Efficacy of blood-lettingpuncture and cupping in the treatment ofperiarthritis ofshoulder:a systematic review
2018-12-26LiHuiZhangLiXinWangQianCuiGuoWeiZhang
Li-Hui Zhang,Li-Xin Wang,Qian Cui,Guo-Wei Zhang
1College of Chinese Medicine,Hebei University,Baoding,Hebei province,China.
Introduction
Periarthritis of shoulder is a chronic aseptic inflammation which caused by injury and degeneration of shoulder capsule and periarthritic soft tissue(including ligaments,muscles,tendons,synovial sacs,etc.).The main clinical features were shoulder and arm pain and limited movement[1].The etiology and pathogenesis of this disease is not clear, and it is predominant in middle-aged and elderly people over 40 years old.Females are more than males,left side is more common than right side,and bilateral concurrent disease is rare.At the same time, the disease is a self-limiting disease, the average course of disease was about 2-10 years[2].This disease belongs to the scope of Bi syndrome in TCM,also known as 50 shoulders,shoulder leakage,shoulder coagulation, frozen shoulder,etc. If the disease lasts for a long time,the Qi and blood stasis and the meridians are blocked. Blood-letting puncture and cupping in TCM can promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis, warming meridians,dispelling cold and dredging collaterals,which achieved good clinical results. We comprehensively retrieved the literature reports on the treatment of periarthritis of shoulder by blood-letting puncture and cupping.Based on the Cochrane system evaluation method of evidence-based medicine, the efficacy of blood-letting puncture and cupping therapy for periarthritis of shoulder was Meta-analyzed to further clarify the safety and effectiveness of blood-letting puncture and cupping therapy for periarthritis of shoulder.The evidence level and recommendation level of the included literature were graded by GRADA system,so as to be able to be used in future clinical practice. Treatment of periarthritis of shoulder provides a more reliable basis.
Methods
Types of studies
This study apply the randomized controlled trials(RCTs).
Inclusion criteria
Research designWe electronically searched databases and collect RCTs and quasi-randomized controlled trials about blood-letting puncture and cupping for periarthritis of shoulder,inclusion of blind method or not.
Research objectReferring to the diagnostic criteria of periarthritis of shoulder in the Criteria for Diagnosis and Therapeutic Effect of Diseases and Syndromes of Traditional Chinese Medicine,patients with periarthritis of shoulder were definitely diagnosed as periarthritis of shoulder[3].All patients had good comparability in gender,age and severity of illness.
Intervention measuresExperimental group:blood-letting puncture and cupping;control group:general acupuncture, Electroacupuncture, western medicine treatment,other therapies.
Outcome indicatorsClear outcome indicators of therapeutic effect;outcome indicators are the clinical cure rate,total effective rate,VAS score and pain improvement score mentioned in the original literature.
Exclusion criteria
(1)Repeated publication;(2)inadequate provision of raw data;(3)sample size lessthan 10;(4)no control group was set;(5)research types were not consistent with non-RCT studies; (6) contents were not consistent;(7)retrospective studies;(8)animal or cell tissue tests;(9)empirical articles;(10)dose or drug administration.The method is not explained;(11)there is only a summary but no full text.
Search methods for identification of studies
Database selection:computer searches CBM,CNKI,VIP and Wanfang data,Pubmed,EMBase,Cochrane Library English databases.All the above databases were searched until October 2018.Chinese search terms:刺络拔罐and 肩周炎.English search terms:blood-letting punctureand cupping and periarthritis.
Literature evaluation
Document quality was evaluated according to Cochrane 5.1.0 Systematic Evaluation Manual.
Data analysis
RevMan 5.3 statistical software provided by Cochrane Collaborative Network was used for statistical analysis.Mean difference(MD)and 95%CI were used to analyze the measurement data of continuous variables.Ratio ratio(OR)and 95%CI were used to represent and analyze the counting data of classified variables. When there is statistical homogeneity among the studies,the results(P>0.05,I2<50%)are homogeneity among the studies,then the fixed model is used;if the results(P<0.05,I2>50%)indicate heterogeneity among the studies,the random effect model is used.
Publication bias
Using RevMan 5.3 statistical software to draw funnel diagram,we can see the distribution of the data studied. If the scatter points on both sides are symmetrical,there is no obvious publication bias,and if the two sides are asymmetrical,there may be publication bias.
Results
Results of the search
The initial search yielded 145 records after we searched key words as“blood-letting puncture and cupping” and “periarthritis of shoulder”. After scrutinising these records,we assessed 30 full-text records for eligibility(see Figure 1 for details of the screening process of the search results).The results showed that 30 RCTs were moderately biased,and the risk of bias was summarized in Figure 3.
Trial characteristics of eligible studies
Totally 30 RCTs accorded with research criteria including 2556 cases were analyzed,published from 1994 to 2018(see Table 1 for the general condition of eligible studies)
Quality evaluation of eligible studies
Evaluating the quality of original documents according to Jadad quality scoring table and Jadad evidence quality classification(Table 2).The bias risk are shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
Results of Meta-analysis
Total effective rate30 studies reported total effective rate a total of 2556 cases,with 1277 cases in the experimental group and 1214 cases were effective,1279 cases in the control group and 952 cases are effective.In 16 studies,95%CI horizontal lines did not intersect with equivalent vertical lines,which was statistically significant. There is no statistical heterogeneity between studies(P=0.42,I2=3%).Statistical analysis with fixed effect model and significant test shows Z=12.78,P<0.001.The results showed that the effective rate of blood-letting puncture and cupping therapy for periarthritis of shoulder was higher than that of other therapies.The difference has statistical significance.OR=6.21[OR=6.21,95%CI(4.69,8.21),P<0.001](Figure 4).
Blood-letting puncture and cupping VS Routine Electro acupuncture4 studies[5-7,16]reported the ratio of blood-letting puncture and cupping and routine electro acupuncture.Statistical analysis with fixed effect model(Significant test shows that Z=2.84,P=0.005)The results showed that effective ratio OR=2.46[OR=2.46,95%CI(1.32,4.59),P=0.005], 95%CI horizontal lines intersected with equivalent vertical lines,which was no statistically significant in the ratio of blood-letting puncture and cupping and routine electro acupuncture.(Figure 4)

Figure 1 Literature screening process
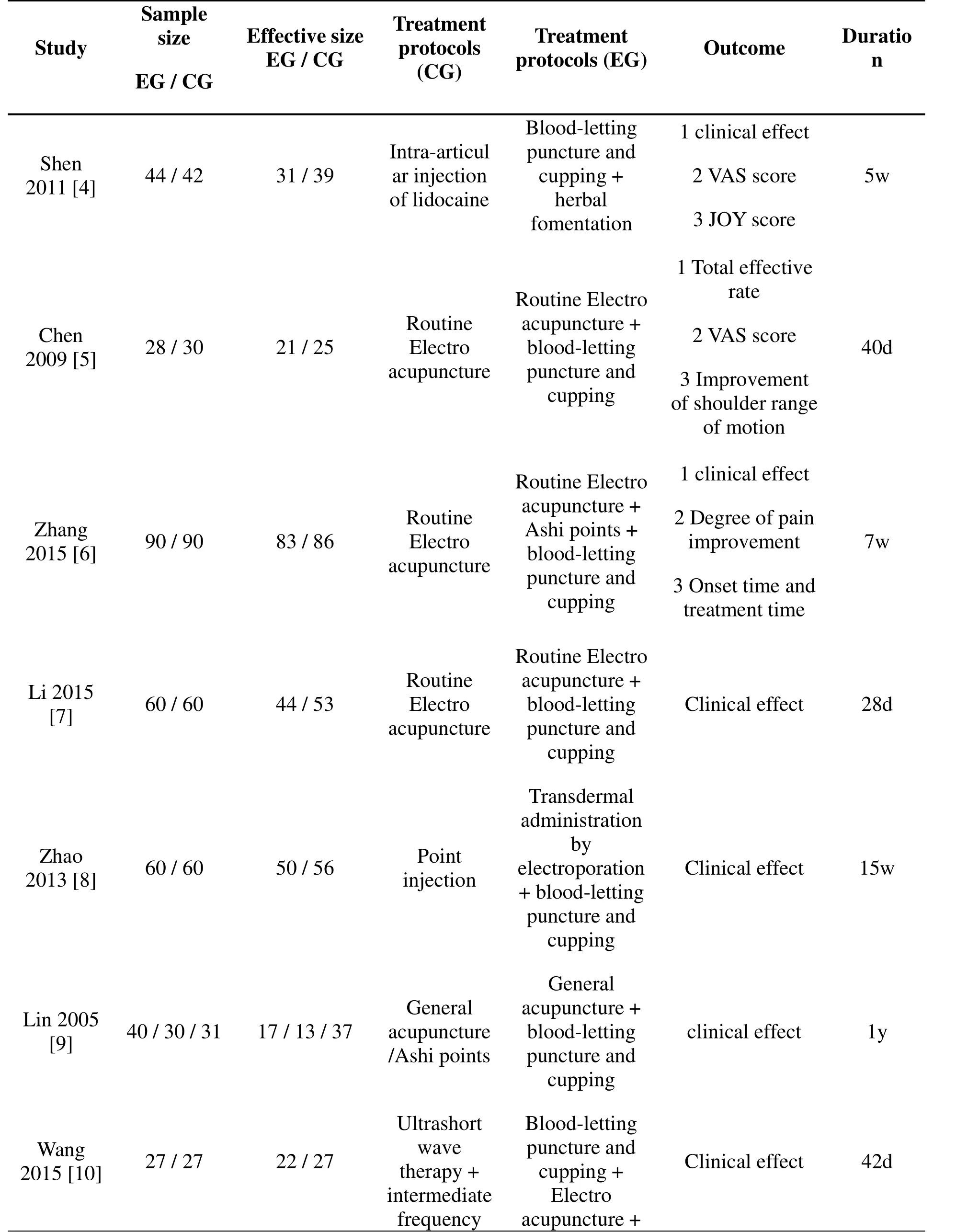
Table 1 General information of included literature

therapy Infrared polarized light H 20u 1a0n g[11] 40/56 32/56 a abgn cl Guodp po u e c ud nnu+necplcretp au ttuit lrnireng e Sbp hluoannc roeuc pdetp-ud-p hlrlei oeento tg+ai knn egd d Clinical effect 5d Fire needle +Lu[ 1 220]1 3 42/42 34/41 acGupe unnecr a tu l re bpluonocdt u-l ree t t ing andClinical effect 20d cupping 1 clinical effect Electro 20Z 1h2an[1g 3] 40/40 37/40a+cGuCpeuunpnepcriatnul g re+p abuclnuocpotudun-rlceet taut in rnedg 2tb hCeeto wrmeelepanat i roci snoosunhr s i opef 20d cuppingof treatment and recovery Mongolian Ba[o1 240] 16 52/52 37/48 acGupe unnecr a tu l reb p lu monocedtdu-ilrceeitn taienn gd Clinical effect 15d cupping 20Z 1h8an[1g 5] 59/59 45/54 ASCRusaesip mtlaseu eianxlseeeis nd p b MluMonc ooucendtp du g-p ilr oceien i lt nitga aienn ngd 1 c 3 l2V in A A ic S R a Os l c eMo ff re ect 30d Functional Routineexercise+Ye[ 1 260]1 3 34/34 28/33acuE p le ucn tcrto urep b u lo nc oucdtpu-plreient tgai nn g dClinical effect 20d Electro 20C12he[n17] 30/30 21/29a+cfe Guuxpeneuncrnect ci rios a tu e n l rael apbculcf uounu poncp udctp nu-tili crneoetg utn taria+ennl gd+Clinical effect 4w exercise Massage+20H 0u6a[n1g 8] 24/28 21/27b g l opoudn-cl e tu tt r ien Massage Clinical effect 20d and cupping Wang 45/45 37/44 acGupe unnecr a tu l reacuGpue nncetruarl e+Clinical effect 45d

2012[19] +moxibustion+moxibustionblood-letting puncture and cupping Warming 20H 1u4a[n2g 0] 40/40 29/38A e Wnc+euaepkrd mui nl ni iencntgtgiucr kA+ipncbueulntopiccout du nn-r cele teeu dta rtnleiindn+gg Cl J iOn iYc a s l c eofrfee ct 10d cupping Kinetic 20C 0h5e[n2g 1] 31/30/40 30/29/38ac i Gun/pj epeunocnetici rno attun l re nbpc u eluoepnodpcdlti iun-nlrgeget t in g an+dClinical effect 14d Li[ 2 220]1 5 31/30/40 30/29/38ac i Gun/pj epeunocnetici rno attun l re Knbpc u elu ioep nnodpc edltti i iun-nclrgeget t in g an+d Clinical effect 2y Strong stimulation+Short andShort and weak Zh[u2 230] 03 43/43 36/43acuwpue nack turesatcimupuu lan tcio tu nre+Clinical effect 20d stimulationblood-letting puncture and cupping Blood-letting 20M03en[2g 4] 28/58 17/56 V molatsasraegne+pu cnucp tpuirneg a+n dClinical effect 10d massage Dong's extra-ordinary Liu[2 2 50]1 4 25/25 18/23 acGupe unnecr a tu l reblop oodi n-l test t+ingClinical effect 0.5y puncture and cupping General acupuncture Pan[2 260] 11 18/18 14/17 acGupe unnecr a tu l re+bAl o sohdi -p le otitni tnsg+Clinical effect 20d puncture and cupping Zhang 60/60 37/59 General acuGpue nncetruarl e+Clinical effect 20d
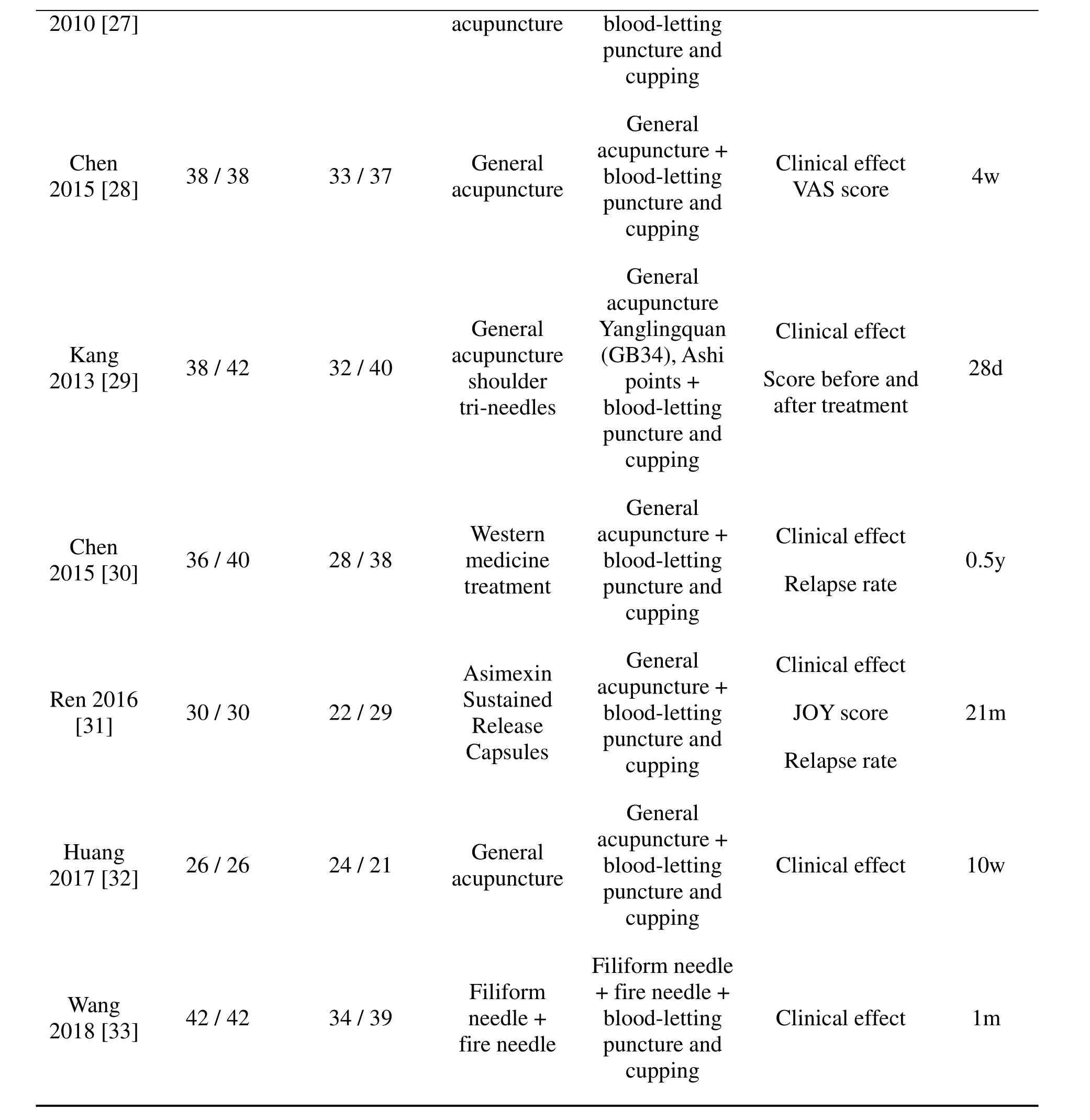
2010[27] acupuncture blood-letting puncture and cupping General 20C15he[n28] 38/38 33/37 acGupe unnecr a tu l re apbcluuonpocudtnul creet ut tari enn gd+Cl V in A ic Sa s l ceof fr ee c t 4w cupping General acupuncture GeneralYanglingquanClinical effect 20K13an[g29] 38/42 32/40ac suhpouunlcd teurr e(GB po3 i4n)t,s A+shi Score before and28d tri-needlesblood-lettingafter treatment puncture and cupping General 20C15he[n30] 36/40 28/38 tmWr eea edtsimtceiernnnet abpcluuonpocudtnul creet ut tari enn gd+C R li e nliacpasle e r faf e te ct 0.5y cupping Re[n3 210] 16 30/30 22/29 ASCRusaesip mtlaseu eianxlseeeis n d abpcluuonc Gpoucuedtp nnu-plcereietrn ut a tgarli enn gd+C R lJieOnl iaYcp a ssle c e or farfeet e ct 21m General 20H 1u7a[n3g 2] 26/26 24/21 acGupe unnecr a tu l re apbcluuonpocudtnul creet ut tari enn gd+Clinical effect 10w cupping Filiform needle 20W18an[3g 3] 42/42 34/39 finF ree il e indfeol ee rm d+l e+pbfluionroecd tnuelreeetd tailnnegd+Clinical effect 1m cupping

Table 3:Jadad quality assessment scale
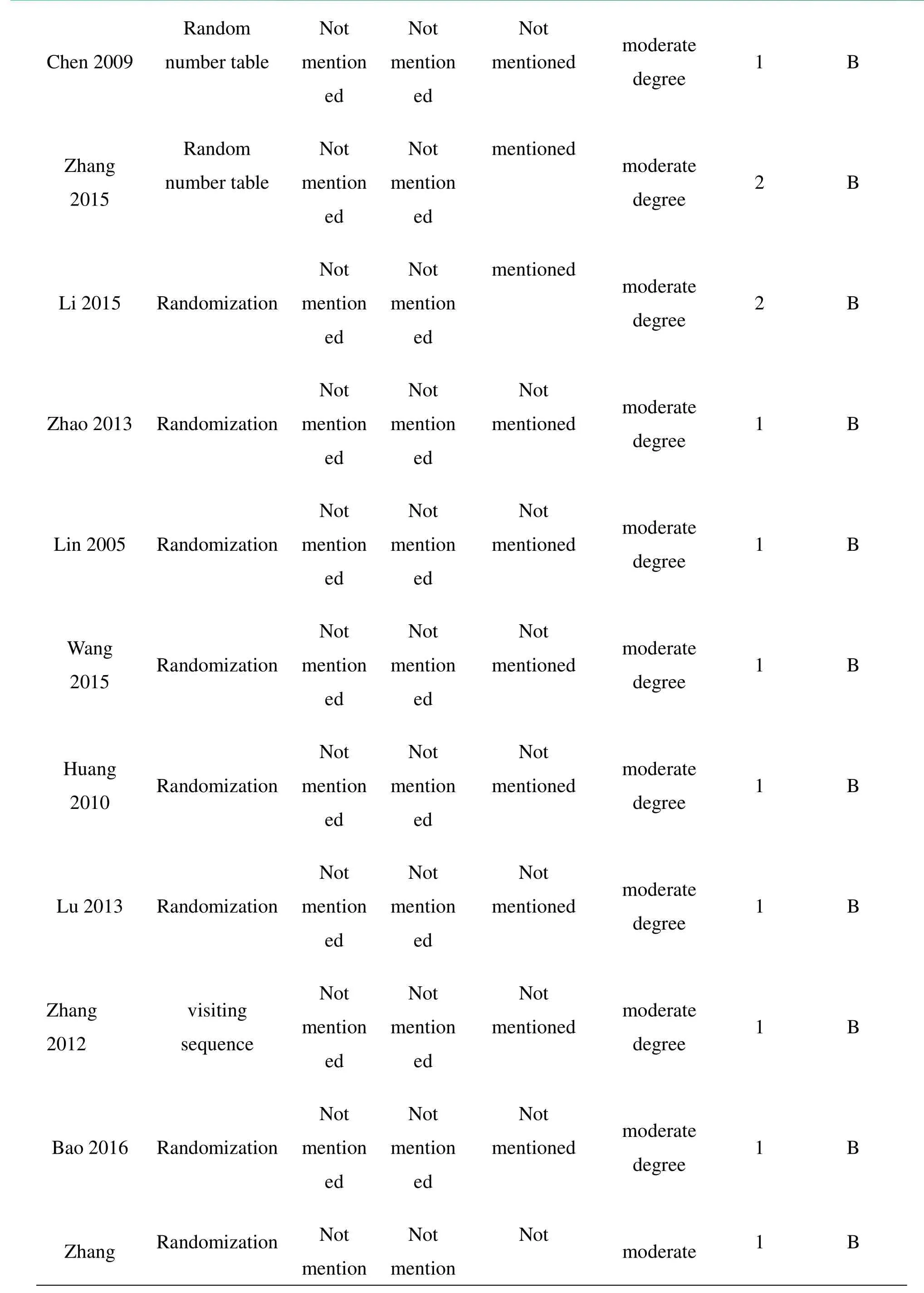
Chen 2009nu Rmabnedro t m ableme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B Z2h0a1n5g nu Rmabnedro t m ableme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t on mentioned m d oedgerreaet e2 B Li 2015 Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t on mentioned m d oedgerreaet e2 B Zhao 2013 Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B Lin 2005 Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B W 20 a1n5g Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B H2u0a1n0g Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B Lu 2013 Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B Z 20 h1a2n g s ve iqsui teinncg eme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B Bao 2016 Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B Zhang Randomization me Nnot i t onme Nnot i t on Not moderate 1 B
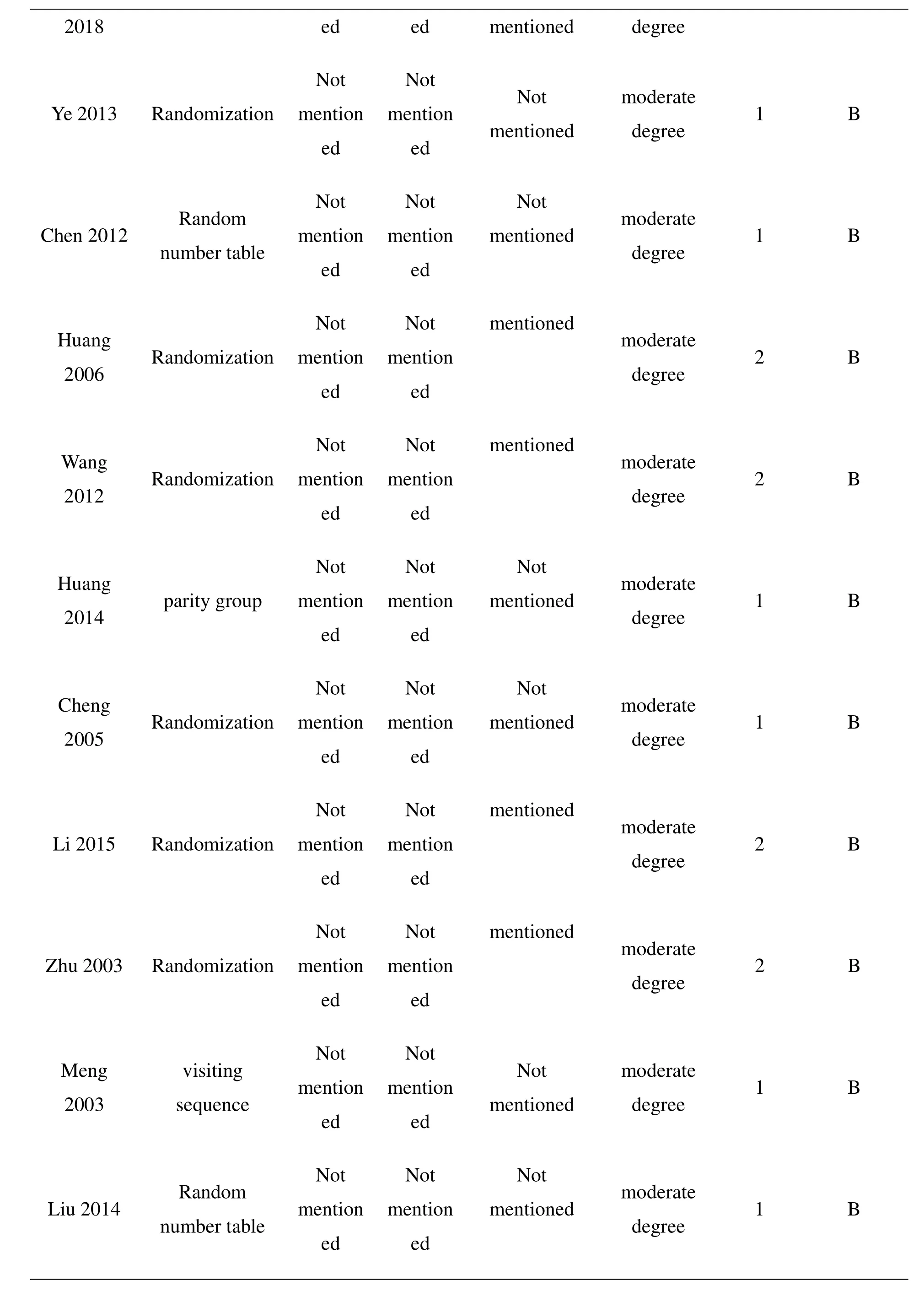
2018 ed ed mentioned degree Ye 2013 Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned mdoedgerreaet e1 B Chen 2012 nu Rmabnedro t m ableme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B H2u0a0n6g Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t on mentioned m d oedgerreaet e2 B W 20 a1n2g Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t on mentioned m d oedgerreaet e2 B H2u0a1n4g parity groupme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B C2h0e0n5g Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B Li 2015 Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t on mentioned m d oedgerreaet e2 B Zhu 2003 Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t on mentioned m d oedgerreaet e2 B M 20 e0n3g s ve iqsui teinncge me Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned mdoedgerreaet e1 B Liu 2014 nu Rmabnedro t m ableme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B

Pan 2011 s ve iqsui teinncge me Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B Z2h0a1n0g Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B Chen 2015 Rand si o mmpi lze ationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B K 20 a1n3g Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B Chen 2015 Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B Ren 2016 Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B H2u0a1n7g Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmen N ti oot ned m d oedgerreaet e1 B W 20 a1n8g Randomizationme Nenodt i t onme Nenodt i t onmentioned m d oedgerreaet e2 B

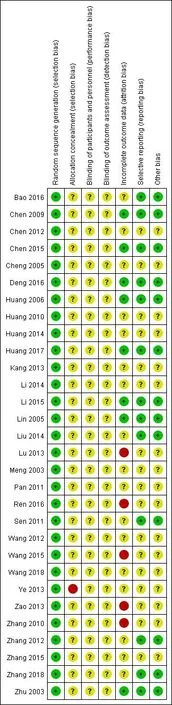
Figure 2 Risk of bias graph

Figure 3 Risk of bias summary
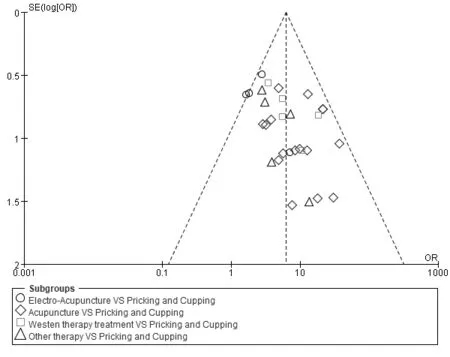
Figure 4 Total effective rate of blood-letting puncture and cupping in the treatment of periarthritis of shoulder
Figure 5 Meta-analysis funnel diagram of total effective rate in experimental group and control group Blood-letting puncture and cupping VS General acupuncture16 studies[9,11-14m 16,17,19,21-23,25-27,29-30,32,]reported the ratio of blood-letting puncture and cupping and general acupuncture.Statistical analysis with fixed effect model(Significant test shows that Z=10.34,P<0.001.The results showed that effective ratio OR=10.06[OR=10.06,95%CI(6.49,15.58),P<0.01],95%CI horizontal lines did not intersect with equivalent vertical lines,which was statistically significant in the ratio of blood-letting puncture and cupping and general acupuncture.(Figure 4)
Blood-letting puncture and cupping VS western medicine treatment5 studies[4,15,24,28,31]reported the ratio of blood-letting puncture and cupping and western medicine treatment.(I2=0%,P=0.52).Statistical analysis with fixed effect model.Significant test shows that Z=5.55,P<0.001.The results showed that effective ratio OR=6.09[OR=6.09, 95%CI (3.22, 11.53), P < 0.01], 95%CI horizontal lines did not intersect with equivalent vertical lines,which was statistically significant in the ratio of blood-letting puncture and western medicine treatment.(Figure 4)
Blood-letting puncture and cupping VS other therapies5 studies[8,10,18,20,33]reported the ratio of blood-letting puncture and cupping and other therapies(I2=0%,P=0.79).Significant test shows that Z=3.96,P<0.001.The results showed that effective ratio OR=4.24[OR=4.24,95%CI(2.07,8.68),P<0.01],95%CI horizontal lines did not intersect with equivalent vertical lines,which was statistically significant in the ratio of blood-letting puncture and other therapies.(Figure 4)
Bias detectionThe total effective rate and recurrence rate were tested for bias.To observe whether there is bias in the results of total efficiency analysis,we evaluated the bias of 30 studies included in Meta-analysis in Revman software Funnel plot.The total benchmark is total efficiency,and the funnel plot is made with log OR as ordinate OR as abscissa(Figure 5).If the scatters on both sides of a straight line are symmetrical in funnel graph,there is no obvious publication bias,and if the scatters on both sides of a straight line are asymmetrical,there may be publication bias.As shown in the figure,the scatters in the funnel plot are obviously asymmetrical and distributed on the right side of transverse axis1.That is to say, there is publication bias in this meta-analysis.
Discussion
Scapulohumeral periarthritis is a chronic traumatic inflammation inside and outside the shoulder joint,often manifested as pain and dysfunction of movement. Conservative treatment of scapulohumeral periarthritis includes physiotherapy,analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,steroid injection, traditional Chinese medicine therapy,etc.[34].According to the characteristics of shoulder periarthritis,it can be divided into primary and secondary types[35].The pathogenesis of TCM is local cold, invasion of exogenous pathogens,long-term strain or discord between Qi and blood,blood does not nourish tendons.There are several methods of TCM treatment, for example,blood-letting puncture,cupping,general acupuncture,drug fumigation,functional exercise and acupoint injection,etc.Blood-letting puncture and cupping is widely used in clinic because of its simple operation,non-toxic side effects, economic and other advantages. This method has the functions of promoting joints,activating blood circulation and removing blood stasis, relaxing meridians and dredging collaterals, strengthening the body's immune function.Good results have been achieved in clinical treatment of scapulohumeral periarthritis[36-37]. This meta-analysis included all eligible clinical randomized controlled trials reported in databases at home and abroad up to October 2018.A total of 2504 patients with scapulohumeral periarthritis were enrolled in 30 studies. Quality evaluation according to GRADE methodology[38].The results of the 30-bias study are all of B-grade medium quality,the possibility of bias is moderate,and the recommendation intensity is "weak recommendation".Because TCM treatment of this disease requires four diagnostic methods,syndrome differentiation and treatment,it is difficult to adopt blind method. It is difficult to do single-blind,double-blind RCT research with high quality,and the sample size of follow-up survey is too small.All of these will increase the risk of bias included in the study[39].The RCT sample size included in the study was small and the quality of evidence was low[40].We need high quality,large sample to provide reliable and strong evidence for future treatment.The conclusion shows that blood-letting puncture and cuppings are superior to other treatments in clinical efficacy and recurrence control. Therefore, the application of blood-letting puncture and cupping in the treatment of scapulohumeral periarthritis can provide strong evidence for future clinical treatment.
1. Qin ZS,Feng HQ,Wang YM.Advances in the treatment of periarthritis of shoulder with traditional Chinese and western medicine.Clinical J Chin Med 2017,9:135-136.
2. Diercks RL,Stevens M.Gentle thawing of the frozen shoulder:a prospective study of supervised neglect versus intensive physical therapy in seventy-seven patients with frozen shoulder syndrome followed up for two years.J Shoulder Elb Surg 2014,13:499-502.
3. SATCM. Standard of TCM disease and syndrome diagnosis. Nanjing: Nanjing University Press,1994.
4. Shen H. Curative effect of acupuncture and collaterals cupping therapy combined with hot compress of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of periarthritis of shoulder.Information Tradit Chin Med 2011,3:160.
5. Chen JJ.Observation on the curative effect of electroacupuncture plus acupuncture and collaterals cupping for scapulohumeral periarthritis. J Clinical Acupun Moxibustion 2009,25:27-28.
6. Zhang JT.90 cases of periarthritis of shoulder were treated by electroacupuncture plus acupoint ashi acupuncture and collaterals cupping.Chin J Orthopedics Traumatology 2015,23:49-50.
7. Li T, Li XL. Clinical analysis of electroacupuncture combined with acupuncture and collaterals cupping therapy for periarthritis of shoulder.Chin Disability Med 2014,1:16-17.
8. Zhao YJ, Fu HX, Shi J. Electroporal percutaneous administration combined with acupuncture and cupping therapy for 60 cases of scapulohumeral periarthritis.Guiding J of TCM,2013,19:87-88.
9. Lin XM,Cheng Y,Liu XQ,et al.Observation on the immediate effect of dynamic balance acupuncture on periarthritis of shoulder. J Practical Chin Med 2005,21:222-223.
10.Wang Y, Wu BX. Clinical observation of blood-letting cupping therapy combined with electric acupuncture and moxibustion and infrared polarized light in the treatment of acute periarthritis of shoulder.Chin J Convalescent Med 2015,24:706-707.
11.Huang WQ. Curative effect observation on scapulohumeral periarthritis treated by crochet needle combined with cupping and bloodletting.Inner Mongolia Tradit Chin Med 2010, 29:32-33.
12.Lu HF. Clinical observation of 42 cases of periarthritis of shoulder treated by fire needle and acupuncture and collaterals cupping.Med Inform 2013,20:611-611.
13.Zhang ZR.Observation on the curative effect of tendon junction electroacupuncture plus acupuncture and collaterals cupping for scapulohumeral periarthritis. Shanghai J Acupunc Moxibustion 2012,31:906-907.
14.Baoan AGL. Clinical study of cupping and bloodletting therapy for periarthritis of shoulder in Mongolian medicine.Acta Academiae Med Neimongol,2006,12:120-121.
15.Zhang YB. Clinical study of cupping and bloodletting therapy for periarthritis of shoulder in Mongolian medicine. Chin J Ethnomed Ethnopharm 2018,24:22-23.
16.Ye WH.Spatting combined with acupuncture and cupping therapy for 34 cases of periarthritis of shoulder.Clinical J Chin Med 2013,5:57-58.
17.Chen QB,Qin JK,Wang YF,et al.Clinical study on the treatment of periarthritis of shoulder by body acupuncture, head acupuncture,electroacupuncture and collaterals puncture therapy.J Chin Med 2012,27:1225-1226.
18.Huang HX.Observation on the curative effect of massage and blood-pricking cupping therapy on adhesion of scapulohumeral periarthritis.Massage 2006,2:9-11.
19.Wang HA.Observation on the curative effect of warm acupuncture combined with acupuncture and collaterals cupping for scapulohumeral periarthritis. China Med Pharmacy 2012, 2:33-34.
20.Huang HF.Clinical observation on 40 cases of scapulohumeral periarthritis treated by warm acupuncture and moxibustion combined with acupuncture and collaterals cupping. New J Tradit Chin Med 2014,46:190-191.
21.Cheng Y,Lin XM, Cheng Z,et al.Clinical observation on 40 cases of periarthritis of shoulder treated by sports acupuncture combined with acupuncture and collaterals cupping.New J Tradit Chin Med 2005,5:60-61.
22.Li SJ. Clinical observation on 40 cases of periarthritis of shoulder treated by sports acupuncture combined with acupuncture and collaterals cupping.J Clin Psycho Diseases 2015,20:203.
23.Zhu JH.Observation on the curative effect of long and short acupuncture combined with acupuncture and collaterals cupping therapy for periarthritis of shoulder. J Clinical Acupunc Moxibustion,2003,4:40-41.
24.Meng KBLG,Su RR.Clinical observation on 58 cases of periarthritis of shoulder treated by acupuncture cupping and bloodletting.Chin J Ethnomed Ethnopharm 2003,17:32-33.
25.Liu Q. Curative effect of acupuncture on scapulohumeral periarthritis with dong shiqi acupoint and collaterals cupping. Practical Clinical Med 2014,15:65-66.
26.Pan CQ.Clinical observation on 18 cases of scapulohumeral periarthritis treated by acupuncture and collaterals cupping.Guiding J TCM 2011,17:70-71.
27.Zhang HB.Clinical observation on 60 cases of scapulohumeral periarthritis treated by acupuncture and collaterals cupping.Shanxi J Tradit Chin Med 2010,26:28-29.
28.Chen R, Yang YH. Clinical observation of acupuncture combined with collaterals cupping in the treatment of periarthritis of shoulder.Sponsored Gubei College Tradit Chin Med 2015,37:65-66.
29.Kang MM, Wang M, Shi XM. Clinical observation on treatment of scapulohumeral periarthritis by acupuncture yanglingquan combined with acupuncture collaterals cupping.World Chin Med 2013,8:442-444.
30.Chen ZW.Clinical observation on the treatment of periarthritis of shoulder by acupuncture and moxibustion combined with acupuncture and blood-letting cupping therapy. Asia Pacific Tradit Med 2015,11:104-105.
31.Ren ZX. Clinical effect of acupuncture and moxibustion combined with collaterals puncture and blood-letting cupping therapy for periarthritis of shoulder.China Med Pharm 2016,6:69-71.
32.Huang XH,Du SH.Clinical observation on 52 cases of scapulohumeral periarthritis treated by acupuncture combined with collaterals puncture and bloodletting and cupping therapy.Electronic J Clinical Med 2017,4:14115.
33.Wang F. Observation of curative effect of cupping combined with acupuncture and collaterals cupping and millisecond fire needle in the treatment of periarthritis of shoulder.J Chin Rural Physician 2018,34:111-112.
34.Nan DK. Rehabilitation Medicine. Beijing:People's Medical Publishing House,2005.
35.Chen JW, Chen SY. Research progress of periarthritis of shoulder. Foreign Med (Bone Science)2005,26:94-96.
36.Liang MZ,Chen HH.TCM classification and treatment of periarthritis of shoulder. TCM Classification Treatment Periarthritis Shoulder 2001,12:28-29.
37.Cui YJ, Geng LQ, Meng ZH. The research progress of acupuncture and cupping therapy for shoulder coagulation syndrome in recent ten years.Heilongjiang J Tradit Chin Med 2017,46:80.
38.Guyatt GH,Oxman AD,Vist G,et al.GRADE:IV.Evidence quality grading-limitations of the study(risk of bias).Chin J Evidence Based 2011,11:456-463.
39.Yang JX, An J, Peng JS, et al. Systematic evaluation of the clinical efficacy of pinxia xiexin decoction plus or minus decoction in the treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis.J Beijing Univer TCM 2015,38:46-52.
40.Li Q,Xia Y,Mu YJ,et al.Systematic review and Meta analysis of literature quality reassessment of TCM published in domestic Chinese periodicals.J Beijing Univer Tradit Chin Med 2012,19:28-33.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
TMR Integrative Medicine的其它文章
- Effects of hypoxia on sodium current in rat cardiomyocytes
- Review of the mechanisms of TCM in relieving the chemotherapy-induced diarrhea
- Efficacy of acupuncture on treating obesity and adipose-incurred illnesses
- Based on theprocess management of traditional Chinese medicine comprehensive intervention method on outcomes inpatients with mild/moderate chronic obstructivepulmonary disease:studyprotocol for apractical randomized controlled trial
