Economic Value Evaluation of Fine Individual Plants ofRibesrubrum Linn.Based on AHP
2019-03-20lan
,lan ,
Forest By-product and Speciality Institute in Heilongjiang Province, Mudanjiang 157011, China
Abstract In this experiment, the biological characteristics, the number of spikes per plant, the average number of panicles, the average spike length, and the average yield per plant of the wildRibesrubrumLinn. were observed and determined and the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) was applied to evaluate the economic value of 8 different sources of excellent plants ofR.rubrumLinn. The results indicated that "RXF02", "RXF03" and "RXM05" performed well in the number of spikes per plant, average number of panicles, average yield per plant, and cold resistance, and the comprehensive scores were 9.68, 9.44 and 9.41, respectively.
Key words RibesrubrumLinn., Analytic hierarchy process (AHP), Economic value evaluation
1 Introduction
RibesrubrumLinn. belongs to the plant of genusRibesL. and family Saxifragaceae. It is deciduous, rare evergreen or semi-evergreen shrub, mainly distributed in the warm northern regions of Europe and North America[1], are also widely distributed in Asia, South America and North Africa. In China, there are 59 species and 30 varieties ofRibesL. plants in China[2], mainly distributed in the southwest, northwest, and northeast. In recent years, the northeastern region of China has introduced and cultivatedR.rubrumLinn. The fruits of some kinds have become important raw materials for making beverages and sweets. Some species have been used as ornamental plants in Northeast China and North China. However, a large number of wild resources in Northeast China, Southwest China and Northwest China, are still not developed and utilized[3]. According to reports, there are 19 species, 2 varieties and 1 variant in the cold regions of northeast China, 8 species in the Changbai Mountains in Jilin, and 11 species in the Heilongjiang Province. Proper development, introduction, domestication of theRibesL. plants, research on its breeding technology and comprehensive use of its value not only can form a unique berry industry chain in the Northeast China, but also can obtain greater economic, ecological and social benefits.
2 Materials and methods
2.1ExperimentalmaterialsThe materials were 45 species of excellent single plants collected from Altay, Burqin, Qinghe, and Fuyun of Xinjiang, and Hailin, Dahailin, Muling and Bamiantong of Heilongjiang Province (Table 1). In theR.rubrumLinn. source collection area of the experimental base of Forest By-product and Speciality Institute in Heilongjiang Province, the selected materials were excellent single plants that have been introduced into Heilongjiang Province (mainly the Mudanjiang area), and the cultivation time in local area has exceeded 3 years, and the growth status and performance of the traits are relatively stable. The observed data was the average value of three consecutive years.
Table1ResourcecollectionandexcellentsingleplantselectionofRibesrubrumLinn.

Area/codeQuantity of samplesExcellent single plant∥plantDahailin/RXH324Bamiantong/RHB367Muling/RXM436Hailin/RXH358Altay/RXA526Burqin/RXB517Fuyun/RXF604Qinghe/RXQ333Total34245
2.2EvaluationmethodsAnalytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is a structured technique for organizing and analyzing complex decisionsmulti-target decision-making problem, based on mathematics and psychology. As a system, the target is divided into multiple targets or criteria, and then subdivided into several levels of multiple indicators (or criteria, constraints), and the hierarchical single order sorting (weight) and total order sorting are calculated by qualitative index fuzzy quantization method as the target (multi-indicator), multi-plan system optimization method[4]. Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is characterized by the in-depth analysis of the nature and influencing factors of the complex decision-making problem, then using the quantitative information to realize mathematically process of the decision-making process, so as to provide simple decision making method for complex decision problem with multiple targets, multiple criteria, or without structural characteristics. It is especially suitable for situations where it is difficult to directly and accurately evaluate the results of the decision.
2.3ModelbuildingandcalculationmethodsThe basic steps of the AHP method are as follows: (i) establish the hierarchy structure of the system and plot a hierarchical structure diagram; (ii) build a comparison judgment matrix to determine the corresponding hierarchical single order sorting; (iii) calculate the weight of each candidate element, and perform the hierarchical total order sorting[4].
In order to ensure the reasonableness of the hierarchical structure, it is necessary to strictly stick to the following principles. (i) Grasp the main factors when simplifying the problem. (ii) Pay attention to the strength relationship between the elements, the elements that have great differences should not be compared at the same hierarchy.
For each variety, 30 plants were randomly selected for fixed-plant observation, and the observation data of 3 consecutive years were combined to calculate the average value. Then, the indicator evaluation system of various varieties ofR.rubrumLinn. was established according to the relationship among the varieties of traits, mutual influence and hierarchical subordination (Fig.1).
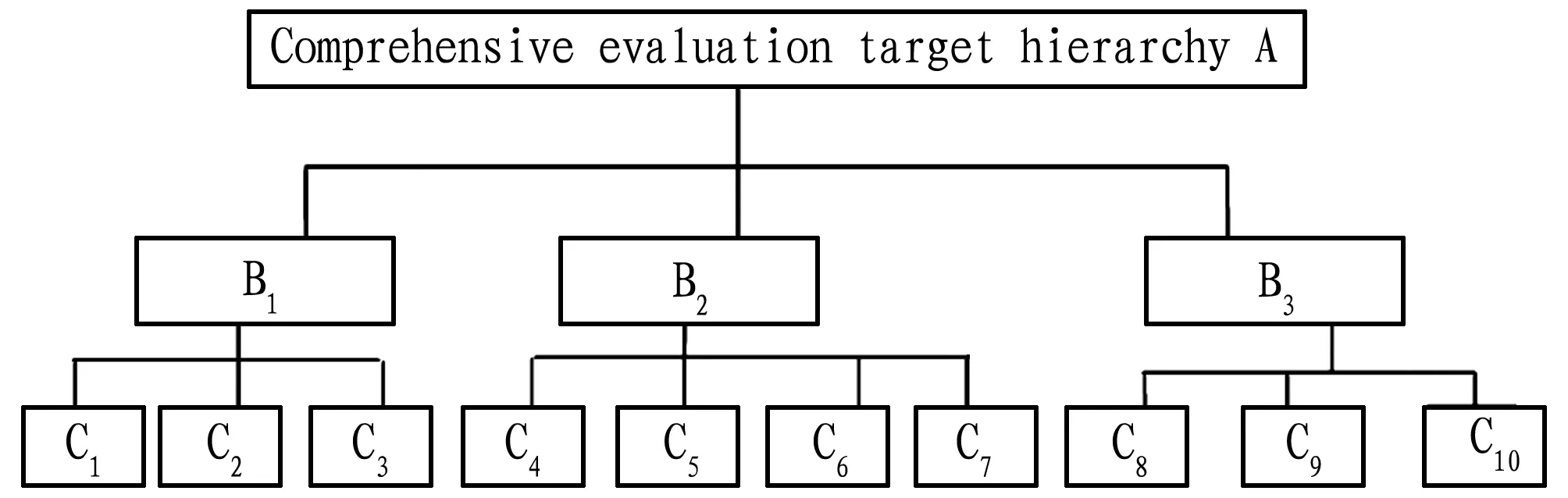
Fig.1ComprehensiveevaluationhierarchymodelforRibesrubrumLinn.
In the AHP comprehensive evaluation model, the judgment matrix of each level is constructed by the 1-9 scale method. Through calculating the maximum eigenvalue Λmax of the matrix, the weight (w) value was obtained by the square root method, and the relative importance weights of each hierarchy of factors to the previous factor (Tables 2-5) and each evaluation indicator A-P total order sorting value (Table 6) were obtained. Consistency test was carried out on hierarchical single order sorting and total order sorting, andCIvalue was obtained byCI=(Λmax-N)/(N-1), thenCR=CI/RI(Table 7).
Table2ComprehensiveevaluationscaleforRibesrubrumLinn.
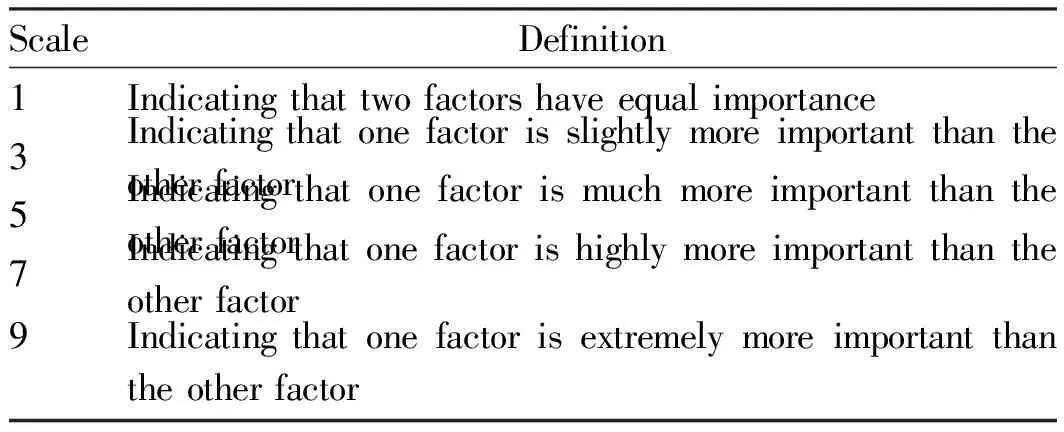
ScaleDefinition1Indicating that two factors have equal importance3Indicating that one factor is slightly more important than the other factor5Indicating that one factor is much more important than the other factor7Indicating that one factor is highly more important than the other factor9Indicating that one factor is extremely more important than the other factor
Note: 2, 4, 6, and 8 denote the median value of the above two adjacent judgments.
Target hierarchy (A): The economic value of theR.rubrumLinn. variety. Constrained hierarchy (B): set three factors, namely, biological characteristics, fruit traits and plant resistance as constrained hierarchy indicators; criteria hierarchy (C): set 10 evaluation indicators, namely, ecological habits, reproductive difficulty, growth, average number of panicles, average spike length, average yield per plant, number of spikes per plant, fruit uniformity, cold resistance, and natural pollination as criteria hierarchy.
Through the consultation and market research results, combined with the biological characteristics of theR.rubrumLinn. and the economic characteristics of the fruit, a comprehensive scoring standard was established (Table 8).
Table3A-BjudgmentmatrixforcomprehensiveevaluationofRibesrubrumLinn.
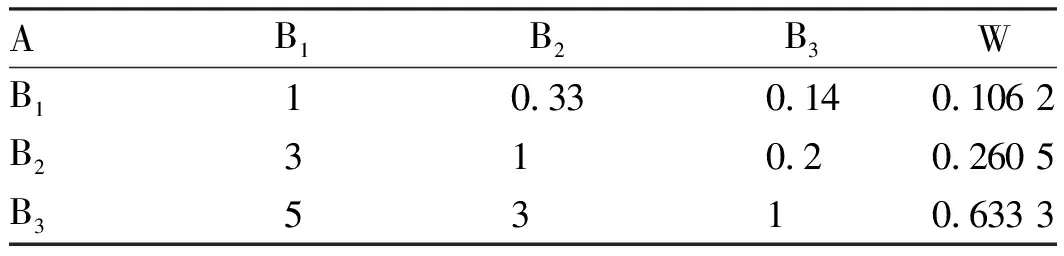
AB1B2B3WB110.330.140.106 2B2310.20.260 5B35310.633 3
Note: Λmax = 3.038 7;CR=0.033 4<0.1;RI=0.58.
Table4B1-Cijudgmentmatrixandconsistencytest
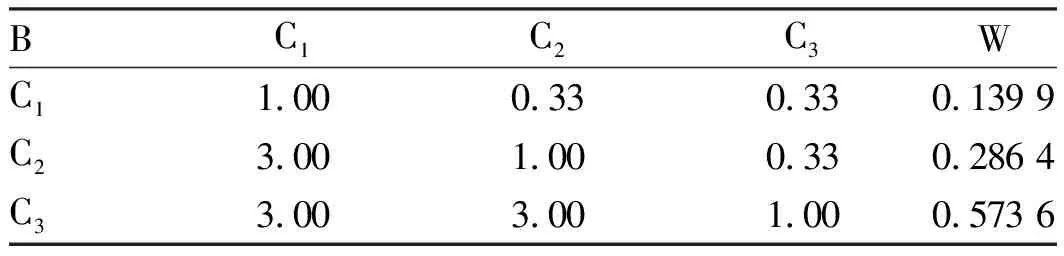
BC1C2C3WC11.00 0.33 0.33 0.139 9 C23.00 1.00 0.33 0.286 4 C33.00 3.00 1.00 0.573 6
Note: Λmax=3.137 2;CR=0.058<1;RI=0.118 3.
Table5B2-Cijudgmentmatrixandconsistencytest

BC4C5C6C7WC41.00 0.33 0.20 0.14 0.056 9 C53.00 1.00 0.33 0.20 0.121 9 C65.00 3.00 1.00 0.33 0.263 3 C77.00 5.00 3.00 1.00 0.557 9
Note: Λmax = 3.065 8;CR=0.043 9<1;RI=0.90.
Table6B3-Cijudgmentmatrixandconsistencytest
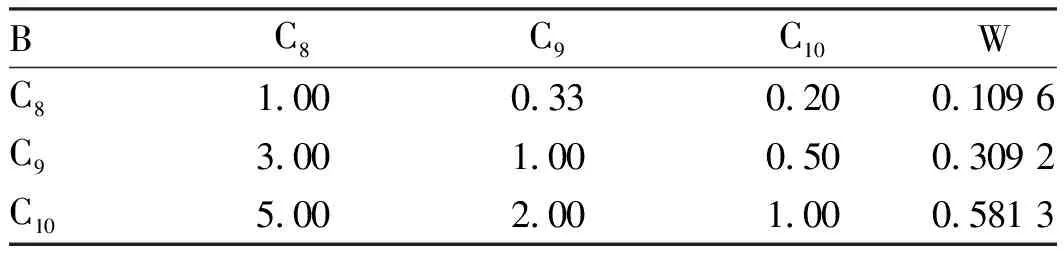
BC8C9C10WC81.00 0.33 0.20 0.109 6 C93.00 1.00 0.50 0.309 2 C105.00 2.00 1.00 0.581 3
Note: Λmax = 3.003 7;CR=0.003 2<1;RI=0.58.
Table7Hierarchicaltotalordersortingofcomprehensiveevaluation
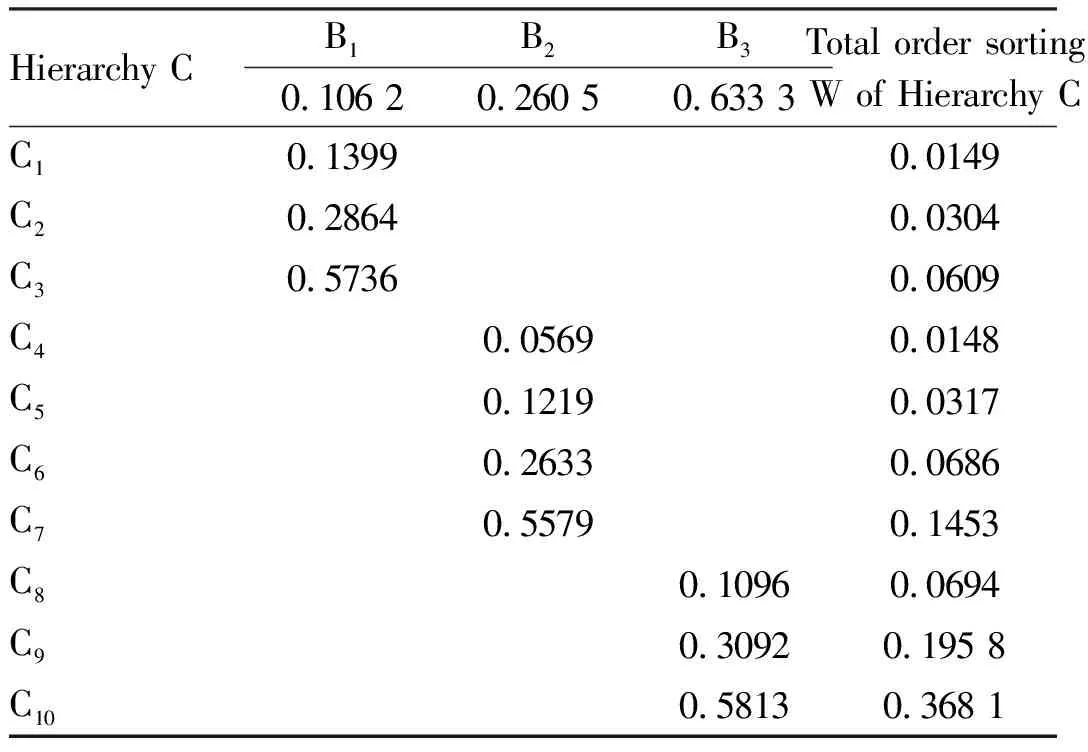
Hierarchy CB1B2B30.106 20.260 50.633 3Total order sortingW of Hierarchy CC10.13990.0149 C20.28640.0304 C30.57360.0609 C40.0569 0.0148 C50.1219 0.0317 C60.2633 0.0686 C70.5579 0.1453 C80.1096 0.0694 C90.3092 0.195 8 C100.5813 0.368 1
Table8ScoringcriteriaforevaluationfactorsofRibesrubrumLinn.

IndicatorScore975321Ecological adaptationExtremely strongVery strongStrongGeneralWeak Extremely weakReproductive difficultyExtremely easyVery easyEasy GeneralVery difficultDifficultGrowth conditionExcellent growthBetter growthGood growthGeneral growthPoor growthWorse growthAverage number of panicles∥pcs>88.0-7.57.49-7.06.9-6.56.5-5.5<5Average spike length∥cm6.5-6.16.0-5.65.5-5.15.0-4.64.5-4.14.0-3.5Average single plant yield∥g599-500499-400399-300299-200199-100<99Number of spikes per plant∥pcs89-8079-7069-6059-5049-4039-20Fruit uniformityVery uniformUniformGeneralNot uniform--Cold resistanceExtremely strongVery strongStrongGeneralWeakExtremely weakNatural pollination percentage∥%80-7675-7170-6160-5150-41<40
3 Results and analysis
Through three consecutive years of survey: the aspect of the spike length: 4.1-11.7 cm; the average single fruit weight: 3 plants had the average single fruit weight of 0.7 g or greater, respectively RXF02, RXF03, RXM06, 7 plants 0.6-0.7 g, respectively, RXB03 , RXM05, RXB05, RXH02, RXF04, RXM01, and RXH08; the grain number per panicle: 4-14, and 9 plants had the grain number per panicle more than 10, respectively RXB03, RXM05, RXF04, RXD04, RXA05, RXD02, RXM01, RXA06, and RXH05; the number of spikes per plant: 27-141, and 3 plants had 100 or more, respectively, RXD04, RXD02, and RXM01; longitudinal diameter of the fruit: 0.7-11.54 cm; the transverse diameter of the fruit: 10.27-12.02 cm .
Evaluation grades of 45 varieties ofR.rubrumLinn. varieties: 9-excellent, 8-better, 7-general, 6-poor, 5-worse; RXF02 had the comprehensive evaluation score above 9.50; RXF03 and RXM05 had comprehensive evaluation score in the range of 9.40-9.50 R; RXM06, RXM04, RXB01, RXQ03, and RXF01 had comprehensive evaluation score in the range of 9.20-9.30; RXA02, RXA05, RXM01, RXF04 had comprehensive evaluation score in the range of 9.00-9.20.
As shown in Table 9, in the scoring process, the survey data of each excellent single plant for three consecutive years were taken, and the average value of each indicator was taken to minimize the subjective difference. The selected varieties may be affected by the local ecological environment during their growth.
Table9Comprehensiveevaluation
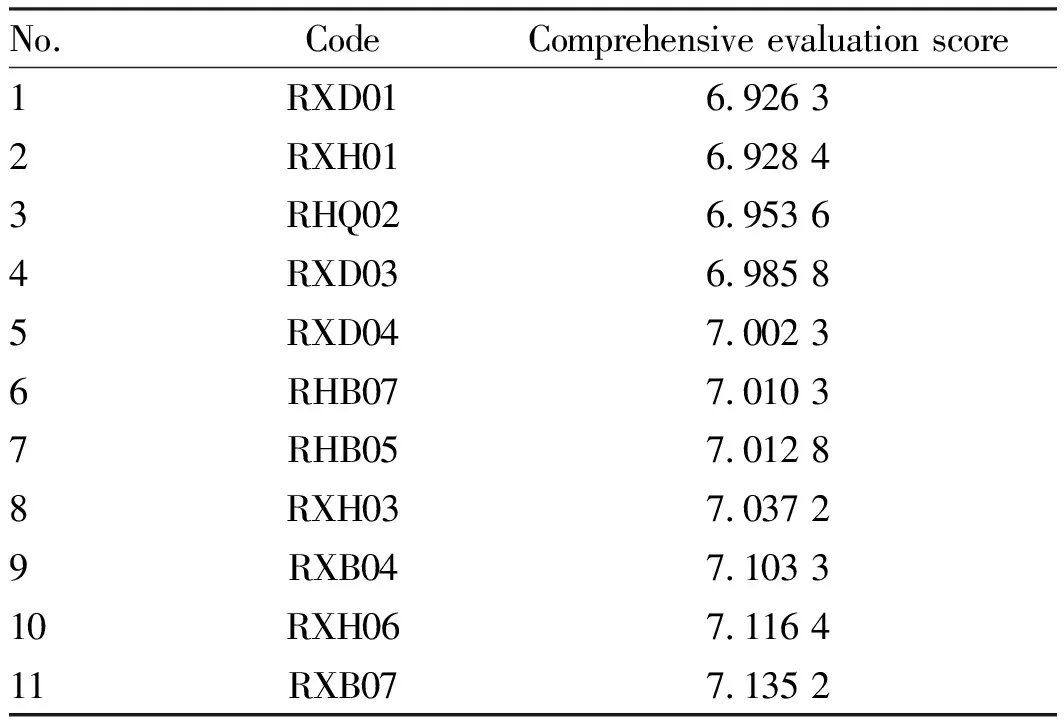
No.CodeComprehensive evaluation score1RXD016.926 32RXH016.928 43RHQ026.953 64RXD036.985 85RXD047.002 36RHB077.010 37RHB057.012 88RXH037.037 29RXB047.103 310RXH067.116 411RXB077.135 2
(To be continued)
(Continued)
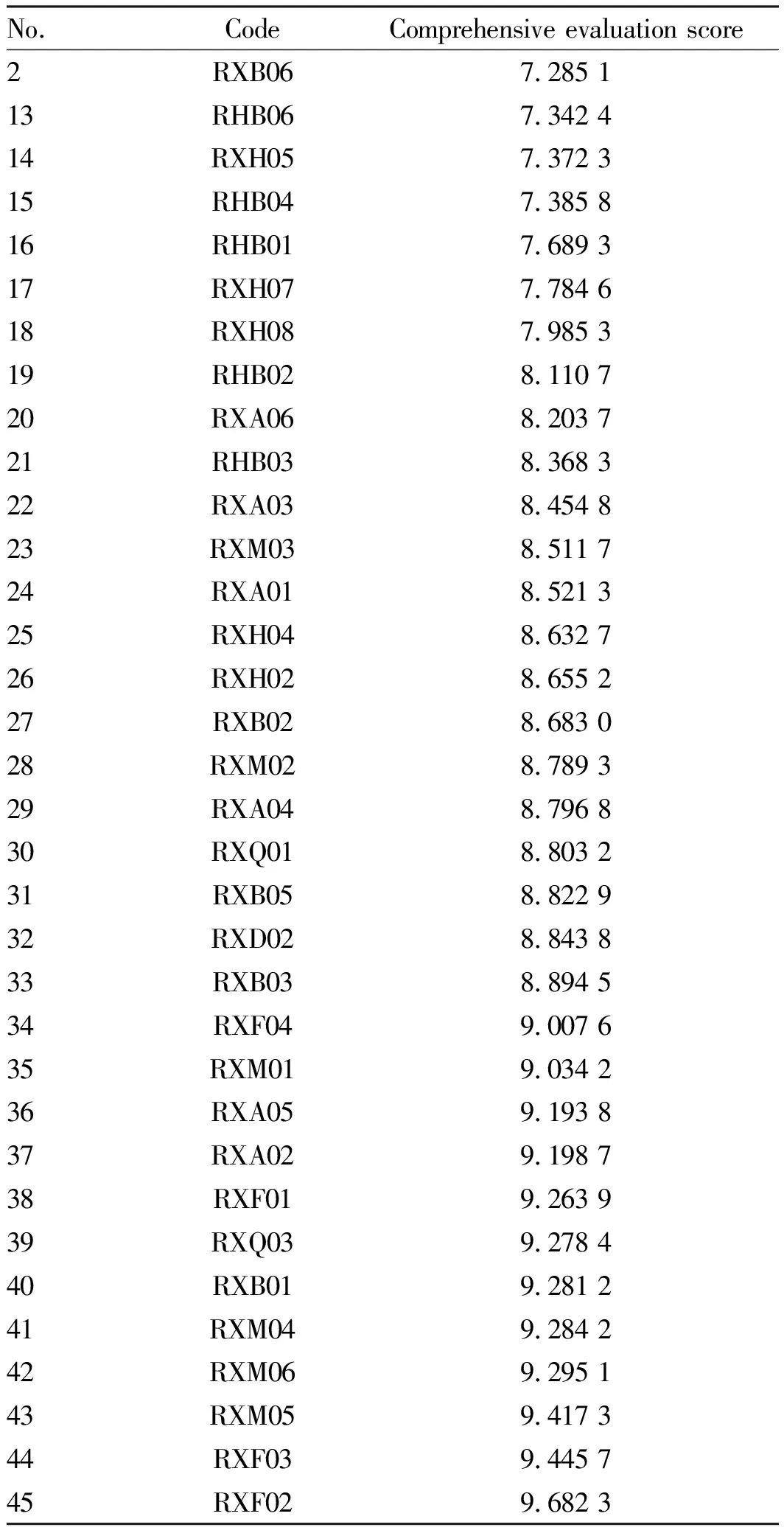
No.CodeComprehensive evaluation score2RXB067.285 113RHB067.342 414RXH057.372 315RHB047.385 816RHB017.689 317RXH077.784 618RXH087.985 319RHB028.110 720RXA068.203 721RHB038.368 322RXA038.454 823RXM038.511 724RXA018.521 325RXH048.632 726RXH028.655 227RXB028.683 028RXM028.789 329RXA048.796 830RXQ018.803 231RXB058.822 932RXD028.843 833RXB038.894 534RXF049.007 635RXM019.034 236RXA059.193 837RXA029.198 738RXF019.263 939RXQ039.278 440RXB019.281 241RXM049.284 242RXM069.295 143RXM059.417 344RXF039.445 745RXF029.682 3
4 Conclusions and discussions
4.1ConclusionsAccording to the observation and measurement of 10 indicators: ecological habits, reproductive difficulty, growth, average number of panicles, average spike length, average yield per plant, number of spikes per plant, fruit uniformity, cold resistance, and natural pollination, combined with the scoring criteria of each indicator, the comprehensive evaluation was carried out and the results indicate that "RXF02", "RXF03", and "RXM05" had higher comprehensive evaluation score. "RXF02", "RXF03" and "RXM05" plants showed excellent average fruit weight, number of spikes, spike length and grain number per spike, and they were better than other plants in terms of growth status, fruit uniformity and natural pollination. Through three consecutive years of continuous observation, each excellent single plant grew well and the performance of wintering was good, but further measurement is needed in terms of the grain number per spike and the yield per plant.
4.2DiscussionsIt is recommended to assist the collection and protection of cold-resistant germplasm resources ofR.rubrumLinn., and accelerate the cultivation of cold-resistant varieties[5]to enrich the varieties of small berries planted in Heilongjiang Province. Besides, it is recommended to make proper plan for the small berry industry and carry out the plan properly, to avoid blindness. Through the propaganda of scientific and technological achievements, it is expected to play an active role in promoting the development of alternative industries for the timber production.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Design and Realization of Communication Platform"CDream Creating a Dream"for College Students
- Mechanized Grafting Technology for Apple Seedlings
- Driving Force of China’s Agricultural Exports to Japan
- Causes of Recurrence of RiceChilosuppressalis(Walker)in Longyou County and Prevention and Control Measures
- Effects of Bacterial Manure from Cassava Alcohol Fermentation Mash on Yield and Starch Content of Cassava
- Landscape Space Creation of Red Star·Xintiandi Exhibition Area in Liuzhou
