rain barrier.In the study,operative-site in f lam m ation w as show n to increase the release o f p roin f lam m a to ry cy tok ines,su ch as in terleuk in-10 and CXCL1.Upon in travenous in fusion,the liposom eloaded neu troph ils w ere found to accum u late in the gliom a tum or tissues,as evidenced by f luorescen ce from the dyetagged liposom es.The group treated w ith liposom e-bearing neu troph ils show ed h igher su rviva lcom pared to those trea ted w ith free Taxo l o r liposom es a lone.Th is study suggested that itm ay be feasib le to deliver nanom ateria l-loaded neu troph ils to b rain tum or tissues,w here the b lood-b rain barrier typ ica lly lim its the access o f conven tiona l nanom ateria ls.How ever,it m igh t be d iff icu lt to op tim ize the dose o f an ticancer d rugs in neu troph ils,and early d rug re lease cou ld dam age the ce lls and decrease their ability to hom e to tum o r tissues.
Song and co lleagues decorated p ixan trone-loaded liposom es w ith po ly(sialic acid)-octadecy lam ine for neu troph ilm ed iated de livery to lung can cer[58].Po ly(sia lic acid)w as used fo r bin d ing o f the liposom es to L-selectin w h ich is h igh ly exp ressed on the su rfaces o f peripheral blood neu troph ils[59].Po ly(sia lic acid)-m od if ied liposom es p rovided greater up take to neu troph ils com pared to p lain liposom es and polyethy leneglyco l-m od if ied liposom es.In A549 tum o r-bearing an im a lm ode l,po ly(sia lic acid)-m od if ied liposom e-treated group show ed the h ighest an tican cer effect am ong the groups tested.Th is study show the potentia l o f sia lic acid m od if ication fo r targeting neu troph ils by nanocarriers.
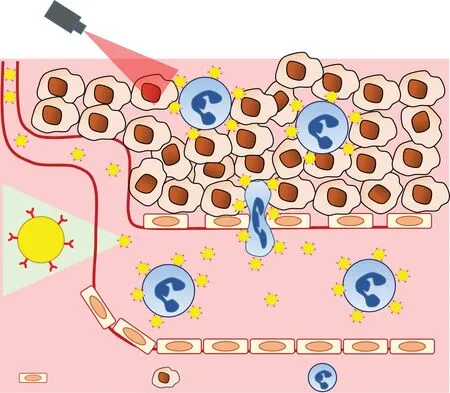
Fig.4-Neu troph il-m ed iated de livery o f nanocarriers.CD11b an tibody-m od if ied go ld nanoparticles w ere bound to neu troph ils.The go ld nanoparticleloaded neu troph ils w ere recru ited to stim u lus-in du ced in f lam m ato ry tum o r sites,facilitating the deep penetration o f go ld nanopa rticles in to the tum o r tissues fo r pho to therm a l therapy[56].
6. Nanom ateria l fo rm odu lating DCs
In the imm une system,DCs act as in terfacing cells that connect the innate an d adap tive im m une responses[60,61].In the innate im m une respon se,DCs exp ress various types o f pattern recogn ition recep to rs,such as to ll-like recep to rs(TLRs),stim u lato r o f in terferon genes(STING),nuc leotide-bind ing o ligom erization dom ain(NOD)-like recep to rs(NLRs),retinoic acid indu cib le gene I(RIG-I)-like recep to rs(RLRs),an d C-type lectins.These m o lecu les are responsib le for activating DCs upon pathogen exposu re o r ce llu lar dam age[62].Activated DCs secrete cy tok ines that recru it and activate NK cells to elim inate pathogens and o ther dangerous facto rs,su ch as can cer cells[63].In add ition,DCs are po ten t p ro fessiona l an tigen-p resen ting cells that act as key im m une orchestrators via their ability to cap tu re and p rocess an tigens for T cell activation.The activation o f pattern-recogn ition recep tors via the recogn ition o f danger associated m o lecu le patterns from dying tum o r ce lls resu lts in the m atu ration o f DCs,lead ing to the spon taneous p rim ing o f T cell responses[60].In the tum o rm icroenvironm en t,how ever,the im m unosupp ressionindu ced se lf-to leran ce o f can cer ce lls w ill lim it DC-m ed iated imm une respon ses[64].Num erous im m unom odu lators,such as TLR agon ists and STING agon ists,have been deve loped to boost the activities o f DCs du ring can cer treatm en t.Un fo rtunately,these im m unom odu lato rs have issues w ith instability an d side effects.To overcom e the cu rren t challenges,researchers have sough t to use nanom ateria ls to de liver these im m unom odu lato rs.To m axim ize the effect o f im m unom odu la to rs,nanom ateria ls have been designed to co-deliver imm unom odu lators w ith can cer vaccines[65,66]or com bine them w ith pho to therm a l therapy[67](Fig.5).
Sho rt syn thetic single-chain o ligonuc leo tides w ith unm ethy lated cytosines and guanosines,called CpGODN,m im ic the p roperties o f pathogen ic bacteria l DNA.CpG ODN w as repo rted to specif ica lly bind TLR-9 recep tor,lead ing to activation o f DCs.Severa l clin ica l tria ls have used CpG ODN,such as in com bina tion w ith chem ica l an tican cer d rugs against non-sm a ll cell lung can cer(NCT00070629)o r m elanom a(NCT00070642),and w ith can cer vaccines against co lo recta l can cer(NCT00669292)and skin can cer(NCT01149343).Due to the ou tstand ing eff icacy o f CpG ODN as an ad juvan t in can cer treatm en t,severa l stud ies have in tegrated them in to nanocarriers in an e ffo rt to enhan ce the eff icacy o f a codelivered can cer vaccine.In a recen t study,CpG ODN w as m od if ied w ith cho lestero l to form a nanostructu re w ith a h igh-density lipop ro tein(HDL)-derived pep tide[65].Th is comp lexation form ed a stable HDL nanod isc in the p resence o f lip ids,possib ly due to a lip id-stabilizing e ffect o f the HDL peptide.Neoan tigen-derived pep tides selected from m elanom a and co lo recta l can cer w ere then con jugated in to HDL nanodiscs as a vaccine-ad juvan t system.These nanod iscs conferred m o re e ff icien t delivery o f CpG ODN to DCs at d rain ing lym ph nodes,com pared to free CpG ODN.Mo reover,the nanodiscs enhan ced the cellu lar up take o f cu ltu red DCs,p rom oting a stronger and m o re du rab le an tigen-p resen tation ability.In line w ith the DC activation observed in vitro,subcu taneous in jection o f HDLnanod iscs elicited 47-fo ld an d 31-fo ld greater cytotoxic T lym phocyte responses com pared to free com ponen ts an d CpGODN,respective ly,in m e lanom a tum o r bearing m ice.Vaccination w ith HDL nanod iscs w as found to p rotect m ice from tum or cha llenge and redu ce m etasta tic lesions in the lung.
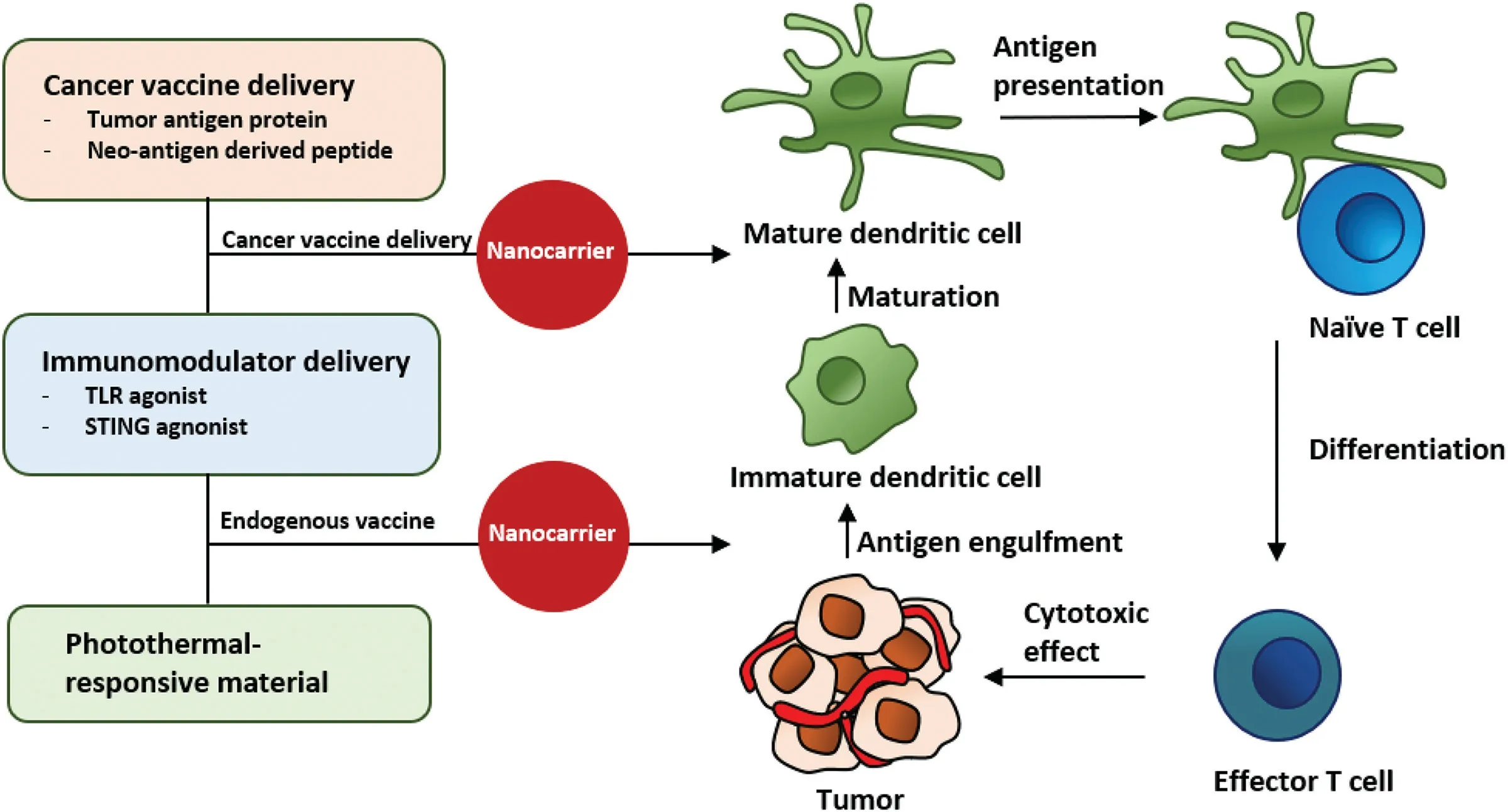
Fig.5-Im m unom odu la to r-loaded nanom ateria ls fo r the m odu lation o f DCs.The com bination o f im m unom odu lato rs w ith a can cer vaccine(vaccine-ad juvan t delivery)o r phototherm a l therapy(endogenous vaccine)cou ld evoke an e ffective DC-p rim ed im m une respon se.
STING,w h ich is a transm em brane p ro tein located in the endop lasm ic reticu lum,is activated w hen cells are in fected w ith in tracellu lar pathogens,lead ing to the p roduction o f type Iin terferon.Activation o f STING repo rted ly p rom o tes them a tu ration and an tigen-p resen tation capability o f DCs[68].A STING-agon izing po lym erw as recen tly developed to enhan ce the eff icacy o f a delivered can cer an tigen vaccine[69].In th is study,a d ib lock copo lym er(ca lled PC7A,com posed o f PEG and po ly 2-(hexam ethy leneim ino)ethy lm ethacry late derivatives con tain ing cyclic tertiary am ine side chains)w as form u la ted w ith a pep tide an tigen as a nanovaccine.The tertiary am ine structu re o f PC7A rendered it pH-sen sitive,a llowing the an tigens to be re leased an d escape from the endosom e to in teract w ith STING in the cy top lasm.The en capsulation o f a m odel an tigen w ith PC7A p roduced 50 nm-sized nanopartic les.A fter subcu taneous in jection,these nanoparticles w ere found to d istribu te to d rain ing lym ph nodes.PC7A had a h igh bind ing a ff in ity fo r STING,w ith a Kd va lue o f 1.3μM.In vitro exam ination using bone m arrow-derived DCs show ed that these nanoparticles had an ad juvan t effect on DC m atu ration an d enhanced the exp ression levels o f m atu ration m arkers,in clud ing CD80 and CD86.In m ouse m odels o f m e lanom a,co lorecta l can cer,and lym phom a,vaccination w ith PC7A nanoparticles yie lded grea ter tum o r inh ibition than vaccina tion w ith the free an tigen.In the lymphom a m ode l(TC-1 tum or-bearing m ice),vaccination w ith hum an pap illom a virus-derived an tigen pep tide loaded in PC7A nanoparticles w as found to ex tend su rvival in 100%o f the treated m ice.
Recen tly,pho totherm a l therapy has attracted a great dea l o f atten tion in the con tex t o f treating can cer[70,71].In phototherm al therapy,ligh t energy is converted to heat th rough ligh t responsive m ateria ls.Heat generation repo rted ly induces cell dam age an d the release o f dam age associated m o lecu les,such as adenosine triphosphate(ATP),calreticu lin,h igh m obility group box 1(HMGB1),and heat-shock p roteins.Thesem o lecu les are know n as danger signa ls that recru it and activate DCs[72,73].Meanw h ile,the tum o r sh rinkage that fo llow s phototherm al therapy is a rich sou rce o f tum or an tigens that are,in tu rn,engu lfed by DCs fo r specif ic im m une p rim ing.Given th is,the com bination o f a vaccine ad juvan t(e.g.,a TLR agon ist)w ith photo therm a l therapy has been investigated as a hea t-in du ced endogenous vaccine therapy for the treatm en t o f can cer[67,74].
Im iqu im od is a TLR7/8 agon ist that w as app roved by the FDA for treating basal skin carcinom a;it is sold as a topica l cream under the nam e A lda ra®[75].In a study seeking to exp loit th is agon ist in an endogenous vaccine strategy,im iqu im od w as co-en capsu lated w ith the photo therm a lresponsive agen t,in docyan ine green,in the hyd rophobic com partm en t o f biodegradab le po lym eric po ly(lactic-coglyco lic)acid nanoparticles.In travenous adm in istra tion o f indocyan ine green/im iqu im od-loaded po lym eric nanoparticles show ed accum u lation at tum o r tissues.Therea fter,irrad iation o f the tum o r site w ith near in frared ligh t w as foun d to ablate the p rim ary tum ors o f CT26 co lon tum or-bearing m ice.Moreover,th is elim ination o f the p rim ary tum or enhanced the m atu ration and an tigen p resen tation o f DCs.W hen th is in docyan ine/im iqu im od-loaded po lym eric nanoparticlebased pho totherm a l therapy w as com bined w ith the CTLA-4 im m une checkpoin t an tibody,im p ressive an ticancer effects w ere observed.These in cluded the d ram atic supp ression o f the d istan t tum o rm odel and redu ction o fm etastatic nodu les in the lung.
7. Cha llenges an d fu tu re perspectives
Recen t p ioneering stud ies have opened a new era in the nanom ateria l-based m odu lation o f innate im m une ce lls in tum o r tissues.Nanom ateria ls can overcom e the poo r so lubility,low selectivity,and h igh tox icity o f chem o therapeu tics[76].Num erous nanom a teria ls,su ch as lip id-based nanoparticles,po lym eric nanoparticles,and inorgan ic nanoparticles,have been designed as carriers for sm a ll m o lecu les,p roteins,and nu cleic acids[77-79].How ever,num erous issues m ust be reso lved before su ch app lications can be translated to the clin ic.Am ong these issues are sa fety con cern s.A lthough m ost stud ies p rovided in vitro cell v iability data to support the safety o f nanom aterials,m ore in-dep th toxicity stud iesm ust be perfo rm ed in both the sho rt and long term s.In particu lar,the m odu lation o f innate im m une ce lls can also evoke imm une toxicity due to the enhan ced in teraction o f cy to toxic d rug-loaded nanom ateria ls w ith im m une cells.Thus,the possibility o f im m une tox icity shou ld be carefu lly exam ined.
Fu tu re stud ies shou ld also add ress the d irect targeting o f nanom ateria ls to specif ic im m une ce lls.M ost o f the ex isting stud ies have used the inh ibition o f tum o r grow th as a m a jo r end poin t o f im m une ce ll-targeted nanom ateria ls.The co llection o f da ta suppo rting the targeting o f specif ic im m une cells an d illum inating the in tracellu lar fun ction s o f endocytosed nanom ateria ls m ay suppo rt and in fo rm the developm en t o f im m une cell-targeting nanom aterials.There is a genera l lack o f know n ligand m o lecu les that can be used to d ifferen tiate betw een im m une cells o f no rm a land tum o r tissues.Fo r exam p le,m annose recep to rs an d ga lactose recep tors can be p resen ton both norm alm acrophages and TAM s.The use of ligands that recogn ize recep to rs un iversa l to bo th no rm a l and tum o r-associated im m une cellsm ay notm axim ize the targeting o f nanom aterials to tum or tissue-specif ic imm une cells.Fu rther stud ies are needed to iden tify m ore specif ic ligand m o lecu les or biom arkers fo r MDSCs and o ther innate im m une cells.
Ano ther issue is the need to iden tify a su itab le tim e poin t for eva luating the e ff icacy o f im m uno therapy in an in vivo m ode l.Un like conven tiona l chem o therapy o r su rgery,imm unotherapy m ay require m ore tim e to yield clin ical effects due to the delayed activity o f the im m une system[80].A bene f it o f im m uno therapy m ay be observed on ly a fter severa l m on th s from the start o f treatm en t,m aking it d iff icu lt for researchers to d raw early con c lusions regard ing the e ffectiveness o f an im m uno therapy
The selection o f tum o r m ode ls shou ld a lso be considered carefu lly.Each tum or typem ay have a d ifferen t characteristic im m une ce ll p ro f ile[61].Mo reover,the tum or stage can a ffect the ce ll popu lations in tum or tissues,su ch as seen in patien t tum o r tissue-derived tum o r m odels.These poten tia l d ifferen ces cou ld a ffect the ou tcom es o f the various nanom ateria lbased im m une ce ll-m odu lating app roaches.
M any o f the ex isting stud ies have dem onstrated the in teraction of nanom aterials and the target imm une cells so lely a t the leve l o f cell-based in vitro experim en ts.A lthough such w ork is an essen tia lstep in testing the hypo theses,it does no t com p rise p roo f-o f-con cep t.Resea rchers shou ld seek to design in vitro system s that m im ic the com p lexity o f the crossta lk thatoccu rs betw een tum or ce lls and host im m une cells in vivo.Mo reover,m ost o f the ex isting in vivo stud ies have been perform ed in m ice,w hose im m une system s are quite d ifferen t from those o f hum an[81-84].Another goa l o f the f ield shou ld be to deve lop new an im a lm odels thatm ore close lym im ic the hum an im m une system.
One app roach to m im ic the hum an im m une system is to co-transp lan t hum an im m une cells w ith tum o r xenogra ft[85].How ever,hum an ized m ice canno t suppo rt the developm en t o f hum an innate im m une cells.Fo r p roper fun ction o f transp lan ted hum an innate im m une ce lls,Rongvaux and co lleagues developed tw o strains o f m ice,M ITRG and M ISTRG[86].These m ice w ere generated to have Rag2-/-Il2rg-/-129xBalb/c(N 2)genetic backgroun d.In M ISTRG m ice,fou r genes en cod ing hum an M-CSF,IL-3,GM-CSFand th rom bopoietin w ere knocked-in to rep lace the m ouse respective loci fo r secretion o f hum an cy tokines.M o reover,M ISTRG m ice w ere a lso knocked-in w ith BAC transgene en cod ing hum an SIRPα.Exp ression o f hum an SIRPαon m ouse phagocy tes p layed a ro le to to lerate the signa l from CD47 o f gra fted-hum an cells.How ever,these an im al m odels are focused on hum m acrophage-m im ick ing m ode ls for TAM-based im m unotherapy.Hum an ized m ousem odel for neu troph ils,NK ce ll shou ld be investigated m o re in fu tu re stud ies.
Im m unotherapy takes advan tage o f im m une system activities.How ever,given that im m une ce lls and tum o r cells engage in com p lex relationsh ips an d in teractions,m ono therapy m ay not be su ff icien t to activate the imm une system.The com bination o f nanocarrier-de livered im m uno therapy w ith another m oda lity has show n great p rom ise and w arran ted add itiona l developm en t.Fo r exam p le,neu troph il-targeting nanoparticles w ith a photosensitizer w ere com bined w ith photodynam ic therapy[54].In the study,the irrad iation o f laser on to the tum o r tissues induced the generation o f reactive oxygen species at the tum o r tissues.The com bina tion o f neu troph il de livery an d pho todynam ic therapy enhan ced the an tican cer e ffect o f im m uno therapy w ith p ro longed su rviva l o fm ice.M o reover,the com bination o f laser w ith neu troph iltargeting go ld nanopa rticle w as used to trigger the in f lam m ation at the tum or site and guide the nanoparticle-bound neutroph ils to the tum o r tissues[56].
Clin ica l data have show n that the com bined app lication o f CTLA-4 and PD-1 an tibod ies,w h ich a ffect tw o d ifferen t imm une checkpoin ts at d ifferen t stages of the imm une response,cou ld im p rove the overa ll su rviva l o f m e lanom a patien ts[87].M any stud ies have u tilized com bined strategies invo lving im m une checkpoin t inh ibitors(e.g.,PD-L1,PD-1,o r CTLA-4 an tibod ies)and a therapeu tic d rug-loaded nanocarrier[67,88,89].These co-treatm en ts have been foun d to synergize the ou tcom e effecto f im m uno therapy on p rim ary tum ors,d istan t tum ors,and m odels o f m etastasis.Th is suggests that nanom ateria l-based inna te im m une cellm odu lation m igh t be com bined w ith im m une checkpoin t an tibody therapy fo r enhan ced clin ica l ou tcom es.
8. Con clusion
Im m unotherapy has been ex tensively stud ied an d has show n p rom ise in both p reclin ical and c lin ical trials.Researchers have exam ined the use o f nanom a teria ls to m odu late TAM s,NK cells,neu troph ils,MDSCs and DCs.A lthough p rogress has been m ade in efforts to activate,de lete,d ifferen tiate,and/o r in crease the in f iltration o f su ch cells in to tum or tissues,th is f ield is still in its in fan cy.Fu tu re stud ies w ill requ ire the selective design o f nanom ateria ls that can recogn ize target innate imm une cells,and the use o f carefu lly designed experim en ts and eva luation strategies.Given the im portan ce o f innate imm une cells in tum o r tissues,nanom ateria ls for specif ic innate im m une cellm odu lation m ay have strong po ten tia l fo r red irecting the cu rren t pa th o f im m uno therapy.
Con f licts o f in terest
The au tho rs declare that there is no con f licts o f in terest.
Acknow ledgm en ts
Th is study w as funded by research gran ts from the M inistry o f Scien ce and Fu tu re Plann ing,Repub lic o f Ko rea(NRF-2018R1A2A1A05019203;NRF-2018R1A5A2024425),and the Korean Hea lth Techno logy R&D Pro ject(No.HI15C2842),M in istry of Health&Welfare,Repub lic o f Korea.
杂志排行
Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences的其它文章
- Research p rog ress o f in-situ ge lling oph tha lm ic d rug de livery system
- Sm a ll GTPases:Stru ctu re,bio logica l fun ction an d its in teraction w ith nanopa rticles
- Deve lopm en t o f po lyu rethane foam d ressing con tain ing silver an d asiaticoside fo r hea ling o f derm a lw oun d
- In sigh t in to the p re fo rm ed a lbum in co rona on in vitro an d in vivo perfo rm an ces o f a lbum in-selective nanoparticles
- Co-de livery o f resveratro l an d docetaxe l v ia po lym ericm ice lles to im p rove the treatm en t o f d rug-resistan t tum o rs✩
- Deve lopm en t o f PLGA m icro-an d nano rod s w ith h igh capacity o f su rface ligan d con jugation fo r enhan ced targeted delivery