天然橡胶机械化采收锯切功耗影响因素试验
2018-09-03张春龙盛希宇张顺路张俊雄
张春龙,盛希宇,张顺路,高 金,袁 挺,张俊雄,李 伟
天然橡胶机械化采收锯切功耗影响因素试验
张春龙,盛希宇,张顺路,高 金,袁 挺※,张俊雄,李 伟
(中国农业大学工学院,北京 100083)
锯切式割胶是天然橡胶机械化采收的重点研究方向之一,该文以锯切式割胶装置为研究对象,开展锯切功耗影响因素研究。该文设计了天然橡胶锯切功耗测量试验台,研究了锯片直径、锯片齿数、切割电机转速、进给速度对锯切式割胶装置切割功耗的影响。构建了以切割电机转速、进给速度及锯片齿数为因素,以切割功耗为指标的割胶刀具切割功耗影响因素模型,并进行了三因素三水平的正交试验。试验结果表明,各因素对切割功耗影响的主次顺序为锯片齿数、进给速度、电机转速、锯片直径;同时得到在给定因素水平下,切割参数最佳组合为进给速度为30 mm/s、电机转速为500 r/min、锯片齿数为10齿,此时电机切割功耗最小,功耗值为2.597 J。该研究可为天然橡胶机械化采收装置的设计提供参考。
机械化;优化;收获;天然橡胶;切割功耗;正交试验
0 引 言
橡胶树是中国热带地区的重要经济作物[1]。天然橡胶因其优良的综合性能,在航空航天等国防领域具有不可替代的作用,是一种不可或缺的战略资源[2-3]。近年来天然橡胶价格大幅下降,同时受胶工短缺与老龄化的影响,部分民营橡胶林出现了弃管、弃割的现象[4-5],给国内天然橡胶产业带来了大量的经济损失。目前,人工割胶依然是获取天然橡胶的主要方式[6],开展天然橡胶机械化采收技术研究,已经迫在眉睫。
机械化割胶中切削参数的选择至关重要,切削参数将影响机械割胶装置的切割性能。目前,国内外针对农林作物切割特性的研究较多。Zhong等[7]研究了木薯茎秆的切割力学特性,研究表明切削角和加载速率对切削强度的影响显著。Igathinathan等[8-9]使用数字扭矩扳手和标准的万能试验机搭建了玉米茎秆切割试验台,测定了玉米茎秆的峰值应力。Chandio等[10]研究了加载速率对小麦和稻草力学特性的影响,结果表明,通过降低加载速率,可以节省剪切能量,有助于降低脱粒能量。Zhao等[11]研究了高茬玉米秸秆的切削性能,其主要研究了切削速度和切削角对最大切削阻力和切削功率的影响。Ghahraei等[12]研究了红麻杆切割系统并进行了切割试验,试验结果表明旋转切割速度对切割扭矩有显著影响。杨永福等[13-15]对竹类的切削性能及加工性能进行了研究,研究发现竹类断面、径向与横向切削力明显不同。郭莹洁[16-18]研究了不同参数对毛竹的切削质量、单位切削功以及超前劈裂的影响。马永康等[19]研制了柠条收割机切割器并进行了试验,试验表明切割器的总功耗会随着枝条密度增加而增加。赵湛等[20]研究了不同切割参数对超级稻单茎秆切割力学性能的影响,研究表明切割功耗会随着切割速度的提高而降低。此外还有针对甘蔗[21]、大麻[22]、苎麻[23]、苜蓿[24]、荔枝[25]等农作物茎秆的切削力和切削功耗的研究。不同农作物的生物特性不同,相同切割参数对不同作物的影响也不同,且针对橡胶树皮切割功耗的研究尚属空白,因此本文针对天然橡胶树皮进行独立试验研究。
本文构建了以切割电机转速、进给速度及锯片齿数为因素,以切割功耗为指标的锯切式割胶装置切割功耗影响因素模型,设计了天然橡胶树皮锯切功耗测量试验平台。根据木材切削原理,对割胶装置的运动切割参数进行了单因素试验和多因素正交试验,获得了不同因素对试验指标的影响效果。针对切割功耗,获得了在给定因素水平下的切割参数最优组合方案,为天然橡胶机械化采收装置的小型化、轻量化设计提供指导和理论依据,对节约机械割胶能耗和增加机械割胶设备林间作业时长有参考意义。
1 材料与设备
1.1 试验材料
试验材料采样于海南省儋州市国营西培农场西青农场三十一队橡胶林,品种为7397品系,树龄8 a,采样时间为2018年1月19日,经保湿处理后于2018年1月24日在中国农业大学工学院农业机器人实验室进行试验。所截取树段树皮为未开割的原生皮,所截取树段上、中、下树围分别为500、510、530 mm,树段圆柱度较好,树皮结构较均匀。根据割胶技术要求,在实际割胶作业中,阳刀割线斜度自左上方向右下方倾斜25°~30°,阴刀割线斜度自左上方向右下方倾斜40°~45°。在实际调研中获知,海南当地割胶主要采用阳刀割胶。根据阳刀的斜度要求与木材切削原理,割胶过程近似于横-端向切割[26]。本文主要考虑阳刀割胶,锯切割胶示意图如图1所示。
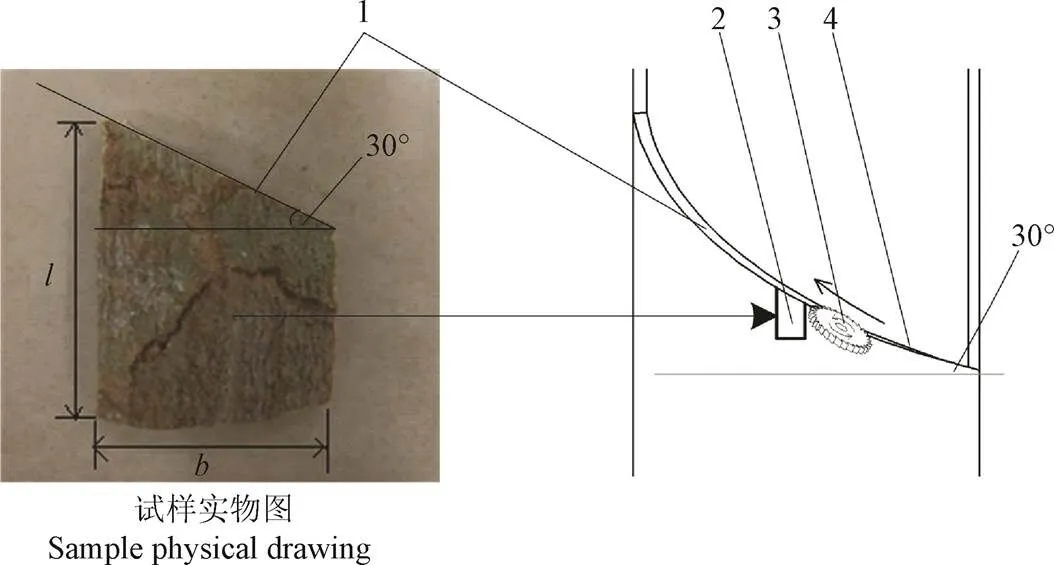
1.待割面 2.试样 3.锯片 4.已割面 1.Uncut surface 2.Sample 3.Saw blade 4.Cut surface
所制备试样的长度(树段轴线方向)、厚度(树段径向方向)和宽度(树段圆周方向)分别为50、5.5和30 mm,根据实际切割工况,再将试样切割至如图1所示的梯形,其中梯形斜边所在平面为待割面。所采试样均用保鲜膜包裹后放入密封袋内密封保存,且均在切割试样被截取后的2 h内完成试验,以保证试样的生物特性不发生变化。
1.2 锯切式割胶装置
试验用锯切式割胶装置主要由传动部件、电机、切割部件及控制部件组成。为提高传动效率,避免造成能量损失,同时考虑到天然橡胶树皮的切割阻力,采用电机轴通过刚性联轴器直接带动转轴的方式。锯片则通过螺母垫片紧固在转轴上,便于更换。
由于橡胶林无供电设施,电动割胶装置多由直流电机提供动力。为模拟实际生产情况,试验用锯切式割胶装置选用57闭环步进直流电机,额定电压为24 V,额定扭矩为2.2 N·m,电机伸出轴直径为8 mm。该电机性能稳定、发热小,降低了电机发热对试验带来的能量损失。
为提高切割效率,本文选用多齿锯片。割胶耗皮量农艺要求为1~2 mm,为保证割胶效果,锯片厚度应大于耗皮量最大值,因此选用的锯片厚度为3 mm。在锯片角度参数方面,根据木材切削原理[26],锯片前角选择一般为15°~35°,但天然橡胶树皮结构复杂,包含粗皮、砂皮、黄皮、水囊皮等,各皮层之间软硬不同,经综合考虑,锯片前角取为25°,后角取为15°。锯片材料选用硬度和耐磨性较好的钨钢。图2为锯切式割胶装置。

1.步进电机 2.控制器 3.联轴器 4.锯片
1.3 功耗测量试验台
天然橡胶锯切切割功耗测量试验台总体结构如图3所示,主要包括:由北京时代超群电器科技有限公司所生产的步进电机同步带线性模组滑台,定位精度为0.3 mm,滑块线速度为0~500 mm/s;泉州冠航达电子科技有限公司生产的KG-3015高带宽隔离变送器,检测信号范围DC0~2 A,输出信号范围DC0~5 V,采样频率为1 kHz,精度为0.004 A;胜利DM6234P+测速仪,测量范围为2.5~99 999 r/min,分辨力为0.1 r/min,基本精度为±(0.05%+1);游标卡尺、单片机、24 V直流稳压电源、十字平口钳、计算机、锯切式割胶装置等。
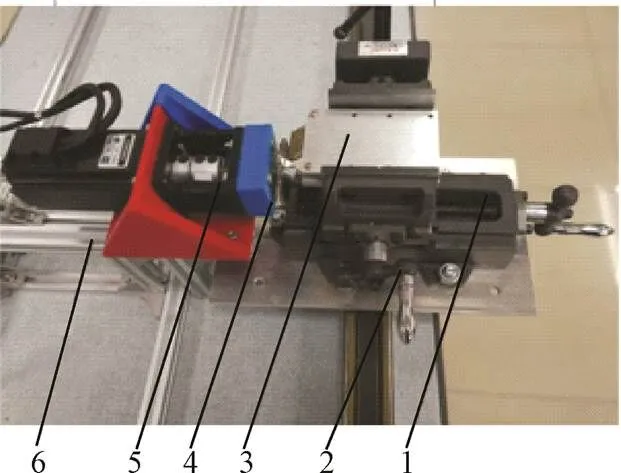
1.十字平口钳 2.滑台 3.夹持装置 4.切割试样 5.割胶装置 6.支座
试验在锯切功耗测量试验台上进行,割胶装置固定在支座上,试验过程中保持固定不动;十字平口钳以及夹持装置固定在滑台上,滑台可提供不同的进给速度。试验通过割胶装置不动、试样运动的方式实现对试样的切割。为避免试样在宽度方向上受力变形,导致试样的生物特性发生变化,夹持装置在厚度方向夹持试样,并将试样水平旋转30°,使得试样被割面与滑台进给方向保持平行,同时确保在切割时为横-端向切割,以模拟实际割胶工况。
直流稳压电源与隔离变送器、锯切式割胶装置串联,隔离变送器输出端连接单片机,由单片机进行AD采集,并且通过RS232串口与计算机实时通讯,进行数据的传输与储存。试验过程中,首先将电机调至预设转速,并用测速仪进行检测,然后用计算机控制单片机开始进行AD采集,再控制滑台以预设速度靠近试样直至完成一次切割,滑台的进给速度即为切割进给速度。通过调节十字平口钳,将每次切割的耗皮量控制在2 mm;每次的切割厚度即试样厚度5.5 mm。功耗测量试验台的进给速度与电机转速均可测可调;单片机与计算机实时通讯,可实时获得电路中的瞬时电流,进而计算出切割功耗。
2 试验方案
2.1 试验指标

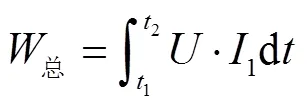
式中为电机两端电压,V;1为切割时流经电机的实时电流,A;1为切割时采样开始时间,s;2为切割时采样结束时间,s;为切割时间,s。
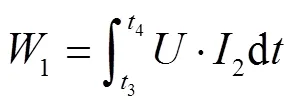
式中2为空载时电机电流,A;3为空载时采样开始时间,s;4为空载时采样结束时间,s。
总和1采样时间相同,则切割试样所消耗的能量为

2.2 试验因素
影响锯切功耗的影响因素主要有2个,一个是锯片切割线速度,另一个是锯片每齿进给量z,其中
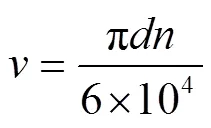
式中为锯片切割线速度,m/s;为锯片直径,mm;为切割电机转速,r/min。
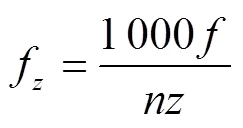
式中f为每齿进给量,mm;为切割进给速度,m/min;为锯片齿数。
根据式(4)、(5),锯片直径、电机转速、进给速度、锯片齿数会对锯片的切割功耗产生一定影响。
所以选取割胶装置电机转速、进给速度、锯片齿数以及锯片直径进行单因素试验,每个因素取3个水平,每个水平重复3次。
2.3 多因素试验设计
在单因素试验结果与分析上,选取3个因素的3个水平进行正交试验,用以寻求参数的最优化组合,选取L9(34)正交表,试验指标为切割功耗。
3 结果与分析
3.1 单因素试验
3.1.1 锯片直径
锯片最小直径定为32 mm,为了拉开因素水平区间,将锯片直径分别定为32、42和52 mm,如图4a所示。
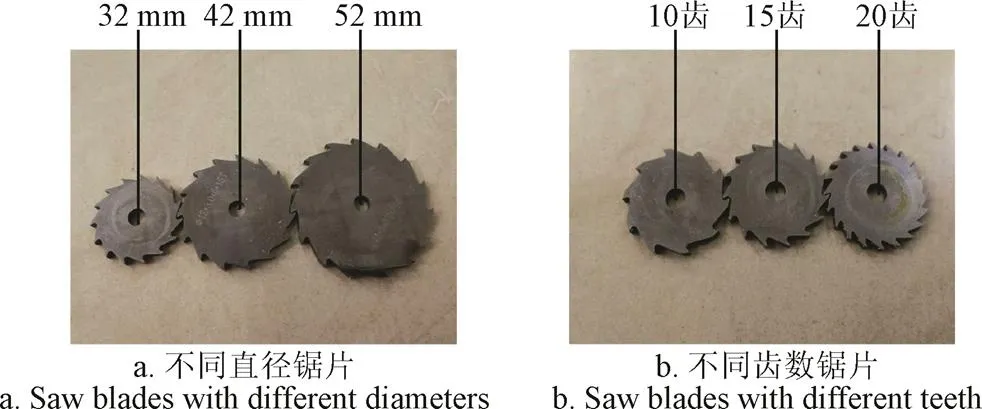
图4 试验用锯片
采集并保存割胶装置电机的10 s包含带负载电流,并记录10 s割胶装置电机空载电流,分别计算出带负载功耗以及空载的功耗,二者差值作为割胶装置切割试样的切割功耗。每个水平进行3次重复试验,试验结果见表1。通过对数据的分析可得出:电机切割功耗随着锯片直径的增加而增加。当锯片的直径为32 mm时,所消耗的功耗最少,此时的切割平均功耗为4.995 J。通过方差分析,= 0.25<0.05(2,6)=5.14,表明锯片直径的变化对割胶装置的切割功耗影响不显著。
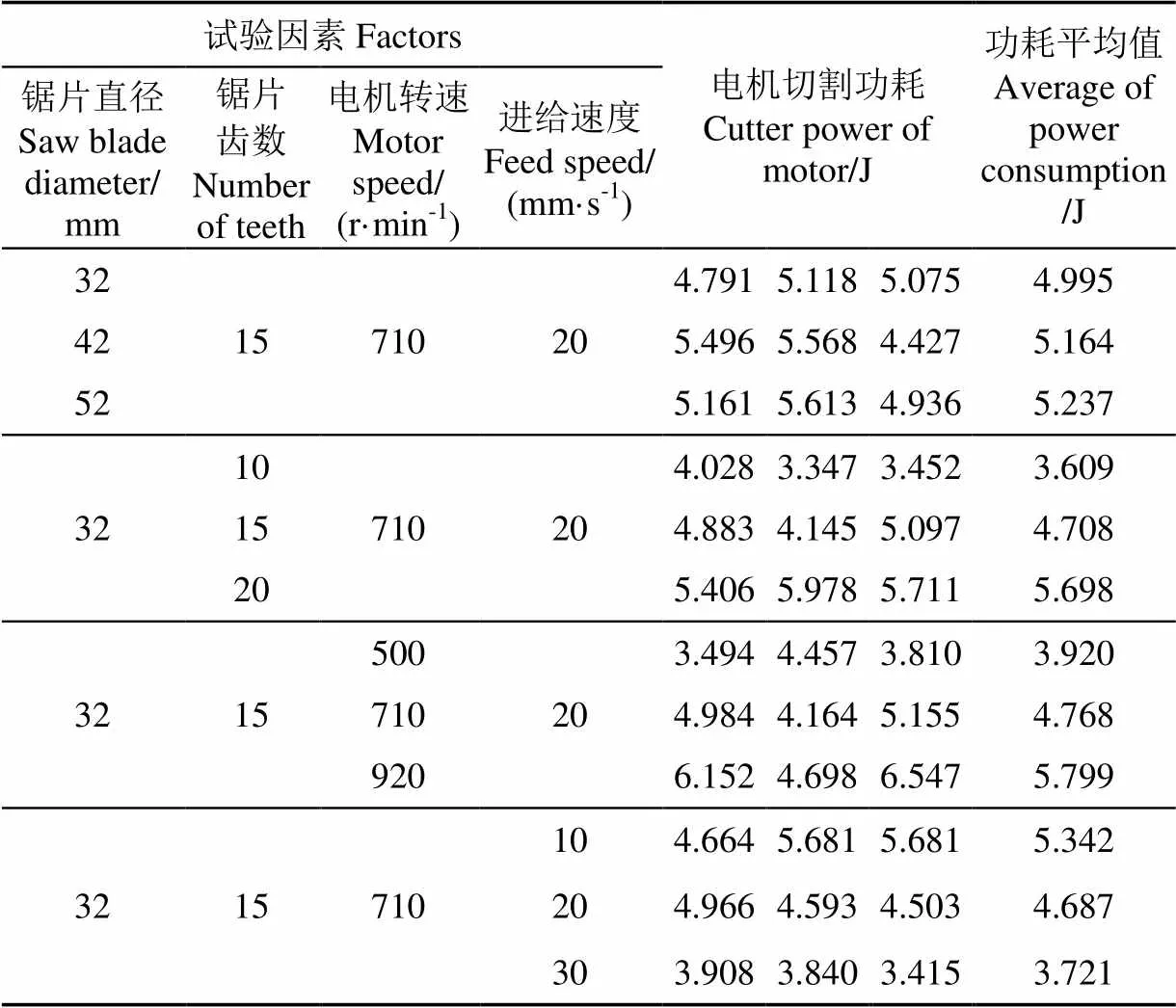
表1 单因素试验方案及结果
3.1.2 锯片齿数
割面平整度随锯片齿数减少而变差,同时考虑到锯片的加工难度会随着齿数的增多而加大。综合考虑定制了齿数分别为10、15、20的锯片,如图4b所示。分别对橡胶树皮试样进行切割,各水平试验重复3次,分别计算出切割电机功耗及平均值,试验结果见表1。通过对数据的分析可得:电机切割功耗随着锯片齿数增加而增加,齿数为10时,所消耗的平均功耗最少为3.609 J。通过方差分析,=21>0.05(2,6)=5.14,表明锯片齿数的变化对割胶装置的切割功耗影响显著。
3.1.3 切割电机转速
在实际切割过程中,切割电机转速过低会影响割面平整度,影响流胶速度,转速过高会对步进电机的使用寿命产生影响。综合考虑,分别用切割电机在转速为500、710、920 r/min的情况下对橡胶树皮试样进行了切割试验,各水平试验重复3次,分别计算出切割电机功耗以及平均值,试验结果见表1。通过对数据的分析可得出:电机切割功耗随着切割电机的转速增加而增加,切割电机转速为500 r/min时,所消耗的平均功耗最少为3.92 J。通过方差分析,=5.42>0.05(2,6)=5.14,表明切割电机转速的变化对割胶装置的切割功耗影响显著。
3.1.4 进给速度
通过控制滑台电机转速从而可以控制切割进给速度,参考实际割胶速度[27],并考虑到进给量太小会影响作业效率,进给量太大会影响割面质量,分别以10、20、30 mm/s的进给速度对橡胶树皮试样进行了切割试验,各水平试验重复3次,分别计算出切割电机功耗以及平均值,试验结果见表1。通过对数据的分析可得出:电机切割功耗随着切割进给速度增大而减少,切割进给速度为30 mm/s时,所消耗的平均功耗最少为3.721 J。通过方差分析,=12.56>0.05(2,6)=5.14,表明切割进给速度的变化对割胶装置的切割功耗影响显著。
3.2 多因素正交试验
在单因素试验结果与分析上,选取割胶装置电机转速、锯片齿数以及进给速度3个因素的3个水平进行正交试验。正交试验因素和水平如表2所示。
表2 正交试验因素水平
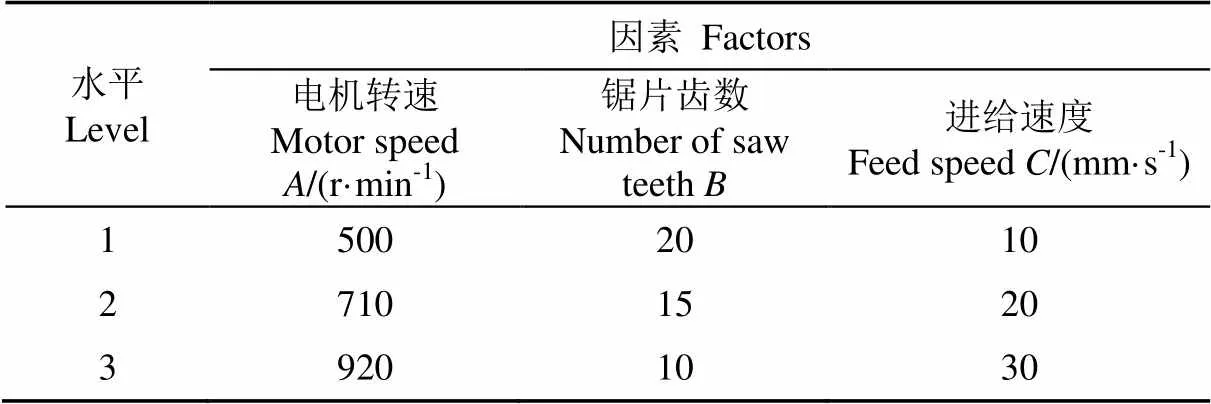
Table 1 Factors and levels for orthogonal test
正交试验结果如表3所示。由表3可以看出,4号试验组最高,切割功耗为12.965 J,3号试验组最低,切割功耗为2.597 J。通过计算值和极差值,比较出锯片齿数、进给速度、割胶装置电机转速各水平对切割功耗的影响。由表3可知,各考察因子的极差值越大,说明该因子对指标切割功耗的影响越大。这样确定了对切割功耗的影响因素的主次关系为锯片齿数、进给速度和割胶装置电机转速。从降低切割功耗的角度出发,选择每个因素中值较小的水平。在锯片齿数方面,选水平3(10齿)较佳;在切割进给速度方面,选水平3(30 mm/s)较佳;在割胶装置电机转速方面,选取水平1(500 r/min)为好,即133为给定因素水平下的最佳试验组合,且133恰好是表3中3号试验组,其切割功耗试验结果(2.597 J)在9组试验中最小。
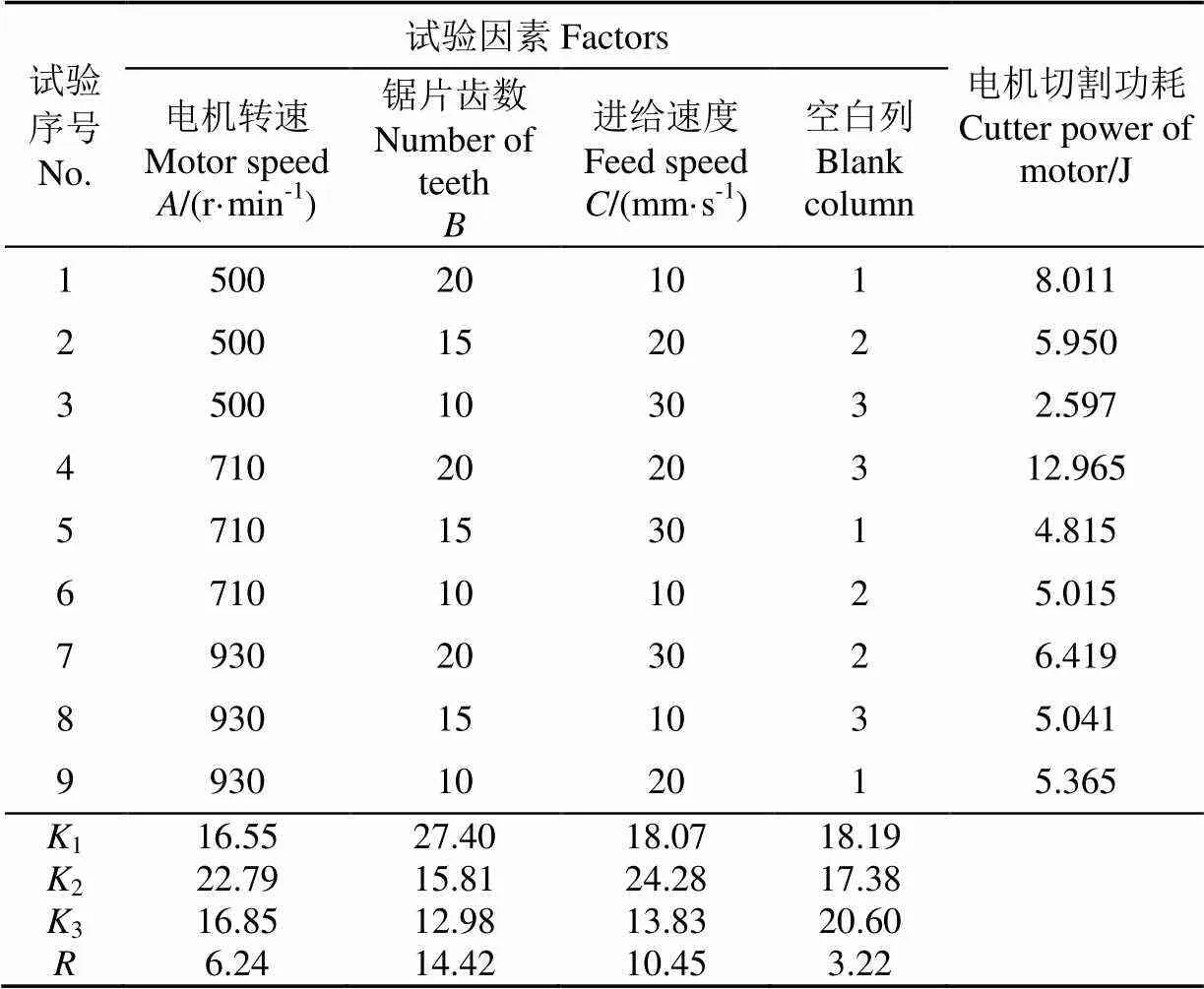
表3 正交试验方案及结果
4 结 论
本文设计了天然橡胶锯切功耗测量试验台,以锯片直径、锯片齿数、切割电机转速及进给速度为试验因素,以品种为7397、树龄8 a的橡胶树为试验对象进行切割功耗测量试验。
1)单因素试验结果表明:割胶装置锯片直径对切割功耗无显著影响;割胶装置锯片齿数对切割功耗有显著影响,切割功耗随锯片齿数的增多而增大;割胶装置电机转速对切割功耗有显著影响,切割功耗随电机转速的增大而增大;切割进给速度对切割功耗有显著影响,切割功耗随进给速度的增大而减小。
2)多因素正交试验结果表明:对锯切功耗影响大小的因素依次为锯片齿数、进给速度、割胶装置电机转速。在给定因素水平下,最优组合为割胶装置电机转速为500 r/min,锯片齿数为10齿,进给为30 mm/s,在此组合下切割功耗最小,功耗值为2.597 J。
本文研究可为天然橡胶机械化采收装置机构设计提供参考。
[1] 刘海清,方佳,张慧坚,等. 中国天然橡胶产业现状研究[J]. 广东农业科学,2009(9):240-243.
Liu Haiqing, Fang Jia, Zhang Huijian, et al. Research on present situation of natural rubber in China[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2009(9): 240-243. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 金华斌,田维敏,史敏晶. 我国天然橡胶产业发展概况及现状分析[J]. 热带农业科学,2017,37(5):98-104.
Jin Huabin, Tian Weimin, Shi Minjing. Current situation and industrial development of natural rubber in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2017, 37(5): 98-104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 刘少军,张京红,蔡大鑫,等. 海南岛天然橡胶主要气象灾害风险区划[J]. 自然灾害学报,2015,24(3):177-183.
Liu Shaojun, Zhang Jinghong, Cai Daxin, et al. Risk zoning of main meteorological disasters of natural rubber in Hainan Island[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2015, 24(3): 177-183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 陈明文. 我国天然橡胶产业发展形势与因应策略[J]. 农业经济问题,2016,37(10):91-94.
[5] 罗富晟,张德生. 我国农垦胶工老龄化原因与影响[J]. 热带农业科技,2012,35(2):42-45.
Luo Fusheng, Zhang Desheng. Aging problem of rubber tapping workers in China state-farm and its affect[J]. Tropical Agricultural Science & Technology, 2012, 35(2): 42-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 闫喜强,廖宇兰. 橡胶树割胶技术的探索[C]//三亚,第三届全国地方机械工程学会学术年会暨海峡两岸机械科技论坛,2013:4.
[7] Zhong Xue, Zhang Jin, Zhang Yanlin, et al. Test and analysis on the mechanical properties of cassava stalks[J]. Journal of Animal and Plant Sciences, 2015, 25(Supp.1): 59-67.
[8] Igathinathane C, Pordesimo L O, Schilling M W, et al. Fast and simple measurement of energy requirements for plant stalk cutting[C]//Providence: American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, 2008.
[9] Igathinathane C, Pordesimo L O, Schilling M W, et al. Fast and simple measurement of cutting energy requirement of plant stalk and prediction model development[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2011, 33(2): 518-523.
[10] Chandio F A, Yi C, TAgAr A A, et al. Effect of loading rate on mechanical characteristics of wheat and rice straw[J]. Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 2013, 19(6): 1452-1458.
[11] Zhao Jiale, Huang Dongyan, Jia Honglei, et al. Analysis and experiment on cutting performances of high-stubble maize stalks[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2017, 10(1): 40-52.
[12] Ghahraei O, Ahmad D, Khalina A, et al. Cutting tests of kenaf stems[J]. Transactions of the ASABE, 54(1): 51-56.
[13] 杨永福. 竹材切削加工性能研究[D]. 北京:北京林业大学,2005.
Yang Yongfu. Studuy on the Cutting Performance of Bamboo[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2005. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 杨永福,习宝田,李黎. 切削参数对竹材切削力影响的研究[J]. 木材加工机械,2005(3):13-15.
Yang Yongfu, Xi Baotian, Li Li. Study on effects of cutting parameters for bamboo on cutting forces[J]. Wood Processing Machinery, 2005(3): 13-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 杨永福,习宝田,李黎. 毛竹切削力的研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2006,28(4):17-21.
Yang Yongfu, Xi Baotian, Li Li. Cutting forces of moso bamboo[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2006, 28(4): 17-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 郭莹洁,杨永福. 铣削参数对毛竹表面粗糙度影响的研究[J]. 林产工业,2009,36(4):21-23.
Guo Yingjie, Yang Yongfu. Study on the effects of milling parameters for moso bamboo on its surface roughness[J]. China Forest Products Industry, 2009, 36(4): 21-23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 郭莹洁,杨永福,白雪. 铣削参数对毛竹超前劈裂的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2009,31(增刊1):193-196.
Guo Yingjie, Yang Yongxue, Bai Xue. Effects of milling parameters for Moso bamboo on its advance splitting[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2009, 31(Supp.1): 193-196.
[18] 郭莹洁. 铣削参数对竹材铣削质量与单位切削功的影响[D]. 北京:北京林业大学,2009.
Guo Yingjie, Effects of Milling Parameters for Bamboo on its Milling Qualities and Unit Cutting Work[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 马永康,张振国,边胤. 柠条收割机切割器的设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2007,38(7):202-204.
[20] 赵湛,李耀明,徐立章,等. 超级稻单茎秆切割力学性能试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2010,41(10):72-75.
Zhao Zhan, Li Yaoming, Xu Lizhang, et al. Experiment on cutting mechanical property of single super rice stalk[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2010, 41(10): 72-75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 刘庆庭,区颖刚,卿上乐,等. 甘蔗茎秆在光刃刀片切割下根茬破坏试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2007,23(3):103-107.
Liu Qingting, Qu Yinggang, Qing Shangle, et al. Stubble damage of sugarcane stalks in cutting test by smooth-edge blade[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2007, 23(3): 103-107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 田昆鹏,李显旺,沈成,等. 天牛仿生大麻收割机切割刀片设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(5):56-61.
Tian Kunpeng, Li Xianwang, Shen Cheng, et al. Design and test of cutting blade of cannabis harvester based on longicorn bionic principle[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(5): 56-61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 苏工兵,刘俭英,王树才,等. 苎麻茎秆木质部力学性能试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2007,38(5):62-65.
Su Gongbing, Liu Jianying, Wang Shucai, et al. Study on mechanical properties of xylem of ramie stalk[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2007, 38(5): 62-65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 邬备,王德成,王光辉,等. 割草机切割压扁装置运行参数优化与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(10):76-83.
Wu Bei, Wang Decheng, Wang Guanghui, et al. Optimization and experiments of cut-condition device working parameter on mower conditioner[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(10): 76-83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 吴良军,杨洲,洪添胜,等. 荔枝树枝力学特性的试验研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(16):68-73.
Wu Liangjun, Yang Zhou, Hong Tiansheng, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of litehi branches[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(16): 68-73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 李黎. 木材切削原理与刀具[M]. 北京:中国林业出版社,2008.
[27] 张万桢,黄慧德. 橡胶割胶工[M]. 北京:中国农业出版社,2014.
Experiment of influence factors on sawing power consumption for natural rubber mechanical tapping
Zhang Chunlong, Sheng Xiyu, Zhang Shunlu, Gao Jin, Yuan Ting※, Zhang Junxiong, Li Wei
(,,100083,)
Natural rubber (NR) is an important economic crop in tropical regions of China and is also an indispensable strategic resource which has excellent capability. With the growing shortage of tappers, mechanization of NR tapping becomes an inevitable trend. There are many studies on cutting characteristics of agricultural and forestry crops both at home and abroad. However, the study on the cutting power consumption of rubber mechanical harvesting is still blank, so it is necessary to carry out independent experiments on NR bark. The selection of cutting parameters is very important in mechanized harvesting. Cutting parameters will affect the cutting ability of the cutter. In order to reduce the power consumption of the NR mechanized harvesting sawing cutter and prolong the working time of the mechanical tapping equipment in the forest, the influence factors on sawing power consumption were studied. At first an experiment bench for NR tapping was developed based on the actual working conditions. The bench was mainly composed of a sawing cutter, a data acquisition module, a feeding motion module and a microcontroller. Sawing cutter was fixed on the ground, while cutting samples were mounted on feeding motion module which was able to supply cutting force. Saw blade could be replaced to change the diameter and the teeth number, and both the motor speed of the cutter and the speed of the feeding module could be adjusted through programming. The DC (direct current) stabilized voltage power supply was connected in series with the isolating transmitter and sawing cutter. The output of the isolation transmitter was connected with the microcontroller. And the microcontroller was used to collect the instantaneous current of sawing motor. Then the data were transmitted to the computer through the RS232 serial port and the computer could calculate cutter power of motor as an experiment evaluation index. All samples were taken from Xiqing Farm in Danzhou City, Hainan Province. The truncated tree was untapped and the tree bark was original. Meanwhile, all cutting samples with size of 50 mm × 30 mm × 5.5 mm (length × breadth × height) were cut from a same truncated tree and in order to simulate the actual cutting condition, the sample was pruned into trapezium. The cutting samples were tested within 2 h to prevent the biological characteristics of samples from changing. Then single factor experiments were conducted, and the effect of the diameter and the teeth number of saw blade on power consumption was tested by using different saw blades with different teeth numbers and diameters, while that of the motor speed of cutter and the feeding speed of samples was tested through changing programs. And the results showed that the diameter of saw blade had no significant influence on power consumption, and the teeth number, feeding speed and motor speed had significant influence on power consumption. Power consumption decreased with the decrease of teeth number and motor speed, while it increased with the decrease of feeding speed. Finally an orthogonal experiment with 3 factors (teeth number, feeding speed and motor speed) and 3 levels was carried out based on the single factor experiments. And the results indicated that the significant level order of the effect of different factors on power consumption from high to low was teeth number, feeding speed and motor speed. Moreover, the optimal sawing parameters for NR mechanical tapping were obtained as follows: Teeth number was 10 teeth, feeding speed was 30 mm/s, and motor speed was 500 r/min, and under the optimal condition the cutter power of motor was 2.597 J. As the selection of cutting parameters is essential for NR mechanical tapping devices, which significantly affects the working ability of the tapping devices, this study can provide a reference for the device design of NR mechanized tapping.
mechanization; optimization; harvesting; natural rubber; power consumption; orthogonal test
2018-04-04
2018-06-30
国家重点研发计划(2016YFD0701501);国家自然科学基金(31601217)
张春龙,副教授,博士,主要从事农业机器人技术、机器视觉检测技术研究。Email:zcl1515@cau.edu.cn
袁 挺,副教授,博士主要从事农业智能装备、机器视觉技术研究。Email:yuanting122@hotmail.com
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.17.005
S225.93
A
1002-6819(2018)-17-0032-06
张春龙,盛希宇,张顺路,高 金,袁 挺,张俊雄,李 伟. 天然橡胶机械化采收锯切功耗影响因素试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(17):32-37. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.17.005 http://www.tcsae.org
Zhang Chunlong, Sheng Xiyu, Zhang Shunlu, Gao Jin, Yuan Ting, Zhang Junxiong, Li Wei. Experiment of influence factors on sawing power consumption for natural rubber mechanical tapping[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(17): 32-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.17.005 http://www.tcsae.org
