Investigation and Analysis on Agricultural Biological Resources of Wuchuan Gelao and Miao Autonomous County,Guizhou Province
2019-03-20,,,,,,
, , , , , ,
1.Institute of Vegetables and Flowers, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences/Key laboratory of Biology and Genetic Improvement of Horticultural Crops, Ministry of Agriculture,Beijing 100081, China; 2.Guizhou Institute of Germplasm Resource/Institute of Modern Chinese Herbal Medicines, Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Guiyang 550006, China; 3.Horticultural Crops Research Institute, Yunnan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Kunming 650000, China; 4.Zunyi Agricultural Institute, Zunyi 563100, China; 5.Bureau of Agriculture and Animal Husbandry of Wuchuan, Zunyi 564300, China
Abstract Wuchuan Gelao and Miao Autonomous County is located in the northeast of Guizhou Province, and in the border of Guizhou and Chongqing, having a subtropical humid monsoon climate. There is no severe heat in summer, and no severe cold in winter. It has distinct national characteristics, and there are many biological resources with national characteristics. A systematic investigation of biological resources in the county for nearly a month was carried out by organizing a professional investigation team. The investigation covered 5 townships and we visited 12 village committees and 26 villagers’ groups, involving three ethnic groups: Gelao, Tujia and Miao. The biological resources closely related to the agricultural production and life of local ethnic groups were investigated, collected and sorted out. A total of 230 samples of all kinds of resources were collected, including 47 food crops, 75 vegetables and annual crops, 37 fruit trees and perennial crops, and 71 medicinal plants. Of these, a total of 73 were unique, superior and special resources. Based on general investigation and professional investigation, this paper analyzes the present situation, growth and decline of local agricultural biological resources, and puts forward some suggestions for the protection, development and utilization of agricultural biological resources.
Key words Guizhou, Wuchuan County, Investigation of biological resources
1 Introduction
Guizhou Province is rich in biological resources[1-5], and Wuchuan Gelao and Miao Autonomous County[6], located in the northeast of Guizhou Province, along the border of Guizhou and Chongqing, the geographical coordinates are between 107°37′-108°13′ E and 28°10′-29°05′ N[7]. The county is narrow from east to west, slender from north to south, 100.8 km from north to south, 42 km from east to west, and the total land area is 2 777.59 km2. It is adjacent to Dejiang County and Yanhe Tujia Autonomous County in the east; to Fenggang County in the south; to Zheng’an County and Daozhen Gelao and Miao Autonomous County in the west; and to Pengshui Miao and Tujia Autonomous County in Chongqing in the north. The county seat is 375 km away from Guiyang, the capital of the province, and 182 km from Zunyi City. The terrain tilts from north to south, with an average altitude of 500-1 000 m, the highest altitude of 1 665.5 m, and the lowest altitude of 303 m. It has a subtropical humid monsoon climate. It has long summers and short winters, with no severe heat in summers and no cold in winters. The annual average temperature is 18℃ and the precipitation is 1 349 mm. The average frost-free period is 328 d. Wuchuan Autonomous County is one of the two autonomous counties with Gelao and Miao nationalities as the main ethnic groups in the country[7]. It has jurisdiction over 10 towns and 5 townships, namely, Duru Town, Fengle Town, Huangdu Town, Fuyang Town, Zhennan Town, Yanshan Town, Yushui Town, Maotian Town, Baicun Town, Daping Town, Nigao Township, Fenshui Township, Jiaoba Township, Hongsi Township, and Shichao Township. There are a total of 270 villages, 4 village committees and 2 413 village groups. The total population is 451 000, of which 96.56% are ethnic minorities. There are 198 000 Gelao people, accounting for 43.9% of the total population, 182 000 Miao people, accounting for 40.4% of the total population, and 55 000 Tujia people, accounting for 12.2% of the total population. All ethnic groups live in villages and towns, intermarry with each other and their folk habits permeate each other.
Wuchuan County is a typical mountain agricultural county[6]. In 2011, the total agricultural output value was 1.376 8 billion yuan, of which, the output value of planting, forestry, animal husbandry, aquaculture and agricultural services reached 890 million yuan, 47.5 million yuan, 406.55 million yuan, 14.17 million yuan and 18.58 million yuan, respectively, accounting for 64.6%, 3.45%, 29.53%, 1.03% and 1.39% of the total agricultural output value, respectively. The area is rich in biological resources, livestock and poultry species resources are cattle, horses, sheep, pigs, chickens, ducks and economic insects-bees. Wildlife resources are amphibians, reptiles, and mammals, with giant salamander included in the national protection of precious animals. There are 393 varieties of crop resources, including 256 varieties of food crops, 43 varieties of oil crops, 11 varieties of cash crops and 3 varieties of green-mature crops. There are 33 varieties of fruits and 47 varieties of vegetables. There are 36 genera and 70 varieties of natural enemies of pests. The main crops are corn, rice, soybeans, peanuts, and the main cash crops are flue-cured tobacco, mulberry, paulownia and so on. There are 114 families, 245 genera and 299 species of forest vegetation resources, including 128 species of trees, 12 species of bamboo, 12 species of woody flowers, 46 species of shrubs, 14 species of lianas, 6 species of ferns and 81 species of herbs. The main timber tree species are pine, fir and cypress, and the forest coverage rate of the whole county is 26%.
Wuchuan County is rich in biological resources, and it is of great significance to enrich the genetic diversity of national crop species genebank and variety improvement by sending professional investigation teams to investigate, collect and preserve the biological resources in Wuchuan County[8].
2 Materials and methods
2.1MethodsofinvestigationThe investigation lasted 28 days, according to the requirements of Ministry of Science and Technology project "Guizhou Agricultural Biological Resources Investigation" and systematic investigation training requirements[9]. The steps are as follows: to hold group meeting, study the general investigation table, hold the team meeting, carry out the division of labor for the team members; to discuss with the leaders of the county bureau of agriculture and relevant experts to understand the characteristic biological resources and national characteristics of the county; to determine the villages and towns to be investigated, and formulate the investigation route; to discuss with the township government and agricultural technicians to determine the village committees for systematic investigation; to discuss with the cadres of the village committee to understand the basic situation of the village, agricultural biological resources and the customs and habits of the main investigation nationalities, and fill in the village-level questionnaire; to carry out door-to-door investigation, collect the local national knowledge and resource samples related to agricultural biological resources, carry out the GPS localization, number and photograph the collected samples, fill in the record form and the household questionnaire; to arrange samples and compile materials, arrange and summarize the national knowledge and collected resource samples in time.
2.2SamplingprinciplesAccording to the four majors of crops, vegetables, fruit trees and medicinal plants related to national specialty and superiority, and according to the Technical Specification for the Collection of Crop Germplasm Resources and the Technical Specification for the Preservation of Medicinal Plant Germplasm Resources, we collected the seeds, plants, tubers, branches and so on of each resource. The specimens of typical germplasm were made according to the relevant technical specifications.
2.3StatisticalanalysisofdataThrough EXCEL analysis software, the collected samples were statistically analyzed according to the types, collection sites and ethnic biology, and compared with the existing resources of the national database (nursery). According to the questionnaire, this paper analyzes the current conservation situation of all kinds of biological resources in the local area and the reasons for the fluctuation and change.
3 Results and analysis
3.1Typesanddistributionofbiologicalresourcescollected
A total of 230 samples of local varieties and wild species were collected from various resources, including 47 food crops, 75 vegetables and annual crops, 37 fruit trees and perennial crops and 71 medicinal plants (Table 1).
The distribution of collected resources in the villages and towns was: 93 in Maotian Town, 99 in Nigao Township, 19 in Hongsi Township, 11 in Daping Town and 8 in Duru Town. The distribution of all kinds of resources in the investigated villages and towns is shown in Table 1. It can be seen from the table that the number of samples collected from Nigao Township in this investigation was the largest, followed by Maotian Town, Hongsi Township, Daping Town, and Duru Town. In addition to the time arrangement factors in the investigation, the main reasons are that Maotian Town and Nigao Township are far from the county, with a large area and inconvenient transportation, it is little affected by commercial varieties, and the resources of the old varieties are well preserved. However, due to the proximity of Daping Town and Duru Town to the county seat and the prefecture capital, the traffic is good, the economy is more developed, and the commercial varieties have a great impact on the old varieties. In the investigation, for example, most farmers who grow old varieties in Duru Town say they will no longer grow these old local varieties next year or in the near future. However, it is worth mentioning that Daping Town is a typical national cultural tourism town, so the understanding of national culture and agricultural biological resources is more complete and scientific. Therefore, in Daping Town, we have perfected and supplemented the cognitive story of the nation.
This investigation involves three ethnic groups: Gelao, Miao and Tujia. Among them, the Gelao nationality is the most important ethnic group in this investigation. The distribution of all types of resources among the investigated ethnic groups is shown in Table 2. From the table, we can see that there are the most samples from Gelao and Miao residential areas, 107 and 115 respectively, accounting for 46.52% and 50.00% of the total number of samples, respectively, only 8 from Tujia, accounting for 3.48% of the total number of samples. A total of 46 food crops were collected, of which 25, 19 and 2 were distributed in Gelao, Miao and Tujia nationalities, respectively. A total of 75 vegetables and annual classics were collected, of which 40, 31 and 4 were distributed in Gelao, Miao and Tujia nationalities, respectively. A total of 37 fruit trees and perennial cash crops were collected, of which 19, 18 and 0 were distributed in Gelao, Miao and Tujia nationalities, respectively. A total of 71 medicinal crops were collected, of which 22, 47 and 2 were distributed in Gelao, Miao and Tujia nationalities, respectively.
Table1Thetownships(towns)investigatedandgermplasmresourcesdistribution

Township (towns)Village committeeVillage groupEthnicgroup FoodcropsVegetables andannual cash cropsFruits and perennialcash cropsMedicalplantsTotalMaotian Town(93)Hongxin VillageDabanglin GroupMiao13127Dazhuyuan GroupMiao112Qianfeng GroupTujia22Weijia GroupMiao112Xiaojia GroupMiao2525Tongxin VillageGuangming Group√Gelao55212Shangba GroupMiao635115Changshang Group√Miao123Xinglong VillageShipen GroupGelao761225Nigao Township(99)Liyuan VillageLiyuan Grassland√Gelao213Maoniu GroupGelao81072247Qingba Group√Gelao1539Nigao VillageNigao GroupGelao11Xiaba GroupGelao437Zhuyuan VillageBanqiaotu Group√Gelao36312Xuetangbao GroupMiao111820Hongsi Township(19)Shangba VillageMacaoxi GroupMiao99Qingshan GroupMiao22Bainichi GroupGelao134Yueliang VillageHuohuogang GroupGelao11Qianzhaichi GroupGelao112Taiba VillageShijieshui GroupGelao11Daping Town(11)Longtan VillageZhongzhai GroupGelao268Huangyang VillageDongzu GroupGelao22Yinshan GroupMiao11Duru Town(8)Jieguan VillageShangoutang GroupGelao2428Total47753771230
Note : “√” means the major village groups investigated, and the corresponding village committees are also the major villages to be investigated.
Table2Thedistributionofgermplasmresourcesintheethnicgroupsinvestigated

Ethnic group Food cropsVegetables and annual cash cropsFruits and perennial cash cropsMedical plantsTotalGelao19402522107Miao18311947115Tujia04228Total47753771230
3.2Comparativeanalysisofcollectedresourcesandexistingresourcesinthenationalgenebank
3.2.1Food crops. As shown in Table 3, 8 rice resources were collected from the investigation of food resources in Wuchuan County, and one rice resource was found in the China Crop Germplasm Resources Information Network, which is a local variety resource, Chuan’gu. 12 maize resources and 9 coarse cereal crops were collected. There were 18 samples collected from bean resources, including 4 species (soybean, cowpea, pea and rice bean), of which 4 were soybean, 2 were cowpeas, 1 was pea and 11 were rice bean. There is no duplication of resources by comparing them with food crops preserved in the national genebank. The results showed that all the collected samples were all new types.
Then he felt some one touch him on the shoulder; and he turned, and saw a young man like a king s son, having with him a tall and beautiful lady, whose blue eyes shone like stars
3.2.2Vegetable crops. As shown in Table 3, through a query on the national genebank, there were a total of 16 vegetable resources from Wuchuan County, Guizhou Province, namely, white cowpea, Wuchuan green vegetables, Wuchuan cucumber, Wuchuan pumpkin, inverted bean, August cowpea, Wuchuan cowpea, Zhuyuan old cabbage, Xinglong Ercai, Zhuyuan Eruca, creeping cabbage, Gaoshanpadi cabbage, Banjiehong radish, Xinglong radish, Tongxin white radish, Lanhua fruit. These resources do not have the same name as the vegetable resources in this investigation. However, we collected 3 cucumber resources, Tongxin cucumber, Zhuyuan cucumber, Nigaopadi cucumber; 2 green vegetables, Liyuan vegetable, Jieguanping vegetable; 2 pumpkins, Liyuan pumpkin, Zhuyuan pumpkin. Whether these resources are synonymous with the corresponding species in the genebank still needs to be further identified.
Table3Comparisonofresourcescollectedwiththosekeptinnationalgenebank
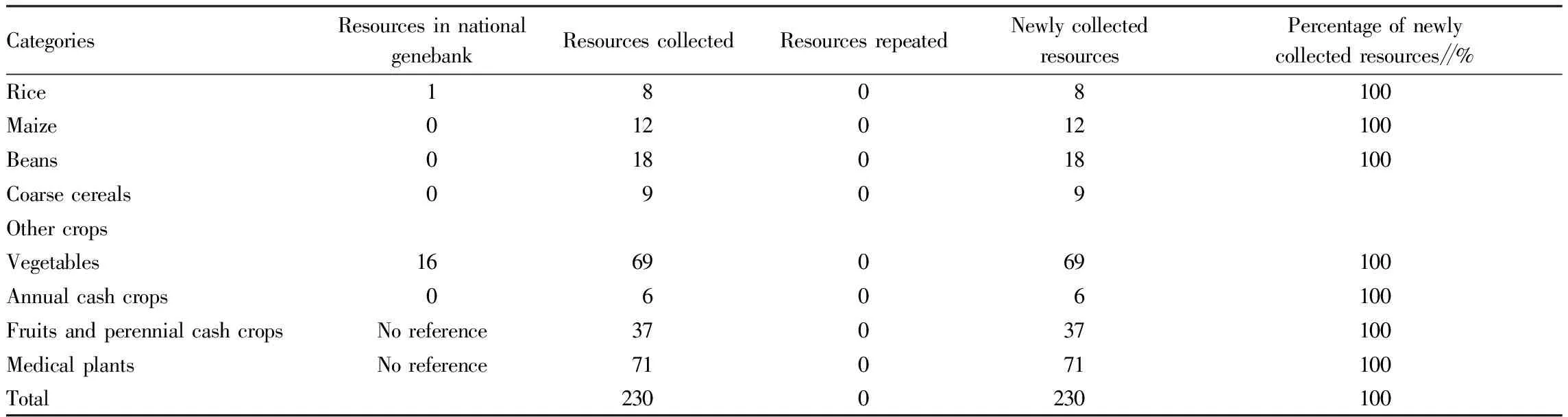
CategoriesResources in nationalgenebankResources collectedResources repeatedNewly collectedresourcesPercentage of newlycollected resources∥%Rice1808100Maize012012100Beans018018100Coarse cereals0909Other cropsVegetables1669069100Annual cash crops0606100Fruits and perennial cash cropsNo reference37037100Medical plantsNo reference71071100Total2300230100
3.3Botanicalclassificationofcollectedresources
3.3.1Food crops. The investigation of food resources in Wuchuan County involved 11 village committees and 19 village groups in 5 townships, and 2 ethnic minorities of Gelao and Miao were investigated. 8 rice resources and 2 sorghum resources were collected. Most of the 5 townships investigated are poor areas, with small farming area, barren land, and single planting structure. Because of the high altitude and cold climate in most areas, most of the crops prefer the cold and cool climate, and the diversity of species is not rich. In this investigation, the collected food germplasm resources closely related to the life, production and culture of the local people belong to 3 families (Leguminosae, Gramineae and Polygonaceae), 8 genera (Vigna,Phaseolus,Glycine,Oryza,Zea,Sorghum,Setaria,Fagopyrum), 47 in total (Table 4).
Table4Thecategoriesoffoodcropresourcescollected
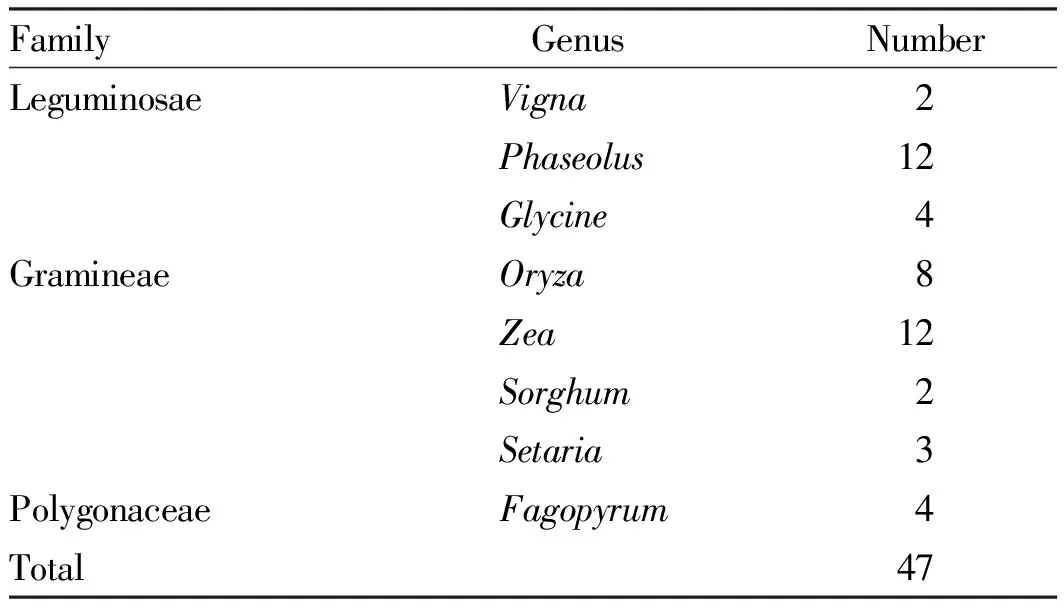
FamilyGenus NumberLeguminosaeVigna2Phaseolus12Glycine4GramineaeOryza8Zea12Sorghum2Setaria3PolygonaceaeFagopyrum4Total47
3.3.2Vegetables and annual cash crops. The investigation of vegetables and annual cash crop resources in Wuchuan County involved 12 village committees and 22 village groups in 5 townships, and the three ethnic minorities of Gelao Miao and Tujia were investigated. A total of 76 samples were collected, including 64 vegetables, 6 peanuts and 3 sunflowers, 1 sesame, 1 rape and 1 tobacco. They belong to 12 families (Chenopodiaceae, Liliaceae, Leguminosae, Pedaliaceae, Cucurbitaceae, Solanaceae, Umbelliferae, Araceae, Cruciferae, Saururaceae, Labiatae, Asteraceae), and 26 genera (Spinacia,Allium,Hemerocallis,Arachis,Phaseolus,Vigna,Pisum,Vicia,Sesamum,Benincasa,Momordica,Cucurbita,Luffa,Benincasa,Cucurbita,Luffa,Cucumis,Capsicum,Solanum,Nicotiana,Foeniculum,Coriandrum,Dioscorea,Amorphophallus,Raphanus,Brassica,Houttuynia,Stachys,Elsholtzia,Helianthus,Gnaphalium) (Table 5).
Table5Thecategoriesofvegetablesandannualcashcropsresourcescollected

FamilyGenus NumberChenopodiaceaeSpinacia2LiliaceaeAllium14Hemerocallis1LeguminosaeArachis4Phaseolus11Vigna1Pisum3Vicia2Pedaliaceae Sesamum1CucurbitaceaeBenincasa1Cucurbita3Luffa1Cucumis3SolanaceaeCapsicum5Solanum1Nicotiana1UmbelliferaeFoeniculum1Coriandrum3Araceae Amorphophallus1Cruciferae Raphanus3Brassica7SaururaceaeHouttuynia1LabiataeStachys1Elsholtzia1Asteraceae Helianthus2Gnaphalium1
3.3.3Fruit trees and perennial cash crops. 3 townships (Maotian Town, Nigao Township, Duru Town), 6 village committees and 12 groups were investigated. A total of 37 fruit trees and perennial cash crops were collected. Among them, 9 (7 Miao, 2 Gelao) resources were collected in Maotian Town, with 9 special resources; 26 (11 Miao, 15 Gelao) resources were collected in Nigao Township, with 12 special resources and 14 uncollected resources; 2 tea resources were collected in Duru Town. The results of the resource investigation are shown in Table 1. These resources belong to 9 families (Fagaceae, Rhamnaceae, Rosaceae, Theaceae, Myricaceae, Vitaceae, Ebenaceae, Rutaceae, Lardizabalaceae) and 13 genera (Castanea,Ziziphus,Armeniaca,Amygdalus,Prunus,Fragaria,Eriobotrya,Camellia,Myrica,Vitis,Diospyros,Citrus,Akebia) (Table 6).
Table6Thecategoriesoffruitsandperennialcashcropsresourcescollected

FamilyGenus NumberFagaceaeCastanea1RhamnaceaeZiziphus1RosaceaeArmeniaca1Amygdalus8Prunus13Fragaria1Eriobotrya1TheaceaeCamellia1MyricaceaeMyrica1VitaceaeVitis2EbenaceaeDiospyros2RutaceaeCitrus4LardizabalaceaeAkebia1
3.3.4Medicinal plants. The investigation of medicinal plants involved three townships, namely, Maotian Town, Nigao Township, Hongsi Township, including 71 medicinal plants, of which 11 were special resources. It has been learned that most of the herbal resources are basically intact, but for some herbal resources, due to economic speculation, they are picked seriously, for example, local wildGastrodiaelataBlumeis frequently collected in the mountain because of the high price, which has led to a sharp decline in the number of these wild resources. The local Gelao nationality has a long history of using herbs to treat various diseases in the region, which has played a more positive role in the protection and utilization of herbal resources. We interviewed Zhu Mingsheng, a 78-year-old herbalist in the Maoniu Group of Liyuan Village, Nigao Township, to learn about his practice and the herbs he used, and to collect specimens of important medicinal plants, so as to understand the important role of these important herbs in the treatment of local diseases. These herbalists play an important role in the protection of local herbal resources. In addition, since most of the medicinal plants collected have popular names or national terms, it is difficult to directly inquire about their scientific names, and after preliminary identification, they involve at least 16 families, mainly including Araliaceae, Iridaceae, Gentianaceae, Ranunculaceae, Dipsacaceae, Rubiaceae, Ericaceae, Cucurbitaceae, Vitaceae, Umbelliferae, Polypodiaceae, Saxifragaceae, Liliaceae, Araceae, Compositae, and Rosaceae.
3.5SpecialresourcesThe diversity of ecological environment in Guizhou Province and its surrounding areas, as well as the diversity of ethnic minorities, give birth to a large number of excellent biological resources. In the course of the investigation, according to the local people’s understanding of the resource (such as planting history, area, cultivation management,etc.), the performance of excellent traits (yield, disease and insect resistance, barrenness tolerance, maturity, quality,etc.) and the information related to national biology, some special resources can be explored. A total of 230 samples were collected in this investigation, and the special, unique and excellent nature of the samples was analyzed through questionnaires and consultations. There were 73 superior resources (Table 7), of which 21 were special resources, including 9 food resources, 1 vegetable resource and 11 medicinal plants; 28 excellent resources, including 2 food crops, 9 vegetables and annual cash crops, 17 fruit trees and perennial cash crops; 6 unique resources, including 3 food crops, 2 vegetables and annual cash crops, 1 fruit tree and perennial cash crops; 11 excellent and special resources, including 3 food crops, 3 vegetables and annual cash crops, 5 fruit trees and perennial cash crops; 6 excellent and unique resources, including 5 vegetables and annual cash crops, 1 fruit tree and perennial cash crop; 1 unique and special resource, namely vegetable and annual cash crop. These special resources include local food crop varieties planted locally for hundreds of years, such as Bainuo (2013521014), Heidou (2013521100), and Baidou (2013521108); vegetable resources with national edible characteristics such as Hongpisuan (2013521004), Huiluobo (2013521146); some fruit trees and perennial cash crops with high quality and strong adaptability, such as Yinxing (2013521136), and Qingli (2013521153); the local special medicinal plants such as Haijiaoqi (2013521030), and Shidagonglao (2013521175). These resources will provide an important material basis for the in-depth evaluation of resources and ethnobotany research.
Table7Classificationanddistributionofspecialgeneticresources

Germplasm categoriesSpecial ExcellentUnique Special &ExcellentExcellent &unique Unique &special Special, excellent& unique UncollectedTotalFood crops923300173046Vegetables and annual cash crops192351215675Fruits and perennial cash crops0171510241337Medical plants1100000116071Total21286116173159229
3.6AnalysisonthecausesofthegrowthanddeclineofagriculturalbiologicalresourcesinWuchuanCountyThe agricultural biological resources (including wild edible plant resources and agricultural germplasm resources) are rich and well preserved in Wuchuan Gelao and Miao Autonomous County because of the warm climate and abundant rainfall. By consulting the relevant information and comparing the number and acreage of the main varieties of food crops, vegetables and fruit trees in 1956, 1981 and 2011, it is found that the number of old varieties of food crops, vegetables and fruit trees in 1981 was higher than that in 1956, and the number of new varieties of food crops increased significantly. Vegetables and fruit trees were still dominated by old varieties, and no new varieties were planted. However, after 2011, the number of varieties of food and vegetable crops gradually decreased, while the number of varieties of fruit trees increased significantly. The cultivation area in 2011 was significantly higher than that in 1981 and 1956, with a significant increase in the extension area of new varieties of food, vegetables and trees.

Fig.1Somespecialfoodcropgermplasmresources
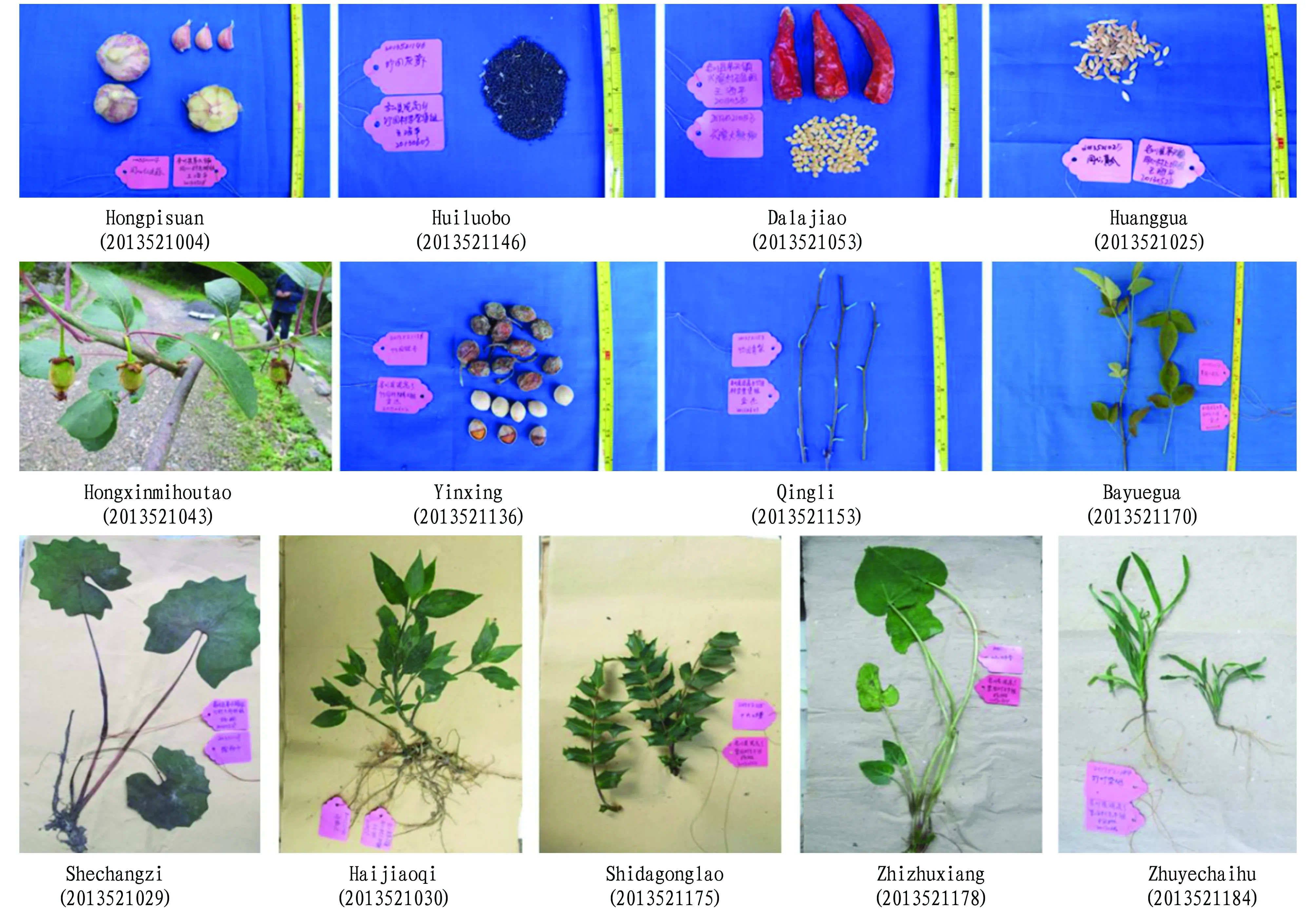

Fig.2Somespecialvegetable,fruitandmedicinalplantgermplasmresources
In general, there are still many old variety resources to be preserved in Wuchuan County, and the reasons are as follows:
First, due to historical reasons, so far, some villages and towns have not yet had access to the highway, for most of the villages and towns that have access to the highway, the road surface is rotten, the car is difficult to drive on it, and few people outside the mountain set foot on it. Second, it is related to the fact that the Miao and Gelao people in Wuchuan like to eat spicy, sour, fragrant, waxy (waxy rice and waxy corn) food, wine and so on. Third, with the development of rural economy, national assimilation, the continuous improvement of living standards, the promotion of new hybrid varieties, the adjustment of industrial structure and the improvement of economic benefits, combined with the low yield and non-commercialization of the old variety resources, it led to the gradual reduction of the types and stocks of the old variety resources, and some even died out. Rice varieties have been basically replaced by hybrid rice, only a small number of glutinous rice and minor food crop species are still retained, especially wheat, which has not been planted for 4 to 5 years.
This resource investigation involves Maotian Town, Nigao Township, Hongsi Township, with mountain traffic inconvenience, closed state and relatively few exchanges with the outside world, as well as the slow promotion of new varieties. At the same time, the local ethnic minorities have their own customs and habits on these local varieties, so that some old varieties of food resources can be preserved, mainly for self-growing and self-feeding. In the investigation, it was found that the main reasons for the cultivation and consumption of local varieties were that the local varieties had better taste, better quality and more barrenness tolerance than the new varieties. In addition, the young labor forces go out to work so that the rural labor force is reduced, most of them are left-behind children and the elderly at home. Traditional old people take slash-and-burn cultivation, spring sowing and autumn harvest, apply no pesticides and no chemical fertilizers, and harvest depending on heaven. The income from extensive cultivation of new improved varieties is even less.
Some food crops have special uses in ethnic minority areas, which is also the reason why they have been handed down. For example, the people of Maotian Town like to use local corn-Shibalu for brewing local rice wine, and they feel that the taste is much mellower and the distillation yield is also higher than hybrid corn. It is used for some special purposes, such as making rice dumplings from glutinous rice for ancestor worship. So some local varieties have been planted for hundreds of years.
Vegetable planting area in Wuchuan County is small, and the scattered planting is mainly for family consumption[10]. According to the varieties planted, it is mainly the same as other remote areas of Guizhou, mainly green vegetables (leaf mustard), chili peppers coupled with a variety of seasoning vegetables. There are many kinds of vegetables grown in each family, mainly garlic, pepper, ginger, pumpkin and green vegetables (leaf mustard), but they also have their own characteristics.
Especially in Liyuan Village, most people grow old varieties of legume crops, the species are rich. In the villages and towns near the county seat and the prefecture capital, the local varieties are replaced by commercial varieties seriously, but in the mountainous areas because of the inconvenience of transportation, the local ethnic groups have their own customs and habits for the use of local varieties, and most of the resources are still preserved in a small amount. Wild vegetables are an important source of vegetables for all ethnic groups. Although most varieties are still preserved, the area tends to decrease compared with 10 years ago, and there is an imbalance in the development and utilization of different kinds of wild vegetable resources. For example, locals have a greater demand for Guangcai than other wild vegetables, and this situation is bound to lead to the overexploitation of a resource and accelerate the imbalance of diversity.
The number of fruit trees and perennial asexual crop varieties did not decrease, but the area of the old varieties decreased.
The main reason is the local promotion of tea, and five new tea varieties were introduced in 2011. One of the reasons why these old variety resources can be retained is good characters, and the resources with good disease resistance, good taste and strong adaptability are retained. For example, Hongxinmihoutao (2013521043) collected by Dazhuyuan Group, Hongxin Village, Maotian Town, Wuchuan County, is juicy, sweet, fragrant, nutritious, disease-free, and productive. The local chestnut (2013521024) collected by Shangba Group, Tongxin Village, Maotian Town, Wuchuan County, is sweet, fragrant, crisp in taste, juicy, high in nutritional value, delicious than foreign varieties, has no diseases and has strong resistance. The Liyuan Bayuegua (2013521170) collected by Maoniu Group, Liyuan Village, Nigao Township, Wuchuan County, is large, sweet, juicy, tender and smooth.
Table8Growthanddeclineofagriculturalbiologicalresources
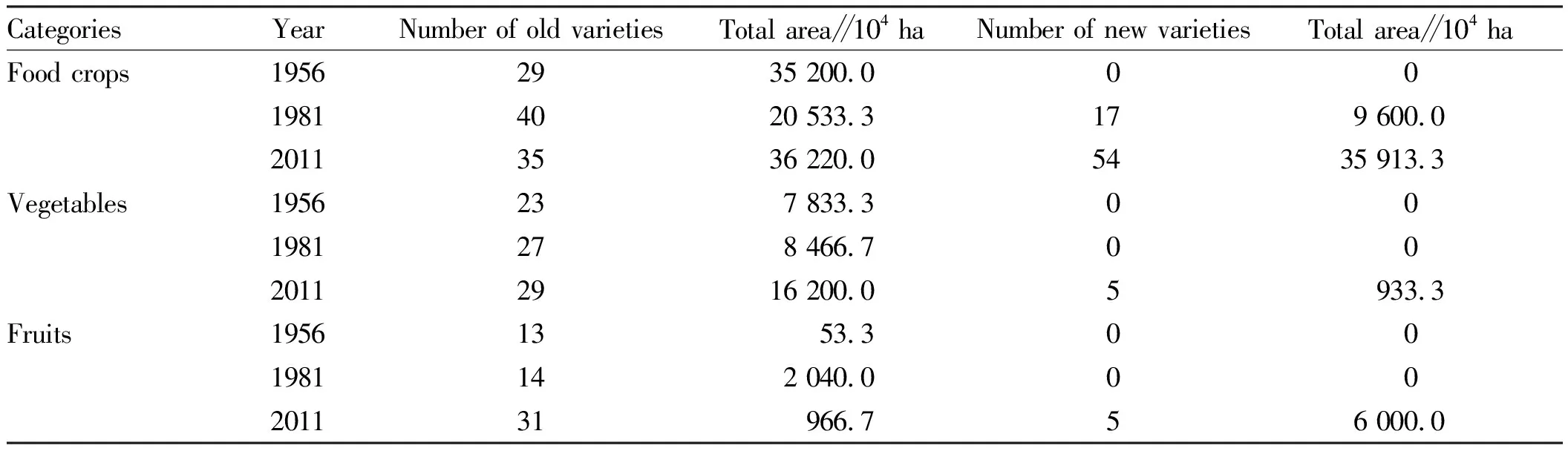
CategoriesYearNumber of old varietiesTotal area∥104 haNumber of new varietiesTotal area∥104 haFood crops19562935 200.00019814020 533.3179 600.020113536 220.05435 913.3Vegetables1956237 833.3001981278 466.70020112916 200.05933.3Fruits19561353.3001981142 040.000201131966.756 000.0
The investigation of medicinal plants involved a total of three townships, namely Maotian Town, Nigao Township, Hongsi Township. It is learned that most of the herbal resources are basically intact, but some herbal resources, due to economic speculation, are picked seriously. Take the local wild Gastrodia elata Blume for example, because of the high price, people go up the mountain to dig frequently, leading to a sharp decline in the number of these wild resources. The local Gelao people have a long history of using herbs to treat various diseases in the region, which has played a more positive role in the protection and utilization of herbal resources. Zhu Mingsheng, a 78-year-old herbalist, was interviewed in the Maoniu Group of Liyuan Village, Nigao Township, to learn about his practice and the herbs he used, and to collect specimens of important medicinal plants. These important herbs play an important role in treating local diseases. These herbalists play an important role in the protection of local herbal resources. For example, the root of special Shechangzi (2013521029) can be used as medicine for the treatment of venomous snake bites, and it is one of Zhu Mingsheng’s ancestral medicinal materials for treating snake bites.
4 Discussions
4.1ThecollectedresourcesenrichthediversityofagriculturalbiologicalresourcespreservedinChinaA total of 230 resources were collected, and compared with the national genebank, the newly collected resources accounted for 100% of the total collected resources. These may be the main biological resources in Wuchuan County, which were not fully available in the past biological resource collection process. Or, the resources obtained in the past have been replaced by their varieties in the course of this investigation. At the same time, the villages and towns investigated are still limited and we do not have access to the resources already received in the national genebank. It is worth noting that due to the lack of national genebank resources available for reference, the collected fruit tree resources and medicinal plants are considered newly collected resources. In addition, when comparing with the resources in the resource genebank, the comparison search can only be carried out according to the variety name. However, there are great differences in the name of resources called by the local people in the investigation, and some of the resources actually collected may still be duplicate resources, which need to be further identified and verified, especially at the molecular level. These germplasm resources are obtained on the basis of the investigation of ethnic minorities and related cultures in Wuchuan County, Guizhou Province. They are precious heritage handed down from generation to generation[11], and are also the material basis for the life and production of ethnic minorities in Guizhou. The collection of these resources will enrich the genetic diversity of biological resources preserved in China and provide important basic materials for biological development and utilization[12-13].
4.2SuggestionsontheutilizationandprotectionofagriculturalbiologicalresourcesThe protection and development and utilization of local varieties should be combined. On the one hand, it is necessary to make efforts to better know the family situation and establish archives; on the other hand, it is necessary to organize the development and utilization of excellent varieties. For example, glutinous rice can be packed as gifts to increase its added value. There is a need to strengthen the development and utilization of wild resources, such as wildHouttuyniacordataand bamboo shoots, they can be properly developed and utilized under the protection of resources, so as to achieve protection in development, utilization in protection, and promote the healthy development of the local characteristic vegetable industry. In places where conditions permit, we can make use of the local favorable ecological environment and human environment, combined with characteristic tourism to open up wild characteristic vegetable picking gardens, open ethnic flavor restaurants, and introduce wild vegetable characteristic delicacies. For example, the Liyuan area can strengthen tourism culture with the local national characteristics based on the local grassland environment. For wild vegetables, it is necessary to carry out fresh-keeping and deep processing, to overcome the seasonal and regional limitations of the production of these vegetables, to build a national brand. We should also strengthen the exploration of wild fruit tree resources. In the interview and investigation, it is found that Miao, Buyi and Gelao people have the habit of collecting and eating wild fruit, and some wild fruit tree resources with characteristics should be selectively cultivated and domesticated[14], to develop their potential value. It is necessary to strengthen the protection and research of medicinal plants, build medicinal plant resource pool, build national brand, and strengthen the consciousness of protection.
4.3ThesamplescollectedrequirefurtheridentificationandevaluationGuizhou is an important treasure trove of natural drugs[12-13, 15]and one of the four major drug producing areas in China[16]. Gelao is a nation with a long history and culture, and traditional Gelao medicine mainly uses local medicinal materials for prescription formulation and compatibility. Like other ethnic medicine, it is an important part of minority medicine in our country, and it is also the precious wealth of traditional medicine in our country[17]. Due to time constraints, several key towns were selected to carry out the investigation. Zhu Mingsheng, a 78-year-old herbalist of Maoniu Group in Liyuan Village, Nigao Township, has also built his own herbal garden. The distribution of resources in other townships needs to be investigated and studied in the future. The collected samples need to be propagated into the genebank for in-depth identification and evaluation in order to determine their scientific utilization value. Because most of the medicinal plants collected have popular names or national terms, it is difficult to directly inquire about their scientific names, and after preliminary identification, they involve at least 16 families, but their classification and medicinal value need to be further identified and evaluated.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Economic Value Evaluation of Fine Individual Plants ofRibesrubrum Linn.Based on AHP
- Mechanized Grafting Technology for Apple Seedlings
- High Efficiency Hypocrellin Production by a Novel Mutant Isolated fromShiraiabambusicola
- The Mode of Promoting Industrial Targeted Poverty Alleviation through Land Circulation in Western Mountainous Region of China
——A Case Study of Luquan Yi and Miao Autonomous County in Yunnan Province - Reconstruction Mode of Rural Dilapidated Houses in Alpine and Gorge Area of Southwest China
——A Case Study of Scientific Identification and Precision Reconstruction of Rural Dilapidated Houses in Luquan County, Yunnan Province - Research on Satisfaction ofexsitu Relocated Households
