大型高地隙喷雾机喷杆主动悬架自适应模糊滑模控制
2018-11-06杜岳峰毛恩荣温浩军
薛 涛,李 伟,杜岳峰,毛恩荣※,温浩军
大型高地隙喷雾机喷杆主动悬架自适应模糊滑模控制
薛 涛1,李 伟1,杜岳峰1,毛恩荣1※,温浩军2
(1. 中国农业大学工学院现代农业装备优化设计北京市重点实验室,北京 100083;2. 新疆农垦科学研究院,石河子 832000)
针对喷杆被动悬架在低频下隔离干扰性车身摆动性能不足的问题,该文在双连杆梯形喷杆被动悬架的基础上加装作动液压缸而获得喷杆主动悬架,并提出了基于自适应模糊滑模控制算法的喷杆主动悬架控制方法;在建立了喷杆主动悬架动力学模型和液压系统模型的基础上,应用Matlab/Simulink对主动悬架系统进行整体仿真分析,验证了该文控制方法的有效性;基于课题组开发的大型高地隙喷雾机搭建了实车试验平台,分别进行了实车静态跟随试验和田间试验。试验结果表明:采用基于自适应模糊滑模控制算法的喷杆主动悬架控制方法,喷杆倾角实车静态跟随响应时间和误差分别为2 s和0.002 rad,相较于PID控制的4 s和0.002 rad响应时间减小;同时,喷杆倾角田间试验摆动范围保持在–0.005~0.005 rad内。结论表明,该文提出的喷杆主动悬架控制方法具有良好的响应性、稳定性和准确性,可有效隔离干扰性车身摆动并保持喷杆稳定。该研究有利于提高中国大型高地隙喷雾机喷雾均匀性和喷杆作业稳定性。
农业机械;喷雾;控制;大型高地隙喷雾机;喷杆主动悬架;自适应模糊滑模控制

0 引 言
喷杆作为大型高地隙喷雾机的主要工作部件,其工作性能好坏直接决定农药的利用率和整机作业稳定性。试验研究表明,喷杆的不规律运动会引起喷雾沉积均匀性超过或者低于期望值(100%)0%到800%不等[1-4],所以提高喷杆的运动稳定性,对增加喷雾均匀性并提升农药的使用效率具有重要意义[5-7]。喷杆悬架可以将喷杆与喷雾机车身之间的刚性连接转换成柔性连接,极大地减少车身传递给喷杆的振动,在高端喷杆喷雾机上应用广泛[8-10]。
大型高地隙喷雾机作业速度快、作业环境恶劣,在作业过程中喷杆需要面对地形起伏变化或者局部地形突变(如凹坑或者凸起)引起的车身高频或者低频摆动,从国内外研究学者对喷杆被动悬架的研究成果来看,喷杆被动悬架可以很好的隔离喷雾机工作在崎岖路况时车身的高频摆动,但当喷雾机因轮胎遇到地形突变(如凸起或者凹坑)而产生干扰性车身摆动时,喷杆被动悬架的低频跟随性能反而会引起喷杆的失衡,导致喷杆离地或者植物冠层的高度改变[11-14]。
本文针对喷杆被动悬架在低频下隔离干扰性车身摆动性能不足,通过在喷杆双连杆梯形被动悬架上加装液压缸的方式获得喷杆主动悬架[15-20],这样喷杆悬架既可以利用外部能源的输入对喷杆姿态进行主动调整,提高喷杆被动悬架低频时隔离干扰性车身摆动的性能,还能保留被动悬架的高频隔离性能,避免主动悬架高频响应耗费大量的能量。为了保证主动悬架性能达到最佳,针对喷杆主动悬架系统的非线性、不确定性和参数时变性,提出了一套基于自适应模糊滑模的喷杆主动悬架控制算法[21-25],使喷杆主动悬架控制的响应性、稳定性和准确性都得到较大的提升。
1 主动悬架动力学建模与仿真
1.1 主动悬架动力学建模
喷杆主动悬架结构如图1a所示,外提升架3通过双连杆2铰接在与车身一体的内提升架1上组成双连杆梯形被动悬架,主动悬架液压缸4铰链在外提升架3和内提升架1之间。当作为被动悬架时,喷杆5带动外提升架3和内提升架1,使得二者之间产生相对运动,而相对运动可以通过主动悬架液压缸4伸缩过程中油液流过阻尼小孔产生的阻尼衰减掉;当作为主动悬架时,主动悬架液压缸4主动伸缩推动外提升架3运动,外提升架3带动喷杆5跟随内提升架1运动实现喷杆姿态主动调整。
喷杆主动悬架受力如图1b所示,喷杆通过双连杆和连接到车身上,点、、、分别是车身和喷杆上的铰接点,整个喷杆(两侧喷杆、外提升架)的重心点为。两侧主动悬架液压缸通过铰接点、、和连接在车架与喷杆之间。同时,假设喷雾机车身围绕一条穿过点且平行于车身前进方向的固定轴旋转,并以点为原点建立坐标系。为更简单、更方便描述喷杆主动悬架动力学特性,暂不考虑喷杆弹性变形、各个连接杆件的质量、关节处摩擦阻尼和喷雾机底盘悬架的影响。

1. 内提升架 2. 连杆 3. 外提升架 4. 主动悬架液压缸 5. 喷杆
1. Inner lift frame 2. Connecting rod 3. Outer lift frame 4. Active suspension hydraulic cylinder. 5. Sprayer boom
a. 喷杆主动悬架结构图
a. Structure diagram of spray boom active suspension
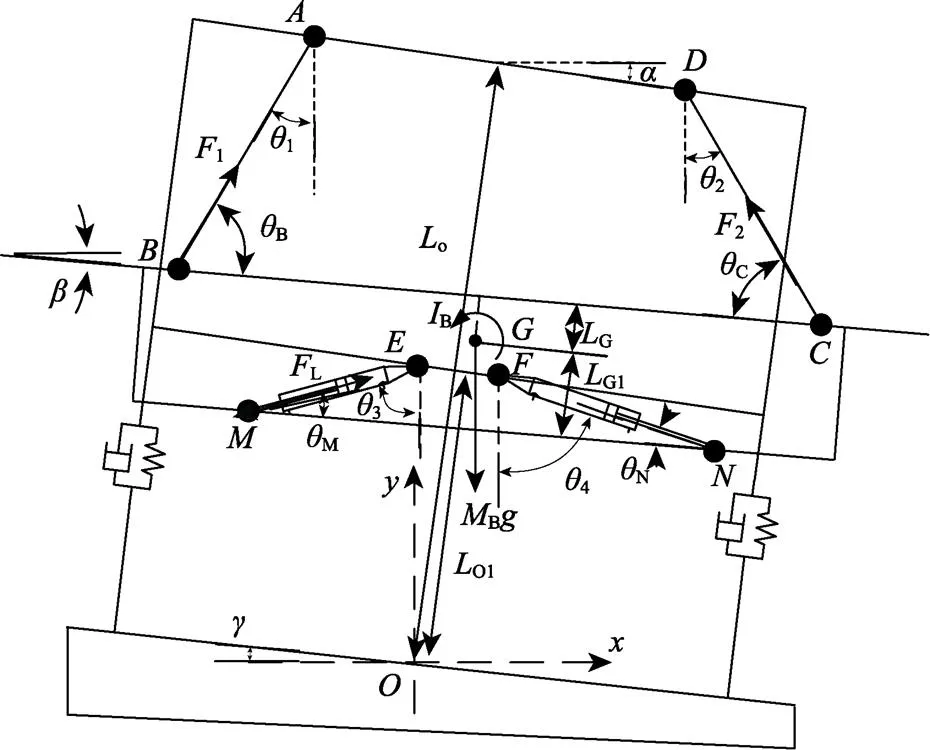
注:为坐标系原点;为地面倾角,rad;为车身倾斜角度,rad;为喷杆与水平面夹角,rad;1、2分别为连杆、与垂直方向夹角,rad;3、4分别为两侧主动悬架液压缸与垂直方向之间的夹角,rad;L为连杆到地面距离,m;G为连杆到整个喷杆重心的距离,m;O1为连杆到地面距离,m;G1为连杆到喷杆重心的距离,m;B、C为连杆、与喷杆之间的夹角,rad;M、N分别为两侧主动悬架液压缸与连杆之间的夹角,rad;B为整个喷杆的质量,kg;B为整个喷杆围绕质心转动惯量,kg×mm2;L为主动悬架液压缸负载力,N;1为连杆所受力,N;2为连杆所受力,N。为重力加速度,m/s2;为喷杆重心点;、、、、、、、为连杆铰接点。
Note:is origin of coordinate system;is the ground angle, rad;is sprayer bodyangle, rad;is the angle between the spray boom and the horizontal plane, rad;1,2are the angle between connecting rod,and the vertical direction respectively, rad;3and4are the angles between 2 sides active suspension hydraulic cylinders and the vertical direction respectively, rad;Lis the distance from the connecting rodto the ground, m;Gis the distance from connecting rodto the center of gravity of whole boom, m;O1is the distance from the connecting rodto the ground, m;G1is the distance from connecting rodto the center of gravity of whole boom, m;B,Care the angles between the connecting rod,and the spray boom respectively, rad;M,Nis the angle between the two sides hydraulic cylinders and the connecting rod, rad;Bis the weight of the whole spray boom, kg;Bis the moment of inertia around the center of mass for the whole spray boom, kg×mm2;Lis the load force of the hydraulic cylinder for the active suspension, N;1is the force of the connecting rod, N;2is the force of the connecting rod, N.is the acceleration of gravity, m×s-2;is the center of gravity of spray boom;,,,,andare connecting rod joints.
b. 喷杆主动悬架受力图
b. Schematic of force analysis on spray boom active suspension
图1 喷杆主动悬架结构与受力图
Fig.1 Structure and force analysis of spray boom active suspension
在四边形中,喷杆重心横竖坐标,分别表示为
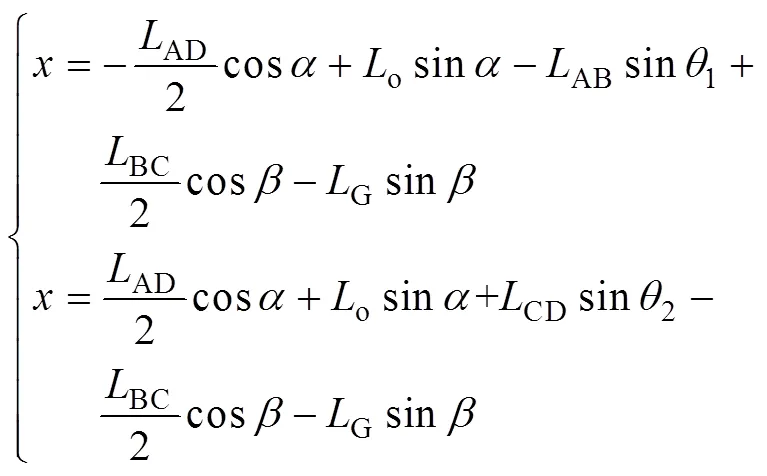
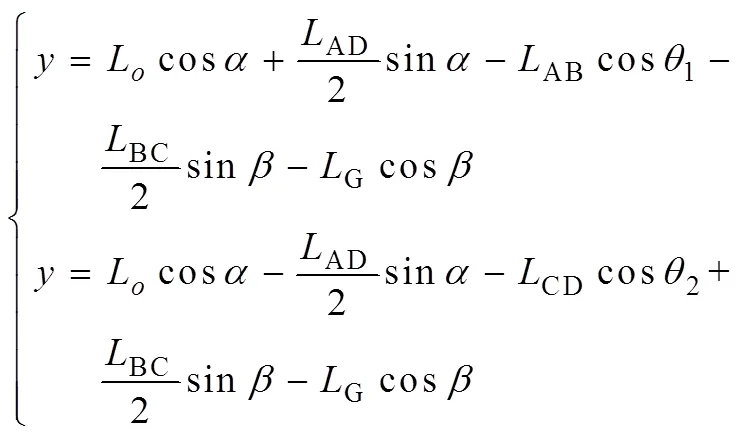
式中AD为悬架连杆长度,m;AB为悬架连杆长度,m;BC为悬架连杆长度,m;CD为悬架连杆长度,m;o为连杆到地面距离,m;为车身倾斜角度,rad;为喷杆与水平面夹角,rad;1、2分别为连杆、与垂直方向夹角,rad。
喷雾机田间作业时,车身倾斜角度和喷杆倾斜角度都较小,近似有
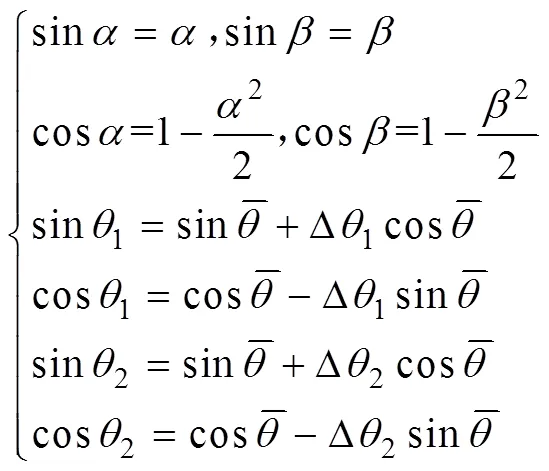

通过式(1)~(3)得
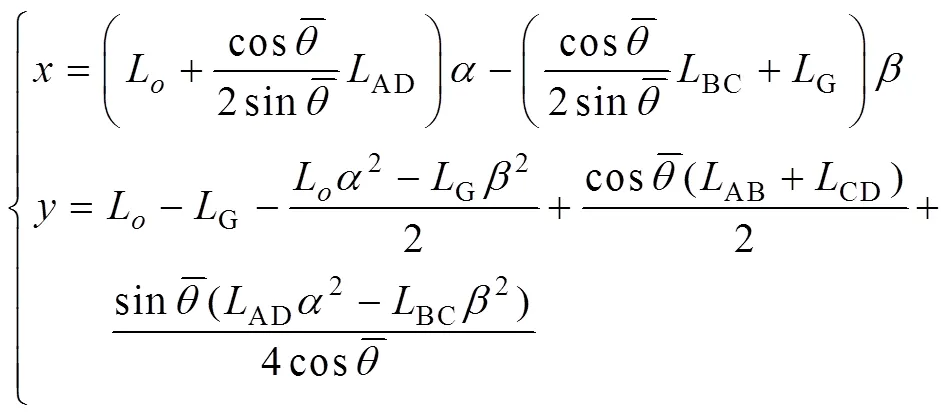
对式(4)和(5)求导并忽略二阶小量得
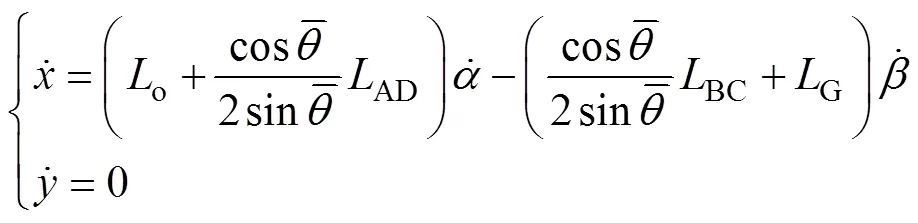
在四边形中,喷杆重心横竖坐标,分别表示为


式中3、4分别为两侧主动悬架液压缸与垂直方向之间的夹角,rad;O1为连杆到地面距离,m;G1为连杆到喷杆重心的距离,m;EF为连杆长度,m;MN为连杆长度,m;BC为悬架连杆长度,m;CD为悬架连杆长度,m;
喷杆摆动角度很小,3、4的值变化范围较小,近似取
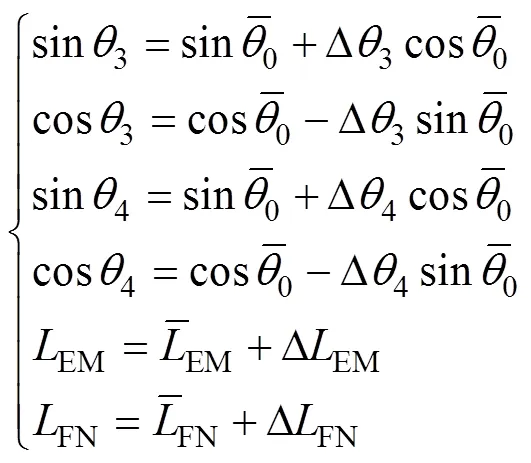
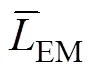
通过式(5)~(8)得:


通过几何关系可知:
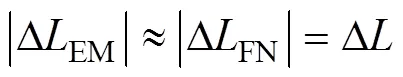
对式(9)和(10)求导并忽略二阶小量得:
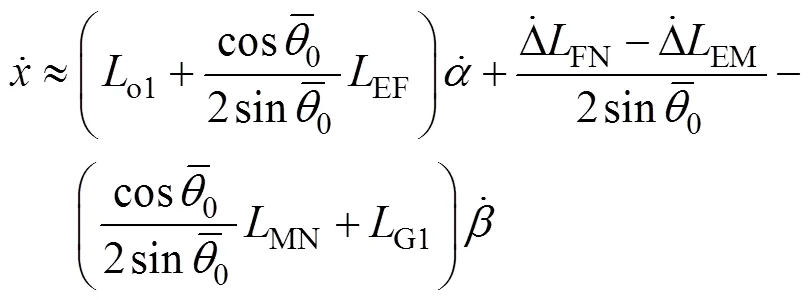

在喷杆被动悬架和主动悬架工作过程中,喷杆重心坐标变化一致,根据式(5)、(11)~(13)得:
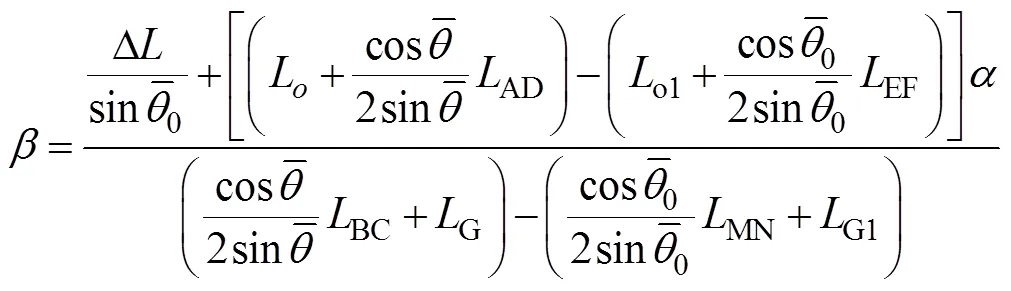
根据平面达朗贝尔原理得
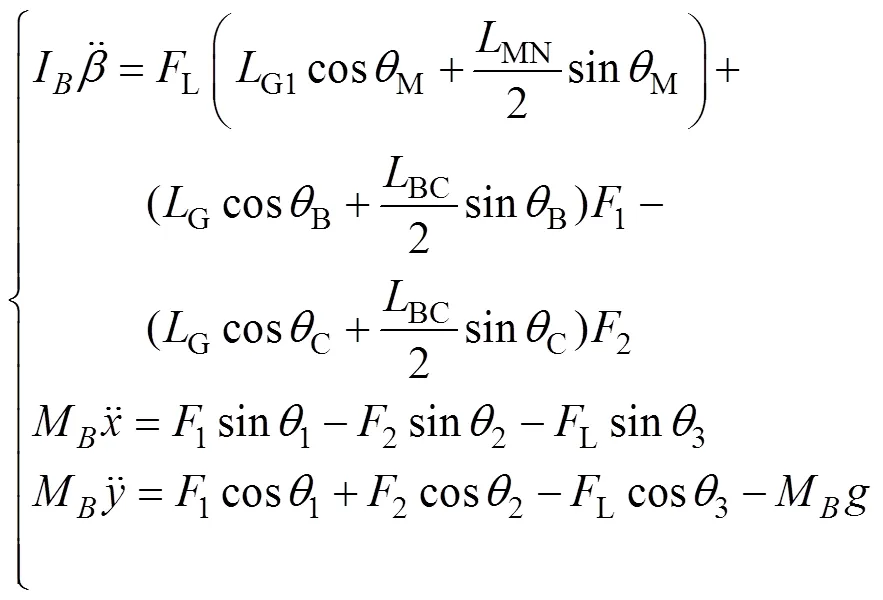
式中M为整个喷杆的质量,kg;I为整个喷杆围绕质心转动惯量,kg×mm2;L为主动悬架液压缸负载力,N;1为连杆所受力,N;2为连杆所受力,N。
1.2 主动悬架动力学特性仿真
依据喷杆被动悬架设计优化结果及其CREO三维模型,分析可得喷杆主动悬架主要参数如表1所示。
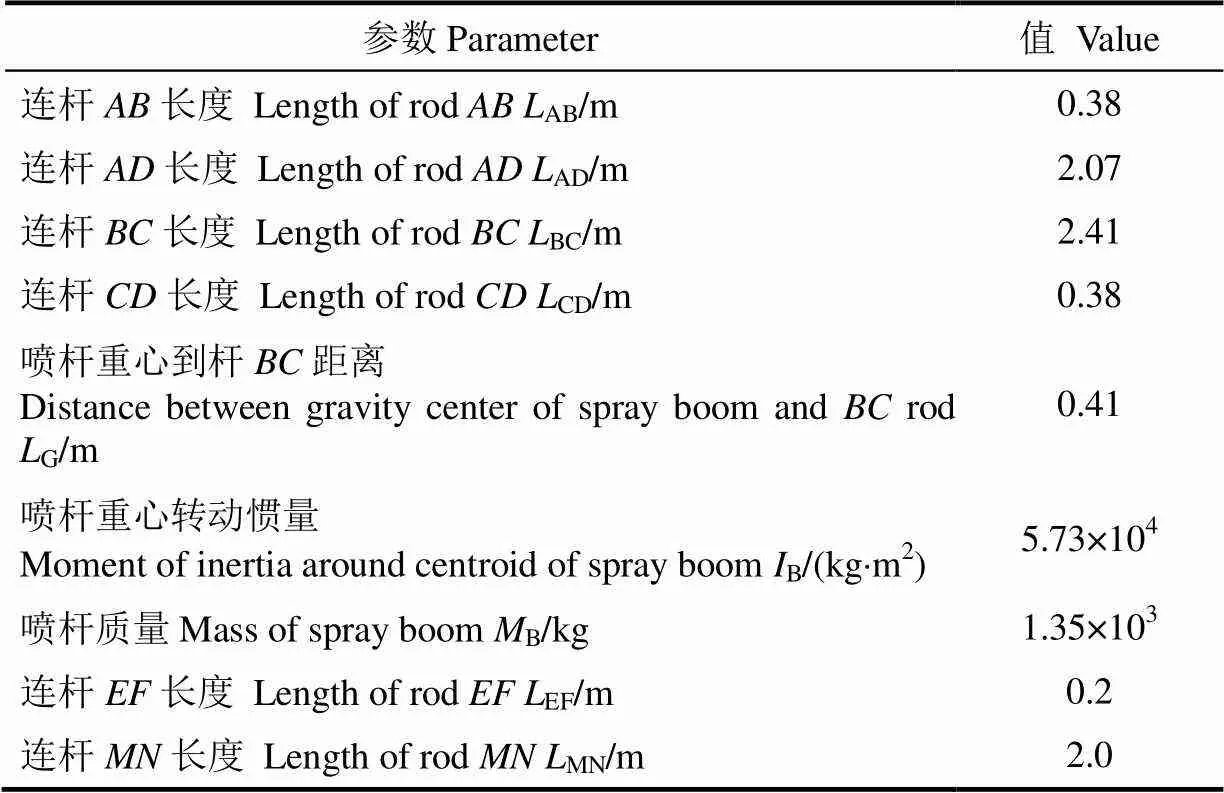
表1 喷杆主动悬架参数
采用具有独立式空气悬架的喷雾机行驶在水平路面上时,车身侧倾角度可近似表示为

式中s位喷雾机左右悬架之间的宽度,m;L、R分别为左右悬架减振行程,m。
根据课题组喷雾机底盘悬架设计参数[26],喷雾机左右悬架之间的宽度为4 m,其减振行程范围为±100 mm,考虑极限工况时,通过式(16)计算得到此时车身侧倾角度达到最大值约为0.05 rad,以此为依据,设计喷杆主动悬架最大摆动角度为0.06 rad左右。
结合上述建立的主动悬架动力学模型,在Matlab/ Simulink中构建喷杆主动悬架动力学仿真模型,为使喷杆倾角能在仿真时间内达到最大值0.06 rad,以斜率0.032 rad/s的液压缸伸出长度斜坡信号为输入仿真分析主动悬架的运动学与动力学特性,结果如图2所示。
从图2a可知,喷杆倾角随着主动悬架液压缸活塞杆伸出长度的增加而线性变化,当主动悬架液压缸活塞杆伸出长度为0.16 m时,此时喷杆倾角达到设计角度0.06 rad;从图2b可知,随着主动悬架液压缸活塞杆伸出长度的增加,油缸受力增大,最大受力为1.7×104N。根据以上仿真分析结果并结合文献[27]确定喷杆主动悬架液压缸主要参数为:缸径0.063 m,杆径0.035 m,行程0.32 m[27]。
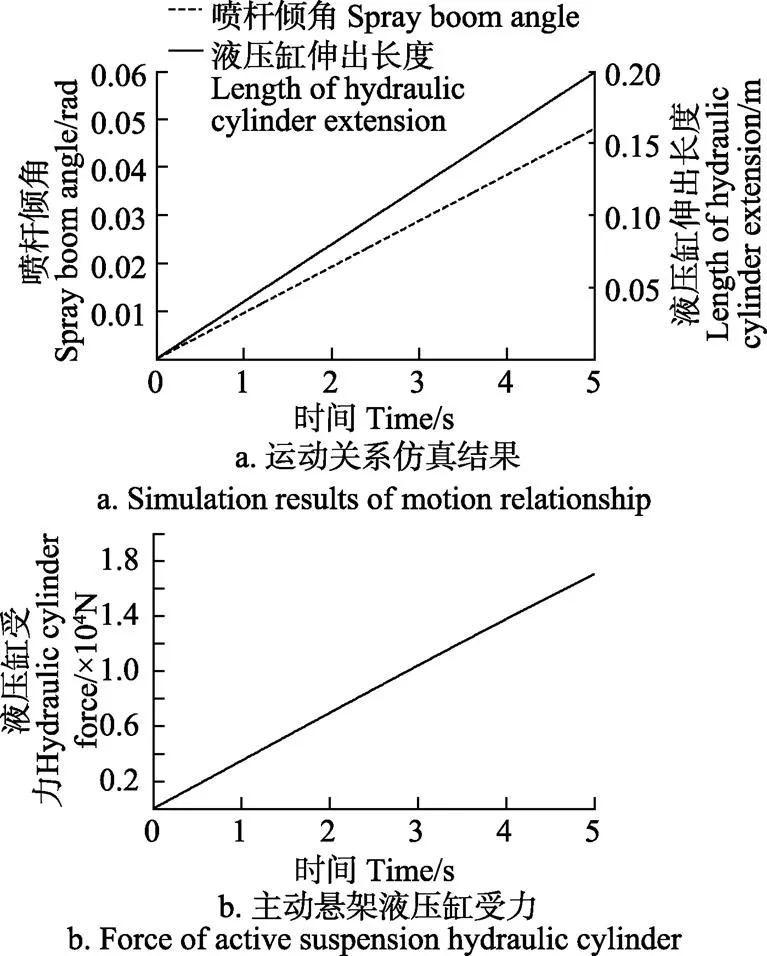
图2 喷杆主动悬架动力学仿真曲线
2 喷杆主动悬架液压系统
2.1 液压系统原理
喷杆主动悬架液压系统原理如图3所示,液压系统参数如表2所示。当阻尼控制阀关闭时,油液无法流动,2个主动悬架液压缸锁死,喷杆悬架处于关闭状态;当2个阻尼控制阀通电打开,主动悬架比例阀处于中位时,2个主动悬架液压缸活塞杆在喷杆重力作用下伸出或者缩回,油缸内油液流过开度可调的单向节流阀产生不同的阻尼,此时喷杆悬架处于被动悬架状态;当2个阻尼控制阀通电打开,主动悬架比例阀通电时,高压油进入主动悬架液压缸内推动活塞杆伸出和缩回,此时喷杆悬架处于主动悬架状态。
2.2 喷杆主动悬架比例阀模型
图4为喷杆主动悬架比例阀节流口通流面积示意图。
取阀芯右移时阀芯位移为正,则喷杆主动悬架比例阀节流口通流截面积PV为
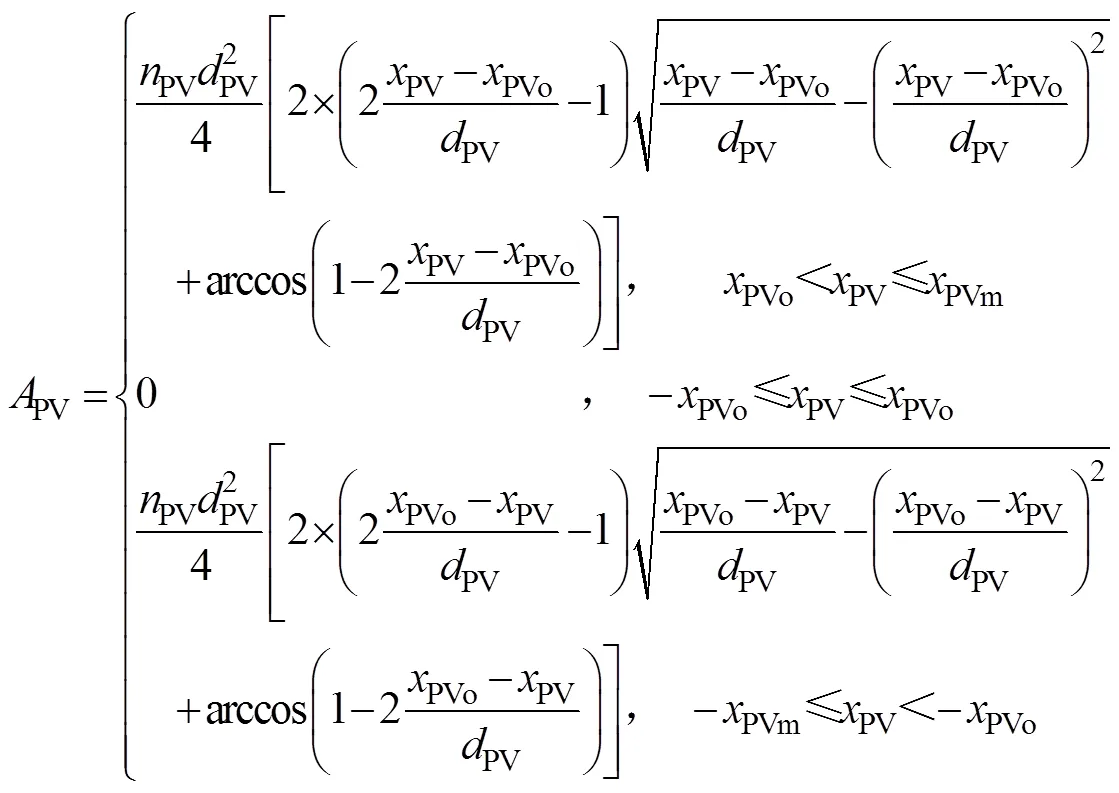
注:PVS为喷杆主动悬架比例阀进口压力,Pa;PV1、PV2分别为喷杆主动悬架比例阀阀口④、②压力,Pa;PV1、PV2为喷杆主动悬架比例阀阀口④、②流量,L·min–1;HC1、HC2分别为左右主动悬架液压缸无杆腔内流量,L·min–1;HC1、HC2分别为左右主动悬架液压缸无杆腔内压力,Pa;T为回油压力,Pa;s为系统压力,Pa;FS为系统负载反馈压力,Pa。
Note:PVSis the inlet pressure of the spray boom active suspension proportional valve, Pa;PV1andPV2are pressure of the spray boom active suspension proportional valve port 4 and 2, Pa;PV1andPV2are flow rate of the spray boom active suspension proportional valve port 4 and 2, L·min–1;HC1andHC2are flow rates of left and right active suspension hydraulic cylinder of rodless cavity respectively, L·min–1;HC1,HC2are rod pressure of left and right active suspension hydraulic cylinder respectively, Pa.Tis return oil pressure, Pa;sis pressure of system, Pa;FSis feedback pressure of system load, Pa.
图3 喷杆主动悬架液压系统原理图
Fig.3 Schematic of hydraulic system for spray boom active suspension
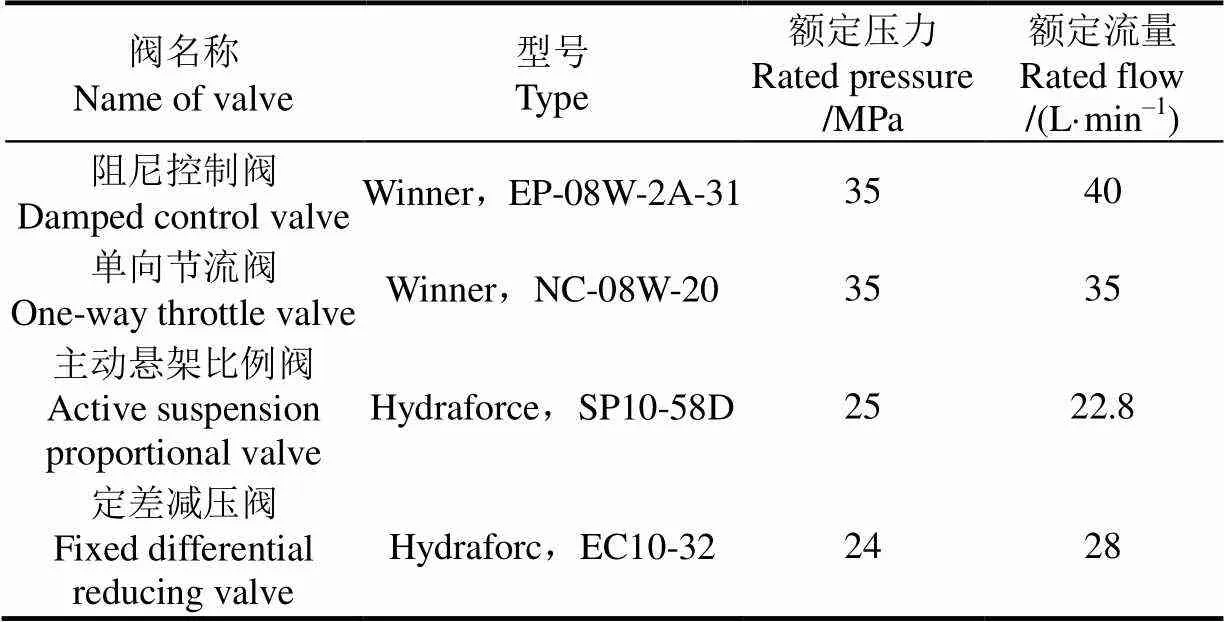
表2 喷杆主动悬架液压系统参数
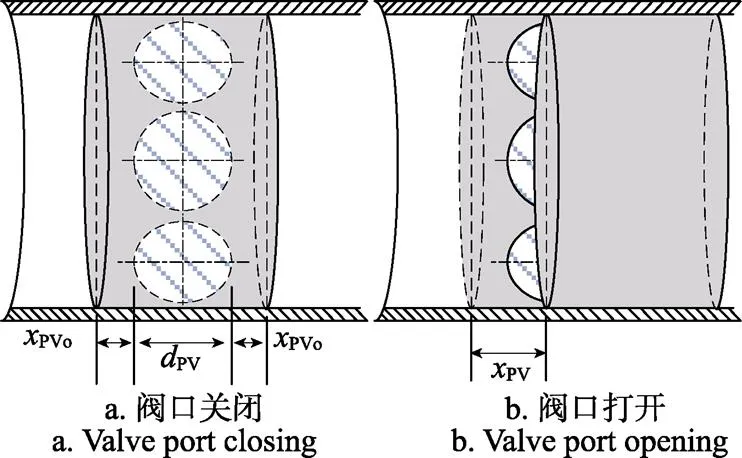
注:xPVo为喷杆主动悬架比例阀阀芯单侧重叠量,m;dPV为喷杆主动悬架比例阀圆形节流孔直径,m;xPV为喷杆主动悬架比例阀阀芯位移(右位移为正),m。
式中PVo为喷杆主动悬架比例阀阀芯单侧重叠量,m;PV为喷杆主动悬架比例阀圆形节流孔直径,m;PV为喷杆主动悬架比例阀阀芯位移,(右位移为正),m;PV为喷杆主动悬架比例阀圆形节流孔数目;PVm为喷杆主动悬架比例阀阀芯最大位移量,m。
根据阀芯结构取PVo=5.9×10–4m,PV=3×10–3m,PV=6,PVm=2.24×10–3m[28]。在进行喷杆主动悬架液压系统建模时,将左右两侧主动悬架液压缸看作一条无杆腔进油的双作用液压缸,忽略阻尼控制阀打开时的压降,则喷杆主动悬架控制阀流量方程表示为

式中d为阀口流量系数;为液压油密度,kg/m3。
喷杆主动悬架液压缸流量连续性方程如下

式中HC0为喷杆主动悬架液压缸有效体积,m3;HC为喷杆主动悬架液压缸无杆腔有效作用截面积,m2;HC为喷杆主动悬架液压缸活塞杆的位移(无杆腔增大的方向为正),m;e为液体的体积弹性模量,Pa;I为喷杆主动悬架液压缸无杆腔外泄漏系数。
忽略弹性负载,则喷杆主动悬架液压缸活塞力平衡方程为
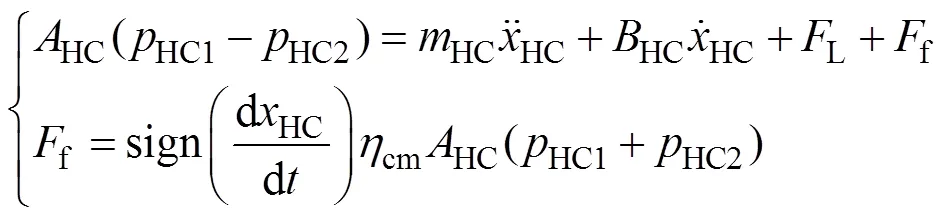
式中HC为喷杆主动悬架液压缸等效质量,kg;L为作用在喷杆主动悬架液压缸活塞杆上的外负载力,N;HC为喷杆主动悬架液压缸的黏性阻尼系数,N×s/m。f为作用在喷杆主动悬架液压缸活塞运动的总等效摩擦力,N;cm为喷杆主动悬架液压缸在无回油压力且仅无杆腔供油驱动时的机械效率,一般为0.9~0.95。
将左右两侧主动悬架液压缸看作是一条无杆腔进油的双作用液压缸时,定义负载压力L和负载流量L为
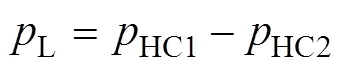

由式(18)~(22),负载流量L可表示为
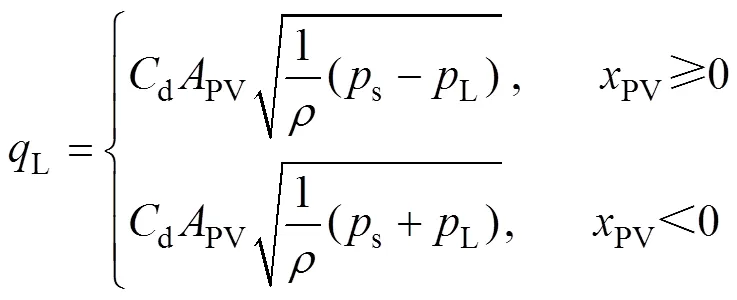
其中s为系统压力,Pa。
由式(21)~(23)得
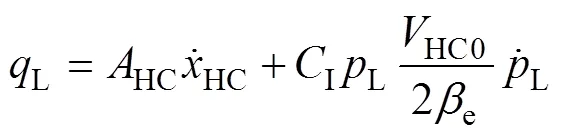
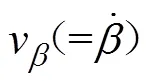

式中v、a、u、F为状态方程系数;为所有不确定因素的总和。e为液体的体积弹性模量,Pa;v为喷杆倾角变化率,rad/s;a喷杆倾角加速度,rad/s2。
3 喷杆主动悬架控制算法
3.1 喷杆主动悬架控制特点分析
当自走式喷雾机进行田间作业时,地形起伏变化引起的车身摆动通过喷杆悬架传递给大幅宽喷杆后易引起喷杆的失衡,导致喷杆离地距离产生较大变化,严重影响喷雾质量和喷杆的安全。喷杆失衡一个激励来源于长波段地面起伏引起的车身摆动,此激励的变化与喷雾机作业车速有关,随着自走式喷雾机作业车速的提高,此激励变化速度也随之增加;一个激励来源于地形突变(如凸起或者凹坑)引起的干扰性车身摆动,喷杆被动悬架可以隔离此激励中的高频部分,但其对于低频部分的跟随在此时却发挥了消极作用,导致喷杆产生干扰性摆动。相较于第一个激励,第二个激励来源更广泛、突发性更强、激烈程度更大。
3.2 喷杆主动悬架控制器设计
根据喷杆主动悬架控制特点分析,其控制目标是在控制信号的作用下,使得系统的输出喷杆倾角能够迅速、稳定和准确的跟踪系统参考输入d。定义跟踪误差e为
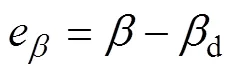
滑模变结构控制的滑模面可设置为

式中1和2为滑模系数,1和2>0且满足Hurwitz条件。
根据滑模变结构控制的原理,滑模控制率由等效控制eq和切换控制es两部分组成,即

由式(25)和(27)可得
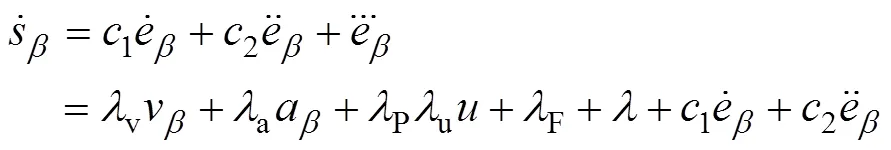

由于喷杆主动悬架系统具有很强的非线性、不确定性和参数时变性,使得系统动态特性非常复杂,其等效控制部分很难通过建立精确的数学模型准确获得。为了使系统能够保持良好的控制效果,故采用模糊控制来代替系统的等效控制,通过制定合理的模糊规则来逼近滑模控制等效部分[29],其控制器原理如图5所示。
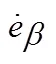

图5 喷杆主动悬架自适应模糊滑模控制原理图
Fig.5 Self-adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control principle diagram for spray boom active suspension



表3 喷杆主动悬架模糊控制器控制规则
而模糊控制器输入、输出的隶属函数设计如式(31)、(32)所示,隶属函数图如图6所示。
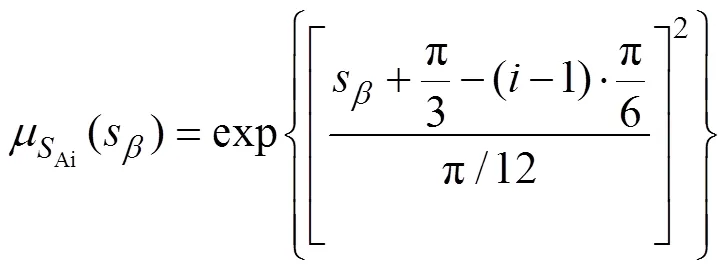


图6 隶属函数图
经过单值模糊化、乘积推理机和平均解模糊的模糊推理过程,最终得模糊控制系统的输出为
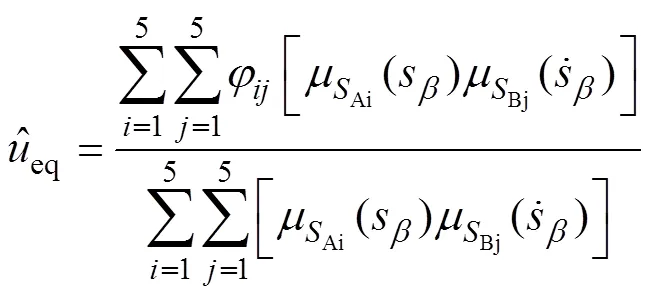


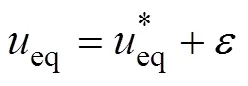
式中为逼近误差。
滑模变结构控制的切换控制es为
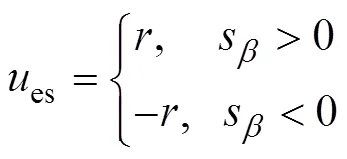
式中为切换值。


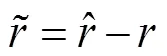
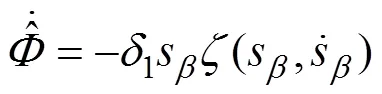
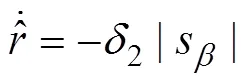
式中1为切换控制的自适应参数;2为切换控制的自适应参数。
定义Lyapunov函数为
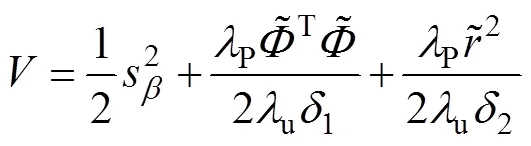
综合式(25)、(35)~(41)得
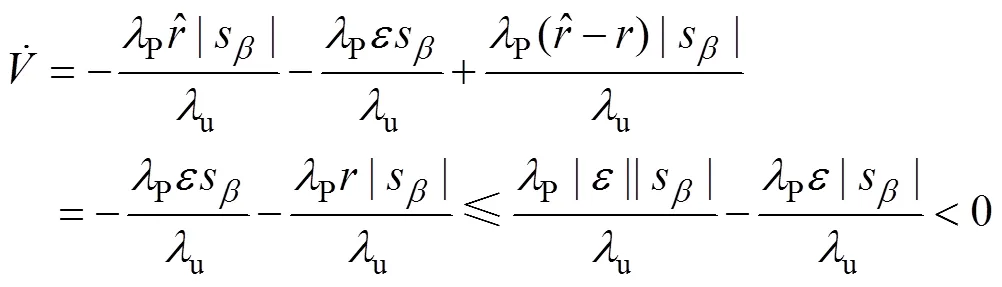
根据式(42),利用Lyapunov稳定性理论,分析该系统是稳定的。
4 喷杆主动悬架控制仿真及分析
为验证喷杆主动悬架控制算法控制效果,结合已建立的主动悬架系统的动力学模型和液压系统模型,在Matlab/Simulink中构建喷杆悬架主动悬架系统仿真模型,对比仿真分析本文所设计的自适应模糊滑模控制算法与PID控制算法的信号跟踪能力,控制算法仿真参数如下表4所示。

表4 控制算法仿真参数
通过主动悬架控制特点分析可知,喷杆主动悬架控制主要针对2种激励,即变化较缓的地面坡度和突发的地面凸起或者凹坑。以幅值0.05 rad的阶跃信号模拟主动悬架控制中的第二种激励,即喷雾机遇到突发的地面凸起或者凹坑时引起突发的、短时间的车身摇摆;以幅值为0.05 rad,频率为0.5 rad/s的正弦信号来模拟车身连续摆动工况,仿真分析结果如图7所示。
从图7a阶跃响应仿真结果可知,PID控制存在着明显的超调量和系统振荡,最大超调量为0.005 rad,响应时间较长,为3 s左右,而本文设计的自适应模糊滑模控制器则不存在明显的超调量和系统振荡,响应时间进一步减少到1.5 s,调整到位后的误差几乎为0;从图7b中可以看出,PID控制存在着明显的滞后,且最大跟随误差达0.025 rad;自适应模糊滑模控制跟随性能良好且平稳,跟随误差几乎为0。
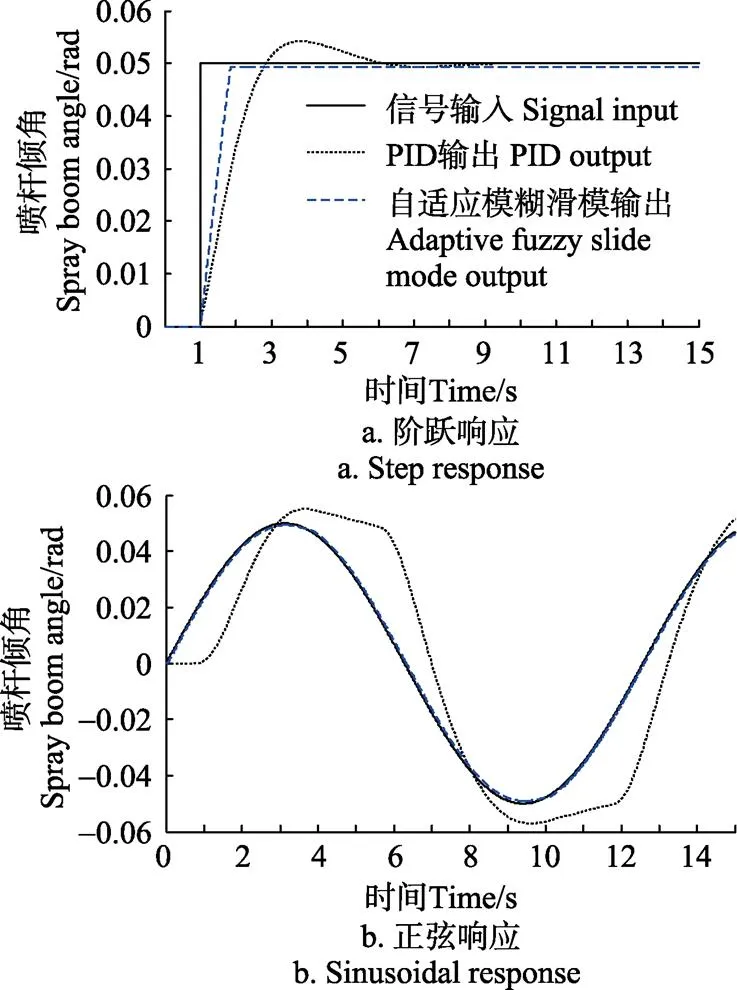
图7 喷杆主动悬架仿真响应曲线
5 实车试验
5.1 实车平台搭建
为了验证分析所设计的喷杆主动悬架控制系统的性能,以课题组开发的大型高地隙自走式喷雾机为平台[30],搭建喷杆主动悬架性能实车测试平台,实车平台主要由大型高地隙自走式喷雾机平台、超声波传感器(Banner,T30UXIA)、控制器(Hydac,HY-TTC 60)、采集卡(NI USB-6351)、信号发生器(DG1022U)、倾角传感器(Rion,SCA118T)和位移传感器(MIRAN,KTC-400)等组成,如图8所示。
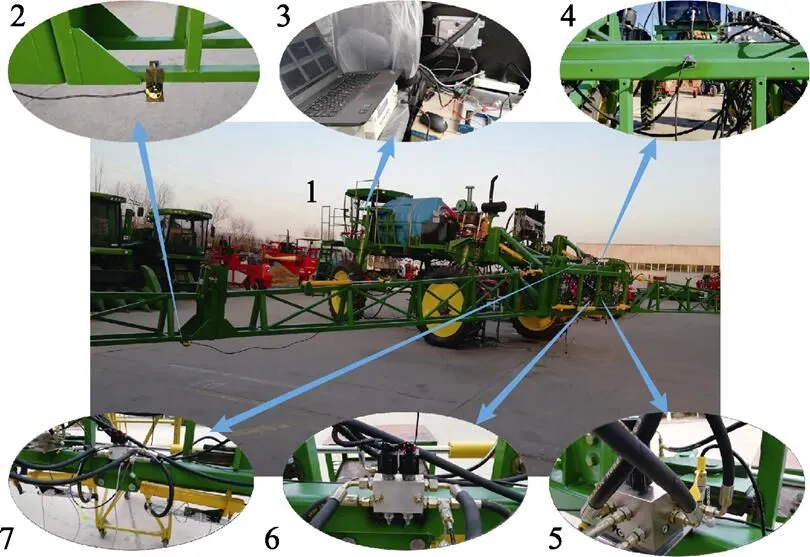

1. 大型高地隙自走式喷雾机平台 2. 超声波传感器 3. 测控系统(包括控制器、采集卡、PC、电源和信号发生器)4. 倾角传感器 5.喷杆主动悬架比例阀 6. 喷杆悬架阻尼控制阀 7. 喷杆主动悬架液压缸
5.2 主动悬架动力学试验
将喷杆完全展开至水平状态,分别手动打开主动悬架控制阀至最大开口,控制主动悬架液压缸活塞杆以最大速度伸出使喷杆倾斜,试验结果如图9所示。
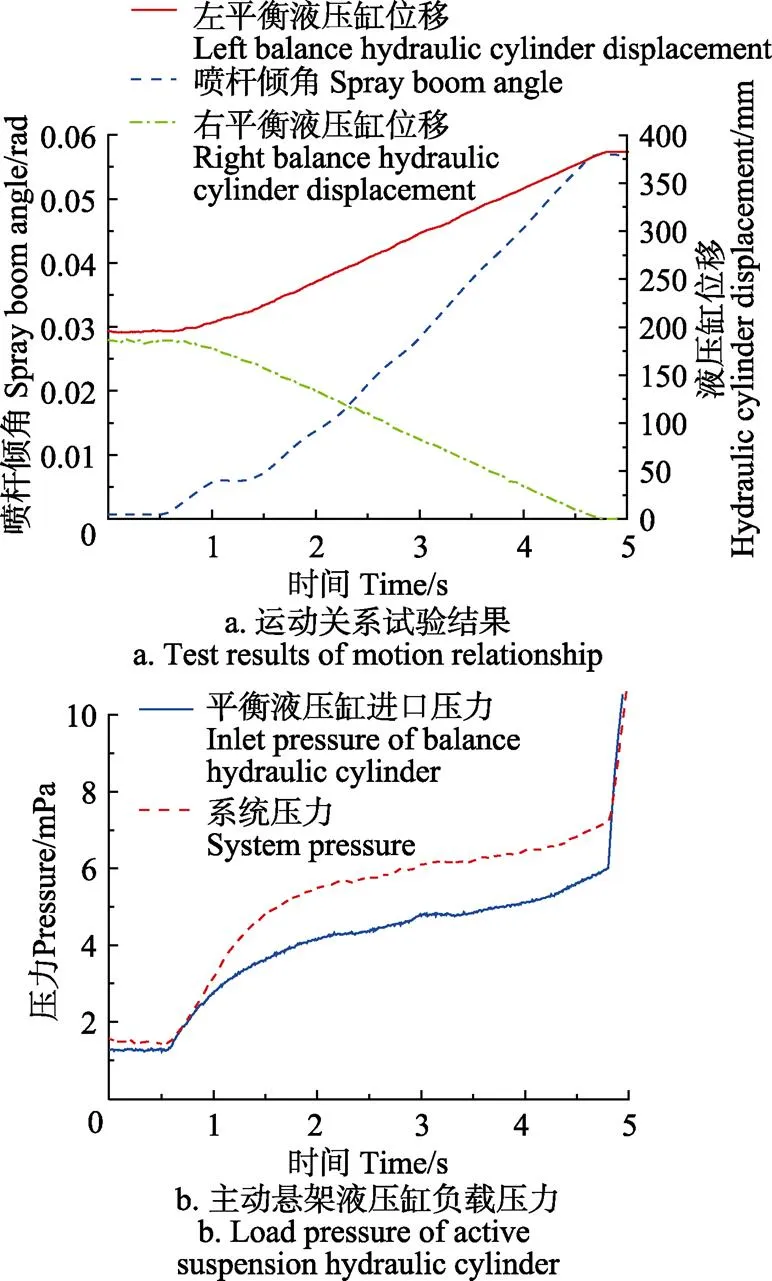
图9 喷杆主动悬架动力学实车试验曲线
由图9a分析可知,在液压系统推动下,一侧主动悬架液压缸活塞杆位移成线性增加,4.8 s时增加到最大值160 mm,伴随着一侧主动悬架液压缸活塞杆位移的增加,另一侧液压缸位移线性减小160 mm,同时喷杆倾角基本成线性增加到0.56 rad左右;由图9b可知,在喷杆主动倾斜过程中,主动悬架液压缸负载压力从1.5 MPa左右增加到6.8 MPa,此时液压缸负载力最大为1.87×104N。以上试验结果和图2仿真结果中的喷杆最大倾角0.06 rad和最大负载1.7×104N有着较好的一致性,证明了所建立的喷杆主动悬架动力学模型的正确性。
5.3 实车跟随试验
试验中,通过安装在喷杆两侧超声波传感器实时测量喷杆两侧距离地面的高度,为排除田间地面不平整或者植物冠层高度层次不齐的干扰,需以1时间间隔连续进行10次离地或者冠层高度数据采集,并且剔除掉与其他数据差值绝对值大于D的数据,最终将10次采集数据的平均值作为有效高度值,然后根据式(43)计算获得喷杆倾角反馈量。

式中1,2分别为两侧超声波测量距离,m;为两侧超声波安装距离,m。
1和D分别通过作业车速和植物高度进行确定,经过多次田间试验确定两者的取值分别为0.02 s和5 cm。
以信号发生器产生的方波、不同频率正弦车身倾角模拟信号为输入,以试验时间为横坐标,以喷杆倾角为纵坐标,得到不同控制算法、不同信号下的喷杆主动悬架控制试验曲线,如图10所示。
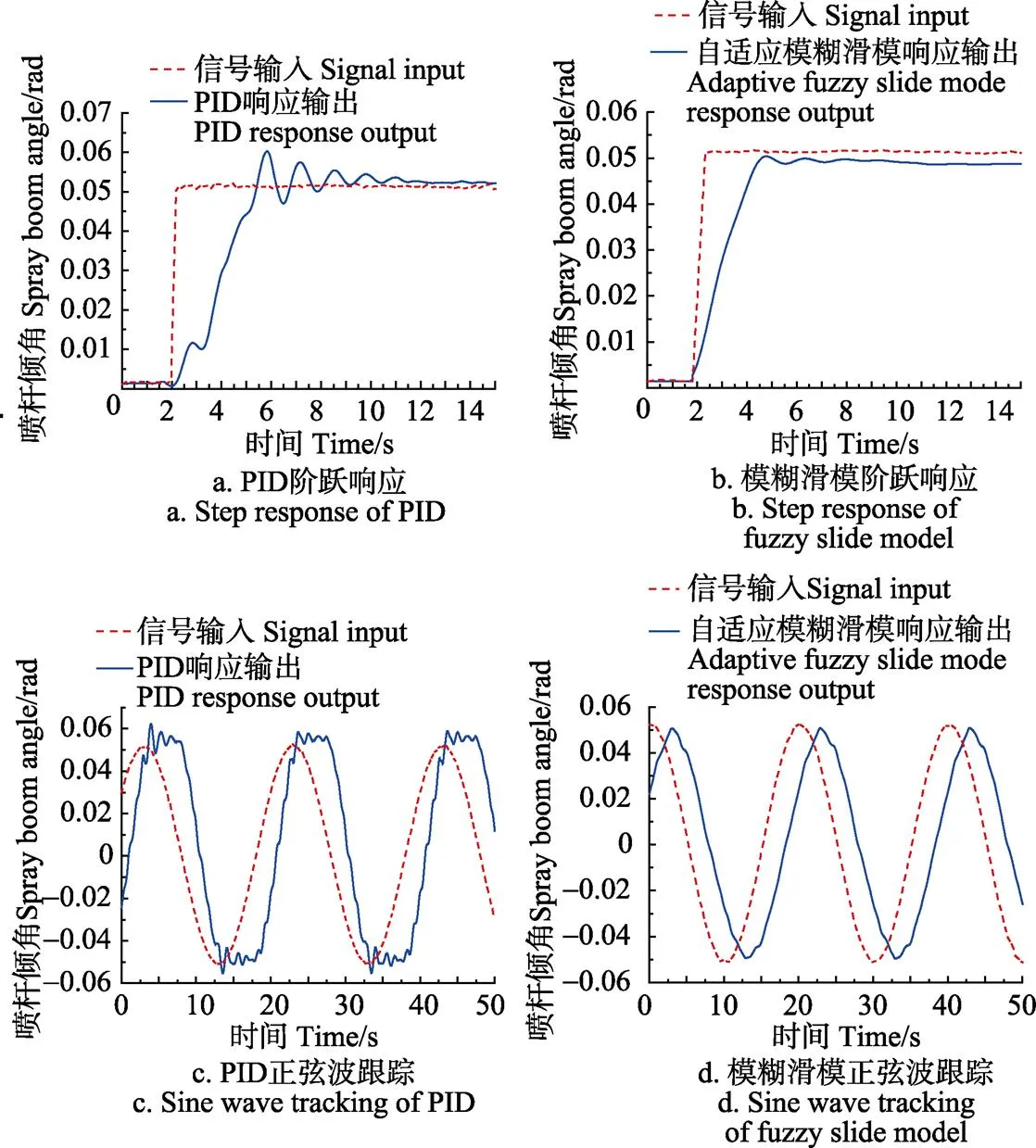
图10 喷杆主动悬架实车跟随试验曲线
由图10分析可知,输入阶跃信号时,主动悬架PID控制存在比较明显的振动过程,响应时间为4 s,超调量0.01 rad,静态误差0.002 rad,而自适应模糊滑模控制的响应时间在2 s左右,且曲线基本不存在振动,但存在静态误差0.002 rad左右;输入信号为正弦信号时,PID控制滞后和振动都较明显,而自适应模糊滑模控制的响应曲线仅滞后2 s,基本不存在振动,但存在0.002 rad的跟随误差。通过喷杆主动悬架的PID控制和自适应模糊滑模控制效果对比,可以看出本文设计的自适应模糊滑模控制相较于普通的PID控制响应速度更快、稳定性更好、精确度更高,可以满足喷杆主动悬架的控制要求。
5.4 田间试验
为了验证喷杆主动悬架隔离干扰性车身摆动的性能,在冬季时选择五征一处凹凸不平的沙土地为试验地点,进行喷杆主动悬架田间试验。喷杆主动悬架性能实车测试平台以3 km/h车速行驶,如图11所示,利用超声波传感器实时采集喷杆两侧距离地面的高度以获得喷杆倾角,利用车身倾角传感器采集车身的倾角变化,以试验时间为横坐标,以车身倾角和喷杆倾角作为纵坐标,得到主动悬架过程田间喷杆倾角试验曲线如图12所示。
由图12可知,喷雾机在田间行驶的过程中,相对于车身摆动倾角–0.015~0.015 rad,喷杆悬架主动悬架控制使喷杆倾角始终保持在–0.005~0.005 rad范围内。通过田间试验可以证明本文设计的喷杆主动悬架控制算法能够保证喷杆不受车身摆动的影响保持在平衡位置,可以满足喷雾机作业需求。

图11 喷杆主动悬架田间试验
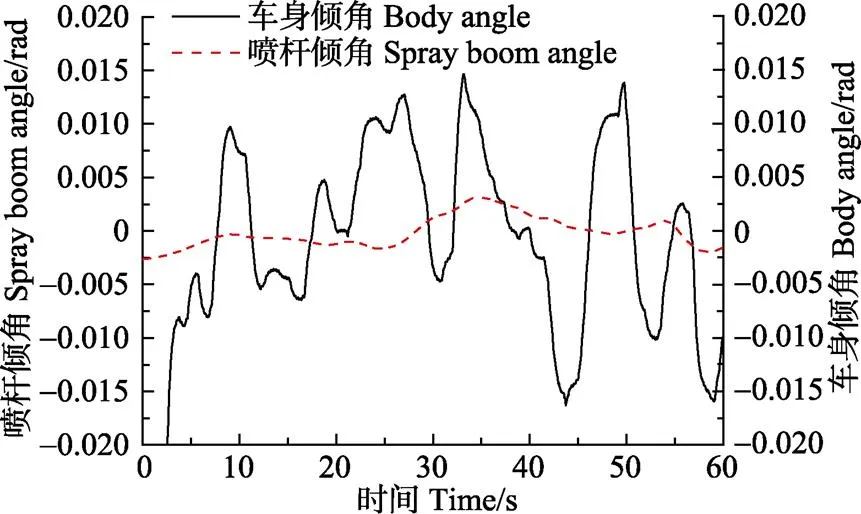
图12 喷杆主动悬架田间试验曲线
6 结 论
1)在建立了喷杆主动悬架动力学模型和喷杆主动悬架液压系统模型的基础上,充分考虑喷杆主动悬架控制特点,提出了基于自适应模糊滑模控制算法的喷杆主动悬架控制方法。通过和传统的PID控制的对比仿真验证,结果表明在喷杆主动悬架系统存在非线性、不确定性和参数时变性的情况下,所设计的自适应模糊滑模控制算法仍能保持良好的信号跟踪性能,且控制信号更平稳,没有高频抖振。
2)在系统输入为车身模拟摆动时,采用基于自适应模糊滑模控制算法的喷杆主动悬架控制方法,喷杆倾角实车跟随响应时间为2 s,跟随误差0.002 rad,相较于PID控制都有所减小;进行田间试验时,喷杆主动悬架可以使喷杆倾角保持在–0.005~0.005 rad范围内,验证了喷杆主动悬架控制的响应性、稳定性和准确性。
论文提出的基于自适应模糊滑模控制算法的喷杆主动悬架控制方法,可以很好的隔离干扰性车身摆动,保证喷杆的稳定性。
[1] Langenakens J J, Clijmans L, Ramon H, et al. The effects of vertical sprayer boom movements on the uniformity of spray distribution[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1999, 74(3): 281-291.
[2] Ramon H, Baerdemaeker J D. Spray boom motions and spray distribution: Part 1,Derivation of a mathematical relation[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1997, 66(1): 23-29.
[3] Ramon H, Missotten B, Baerdemaeker J D. Spray boom motions and spray distribution: Part 2, Experimental validation of the mathematical relation and simulation results[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1997, 66(1): 31-39.
[4] Langenakens J J, Ramon H, et al. A model for measuring the effect of tire pressure and driving speed on horizontal sprayer boom movements and spray pattern[J]. Transactions of the ASAE, 1995, 38(1): 65-72.
[5] Ramon H, Anthonis J, Moshou D, et al. Evaluation of a cascade compensator for horizontal vibrations of a flexible spray boom[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1998, 71(1): 81-92.
[6] Parloo E, Guillaume P, Anthonis J, et al. Modelling of sprayer boom dynamics by means of maximum likelihood identification techniques, Part 1: A comparison of input-output and output-only modal testing[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2003, 85(2): 163-171.
[7] Heylen W, Parloo E, Swevers J, et al. Modelling of sprayer boom dynamics by means of maximum likelihood identification techniques, Part 2: Sensitivity-based mode shape normalisation[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2003, 85(3): 291-298.
[8] 张际先. 喷雾机悬架的优化设计[J]. 农业机械学报,1995(1):50-55. Zhang Jixian. Design optimization of sprayer suspension[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 1995, (1): 50-55.
[9] 陈晨,薛新宇,顾伟,等. 喷雾机喷杆悬架系统的研究现状及发展[J]. 中国农机化学报,2015,36(3):98-101. Chen Chen, Xue Xinyu, Gu Wei, et al. Current situation and development trend of spray boom suspension system for sprayer[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization,20l 5, 36(3): 98-101.
[10] Anthonis J, Deprez K, Lannoije M, et al. Mathematical modelling and comparison of several passive vertical spray boom suspensions[J]. Theatre Journal, 2002, 54(3): 499-500.
[11] 崔龙飞,薛新宇,丁素明,等. 大型喷杆及其摆式悬架减振系统动力学特性分析与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(9):61-68. Cui Longfei, Xue Xinyu, Ding Suming, et al. Analysis and test of dynamic characteristics of large spraying boom and pendulum suspension damping system[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of CSAE), 2017, 33(9): 61-68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] Frost A R. Simulation of an active spray boom suspension[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1984, 30(84): 313-325.
[13] Marchant J A, Frost A R. Simulation of the performance of state feedback controllers for an active spray boom suspension[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1989, 43(43): 77-91.
[14] Marchant J A, Frost A R. Simulation of the performance of state feedback controllers for an active spray boom suspension[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1989, 43(43): 77-91.
[15] O'Sullivan J A. Verification of passive and active versions of a mathematical model of a pendulum spray boom suspension[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1988, 40(2): 89-101.
[16] Deprez K, Anthonis J, Ramon H, et al. PM—power and machinery: Development of a slow active suspension for stabilizing the roll of spray booms, Part 2: Controller design[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2002, 81(3): 273-279.
[17] 崔龙飞,薛新宇,丁素明,等. 双钟摆主被动悬架式大型喷雾机喷杆动力学仿真与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(2):82-90. Cui Longfei, Xue Xinyu, Ding Suming, et al. Modeling and simulation of dynamic behavior of large spray boom with active and passive pendulum suspension [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(2): 82-90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] Tahmasebi M, Rahman R A, Mailah M, et al. Roll movement control of a spray boom structure using active force control with artificial neural network strategy[J]. Journal of Low Frequency Noise Vibration & Active Control, 2015, 32(32): 189-202.
[19] Anthonis J, Ramon H. Design of an active suspension to suppress the horizontal vibrations of a spray boom[J]. Journal of Sound & Vibration, 2003, 266(3): 573-583.
[20] Hasan A R, Prehim J. Ag sprayer boom control using fuzzy controller[J]. International Proceedings of Economics Development & Research, 2013, 63(17): 83-87.
[21] 魏新华,邵菁,缪丹丹,等. 喷杆式喷雾机喷杆高度及平衡在线调控系统[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(8):66-71. Wei Xinhua, Shao Jing, Miao Dandan, et, al. Online control system of spray boom height and balance[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(8): 66-71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] Bonchis A, Corke P I, Rye D C, et al. Variable structure methods in hydraulic servo systems control [J]. Automatica, 2001, 37(4): 589-595.
[23] Benayache R, Chrifi-Alaoui L, Bussy P. Adaptive backstepping sliding mode control of hydraulic system with nonlinear unknown parameters[C]. Control & Automation. IEEE, 2010: 23-28.
[24] Guan C, Pan S. Adaptive sliding mode control of electro- hydraulic system with nonlinear unknown parameters[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2008, 16(11): 1275-1284.
[25] 刘金琨,孙富春. 滑模变结构控制理论及其算法研究与进展[J]. 控制理论与应用,2007,24(3):407-418. Liu Jinkun, Sun Fuchun. Research and development on theory and algorithms of sliding mode control [J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2007, 24(3): 407-418. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 陈雨. 高地隙喷雾机独立式立轴空气悬架设计方法与特性研究[D]. 北京:中国农业大学, 2017. Chen Yu. Research on Dynamic Characteristics of Independent Strut Type Air Suspension System for High Clearance Sprayer[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 宋锦春. 液压技术实用手册[M]. 北京:中国电力出版社,2011.
[28] Liu Jinyi, Tan Jingquan, Mao Enrong, et al. Proportional directional valve based automatic steering system for tractors[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2016, 17(5): 458-464.
[29] 李良,李锋,冯永保,等. 基于自适应模糊滑模的大型液压起竖系统控制策略研究[J]. 兵工学报,2016,37(1):71-76. Li Liang, Li Feng, Feng Yongbao, et al. Research on control strategy of large hydraulic erecting system based on adaptive fuzzy sliding mode[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2016, 37(1): 71-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 陈随英. 高地隙自走式喷雾机全工况滑转率控制方法研究[D]. 北京:中国农业大学,2017. Chen Suiying. Research on Slip-Ratio Control Method for High Clearance Self-Propelled Sprayer Over all Operating Conditions[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control of spray boom active suspension for large high clearance sprayer
Xue Tao1, Li Wei1, Du Yuefeng1, Mao Enrong1※, Wen Haojun2
(1.100083,; 2.832000,)
The large high clearance self-propelled sprayers with the advantages of high efficiency, environmental protection and intelligentization have been widely used worldwide. The spray boom suspension system is an important part of the large high clearance self-propelled sprayer, whose structure and performance have an important influence on the stability and life of the spray boom as well as the uniformity of spray. In order to solve the problems that the spray boom is easily affected by the body swing of the sprayer to generate harmful motions such as rotation, deflection, shaking and the like, the structure and function of the existing spray boom suspension systems were comprehensively analyzed, and a two-link trapezoidal spray boom suspension system was designed. In view of the problems of poor performance of isolated interference body swing of spray boom passive suspension, a hydraulic cylinder is added on the spray boom passive suspension to obtain an active suspension, which can not only take advantage of the input of external energy to actively adjust the spray boom posture, but also retain the high-frequency isolation performance of the spray boom passive suspension to avoid the high frequency response of the active suspension that consumes a lot of energy. In the light of the dynamics and the hydraulic system characteristics of spray boom active suspension, the control method based on adaptive fuzzy sliding model control algorithm of boom active suspension were developed with the spray boom inclination angle as the control object and the control objectives of fast response, stability and accuracy. On the basis of the established dynamic model of the spray boom active suspension, the dynamic characteristics of the active suspension were simulated and analyzed by Matlab/Simulink, which provides the basis for the effectiveness of the control method. A real vehicle test platform of the spray boom suspension system based on high clearance self-propelled sprayers developed by the research group were built. The dynamic characteristics of the active and passive suspensions of spray boom were tested by the actual vehicle following test and field test, and the results were compared and analyzed with the simulation results of the model. The test result shows that: when adopting the active boom suspension control method based on adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control algorithm, the step response time and the following error of the boom dip angle is 2 s and 0.002 rad, which are decreased compared to PID control. In the field test, the spray boom active suspension can keep the inclination angle of the boom in the range of –0.005-0.005 rad. The results show that the active suspension control method proposed in this paper has good responsiveness, stability and accuracy, and can effectively isolate the disturbing body swing and keep the spray rod stable. The study promote the development of theory for the spray boom active suspension in China, and it is conducive to the development of the large high clearance sprayer in China.
agricultural machinery; spraying; control; large high clearance sprayer; spray boom active suspension; adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.21.006
210.7015
A
1002-6819(2018)-21-0047-10
2018-05-23
2018-08-22
“十三五”国家重点研发计划“研发自走式高杆作物施药技术和智能化装备”(2016YFD0200705)
薛 涛,山东淄博人,博士生,主要从事车辆智能控制研究。Email:xuexintao@126.com
毛恩荣,山西运城人,教授,博士,博士生导师,主要从事农业机械设计,液压传动以及自动控制研究。Email:gxy15@cau.edu.cn
薛 涛,李 伟,杜岳峰,毛恩荣,温浩军.大型高地隙喷雾机喷杆主动悬架自适应模糊滑模控制[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(21):47-56. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.21.006 http: //www.tcsae.org
Xue Tao, Li Wei, Du Yuefeng, Mao Enrong, Wen Haojun.Adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control of spray boom active suspension for large high clearance sprayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(21): 47-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.21.006 http: //www.tcsae.org
