基于多相机成像的玉米果穗考种参数高通量自动提取方法
2018-08-10侯佩臣
宋 鹏,张 晗,罗 斌,侯佩臣,王 成
基于多相机成像的玉米果穗考种参数高通量自动提取方法
宋 鹏1,2,张 晗1,2,罗 斌1,2,侯佩臣1,2,王 成2,3※
(1. 北京农业信息技术研究中心,北京 100097;2. 北京农业智能装备技术研究中心,北京 100097;3. 国家农业智能装备工程技术研究中心,北京 100097)
实现玉米果穗考种性状的准确、快速获取是提高玉米育种效率的关键环节。该文在前期设计的玉米高通量自动化考种装置基础上,提出了一种基于多相机的玉米果穗考种参数提取方法,通过4个等间隔均匀分布的摄像头同时获取果穗4个方向图像,针对每副图像分别经过背景去除、投影模型构建、籽粒跟踪、考种参数提取等处理,最后根据4副图像的处理结果,综合计算穗长、穗粗、平均粒厚、穗行数、行粒数、穗粒数等考种参数。在玉米高通量自动化考种装置的果穗考种模块上进行试验,结果表明,该文所提方法测得的穗长、穗粗、平均粒厚与人工方法测量值之间的决定系数2分别为0.997 3、0.984和0.941 5,对穗行数、行粒数的测量精度分别为98.63%、95.35%,为玉米果穗考种参数提取提供了一种新思路,为高通量自动考种装置的实现奠定了基础。
农作物;提取;图像分割;玉米考种;四相机;投影模型;籽粒跟踪;穗行数
0 引 言
考种是玉米育种过程的重要环节[1]。玉米果穗考种包括果穗穗长、穗粗、穗行数、行粒数、平均粒厚、总粒数等多种性状参数的测量,传统果穗考种通过人工测量,费时费力[2],果穗考种的效率和精度制约着商业化玉米育种效率的提高。
随着信息技术的发展,越来越多的学者将机器视觉及图像处理技术应用于玉米检测及分析[3-12]。在玉米考种方面,主要基于视觉技术进行考种参数提取方法研究并形成相应装置[13-20],目前主要通过2种方式进行果穗考种参数的提取:1)使果穗和图像采集装置发生相对旋转,获取玉米果穗的全表面图像信息后进行考种参数提取[21-22];2)通过拍摄静置的玉米果穗单侧图像信息,分析估算出整个果穗的考种参数[23-26]。如柳冠伊等[27]采用2个辊筒驱动玉米果穗匀速转动,用线阵CCD从2个辊筒之间间隙对玉米果穗进行连续扫描并分析,单个果穗检测时间大于30 s;周金辉等[28]通过高拍仪获取玉米果穗单副图像,通过建立投影修正模型估算果穗穗长、穗粗、穗行数、行粒数等参数,测量速度可达30穗/min。
本文针对玉米高通量自动考种装置的果穗考种模块[14],提出一种基于多相机的玉米果穗考种参数提取方法,可快速测量玉米果穗穗长、穗粗、穗行数、行粒数、总粒数等考种参数,为玉米高通量自动考种装置的实现奠定基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 样本材料
本文试验所用玉米果穗均来自辽宁东亚种业有限公司东亚海南育种基地收获的实际待考种玉米材料,部分果穗样本如图1所示。

图1 果穗样本材料
1.2 果穗图像获取装置
本文在前期设计的玉米高通量自动考种装置的果穗考种单元获取图像,其结构如图2所示。果穗置于2根平行安装,间隔可调的钢丝上方,4个彩色相机以90°等间隔沿垂直于穗轴方向,距离穗轴中心30 cm处,水平分布于果穗四周[14],以外触发方式同时获取果穗4个方向图像。该装置具体硬件型号参数如下:摄像头为DH- HV5051Ux-M型号彩色CMOS工业数字相机,分辨率为2 942×1 944像素;镜头为Computar 5mm f/1.5定焦镜头;光源为4只条形LED白光光源。本装置选用的PC机硬件环境为Intel(R) Core(TM) i5 CPU M 450 2.4 GHz,软件由Visual Studio 2010 开发环境编写。

1.摄像头 2.光源 3. 果穗承载装置
本装置获取的玉米果穗原始图像如图3所示。
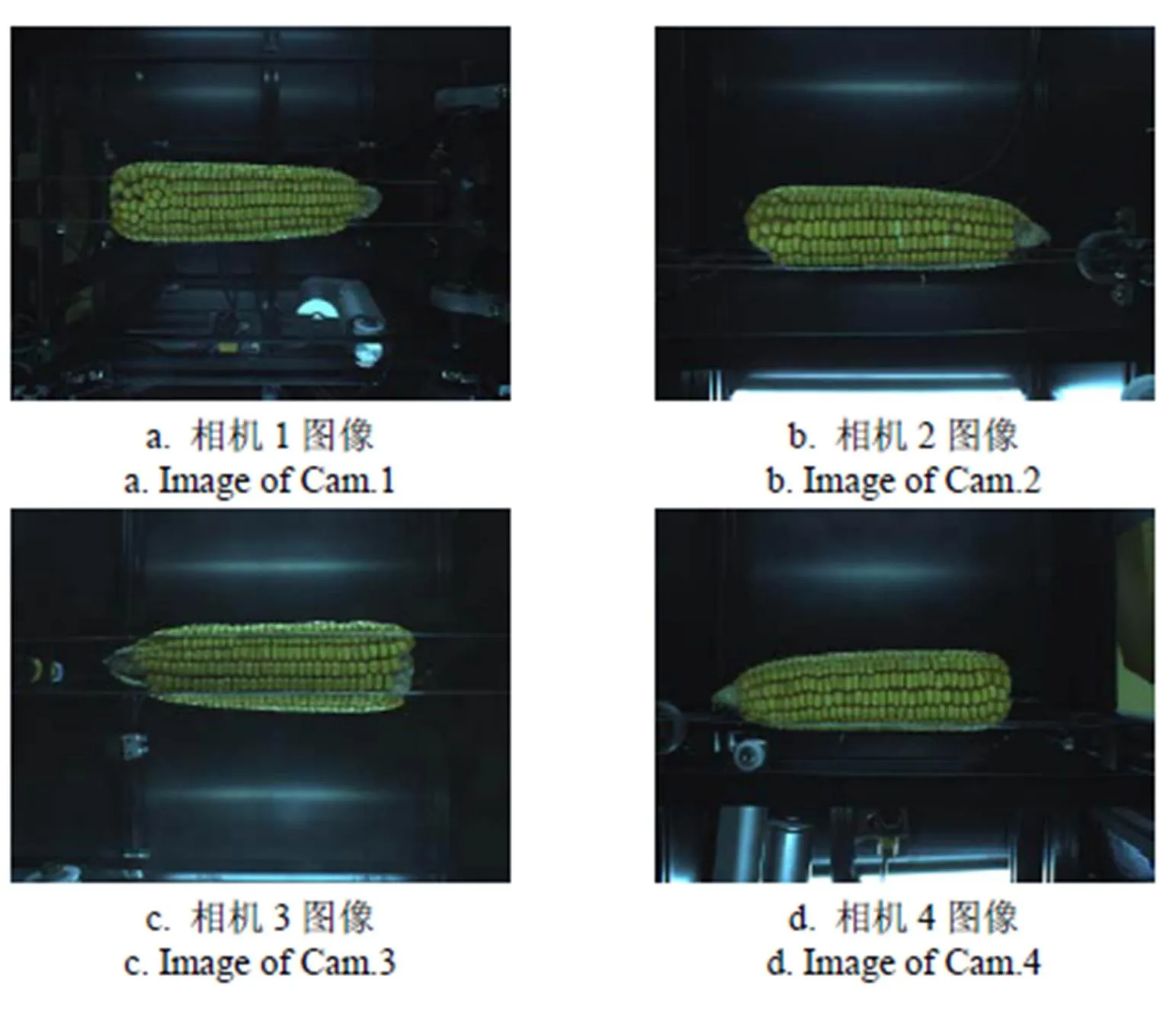
图3 4个相机获取的原始果穗图像
1.3 果穗考种参数提取方法
果穗考种参数中涉及的果穗长度、宽度、籽粒厚度等均为实际物理尺寸,而图像处理过程通常使用像素数来表示尺寸大小。在测量之前,需进行相机标定,将单位像素对应的物理尺寸计为(mm/像素),经标定,本系统中4个摄像头对应的值均为0.126 mm/像素。
1.3.1 图像预处理
在采集果穗图像前,玉米果穗位于2根平行安装的钢丝上方,故其出现在摄像头视场中的位置相对固定,为提高图像处理效率,降低无效数据处理量,仅对每副图像中包含玉米果穗的区域进行处理。采集的果穗原始图像分辨率为2 942×1 944像素,通过试验发现,处于图像中间区域,长度为原始图像长度的7/9,即2 016像素,宽度为原始图像宽度的1/2,即972像素,此区域图像基本包含不同尺寸玉米果穗的完整信息。
分别在RGB(red, green, blue)和HSV(hue, saturation, value)颜色空间对果穗图像进行分析,发现果穗区域与背景区域在H通道和V通道差异较大,如图4所示,可使用V-H模型进行果穗区域提取。
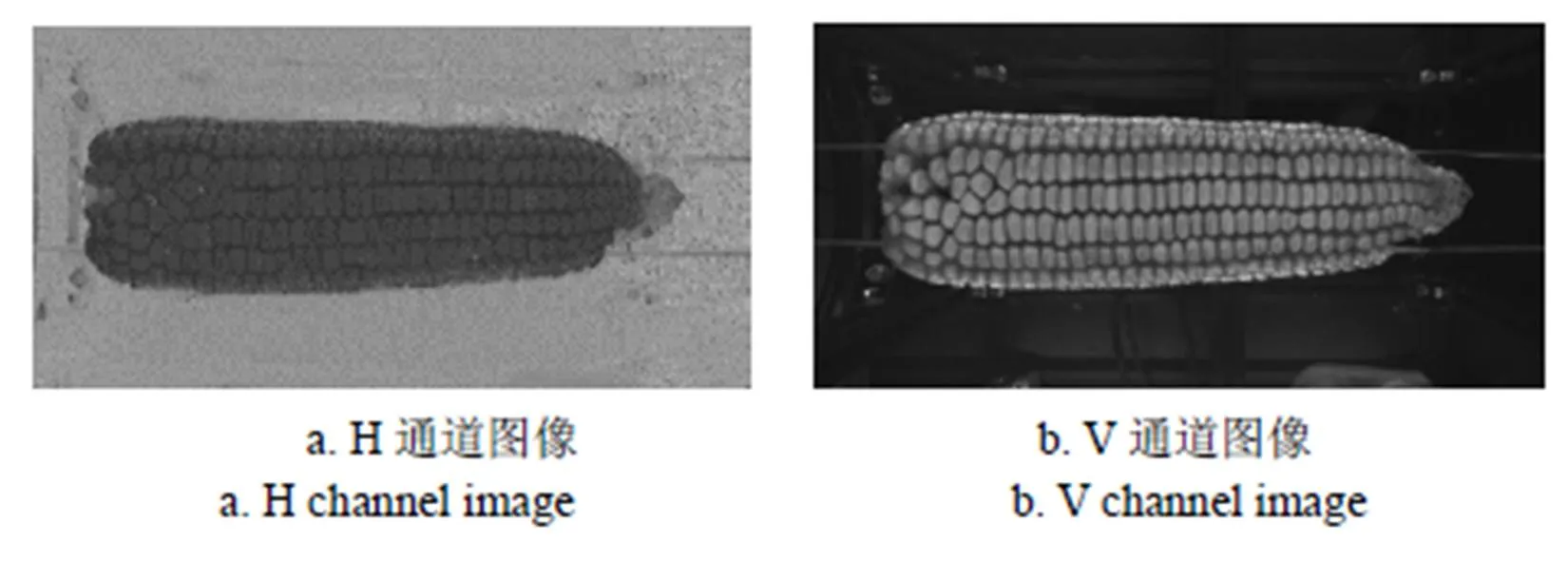
图4 图3a在H、V通道分量图
通过直方图分析发现,采用1.8×(V-H)+180模型二值化后进行去噪、孔洞填充及形态学变换,将获取的果穗区域与原图像进行与操作以去除背景,提取的玉米果穗图像如图5所示。

图5 去背景后的玉米果穗图像
1.3.2 果穗投影模型
本文对获取的4副果穗图像分别处理,综合各图像处理结果获取玉米果穗考种参数。由于摄像头以90°间隔沿垂直于穗轴方向均匀分布于果穗四周,而玉米果穗为类旋转体,可将果穗截面等效于圆形[28],则分布于果穗同一截面的籽粒等效于分布于圆周上的各点,据此原理构建果穗投影模型,如图6所示。
图6中点所处位置为摄像头位置,圆等效于与穗轴方向垂直的果穗截面,圆的半径为该截面位置处的果穗半径。为该截面处果穗边缘投影长,为该截面处穗行数为n的籽粒所对应的投影长。摄像头安装时保证其轴心线与果穗的中心轴线位置处于同一平面,故可近似认为被摄像头所处位置与果穗截面中心点的连线平分,且与垂直。将与的交点定为点。

注:A为摄像头位置;BC为果穗边缘投影长;DE为nr行籽粒投影长;圆O为果穗截面;θ为nr行籽粒对应圆心角;F为AO与BC的交点。
假设,=,,=,由直角三角公式可得到式(1)。

计算可得式(2)~(3)。
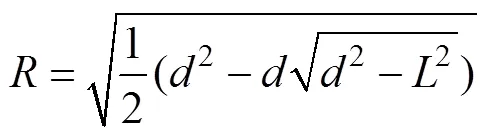
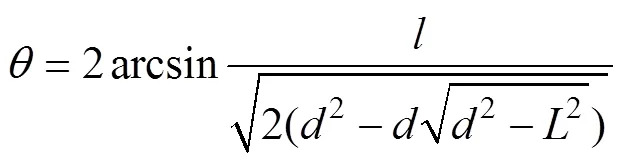
1.3.3 果穗考种参数提取流程
由果穗投影模型可知,将果穗截面等效于圆形时,可通过计算每副图像中的穗行数ri及其所对应圆心角θ换算出果穗的穗行数,结合式(3)可知,由该副图像换算出的果穗穗行数ri由式(4)计算得出。
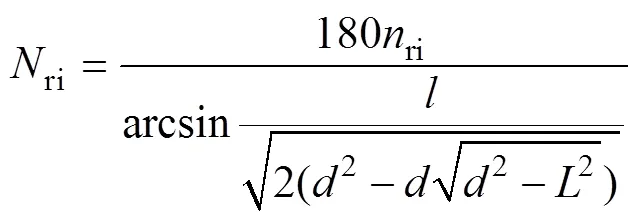
因此,为计算出果穗行数ri,需确定摄像头所获图像中玉米边缘投影长度值;单副图像中提取的穗行数ri,ri行籽粒所对应的投影长度值及摄像头距离果穗中心距离值。

×|eb-ec| (5)
摄像头距离果穗中心距离值由系统设计安装确定,为常量30 mm。由于玉米果穗表面近似圆柱体,处于边缘区域的籽粒受光线影响,难以获取理想提取效果。为提高果穗行数检测精度,需提取各图像中完整有效的穗行数ri及其所对应的投影长度。由于果穗中间区域籽粒排布较规则,在提取有效的穗行数ri时针对果穗中间区域进行处理,具体流程如下:
1)果穗上玉米籽粒提取。针对G通道,采用自适应阈值方法分割后进行形态学变换,采用分水岭方法对果穗上粘连玉米籽粒进行分割,将所分割的单个玉米籽粒区域按照面积大小进行排序,提取面积大小处于中间50%的籽粒,计算其平均宽度k
2)图像轮廓及玉米籽粒中心位置提取。通过分析发现,果穗秃尖区域和籽粒区域在HSV空间的H通道和S通道的灰度呈现差异,采用2×(S-H)+30模型进行处理后阈值分割,可实现凸尖区域和籽粒区域分割,利用此模型提取的果穗籽粒区域图像如图7a所示。提取穗上籽粒中间1/2区域的外轮廓,外轮廓上各点坐标为e(ei,ei),同时提取所分割出的独立籽粒区域的中心点位置坐标c(cj,cj);
3)边缘籽粒剔除。遍历搜索与各独立籽粒区域中心点c(cj,cj)横坐标cj相同的图像边缘轮廓点,由于图像边缘轮廓为封闭状态,因此存在2个满足条件的轮廓点,分别为e1(cj,ej1)及e2(cj,ej2)。定义Dist=min{|cj-ej1,cj-ej2}。当Dist>ej1-ej2/10时,则判定中心点c(cj,cj)对应的籽粒区域处于图像边缘,予以剔除。
4)籽粒跟踪。针对步骤3)剔除边缘籽粒后的图像进行跟踪,跟踪起始点为籽粒区域中心点中横坐标最小点,记为c0(c0,c0),任一跟踪点记为ci(ci,ci)。则c0与点ci的直线距离0i及2点连线的夹角0i为式(6)~(7)。
0i[(cmin-ci)2(c0ci)2]1/2(6)
0iarctan[(c0-ci)/(cmin-ci)](7)
若点c1(c1,c1),满足012012min{0i20i2},则认为点c1(c1,c1)为起始点c0(c0,c0)所跟踪到的下一点,以点c1(c1,c1)作为下一跟踪的起始点继续跟踪,对已经跟踪过的点进行标记,不进行重复跟踪计算。单次跟踪结束后循环进行步骤4)操作,直至遍历所有玉米籽粒中心点跟踪结束。
根据试验情况,本文所设置的单次跟踪终止条件为|0i>40°或0i3k。
5)有效穗行数ri计算。依照步骤4)跟踪的穗行数通常大于等于1行,若所跟踪的穗行包含的籽粒数量明显少于其他行,则表明此行跟踪结果不完整,为无效行,予以剔除,剔除无效行后的穗行数即为有效穗行数ri。
6)ri行对应投影长度值计算。将步骤5)中跟踪所得的有效果穗行数沿穗轴方向等分为10个矩形区域,每个矩形区域包含ri行对应的穗上籽粒。每个矩形的长度用i表示,通过排序获取i的中值m,则ri行有效穗行数对应的投影宽度×m。
7)果穗边缘投影长度计算。步骤6)中长度为m的矩形中心位置记为(m,m,将果穗轮廓上与其对应的具有相同横坐标的2点记为e1(m,e1)及e2(m,e2),则×(e1-e2)。
按照上述步骤,图5a处理效果如图7所示。
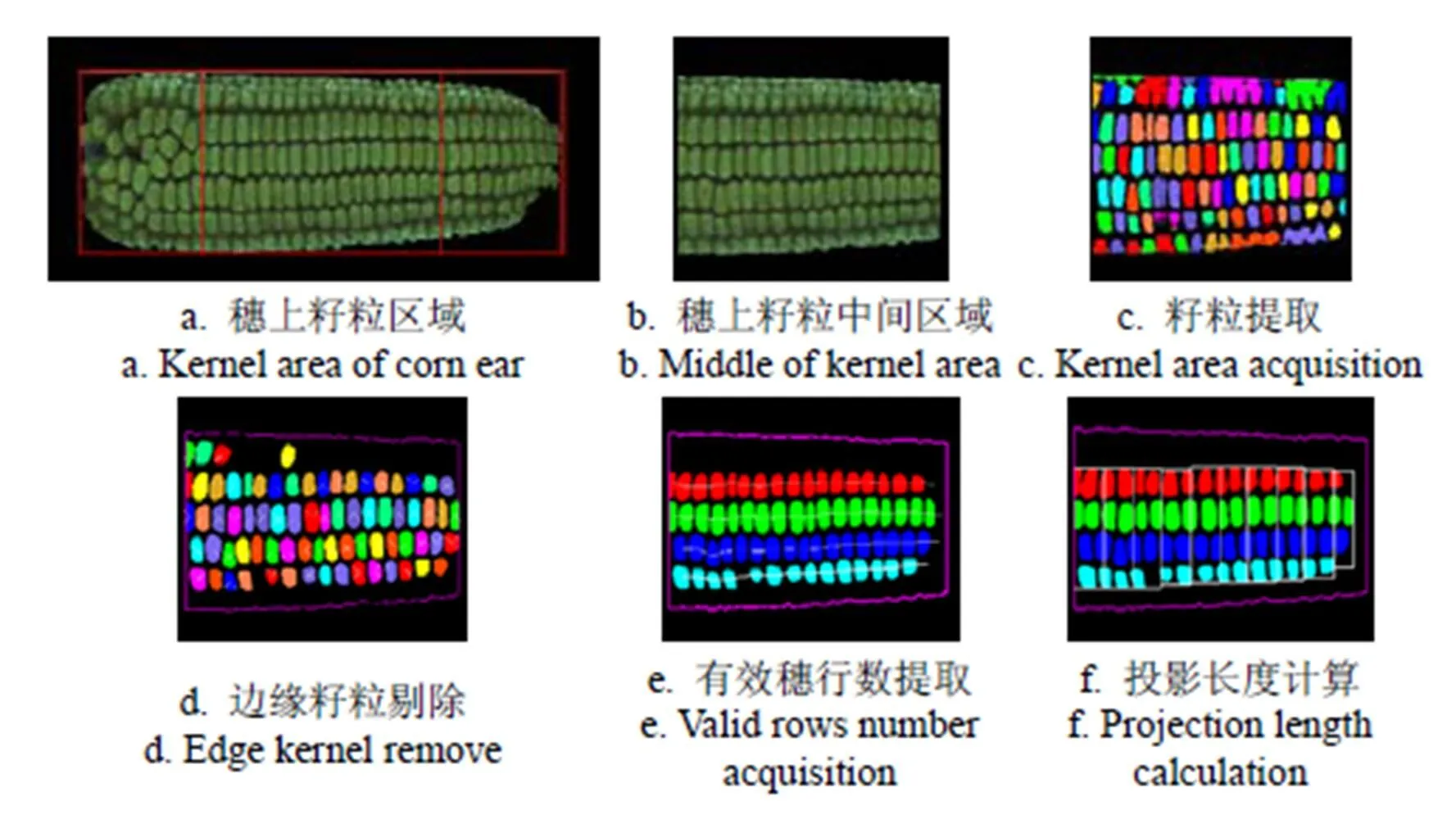
图7 果穗处理过程
1.4 果穗考种参数计算
本装置采用4个相机分别进行玉米果穗图像参数提取,最终测得的果穗考种参数由4副图像提取的参数综合计算得出。
1.4.1 果穗长、宽计算
玉米果穗的长度和宽度分别对应玉米果穗的长轴和短轴,本文通过建立玉米果穗的最小外接矩形获取果穗的长、宽参数[23]。对玉米果穗二值图进行轮廓跟踪,基于Graham扫描法[29]建立其最小外接矩形,将果穗最小外接矩形的长记为ei,最小外接矩形的宽记为ei,则各图像中计算的果穗长为ei×ei,果穗宽为ei×ei,同时计算4副图像的平均果穗长、平均果穗宽、最大果穗长、最大果穗宽,并与人工测量值做对比。结果表明4幅图像的最大果穗长、最大果穗宽与人工测量结果相关性最高,故果穗长度定义为L=max{ei,1, 2, 3, 4},果穗宽度定义为W=max{ei,1, 2, 3, 4}。
1.4.2 穗行数提取
由于处于玉米果穗中间区域的籽粒排列相对规则,在进行穗行数提取时,选取沿果穗最小外接矩形方向玉米籽粒中间的1/2区域进行处理。图5a的提取效果如图7e所示。
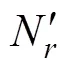
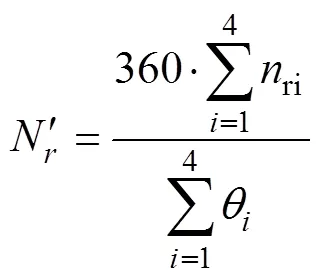
1.4.3 行粒数提取
行粒数提取与有效穗行数提取采用相同的提取规则,区别在于有效穗行数提取针对果穗上全部籽粒的中间1/2区域进行跟踪,而行粒数提取则针对果穗上全部籽粒区域进行跟踪,图7a的籽粒跟踪效果如图8所示。

图8 图7a籽粒跟踪效果
选取所跟踪的有效行数中,行粒数最大值作为图8所测得的果穗行粒数ki,该果穗行粒数n由式(9)中计算的通过四舍五入法取整所得。
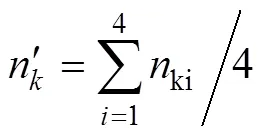
1.4.4 总粒数提取
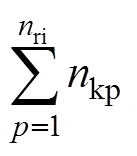
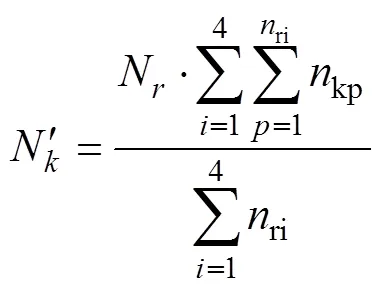
1.4.5 籽粒厚度提取
根据所提出的籽粒跟踪规则,得出每副图像所跟 踪的行粒数ri及该行跟踪路径之和D,则平均籽粒厚度为:
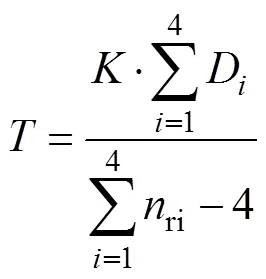
2 结果与分析
为验证本文所提方法测量的准确性,进行玉米考种试验。随机选取20个待考种果穗,用人工方式统计各果穗长、宽、穗行数、行粒数,总粒数后,将其依次置于果穗考种单元的2根平行安装钢丝上方,样本在高通量自动考种装备[14]上进行自动考种并保存测量结果,对比系统测量的数据与人工方式测量数据差异。
2.1 穗长、穗粗、平均粒厚测量精度分析
采用游标卡尺(量程300 mm,精度0.02 mm)进行测量,将测得果穗的最大长度和最大直径作为人工测得的穗长、穗粗参数。选取果穗中间排布较为均匀的区域,测量其所包含籽粒的总厚度,并计算平均粒厚作为人工测得的平均粒厚值。与本文所提方法测量结果相关性如图9所示。

图9 不同方式穗长、穗粗、平均粒厚测定的相关性
结果表明,本文方法穗长测量值与人工方法测量值之间的决定系数2为0.997 3,本文方法穗粗测量值与人工方法测量值之间的决定系数2为0.984,本文方法平均粒厚测量值与人工方法测量值之间的决定系数2为0.941 5。
2.2 穗行数、行粒数、总粒数测量精度分析
采用人工方式对检测样本的穗行数及总粒数进行计算,将数出的总粒数除以穗行数并取整,作为人工测量出的行粒数。本文所提方法与人工测得的穗行数、行粒数、总粒数结果如表1所示。

表1 穗行数、行粒数、总粒数测量结果
结果表明,针对所采用样本,本文所采用的方法对穗行数测量的平均精度为98.63%,其中样本5和样本19由于性状极不规则,测量结果与人工测量结果出现偏差。行粒数平均测量精度为95.35%。
玉米高通量自动考种装置在果穗考种单元和籽粒考种单元均进行了总粒数计算[14]。本文中果穗考种单元的总粒数通过行粒数和穗行数计算得出,其测量值受行粒数和穗行数测量精度影响较大,故测得的每个样本总粒数与人工测量值均存在一定偏差。在籽粒考种单元则直接对果穗脱粒后的籽粒数量进行计算[15],因此针对单个果穗,其总粒数的测量精度优于本文所提方法。玉米高通量自动考种装置考种时以籽粒考种单元测得的总粒数作为果穗总粒数。
3 结 论
本文针对所设计玉米高通量自动考种装置的玉米果穗考种模块,提出了一种基于4相机的玉米果穗考种参数快速测量方法,通过等间隔90°安装的4个摄像头获取果穗四周图像,分别构建投影模型并分析,最终综合4副图像分析结果,实现果穗穗长、穗粗、平均粒厚、穗行数、行粒数、穗粒数等考种参数的获取。针对随机选取的20穗样本,本文所提方法对穗长、穗粗、平均粒厚测量结果与人工方法测量值之间的决定系数2分别为0.997 3、0.984、0.941 5。对穗行数、行粒数的测量精度分别为98.63%、95.35%,满足玉米高通量自动考种 装置作业需求,为玉米高通量自动考种装置的实现奠定基础。
[1] 肖伯祥,王传宇,郭新宇,等. 玉米考种自动化流水线机构设计与仿真[J]. 系统仿真学报,2015,27(4):913-919. Xiao Boxiang, Wang Chuanyu, Guo Xinyu, et al. Automatic pipelining mechanism design for maize ear analysis[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2015, 27(4): 913-919. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 曹婧华,冉彦中,郭金城. 玉米考种系统的设计与实现[J]. 长春师范学院学报:自然科学版,2011,30(4):38-41. Cao Jinghua, Ran Yanzhong, Guo Jincheng. The design and realization of corn test system[J]. Journal of Changchun Normal University: Natural Science, 2011, 30(4): 38-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 刘长青,陈兵旗,张新会,等. 玉米定向精播种粒形态与品质动态检测方法[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(9):47-54. Liu Changqing, Chen Bingqi, Zhang Xinhui, et al. Dynamic detection of corn seeds for directional precision seeding[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(9): 47-54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 温维亮,郭新宇,杨涛,等. 玉米果穗点云分割方法研究[J]. 系统仿真学报,2017,29(12):3030-3034,3041. Wen Weiliang, Guo Xinyu, Yang Tao, et al. Point cloud segmentation method of maize ear[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2017, 29(12): 3030-3034, 3041. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 曹维时,张春庆,王金星,等. 离散小波变换和BP神经网络识别玉米种子纯度[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(增刊2):253-258. Cao Weishi, Zhang Chunqing, Wang Jinxing, et al. Purity identification of maize seed based on discrete wavelet transform and BP neural network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(Supp.2): 253-258. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 马钦,江景涛,朱德海,等. 基于图像处理的玉米果穗三维几何特征快速测量[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(增刊2):208-212. Ma Qin, Jiang Jingtao, Zhu Dehai, et al. Rapid measurement for 3D geometric features of maize ear based on image processing[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(Supp.2): 208-212. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] Liang X, Wang K, Huang C, et al. A high-throughput maize kernel traits scorer based on line-scan imaging[J]. Measurement, 2016, 90: 453-460.
[8] 黄成龙,张雪海,吴迪,等. 基于时间序列的玉米叶片性状动态提取方法研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(5): 174-178,198. Huang Chenglong, Zhang Xuehai, Wu Di, et al. Dynamic extraction method of maize leaf traits based on time series[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(5): 174-178, 198. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 杨锦忠,张洪生,郝建平,等. 玉米果穗图像单一特征 的品种鉴别力评价[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,27(1): 196-200. Yang Jinzhong, Zhang Hongsheng, Hao Jianping, et al. Identifying maize cultivars by single characteristic of ears using image analysis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(1): 196-200. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 仇瑞承,苗艳龙,季宇寒,等. 基于RGB-D相机的单株玉米株高测量方法[J].农业机械学报,2017,48(增刊1):211-219. Qiu Ruicheng, Miao Yanlong, Ji Yuhan, et al. Measurement of individual maize height based on RGB-D camera[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(Supp. 1): 211-219. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] Ge Y, Bai G, Stoerger V, et al. Temporal dynamics of maize plant growth, water use, and leaf water content using automated high throughput RGB and hyper spectral imaging[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2016, 127: 625-632.
[12] 张帆,李绍明,刘哲,等. 基于机器视觉的玉米异常果穗筛分方法[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(增刊):45-49. Zhang Fan, Li Shaoming, Liu Zhe, et al. Screening method of abnormal corn ears based on machine vision[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(Supp.): 45-49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 吴刚,陈晓琳,谢驾宇,等. 玉米果穗自动考种系统设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(增刊):433-441. Wu Gang, Chen Xiaolin, Xie Jiayu, et al. Design and experiment of automatic variety test system for corn ear[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(Supp.): 433-441. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 宋鹏,张晗,王成,等. 玉米高通量自动考种装置设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(16):41-47. Song Peng, Zhang Han, Wang Cheng, et al. Design and experiment of high throughput automatic measuring device for corn[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(16): 41-47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 宋鹏,张晗,王成,等. 玉米籽粒考种信息获取装置设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(12):19-25. Song Peng, Zhang Han, Wang Cheng, et al. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(12): 19-25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 汪珂,梁秀英,宗力,等. 玉米籽粒性状高通量测量装置设计与实现[J]. 中国农业科技导报,2015,17(2):94-99. Wang Ke, Liang Xiuying, Zong Li, et al. Design and realization of a high-throughput maize kernel trait extraction system[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2015, 17(2): 94-99. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 杜建军,郭新宇,王传宇,等. 基于分级阈值和多级筛分的玉米果穗穗粒分割方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(15):140-146. Du Jianjun, Guo Xinyu, Wang Chuanyu, et al. Segmentation method for kernels of corn ear based on hierarchical threshold and multi-level screening[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(15): 140-146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 柳冠伊,刘平义,魏文军,等. 玉米果穗粘连籽粒图像分割方法[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(9):285-290. Liu Guanyi, Liu Pingyi, Wei Wenjun, et al. Method of image segmentation for touching maize kernels[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(9): 285-290. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 赵春明,韩仲志,杨锦忠,等. 玉米果穗 DUS 性状测试的图像处理应用研究[J]. 中国农业科学,2009,42(11):4100-4105. Zhao Chunming, Han Zhongzhi, Yang Jinzhong, et al. Study on application of image process in ear traits for DUS testing in maize[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2009, 42(11): 4100-4105. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 段熊春,周金辉,王思嘉. 面向玉米果穗考种测量的图像标定方法[J]. 农机化研究,2014,36(1):76-79. Duan Xiongchun, Zhou Jinhui, Wang Sijia. Image calibration method for the ear of corn measurement system[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2014, 36(1): 76-79. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 杜建军,郭新宇,王传宇,等. 基于穗粒分布图的玉米果穗表型性状参数计算方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(13):168-176. Du Jianjun, Guo Xinyu, Wang Chuanyu, et al. Computation method of phenotypic parameters based on distribution map of kernels for corn ears[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(13): 168-176. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 王传宇,郭新宇,吴升,等. 采用全景技术的机器视觉测量玉米果穗考种指标[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(24): 155-162. Wang Chuanyu, Guo Xinyu, Wu Sheng, et al. Investigate maize ear traits using machine vision with panoramic photograyphy[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(24): 155-162. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 刘长青,陈兵旗. 基于机器视觉的玉米果穗参数的图像测量方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(6):131-138. Liu Changqing, Chen Bingqi. Method of image detection for ear of corn based on computer vision[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(6): 131-138. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 吕永春,马钦,李绍明,等. 基于背景板比例尺的玉米果穗图像特征测量[J]. 农业工程学报,2010,26(14):43-47. Lü Yongchun, Ma Qin, Li Shaoming, et al. Image features measurement of maize ear based on background plate scale[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(14): 43-47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 李伟,胡艳侠,吕岑. 基于 HSV 空间的玉米果穗性状的检测[J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版),2017,43(1):112-116. Li Wei, Hu Yanxia, Lü Cen. Traits detection of corn ear based on HSV color space[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Sciences), 2017, 43(1): 112-116. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 王慧慧,孙永海,张婷婷,等. 鲜食玉米果穗外观品质分级的计算机视觉方法[J]. 农业机械学报,2010,41(8): 156-159,165. Wang Huihui, Sun Yonghai, Zhang Tingting, et al. Appearance quality grading for fresh corn ear using computer vision[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2010, 41(8): 156-159, 165. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 柳冠伊,杨小红,白明,等. 基于线阵扫描图像的玉米果穗性状检测技术[J]. 农业机械学报,2013,44(11):276-280. Liu Guanyi, Yang Xiaohong, Bai Ming, et al. Detecting techniques of maize ear characters based on line scan image[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(11): 276-280. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 周金辉,马钦,朱德海,等. 基于机器视觉的玉米果穗产量组分性状测量方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2015,46(3): 221-227. Zhou Jinhui,Ma Qin,Zhu Dehai,et al. Measurement method for yield component traits of maize based on machine vision[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(3): 221-227. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 吴文周,李利番,王结臣. 平面点集凸包Graham算法的改进[J]. 测绘科学,2010,35(6):123-125. Wu Wenzhou,Li Lifan,Wang Jiechen. An improved Graham algorithm for determining the convex hull of planar points set[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2010, 35(6): 123-125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
High throughput automatic extraction method of corn ear parameters based on multiple cameras images
Song Peng1,2, Zhang Han1,2, Luo Bin1,2, Hou Peichen1,2, Wang Cheng2,3※
(1.100097,; 2.100097,; 3.100097,)
The efficiency and accuracy of corn ear test are two of the key factors restricting the breeding efficiency seriously. Corn ear test includes the measurement, records, statistics and analysis of parameters such as ear weight, ear length, ear width, number of ear rows, kernels per row, average thickness of kernel, kernels per ear. In this paper, a corn ear parameter extraction method based on 4 cameras was proposed based on the high-throughput automatic measuring device which has been developed previously. Four high-resolution color cameras were evenly distributed around the ear with the interval of 90° to get the corn ear images from 4 directions at the same time. Every image from the corresponding camera was processed including image preprocessing, projection model building, and parameters extraction of corn ear. During image preprocessing process, center part of the original image with the length of 7/9 of the original image length, the width of 1/2 of the original image width was chosen as the processed area. Binarization processing was applied to the area to obtain binary image, and the binary image was processed by image denoising, hole filling and other morphological transform. An AND-operation was then applied between the processing result and the original image to access the corn ear images without background. The projection model was constructed after image preprocessing process, which considered ear cross-section circular, and kernels were distributed on ear cross-section as point on the circumference of a circle. Thus, number of ear rows can be easily calculated according to the relationship between number of ear rows and circumferential angle of those rows. Procedure such as kernels area acquisition, kernels center position acquisition, kernels at edge removal, reserved kernels tracking and corn ear parameters calculation are operated based on the projection model. Since there are 4 images for each ear, the final ear parameters including ear length, ear width, average thickness of kernel, number of ear rows, kernels per row, kernels per ear are calculated based on parameters measured from each image. The ear length and width are represented by the maximum length and width of the smallest external rectangle of the 4 images. Number of ear rows in each image is calculated from the valid row number and the circumferential angle which can be obtained on the basis of the projection model. Kernels per row are acquired by tracking the kernel area for each ear image, the maximum number of kernels in a row for each image is calculated as well as the average value, and the round-of number is considered as kernels per row of the ear. Kernels per ear are calculated from the valid row number, kernel number of the valid rows and corn ear rows. Average thickness of kernel is calculated according to the tracked kernel number and the total tracking path. Experiments are carried out with the high-throughput automatic measuring device for corn, and results show that the determination coefficients (2) of ear length, ear width and average thickness of kernel achieve 0.997 3, 0.984 and 0.941 5 respectively between the values obtained by the proposed method in this paper and that measured artificially. The measuring accuracies of number of ear rows and kernels per ear are 98.63% and 95.35%, respectively, which meet the requirements of corn parameters measurement during maize breeding. The proposed method also provides a new train of thought for the extraction of corn ear parameter, and it also lays a solid foundation for the realization of automatic high-throughput device for corn.
crops; extraction; image segmentation; ear parameters acquision; four cameras; projection model; kernels tracking; ear rows
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.14.023
TP242.6;TP391.4
A
1002-6819(2018)-14-0181-07
2018-02-09
2018-05-23
国家重点研发计划(2017YFD0701205);国家自然科学基金(31601216)
宋 鹏,高级工程师,博士,主要从事农业信息技术及装备研究。Email:songp@nercita.org.cn
王 成,研究员,博士,主要从事农业信息化、农业智能装备及仪器研究。Email:wangc@nercita.org.cn
宋 鹏,张 晗,罗 斌,侯佩臣,王 成.基于多相机成像的玉米果穗考种参数高通量自动提取方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(14):181-187. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.14.023 http://www.tcsae.org
Song Peng, Zhang Han, Luo Bin, Hou Peichen, Wang Cheng.High throughput automatic extraction method of corn ear parameters based on multiple cameras images[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(14): 181-187. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.14.023 http://www.tcsae.org
