FIR数字滤波器零极点灵敏度分析及优化实现
2018-10-18庄陵马靖怡王光宇关鹃
庄陵,马靖怡,王光宇,关鹃
FIR数字滤波器零极点灵敏度分析及优化实现
庄陵,马靖怡,王光宇,关鹃
(重庆邮电大学移动通信技术重庆市重点实验室,重庆 400065)
针对有限字长效应导致滤波器零极点的位置偏移问题,基于状态空间实现结构研究FIR数字滤波器零极点对系数误差的灵敏性。不同于IIR滤波器,FIR滤波器状态空间模型中的系统矩阵具有亏损性。引入亏损矩阵广义特征向量分析极点的灵敏性,导出灵敏度表达式,并依据相似变换理论找寻最佳变换矩阵,提出FIR滤波器零极点灵敏度的优化实现。理论推导及仿真实验表明,FIR滤波器极点对系数误差敏感度较高,且所提优化实现方案能够降低灵敏度。
FIR数字滤波器;状态空间实现;零极点灵敏度;亏损矩阵;广义特征向量
1 引言
有限字长(FWL, finite word length)效应导致的系数量化会影响实际应用中滤波器的性能,使零极点位置发生偏移,从而改变频率响应特性。研究系数变化的灵敏度有多种方式,一类基于衡量传递函数关于参数的扰动[1-3],另一类基于测度系统零极点位置的偏差[4-5]。某些情况下相比于量化引起传递函数中的误差,零极点位置偏移对滤波器性能产生的影响更为重要,例如,在设计陷波滤波器时需要保证零点位置的精确性,或对于闭环系统,其稳定性决定于极点(特别是主导极点)位置[6]。
值得注意的是,以上对零极点灵敏度的分析均基于IIR滤波器,而FIR滤波器相较于IIR滤波器有容易实现线性相位特性、适合多采样率转换等优点,广泛应用于4G移动通信系统、视频与图像处理等领域。然而,FIR滤波器与极点灵敏度有关的系统矩阵为亏损矩阵,其特征向量系是线性相关的,不具有完备的特征子空间,因此,利用非亏损矩阵特征向量的独立性分析极点灵敏度的方法已不再适用[14]。本文引入广义模态理论,利用系统矩阵的一组满足酉正交条件的广义特征向量系及其伴随向量系,对FIR滤波器的极点灵敏度进行理论推导及分析,同时给出FIR滤波器零极点灵敏度的优化方法。
2 FIR滤波器状态空间实现背景理论

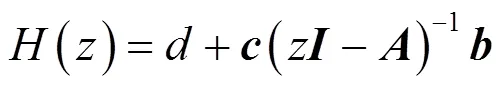

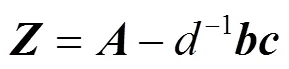

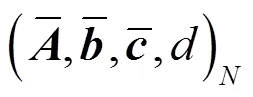
3 零点灵敏度及其最小化




则式(7)亦可表示成
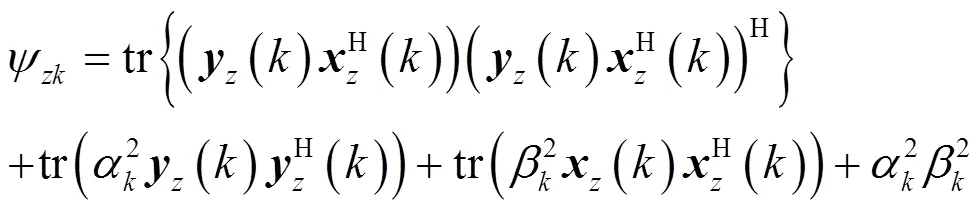
滤波器总的零点灵敏度为
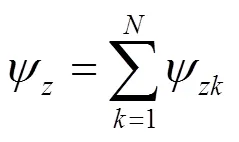


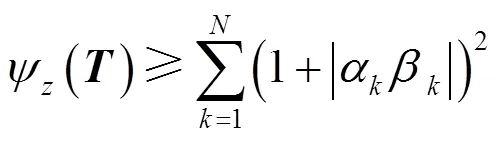
4 极点灵敏度及其优化
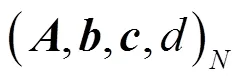
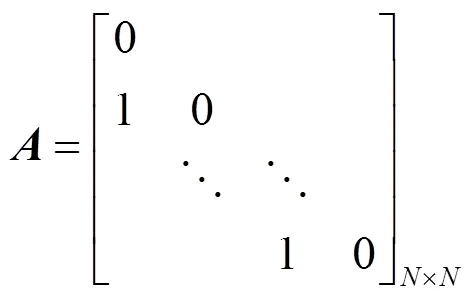
4.1 系统矩阵A的特征值扰动分析
系统矩阵是一个重亏损矩阵,由其结构可知存在如下形式的可逆矩阵

使

其中,是的Jordan标准型。下面对矩阵的列向量进行归一化
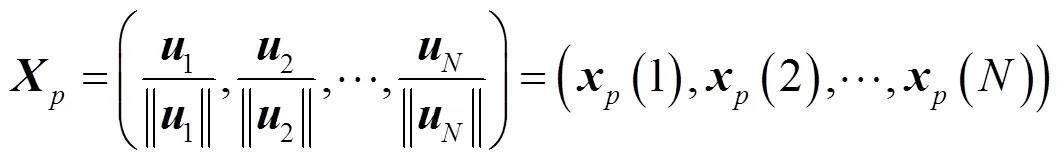

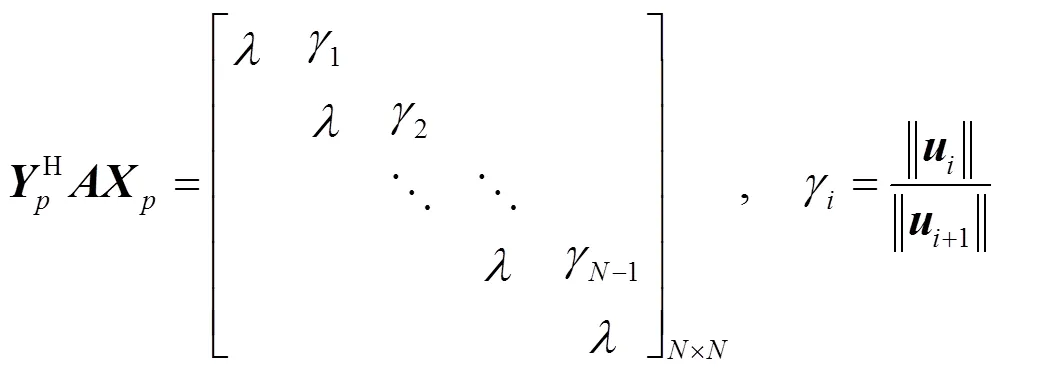
则矩阵受扰动后其特征值的表现形式如定理1所示。
定理1 若系统矩阵的元素产生扰动


则有
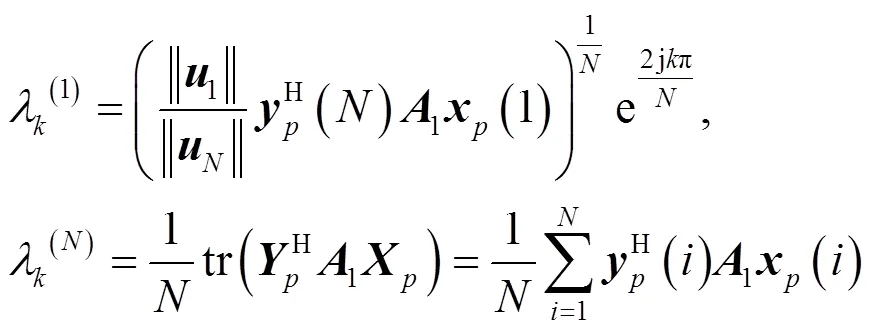


根据文献[15]可推导出

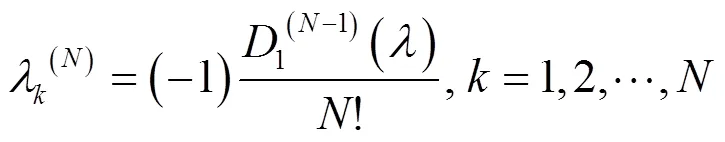
由特征值与矩阵迹和行列式关系的定义可得

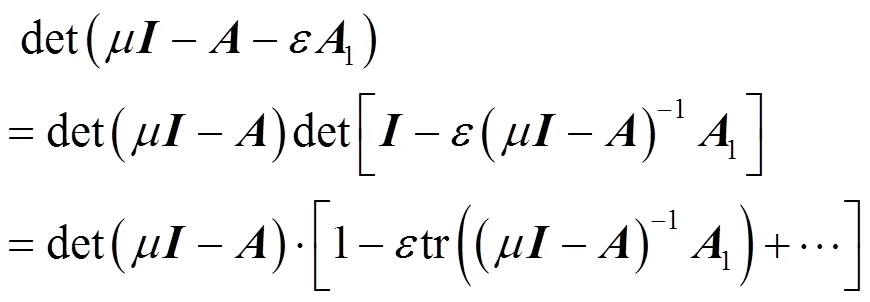
对比式(22),可得

引入广义特征向量矩阵
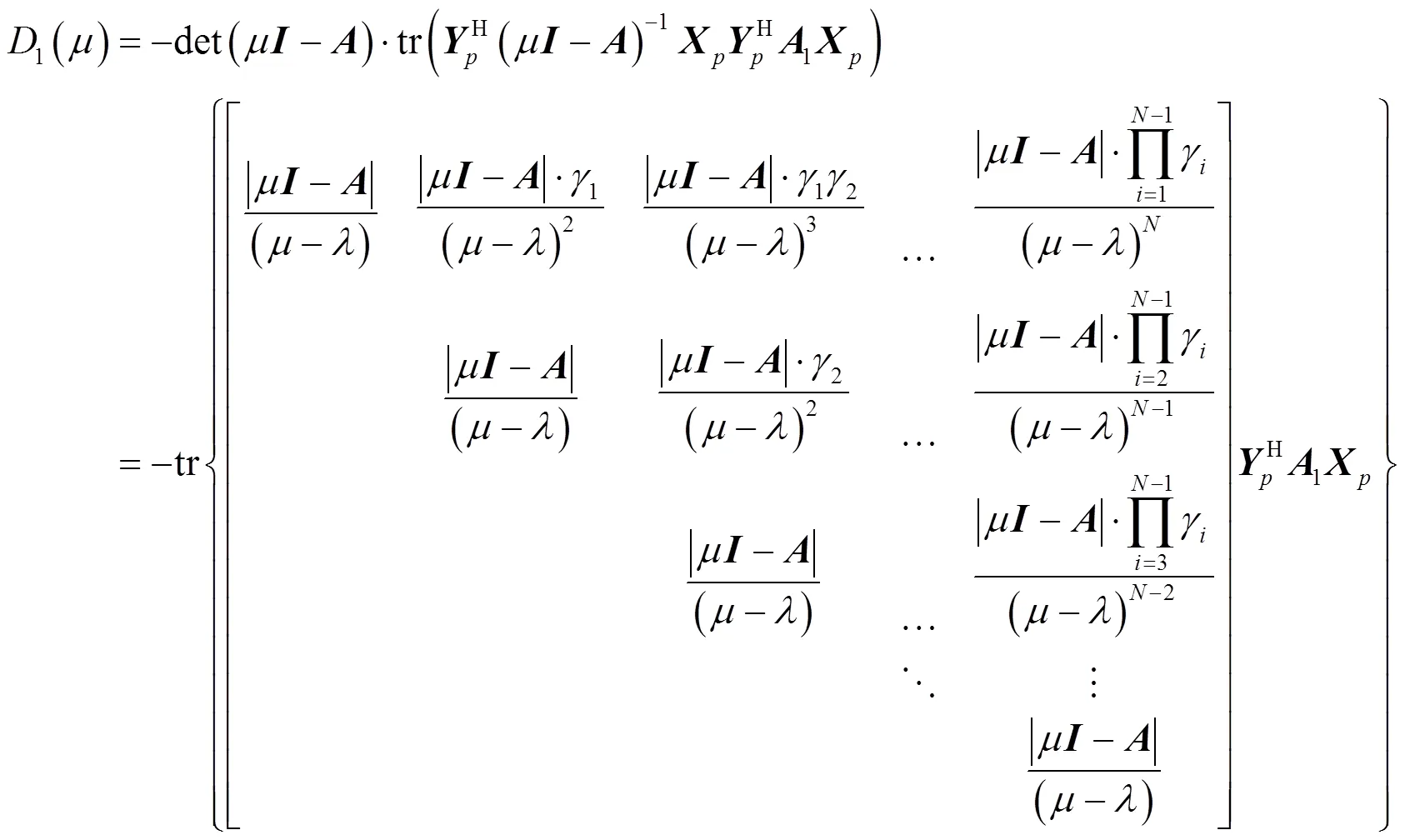

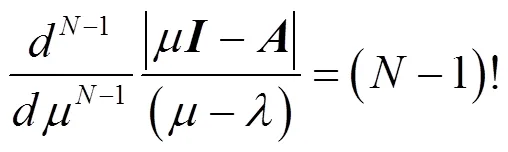
则有
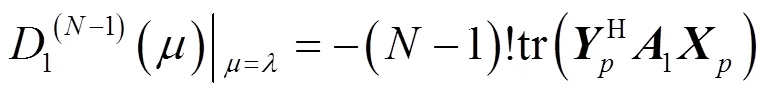
将式(29)和式(31)分别代入式(23)和式(24),即可证得式(20)。
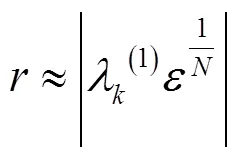
4.2 极点灵敏度优化

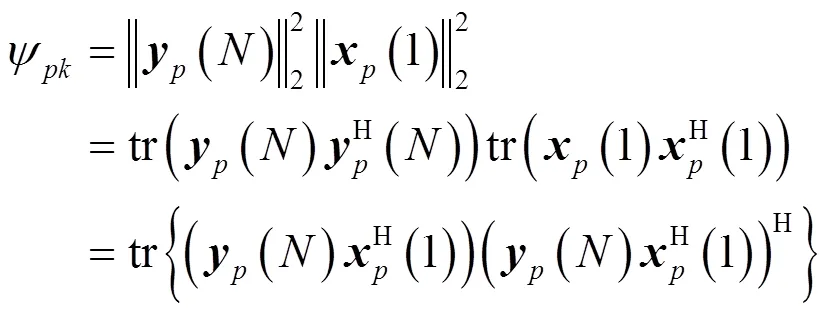
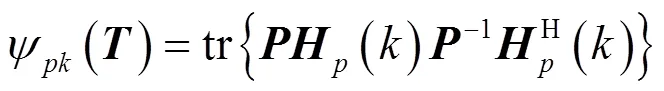
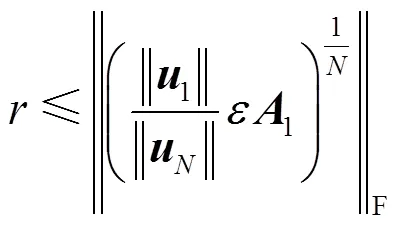
5 零极点灵敏度加权优化
在优化系统零极点灵敏度时,通常不能得到同时使两者达到最优的状态空间实现。最小化零点灵敏度可能优化不了极点灵敏度,甚至会恶化极点灵敏度。然而存在极点与零点扰动都会影响到系统性能的情况,或系统对某些极点(零点)上的扰动更为敏感。对零极点加上特定权重,可以权衡极点与零点灵敏度之间的优化。记系统的加权零极点灵敏度为


其中
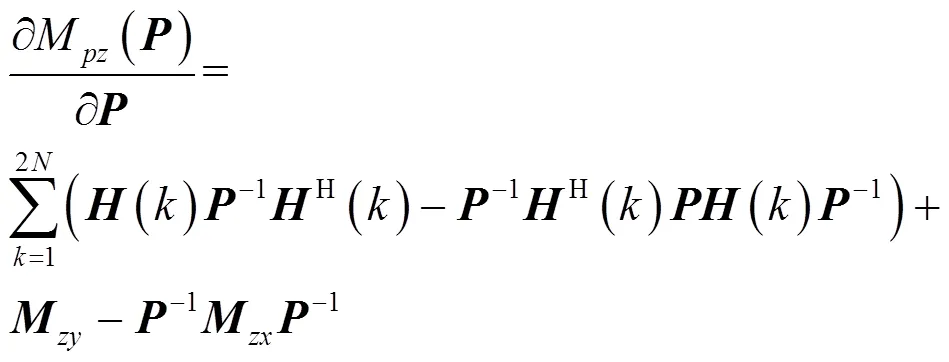
因式(38)等价于
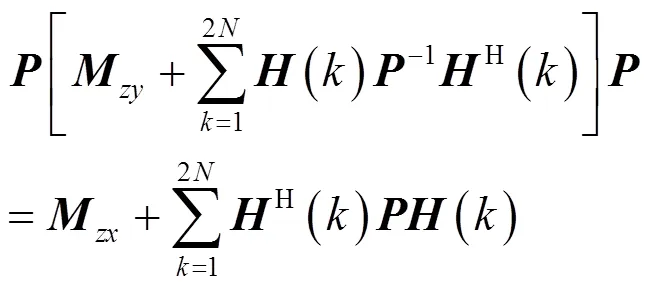
可令
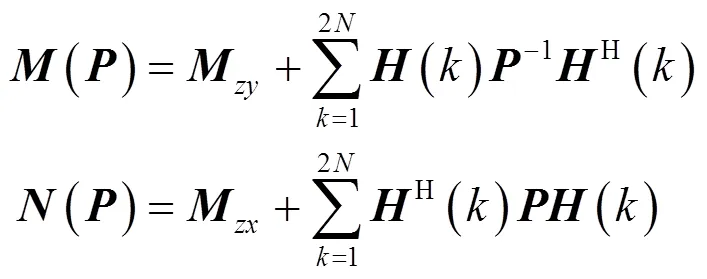
整理式(39)得
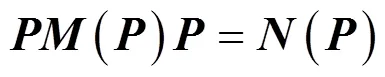

迭代终止条件

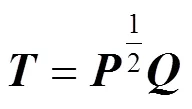
6 仿真实例
下面以23阶线性相位FIR低通数字滤波器为例,利用matlab仿真平台分析零极点的灵敏度以及零极点位置偏移对滤波器频响特性的影响,并比较3种优化方案的优化性能。

表1 23阶线性相位下IR低通滤波器系数h(n)



表2 不同实现的零极点灵敏度
6.1 系数扰动下的灵敏度分析

序号精确解近似解 1,2−0.693 10.097 4i−0.683 70.094 0i 3,4−0.640 60.276 3i−0.633 00.274 9i 5,6−0.546 30.443 2i−0.535 30.435 5i 7,8−0.408 10.586 7i−0.398 00.563 8i 9,10−0.211 50.674 3i−0.231 10.650 2i 11,12−0.023 00.694 5i−0.046 50.679 9i 13,140.171 60.661 7i0.140 40.675 7i 15,160.321 00.577 3i0.317 50.612 7i 17,180.449 80.488 7i0.471 00.504 3i 19,200.574 10.356 6i0.589 60.358 6i 21,220.654 70.201 6i0.664 50.186 2i 230.702 40.000 0i0.690 10.000 0i

图1 状态空间实现下滤波器的零极点扰动分布
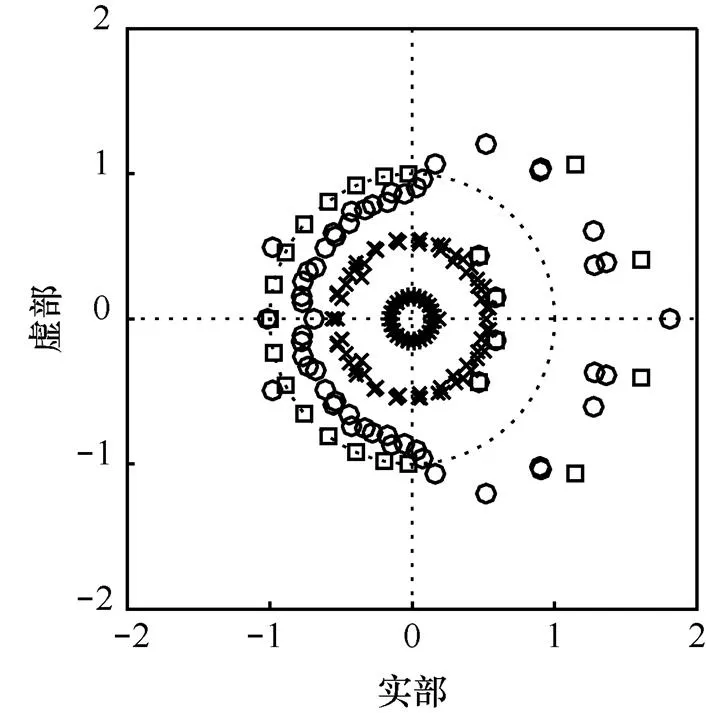
图2 状态空间实现下滤波器的零极点扰动分布

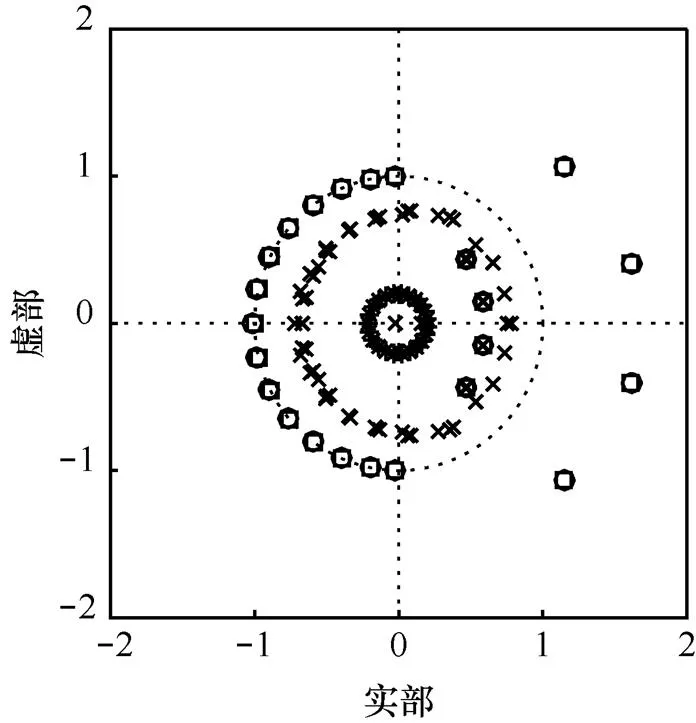
图3 状态空间实现下滤波器的零极点扰动分布

图4 状态空间实现下滤波器的零极点扰动分布
由于系统特性直接与系统函数零极点的分布有关,零极点位置偏移会改变系统原有的频响特性。图5~图12分别对应图1~图4中扰动实现的幅频响应与相频响应变化。

图5 状态空间实现下滤波器的幅频响应变化

图6 状态空间实现下滤波器的相频响应变化
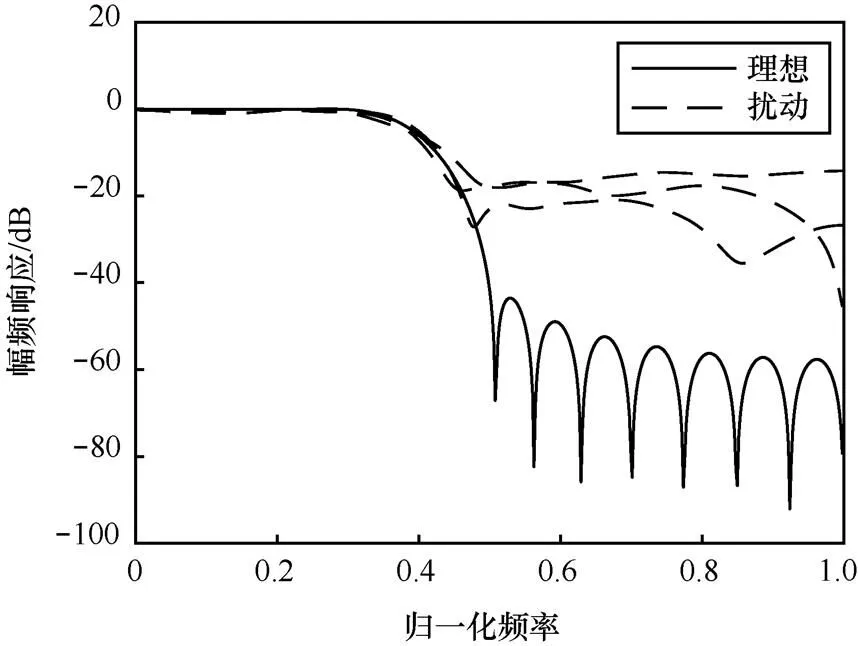
图7 状态空间实现下滤波器的幅频响应变化

图8 状态空间实现下滤波器的相频响应变化
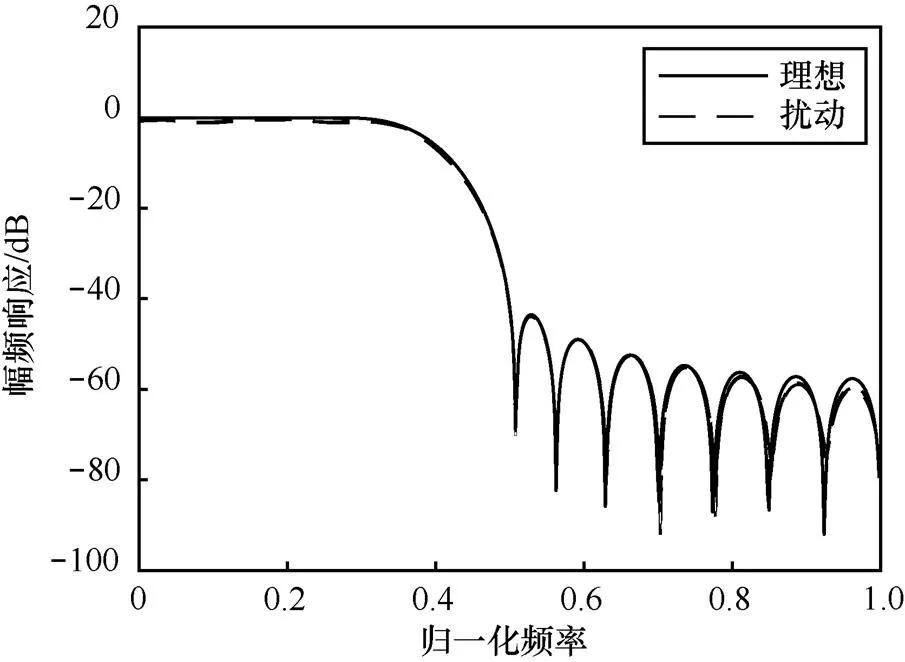
图9 状态空间实现下滤波器的幅频响应变化

图10 状态空间实现下滤波器的相频响应变化

图11 状态空间实现下滤波器的幅频响应变化

图12 状态空间实现下滤波器的相频响应变化

6.2 系数量化下的灵敏度分析

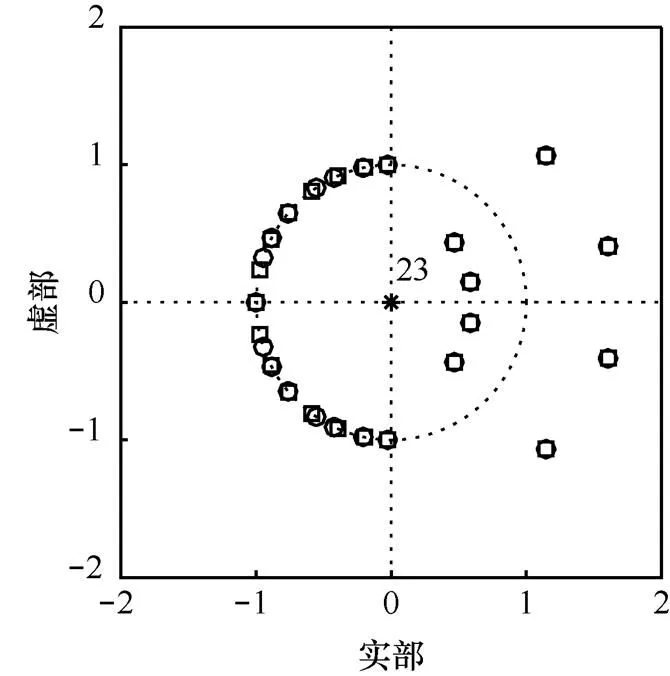
图13 状态空间实现R下滤波器的零极点分布比较(Bc=10 bit)

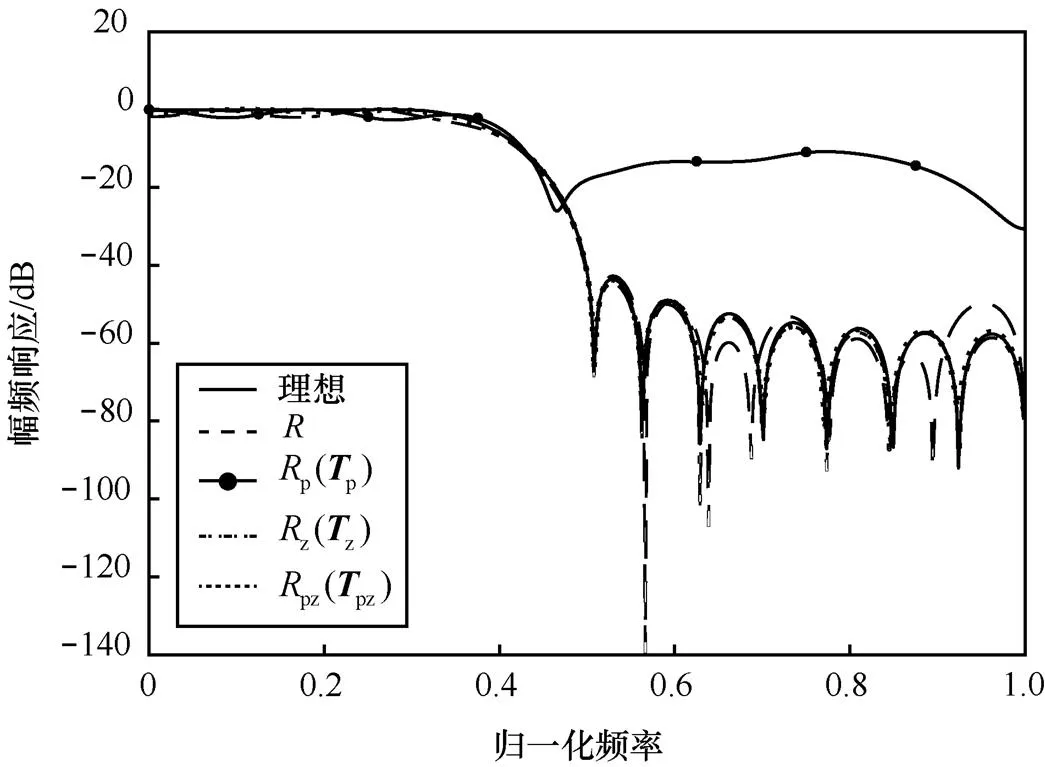
图14 幅频响应比较(Bc=10 bit)实线-理想;虚线-R;
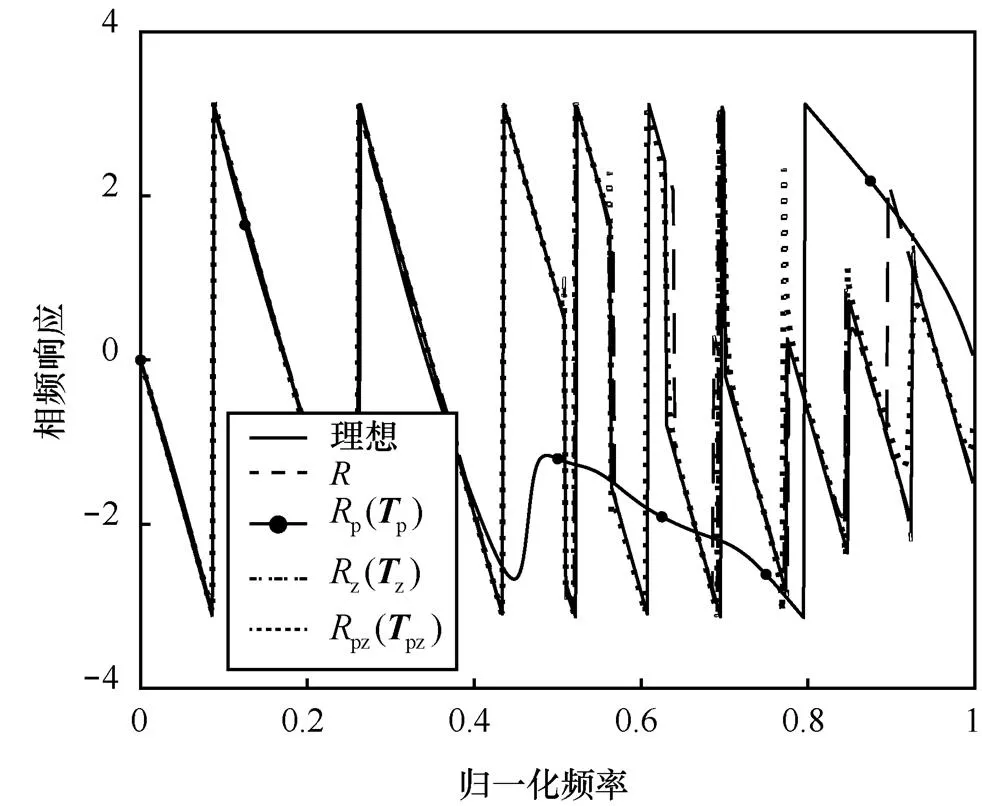
图15 相频响应比较(Bc=10 bit)实线-理想;虚线-R;

7 结束语
本文基于状态空间实现结构讨论FIR滤波器的零极点灵敏度,引用广义特征向量对亏损系统矩阵的特征值进行扰动分析,推导出极点灵敏度表达式,并提出FIR滤波器极点、零点及加权零极点灵敏度的优化方案。数值实例表明,由于系统矩阵的亏损性使FIR滤波器极点敏感于系数变化,零极点位置偏移会影响滤波器的频响特性,仿真结果验证了所提方案的有效性,即优化实现能够降低滤波器零极点的灵敏度。
[1] TAVSANOGLU V, THIELE L. Optimal design of state-space digital filters by simultaneous minimization of sensitivity and round off noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 1984, 31(10): 884-888.
[2] YAN W Y, MOORE J B. On-sensitivity minimization of linear state-space systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 1992, 39(8): 641-648.
[3] LI G, GEVERS M, SUN Y X. Performance analysis of a new structure for digital filter implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 2000, 47(4): 474-482.
[4] WILLIAMSON D. Round off noise minimization and pole-zero sensitivity in fixed-point digital filters using residue feedback[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1986, 34(5): 1210-1220.
[5] LI G. On pole and zero sensitivity of linear systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 1997, 44(7): 583-590.
[6] 徐巍华, 吴俊, 褚健. 有限字长数字控制器的一种极点灵敏度优化结构[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2000, 17(4): 613-618.
XU W H, WU J, CHU J. A class of pole sensitivity optimization structures of an FWL digital controller[J]. Control Theory and Applications, 2000, 17(4): 613-618.
[7] LI G, LIM Y C, HUANG C G. Very robust low complexity lattice filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58 (12): 6093-6104.
[8] 于爱华, 黄朝耿, 李刚, 等. 一种新型低复杂度的IIR格型滤波器[J]. 电子学报, 2013, 41(9): 1703-1709.
YU A H, HUANG C G, LI G, et al. A new class of low complexity IIR lattice filters[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2013, 41(9): 1703-1709.
[9] MANTEY P. Eigenvalue sensitivity and state-variable selection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1968, 13(3): 263-269.
[10] SKELTON R E, WAGIE D A. Minimal root sensitivity in linear systems[J]. Journal of Guidance Control and Dynamics, 1984, 7(5): 570-574.
[11] GEVERS M, LI G. Parameterizations in control, estimation and filtering problems: accuracy aspects[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1993.
[12] HINAMOTO T, DOI A, LU W S. Weighted pole and zero sensitivity minimization for state-space digital filters[C]//2015 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS). 2015: 2193-2196.
[13] HINAMOTO T, DOI A, LU W S. Minimization of weighted pole and zero sensitivity for state-space digital filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2016, 63(1): 103-113.
[14] 徐涛, 于澜, 鞠伟, 等. 计算亏损系统模态灵敏度的逐层递推演算方法[J]. 力学学报, 2008, 40(2): 281-288.
XU T, YU L, JU W, et al. Recursive solution on layer after layer for sensitivity analysis of modes on defective linear vibration system[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2008, 40(2): 281-288.
[15] 陈塑寰, 徐涛, 韩万芝. 线性振动亏损系统的矩阵摄动理论[J]. 力学学报, 1992, 24(6): 747-753.
CHEN S H, XU T, HAN W Z. Matrix perturbation for linear vibration defective systems[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 1992, 24(6): 747-753.
Analysis and optimal realization of pole-zero sensitivity for FIR digital filters
ZHUANG Ling, MA Jingyi, WANG Guangyu, GUAN Juan
Chongqing Key Lab of Mobile Communications Technology, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Chongqing 400065, China
Aiming at the deviation of pole and zero in filters which caused by the finite word length (FWL) effects, the sensitivity of pole and zero for FIR digital filters to coefficient errors was studied based on the state-space model. Unlike the IIR filter, the system matrix in state-space model of the FIR filter was defective. A set of generalized eigenvectors of defective matrix was introduced to analyze the pole sensitivity and derive the measure expression, and optimal realizations with respect to pole-zero sensitivity for FIR filters were proposed by finding optimal transformation matrices according to the similarity transformation theory. Theoretical analysis and simulation experiments show that the poles of a FIR filter are more sensitive to coefficient errors, and the proposed optimal realizations can reduce the sensitivity.
FIR digital filter, state-space realization, pole and zero sensitivity, defective matrix, generalized eigenvector
TN713.7
A
庄陵(1978-),女,重庆人,博士,重庆邮电大学副教授,主要研究方向为通信与信息处理多载波技术、滤波器组理论。

马靖怡(1993-),女,陕西汉中人,重庆邮电大学硕士生,主要研究方向为滤波器结构设计、多载波滤波器组技术。
王光宇(1964-),男,贵州兴义人,博士,重庆邮电大学教授,主要研究方向为高速多载波通信理论。

关鹃(1991-),女,山西运城人,重庆邮电大学硕士生,主要研究方向为移动通信多载波调制技术、滤波器组理论。
2018−01−09;
2018−05−20
中兴5G高速连续接入技术方案与试验系统研发基金资助项目(No.2016ZX03001010-004)
10.11959/j.issn.1000−436x.2018167
The Research and Development Project of ZTE 5G High-Speed Continuous Access Technology and Testing System (No. 2016ZX03001010-004)
