Survey of dose-effect relationship in Chinese materia medica
2018-11-01HsiuYingKaoYongJiang
Hsiu-Ying Kao,Yong Jiang*
1Basic Medical Colleague,Chendu University of TCM,Chendu,Sichuan,China.
Background
Dose-effect relationship of Chinese materia medica refers to the relationship between the effectofChinese medicinal on organismsand its dosage under the guidance of Traditional Chinese Medicine[1].From the point of view of modern medicine,the research on the dose-effect relationship of drugs should be obtained from the laboratory.However,the dose-effect relationship of Chinese materia medica could not be made like chemical drugs simply obtained from the laboratory because of the complex composition of single decocting piece,and the huge composition system built by several decocting pieces in a prescription for clinical use.At the same time,on the basis of accurate differentiation of syndrome,disease and constitution,Chinese materia medica has the characteristics of multi-efficacy and multi-target,which makes the analysis and determination of curative effect lack for the specific experimental data.Some Chinese materials have two-way regulating effect,such as routine dosage of Atractylodes Macrocephala can fortify the spleen and stop diarrhea,but large dosage can defecate.Appropriate Chinese medicinal combination such as‘mutual reinforcement’, ‘mutual assistance’can enhance the efficacy.The different processing,planting region,harvesting,decocting and dosage methods of Chinese medicinal can also affect the exertion of the efficacy.All these complex factors make the research on dose-effect relationship of Chinese materia medica late and difficult.
Survey of Dose-Effect Relationship in Chinese Materia Medica
Research ideas and methods of dose-effect relationship in Chinese materia medica
Because the research on dose-effect relationship of Chinese materia medica is a new discipline,many experts have put forward research ideas and methods.Yao Yingzhi et al.indicated that the dose-effect relationship of Chinese medicinal was mostly in normal distribution[2],and the two ends were Yang medicinal and Yin medicinal respectively.Yang medicinal showed great pungency and heat and Yin medicinal showed great bitterness and cold,so the dose was relatively small.When the medicinal tending to be warm and cool was in the center area and the dose was relatively larger.The Chinese medicinal used in viscera for ‘sealing’as tonification with smaller dose,while used in bowels for“rush down”as purgation with larger dose.The dose for a specific efficacy was smaller at the main meridian entry of Chinese medicinal,while larger dose for the secondary meridian entry.The dose started from small amount and increased by degrees till producing minimum effect for the Chinese medicinal with toxic feature.Fan Xinsheng et al.indicated that the dose-effect relationship of Chinese materia medica should take ‘prescription-medicinal, disease-syndrome [3],constitution’as the basis for research,mainly involving thetheoreticalstudy ofsingle medicinalmaterial,medicinalcombination and prescription.Sovereign,minister,assistant,courier and medicinal combination to build a prescription did not have a linear dose-effect relationship,and the dose of medicinal could shift the dose-effect relationship of a prescription.Fu Yanling et al.indicated that this researches for dose-effect relationship of prescription-medicinal should include seven aspects,such as the research of historical development of prescription-medicinal dose,textual research of classical formula medicinal dose and so on[4].Tong Xiaolin et al.tended to take clinical evaluation as the core of research,integrated with the literature,clinical,pharmacodynamic,pharmacodynamic substances and supramolecular structure researches,formed a scientific theoretical framework of‘medicine-based dose strategy according to syndrome differentiation’ and ‘medicinal-based dose-effect relationship regular pattern’[5].Fu Yanling et al.indicated ‘two principles and fifteen strategies’to control prescription dose for Chinese medicinal[6].Li Bingmin et al.mentioned the study of dose-effect relationship should focus on the‘constitution-dose-efficacy’and ‘treatmentbased on constitution differentiation’which were regarded as the determination basis of controlling prescription medicinal dose,so as to reduce the possibility of side effect as much as possible.In recent years,Systematic Biology has developed rapidly[7].Deng Haishan et al.evaluated prescription medicinal dose,efficacy and curative effect by Metabolomics method, thus recognizing the relationship between the microscopic material basis of Chinese medicinal and Systematic Biochemistry[8].
Literature researches of dose-effect relationship in Chinese materia medica
Ancient dose studies.Traditional Chinese Medicine has been developed more than two thousand years,a large numberofrelevantliterature hasbeen constantly accumulated.In view of the evolution of the dose of Chinese medicinal,Fu Yanling et al.took Treatise on Cold Damage Disease as the research basis,selected 50 commonly used medicinal materials as research cases[9],proceeded data statistics and analysis from representative works of ancient and modern medical experts as well as prescriptions of Chinese medicinal from some hospitals,obtained the dose evolution characteristics shown in the development of Traditional Chinese Medicine He also demonstrated that the weight unit ‘Liang’described in Treatise on Cold Damage Disease was about current 13.8g and found the best medicinal utilization of 1 weight unit ‘Liang’was 9g through the study of experimental data of decocting of medicinal materials[10].
Lin Yiqun et al.proceeded Meta-analysis and statistical analysis on the literature of actual measured weight data of non-metric unit weight of Chinese medicinal from 1984 to 2015[11],for instance found 1 volume unit of “Sheng”of Pinellia Ternate described in Treatise on Cold Damage Disease was about 105.23 g and so on.
Researchesin thecategoriesofmedicalworks,medicalcasesand prescription medicinal.Wang Huanan et al.took the Chinese Medicine Prescription Dictionary as the basis of data research[12],collected the prescriptions related to Evodia Rutaecarpa,statistically analyzed and summarized the influences of combination,dose,preparation form,processing of medicinal and authentic medicinal and other factors on the efficacy,and preliminarily found that it was used for warming the middle and regulating Qi with medium and large dose 15 g-30 g,but moving Qi,drying dampness,dispersing the stagnant,warming the meridian to activate blood with medium and small dose 9 g-15 g etc.There were other 28 kinds of Chinese medicinal including Ginseng and Pinellia Ternate etc.similar to this research.Shang Erxin et al.took the prescriptions medicinal in Synopsis of Prescriptions of the Golden Chamber as the research basis, and preliminarily explored its diversified characteristics and the dose-effect relationship through statistical analysis[13].
Zhang Wei systematically sorted out the relevant articles of Radix Glycyrrhizae in Treatise on Cold Damage Diseases,and statistically analyzed the efficacy relationship in its dose [14],related prescription medicinal numbers,main drug or not in a formula,single oral dosage and other factors.There were similar studies to this research for other medicinals such as Cinnamon Twig,Keel,Bupleurum and so on.Pei Xiangjun et al.statistically analyzed Chinese TraditionalMedicine clinical observation literature and case studies of Evodia Rutaecarpa in recent 17 years[15],found that its threshold dose of was 2 g and the therapeutic window was between 2 g and 30 g.For examples,usual dose from 6 g to 12 g was taken for patients with the symptoms of nausea,3g to 5g for sour regurgitation.Li Chenhui et al.sorted out the cases of prescription of Ephedra,Apricot Kernel[16],Gypsum and Licorice Decoction mainly from ancient and modern books and literature,medical records of physicians of past dynasties and so on,accomplished the research of ‘syndrome,dose,efficacy’based on the main applicable syndromesofthis prescription by mathematicalstatistics and expert investigation method.For instance the wind-heat invading the lung syndrome,it was necessary to increase large dose of Gypsum obviously when fever reached 39°C.Zhang Wenxian et al.found that the dose of Adix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata was applied according to five stages of syndromes as Yang deficiency[17],Yang debilitation,exuberant Yin repelling Yang,Yang collapse and dying when the physician Li Ke used Frigid Extremities Decoction and its categorized formula,the dose was from 1g to 10g for Yang deficiency and 45 g to 90 g for Yang collapse.Besides,the combination and decoction process for Adix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata should be paid much more attention,such as 60 g of prepared Radix Glycyrrhizae was added when the dose of AdixAconiti Lateralis Preparata was more than 30 g.
Researches of physicians by semi-structured interviews.A better understanding of the physician’s thinking aboutdose-effectrelationship while using Chinese medicinal could be obtained by this method.Ni Shenglou et al.discussed the dose-effect relationship of Chinese medicinal in prescriptions and the safety of large dose medication in Treatise on Cold Damage Diseases in the semi-structured interview with the physician Li Ke[18],completed the dose statistical analysis based on the selected 50 commonly used medicinal materials from the prescriptions in Li Ke's Experiences in Emergency,Critical and Difficult Diseases,and found that the dose of 16 kinds of medicinal material reached more than 100g to produce certain efficacy which accounting around 30%of the totalmedicinalmaterials. Similar medical researches also included the physicians Zhu Liangchun,Zhou Yuzhu,Wang Qi and so on.
Experimental researches of dose-effect relationship in Chinese materia medica
Du Qiu et al.studied the dose-effect relationship and its effective mechanism of Cistanche Deserticola on moistening intestines and relaxing the bowels in constipated rats with Yang deficiency syndrome[19],statistical analysis of the experimental results showed that the middle and high doses of experimental group presented obvious effect on moistening intestines and relaxing the bowels and the clinical threshold dose was 20 g·d-1,Table 1 shown as one of the research results.
Wang Junming et al.studied the ethanol extract of Tripterygium Wilfordii and Lysimachia Chrysantha with the combination ratio of 2:1,the results showed that the ethanol extract could inhibit A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro when the concentration was between 50 ug/mL and 400 ug/mL[20].Liu Yuhui et al.fed the rats with type 2 diabetes damp-heat syndrome with the prescription Pueraria [21],Scutellaria,and Coptis Decoction for 10 weeks and took blood samples to measure blood glucose,insulin and otherrelated indicators,the result showed the dose of the prescription increased and its effect on each indicator would also be improved simultaneously within a specific range.The best dose range of efficacy was from 18.15 g·kg-1to 24.15 g·kg-1,Table 2 shown as one of the research results.
Zhao Yanling el al.found the largest dose of experimentgroup ofChi-Dan-Tui-Huang Decoction presenting potent efficacy on the rats with alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate induced cholestatic hepatitis without toxicity,Figure 1 shown as one of the research results[22].
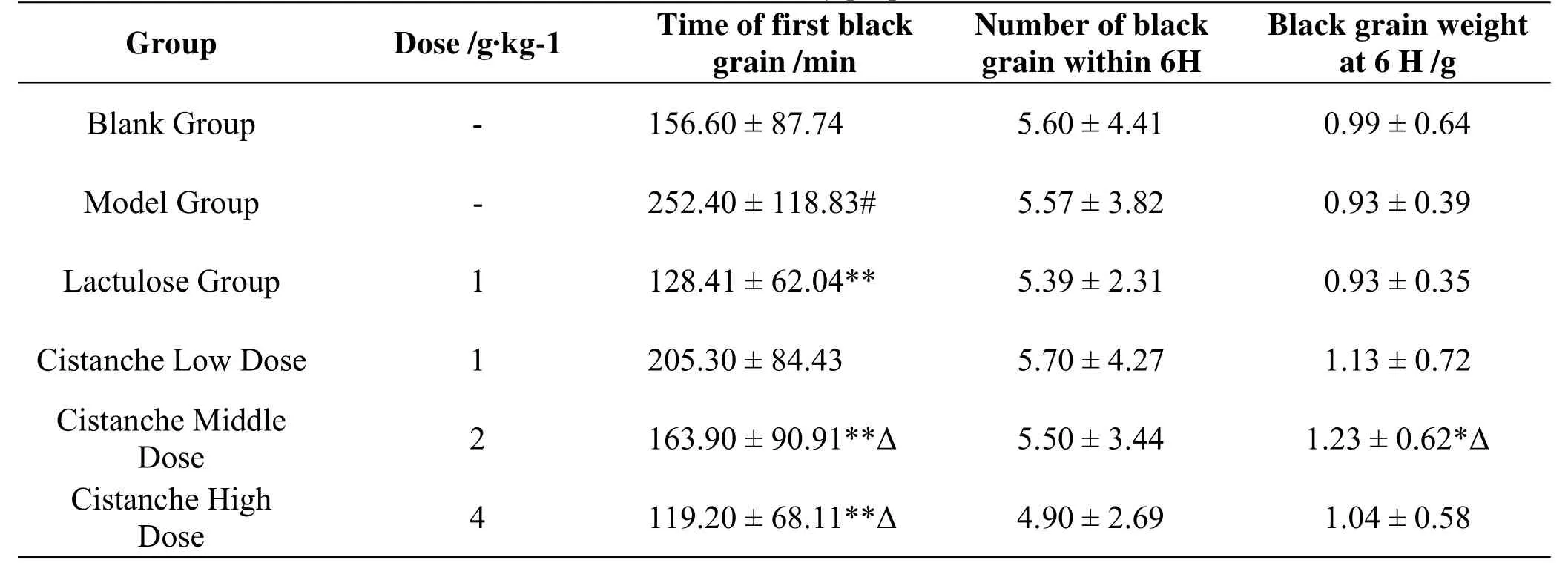
Table 1 Effect of Different Doses of Cistanche on Defecation of SD Rats with Yang Deficiency Constipation(n=10,mean±S.D)[19]

Table 2 The Influences of FPG,FIns,IR for Pueraria,Scutellaria,and Coptis Decoction Treatment on the Rats with Type 2 Diabetes Damp-Heat Syndrome(n=6, mean±S.D).[21]

Figure 1 SerumALT,ALP,AST,TBIL,DBIL and γ-GT levels in 9 group of rats treated with or without CDTHD.
Clinicalresearchesofdose-effectrelationship in Chinese meteria medica
Gong Yuxia et al.collected 60 patients with STC(slow transit constipation)[23],randomly divided them into three groups and were treated respectively with gradient doses of Fructus Aurantii and Atractylodes Macrocephala,it was found that the scores of the three groups were higher than those before treatment,and the high dose group(30 g Aurantium Aurantii,70 g Atractylodes Mcrocephala)was obviously higher than the other two groups after the analysis and calculation of the scoring scale,Table 3 shown as one of the research results.
Han Yaowei et al. collected 42 patients with Bronchopneumonia with wind-heat obstructing the lung syndrome,randomly divided them into three groups which all treated with Azithromycin and Leucomycin and given gradient doses respectively of the prescription Ephedra[24],Apricot Kernel,Gypsum and Licorice Decoction for a 10-day observation cycle,and the results showed that the treatment effect of middle and high dose group was much better than low dose group.
The evaluation method of dose-effect relationship in Chinese materia medica
Different from the scoring scale,Li Bingtao et al.studied the dose-effect relationship of the prescription Pueraria,Scutellaria,and Coptis Decoction in the treatment of type 2 diabetic rats with dampness-heat syndrome by using the method ofMetabolomics [25].On the basisof experimental data analysis and dose standard conversion,it was found that the threshold dose(20%effective)of this prescription was 94.1 g per person and the clinical high dose(80%effective)is 118.0 g per person,thus reduced the application of large dose as far as possible for clinical purpose.Huang Zhi-qiang et al.indicated an advanced method to deal with metabonomic data from the serum of treatment on the rats with type 2 diabetes by Pueraria,Scutellaria,and Coptis Decoction(GQD)which aimed for building a model to evaluate the efficacy of Chinese materia medica with specific parameters,the result was the middle dose group presenting the best dose-effectrelationship and schematic diagram is illustrated as Figure 2[26].

Table 3 First Time Defecation for the 3 Groups of STC Patients after Treatment of FructusAurantii andAtractylodes Macrocephala(mean±S.D)
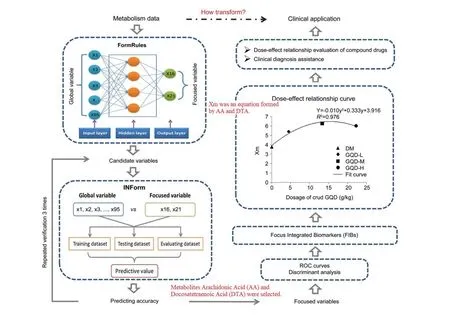
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the “Focus”mode of integrated biomarker identification
Researches of Chinese Materia Medica ComponentsCombination and Dose-Effect Relationship
It is impossible to study all the components of Chinese meateria medica under current technological methods because of its very complex components.However,the main effective components of Chinese medicinal have been preliminarily found at this stage,Zhang Boli et al.thus put forward the concept of Chinese materia medica components combination which should be guided under the theory ofTraditionalChinese Medicine and traditional prescription medicinal combination[27].On the premise of mastering the pharmacodynamic substances and the mechanism of action in traditional Chinese prescriptions, the effective medicinal components from the prescription could be specifically screened out to cure the applicable disease and syndrome.On this basis,research and production methods of medicinal components combination were formulated.
Definition of Chinese materia medica components was,a group of effective components of Chinese materia medica which was a chemical substance with properties of Chinese medicinal,or some known components had certain properties of Chinese medicine[28].Therefore,the components could be regarded as the appearance of Chinese medicinal in the microcosmic world with the characteristics of four Qi and five flavors and its corresponding dose-effect relationship[29].Because the components and relative working mechanism were just able to be studied precisely with pertinency to the appointed disease and syndrome[30],there would be more research literature but relatively few clinical trials due to limited funds and manpower.Guo Yafang et al.analyzed and studied the pharmacodynamic components of the prescription Minor Purgative Decoction in Treatise on Cold Damage Diseases[31],a total of 13 types medicinal components were found and the combination,processing,dose and other factors would lead to the changes of pharmacodynamic components.Li Haozheng et al.studied the five effective components of the prescription Chinese Angelica Blood-Supplementing Decoction by the methods of bone marrow cell culture and animal experiment of rats with dual deficiency of Qi and blood syndrome[32],and found that red blood cells could be significantly increased when the combination ratio of Astragalus Total Saponins and Angelica Sinensis Polysaccharides was in 6:4 after screening and exploring the relevant test data,Table 4 shown as one of the research results.

Table 4 Red Blood Cell Numbers and Hb Weights after the Treatment on the Rats by ChineseAngelica Blood-Supplementing Decoction and its Components Combination(mean±S.D)[32]
Conclusion
The dose-effect relationship of Chinese materia medica was scattered in ancient and modern literature and did not form a theoretical system,it only becomes a new discipline with various new technological methods in recent decades.The direction of clinical research was based on a large number of literature and statistical analysis,as well as doctors interviews.Experimental and clinical studies were carried out to clarify the dose-effect relationship of Chinese materia medica,combination and prescriptions. The introduction of Metabonomics provided a new way of thinking for efficacy evaluation.Chinese materia medica components and its combination were developing in a view of microcosm.
In the basic research of ancient literature,although the medical case monographs can reflect the theory and thinking of doctors,the study is less made because ancient Chinese words are simple and concise which are quite difficult to be understood.If we can explore the dose-effect relationship of Chinese medicinal from these medical case monographs,we can better inherit the experience of relevant doctors in ancient China.The development and innovation of Traditional Chinese Medicine depend on the clinical curative effect,and the study of dose-effect relationship of Chinese materia medica can make clinicians think clearly when they use medicinal combination or prescriptions in order to improve clinical level.
1. Fu YL.The core scientific problemsofthe dose-effect relationship between China and China and their research ideas.Beijing J Tradi Chin Med 2016,35:513-516.
2. Yao YZ,Yi G,Fan XS.An Exploration into Regularities in Relationship between Dosage and Effect of Chinese Drugs.J Nanjing Uni Chin Med 2009,25:10-12.
3. Fan XS,Duan JA,Wang ZY, et al.On characteristic properties of TCM dose-effect relationship.Chin J Tradi Chin Med Pharm 2009,24:270-274.
4. FuYL,CaiKZ,SongJ.Documentaryand theoretical researches about medicinal dose-effect relationship in TCM formulas.J Beijing Uni Tradi Chin Med 2010,33:601-605+640.
5. Ton XL,Jiao YL,Lian FM,et al.Some thoughts aboutthe key pointsin theresearch ofthe dose-response relationship.Global Chin Med 2012,5:401-404.
6. FuYL,WangQ,WangZY.Discussionon Traditional Chinese Medicine Clinical Prescription Dosage Controlling.J Tradi Chin Med 2015,56:1351-1354.
7. Li BW,Zheng YF,Xu XX, et al.Study on the Application of“Constituion-dosage-efficacy”Rationale.J Yunnan Uni Tradi Chin Med 2015,38:25-27.
8. Deng HS,Duan JA,Shang EX, et al.Research advances of metabonomics and application in the study of dose-effect relationship of prescriptions.Int J Pharm Res 2009,36:198-203.
9. Fu YL,Zhang L,Song J,et al.Study on clinical dosage valley of commonly used Chinese herbs in 2000 years.J Beijing Uni Tradi Chin Med 2013,36:581-585+649.
10.Fu YL. Solve the millennium mystery of prescription dosage.Chin News Tradi Chin Med 2016,6:1-2.
11.Lin YQ,Mu LC,Li QW,et al.Literature analysis on the measured weights of unmeasured unit drugs.Chin J Tradi Chin Med Pharm 2018,33:740-743.
12.Wang HN.Study on multiple factors controlling the effectoffructusrubrain compound formula.Chengdu Uni TCM 2007.
13.Shang EX,Fang XS,Duan JA,et al.Study on the change ofprescription dosage and effectin JinGuiYaoLue. J Nanjing Uni Chin Med 2009,25:13-16.
14 Zhang W.DiscussiononMedicationRulesof Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma in Shang Han Lun Based on Dose-response Relationship.Chin J Inf Tradi Chin Med 2016,23:52-55.
15 Pei XJ,Ni SL,Jin MC,et al.Analysis of Dosages of Wuzhuyu in Modern Clinical Literature.Liaoning J Tradi Chin Med 2018,45:525-528.
16 Li CH.A study on the quantity-effect relationship of gump decoction based on medical case.Beijing Univ Chin Med 2017.
17 Zhang WX,Jia B.Thispaperdiscussesthe characteristics of lixilaidecoction from the relationship of quantity and effect.J Tradi Chin Med 2017,58:1157-1159.
18 Ni SL,Yan F,He LQ,et al.Discussion on Characteristics of Chinese Herbs Commonly Used by Old TCM Doctor LI Ke in Clinic from Perspective of Dose-Effect Relationship.Liaoning J Tradi Chin Med 2014,41:50-53.
19 Du Q,Wu Z.Mechanism and dosage-effect relationship of Cistanche on yang deficiency constipation model.Cent South Pharm 2016,14:23-27.
20 Wang JM,Sun YY,Zhang YY et al.Component ratio and dose-effect relationship of Tripterygium wilfordii combined with Lysimachia christina in inhibiting A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro.Chin J Gerontol 2016,36:14-16.
21 Liu YH,Wang YS,Wang YY et al.Study of Gegen Qinlian Decoction on Type 2 Diabetes in Rats and the Dose-effect Relationship.Chin J Exp Tradi Med Formulae 2013,19:258-261.
22 Zhao YL,Ma X,Wang JB,et al.Large dose means significant effect-dose and effect relationship of Chi-Dan-Tui-Huang decoction on alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestatic hepatitis in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med 2015,15:104。
23 Gong YX,Wang H,Qian HW,et al.An Analysis of Effect of Combination of Zhishi and Baizhu on Treating Slow Transit Constipation.Henan Tradi Chin Med 2018,38:1066-1069.
24 Han YW,Li XM,Shi CR.Clinical study on the dose-effect relationship of maxingganshi decoction in treating 42 cases of infantile bronchial pneumonia.Acta Chin Med Pharmacol 2013,41:62-64.
25 Li BT,Zhang QY,Tu J,et al.The study of the dose-effect relationship based on the metabonomics overall therapeutic effect of Gegenqinlian decoction for STZ-induced diabetes rats.Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med 2014,30:5-8.
26 Huang,ZQ;Fan,XM;Wang,YM,et al.A new method to evaluate the dose-effect relationship of a TCM formula Gegen Qinlian Decoction:"Focus"mode of integrated biomarkers,ACTA Pharmacol Sin 2017,38:1141-1149.
27 Zhang BL,Wang YY,Shang HC.Theories and Methods Used in the Research of Modern Chinese Medicine by Drug Combination.Contin Med Educ 2006,20:89-91.
28 Liu LM,Chen X,Yue GX,et al.Some thoughts on definition of“Chinese materia medica components”.Chin Tradi Herb Drugs 2018,49:2489-2495.
29 Yan B,Sun GX,Sun WY,et al.Research methods and thoughts of four-property theory for Chinese medicine.Cent South Pharm 2016,14:572-580.
30 Deng CQ,Huang XP.Research thinking of effective ingredients compatibility of Chinese medicine based on prescription compatibility theory and pharmacological mechanism.J Tradi Chin Med Univ Hunan 2011,31:3-6.
31 Guo YF.Study on the correlation between the pharmacodynamic components and the multicomponent factors of xiaochengqi decoction.Beijing Univ Chin Med,2018.
32 Li HZ.Compatibility and Experiment Research Progress of Angelica Sinensis Decoction of supplementing of blood.Master.Shanxi Univ Chin Med 2015
杂志排行
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- The progress in the chemical constituents of the genus Picrasma during 2007-2017
- Application of LC-MS based glutathione-trapped reactive metabolites in the discovery of toxicity of traditional Chinese medicine
- Clinical observation of Furongtongmai capsule on the lower extremity Atherosclerotic Occlusive Disease after Intervention Operation
- Clinical experience in treating 78 cases of upper limb edema after breast cancer operation by WenYang HuoXue Washing Prescription
- Effect of TongFengNing Decoction on UricAcid Levels and Xanthine Oxidase Activity in Hyperuricemia Rats
- Toxic effects of BuGuZhi and feasibility analysis of ways to synergistic and attenuated
