Coverless Steganography for Digital Images Based on a Generative Model
2018-07-12XintaoDuanHaoxianSongChuanQinandMuhammadKhurramKhan
XintaoDuan,HaoxianSongChuanQinandMuhammadKhurramKhan
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel coverless image steganographic scheme based on a generative model. In our scheme, the secret image is first fed to the generative model database, to generate a meaning-normal and independent image different from the secret image. The generated image is then transmitted to the receiver and fed to the generative model database to generate another image visually the same as the secret image. Thus, we only need to transmit the meaning-normal image which is not related to the secret image, and we can achieve the same effect as the transmission of the secret image. This is the first time to propose the coverless image information steganographic scheme based on generative model, compared with the traditional image steganography.The transmitted image is not embedded with any information of the secret image in this method, therefore, can effectively resist steganalysis tools. Experimental results show that our scheme has high capacity, security and reliability.
Keywords:Generative model, coverless image steganography, steganalysis, steganographic capacity, security.
1 Introduction
Most of current information steganographic techniques [Qin, Ji, Chang et al. (2018); Ma,Luo, Li et al. (2018); Qin, Chang and Hsu (2015); Zhou, Sun, Harit et al. (2015); Zhou,Wu, Yang et al. (2017); Xia, Li and Wu (2017)] apply the cover data (such as digital image, audio and video) as a disguise for the secret data to be transmitted, which embed the secret data into cover data. The popularization of personal computers and the proliferation of digital images on the Internet provide convenient conditions of cover data for conducting information Steganography [Qin, Ji, Zhang et al. (2017); Qin, Chang and Chiu (2014)]. However, on the other hand, the technique for detecting hidden data, also called as steganalysis, has also been rapidly developed, which is mainly based on finding statistical anomaly of cover data caused by data embedding. Hence, steganalysis can be considered as a serious threat to steganography. According to different hiding strategies[Zhang, Qin, Zhang et al. (2018); Qin, Ji, Zhang et al. (2017); Qin, Chang and Hsu(2015)], the commonly used steganographic schemes are classified into two types: Spatial domain schemes and transform domain schemes. The spatial domain hiding method hasthe adaptive LSB hiding method [Yang, Weng, Wang et al. (2008)], the spatial adaptive steganography algorithm S-UNIWARD [Holub, Fridrich and Denemark (2014)], HUGO[Pevny, Filler and Bas (2010)], WOW [Holub and Fridrich (2012)] and so on. The transform domain method is to modify the host image data to change some statistical features to achieve data hiding, such as the hidden method in DFT (discrete Fourier transform) domain [Ruanaidh, Dowling and Boland (1996)], DCT (discrete cosine transform) domain [Cox, Kilian, Leighton et al. (1997)], and DWT (discrete wavelet transform) domain [Lin, Horng, Kao et al. (2008)]. These methods inevitably leave some modifications to the carrier [Yuan, Xia and Sun (2017); Chen, Chen and Wu (2017)]. In order to fundamentally resist the detection of various detection algorithms, this paper presents a new coverless image information hiding method based on generative model.As shown in Fig. 1, we only need to deliver a meaning-normal image which is not related to the secret image to the receiver, so that the receiver can generate an image visually the same as the secret image without worrying about the analysis of the steganography, even less attack.
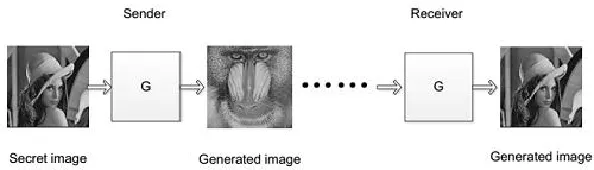
Figure 1: The framework of the research content
As mentioned above, we propose a new scheme to hide image information, which can generate visually the same image as secret image by sending a generated image that is not related to the secret image. The transmitted image is only a normal-meaningful image rather than the image which is embedded any secret information, and also achieve the same effect as transferring the secret image. This method can effectively resist steganalysis tools, and greatly improves the security of the image. To summarize, the major contributions of our work as below:
(1) We do not need to pass the secret image. On the contrary, we transmit a meaningnormal image which is completely unrelated to the secret image. This method has high security.
(2) The image we transmit does not embed any secret information, it is a normal image,and the image steganographic analysis does not work.
(3) As long as the training is enough, this effect can be achieved and the capacity is large.The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section II reviews the related works about generative models. The proposed coverless steganographic scheme for digital images is described in Section III. Experimental results and analysis are given in Section IV, and Section V concludes the paper.
2 Related works
Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs) [Smolensky (1986)], deep Boltzmann machines(DBMs) [Srivastava and Salakhutdinov (2012)] and their numerous variants are undirected graphical models with latent variables. The interactions within such models are represented as the product of unnormalized potential functions, normalized by a global summation or integration over all states of the random variables. This quantity and its gradient are intractable for all but the most trivial instances, although they can be estimated by Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods. Mixing poses a significant problem for learning algorithms that rely on MCMC [Bengio, Mesnil, Dauphin et al.(2013); Bengio, Laufer, Alain et al. (2014)]. Deep belief networks (DBNs) [Hinton,Osindero and Teh (2006)] are hybrid models containing a single undirected layer and several directed layers. While a fast approximate layer-wise training criterion exists,DBNs incur the computational difficulties associated with both undirected and directed models. Variational Auto-Encoders (VAEs) [Glorot, Bordes and Bengio (2012)] and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) [Bengio, Yao, Alain et al. (2013)] are well known to us. VAEs focus on the approximate likelihood of the examples, and they share the limitation of the standard models and need to fiddle with additional noise terms. Ian Goodfellow put forward GAN [Goodfellow, Pougetabadie, Mirza et al. (2014)] in 2014.Goodfellow theoretically proved the convergence of the algorithm, and when the model converges, the generated data has the same distribution as the real data. GAN provides a new training idea for many generative models and has hastened many subsequent works.GAN takes a random variable (it can be Gauss distribution, or uniform distribution between 0 and 1) to carry on inverse transformation sampling of the probability distribution through the parameterized probability generative model (it is usually parameterized by a neural network model). Then a generative probability distribution is obtained. The GAN model includes a generative model G and a discriminative model D.The training objective of the discriminative model D is to maximize the accuracy of its own discriminator, and the training objective of generative model G is to minimize the discriminator accuracy of the discriminative model D. The objective function of GAN is a zero-sum game between D and G and also a minimum -maximization problem. GAN adopts a very direct way of alternate optimization, and it can be divided into two stages.In the first stage, the discriminative model D is fixed, the generative model G is optimized to minimize the accuracy of the discriminative model. In the second stage, the generative model G is the fixed in order to improve the accuracy of the discriminative model D. As a generative model, GAN is directly applied to modeling of the real data distribution, including generating images, videos, music and natural sentences, etc.Because of the mechanism of internal confrontation training, GAN can solve the problem of insufficient data in some traditional machine learning. GANs offer much more flexibility in the definition of the objective function, including Jensen-Shannon, and all fdivergences [Hinton, Srivastava, Krizhevsky et al. (2012)] as well as some exotic combinations. Therefore, it can be used in semi-supervised learning, unsupervised learning, multi-view learning and multi-tasking learning. In addition, it has been successfully used in reinforcement learning to improve its learning efficiency. Although GAN is applied widely, there are some problems with GAN, difficulty in training, lack of diversity. Besides, generator and discriminator cannot indicate the training process. Onthe other hand, training GANs is well known for being delicate and unstable. The better discriminator is trained, the more serious gradient of the generator disappears, leading to gradient instability and insufficient diversity. WGAN (Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Networks [Arjovsky and Bottou (2017); Arjovsky, Chintala and Bottou(2017)]) is an improvement to GAN, and it applies Wasserstein distance instead of JS divergence in the GAN. Compared to KL divergence and JS divergence, the advantage of Wasserstein distance is that it can still reflect their distance even if there is no overlap between the two distributions. At the same time, the problem of training stability and process indicating are solved.
Therefore, this paper chooses Wasserstein GAN so as to guarantee training stability instead of GAN. It is no longer necessary to carefully balance the training extent between generator and discriminator. It basically solves the problem of collapse mode and ensures the diversity of samples.
3 Proposed scheme
The WGAN model is applied to generate the handwritten word by feeding the random noisez, but when the random noisezis changed to a secret imageimg, the model can still generate the meaning-normal and independent imageIMG’which is not related to the secret image we want to transmit. These several images taken from the standard set of images were evaluated in the paper, they areLena,Baboon, CameramanandPeppers,and they have the same size as 256 by 256. The feed is the secret image, and we train the generative model database through the WGAN, then it can generate a meaning-normal and independent image which is not related to the secret image. So we transmit the meaning-normal image to the receiver, and this generated image is fed to the generative model database to generate another generated image visually the same as the secret image.The flow charts of the whole experiment are shown in Fig. 2 and Fig. 3.
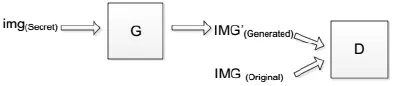
Figure 2: The flow chart of WGAN
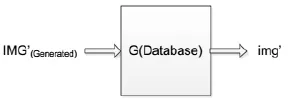
Figure 3: The flow chart of generative model
D andGplay the following two-player minimax game with value functionV(G;D)in WGAN:D(x)represents the probability thatxcame from the data rather thanpg. We trainDto maximize the probability of assigning the correct label to both training examples and samples fromG.We simultaneously trainGto minimize log(1 −D(G(z))).We first make a gradient ascent step onDand then a gradient descent step onG, then the update rules are:
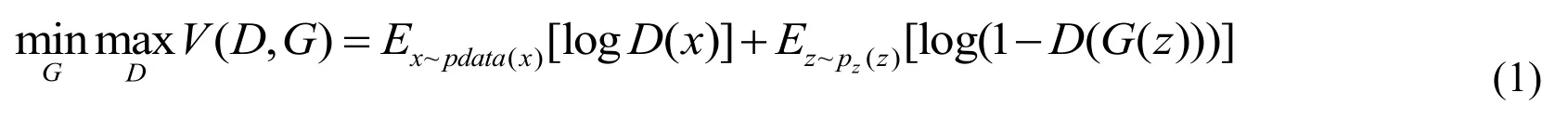
Keeping theGfixed, update the modelwith
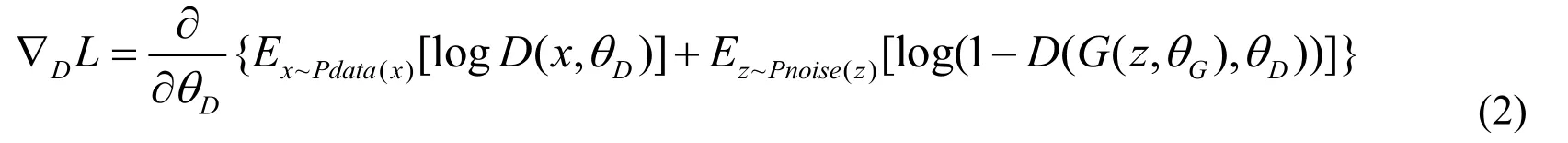
Keeping theDfixed, update the modelGbywhere
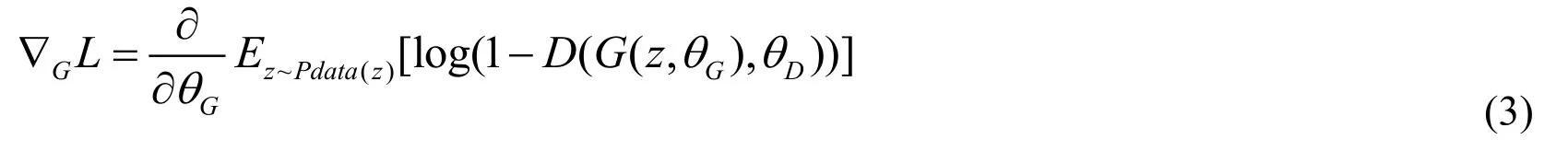
Wasserstein distance is also called the EM (Earth-Mover) distance

Where ∏(Pr,Pg)denotes the set of all joint distributionsγ(x,y)whose marginal are respectivelyPrandPg.Intuitively,γ(x,y)indicates how much “mass” must be transported fromxtoyin order to transform the distributionsPrinto the distributionPg. The EM distance then is the “cost” of the optimal transport plan.
4 Experimental results and analysis
In this paper, 5,000 images are randomly selected from the CelebA dataset to experiment,and the results show that the coverless image information steganography based on generative model method can be implemented well. The sender and receiver share the same dataset and the same parameters. As shown in Fig. 4 and Fig. 5, we feed the secret imageimginto the generative model, generating the meaning-normal and independentIMG’which is not related to the secret image we want to transmit.
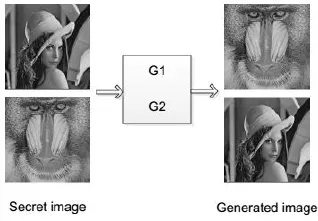
Figure 4: Training generative model G1, G2
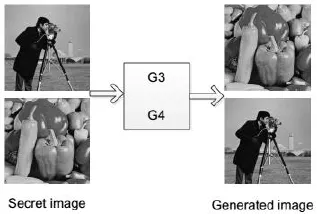
Figure 5: Training generative model G3, G4
As shown above, we chooseLenaas the secret imageimg, it can generate theIMG’visually the same asBaboonwe want to transmit. In the meantime, we also trainedBaboonto generate theIMG’visually the same asLenathrough the WGAN. We save the corresponding generative model G1 and G2 of generating visually the same asBaboonandLenarespectively. Using the same method, we take theCameramanandPeppersas the secret image to experiment respectively, and they can generate correspondingPeppersandCameraman. We also save the corresponding generative model G3 and G4 of generating visually the same asPeppersandCameramanrespectively, and apply them to the next experiment, instead of the WGAN. We put the generative model G1, G2, G3 and G4 of generating visually the same asBaboon,Lena,PeppersandCameramanin a database respectively, so that the generative model database is built. Since both the sender and the receiver train well the generative model database, we perform experiments as shown in Fig. 6 and Fig. 7.
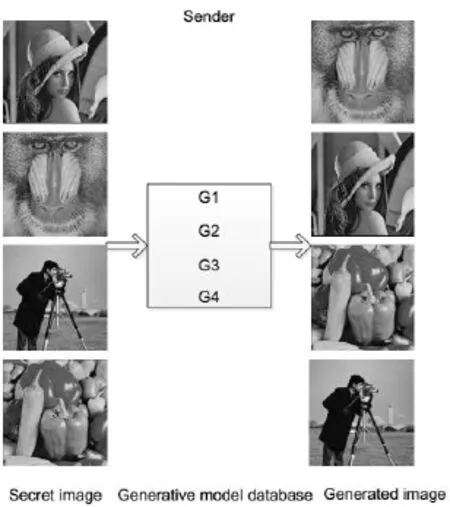

Figure 6: Training generative model database for sender
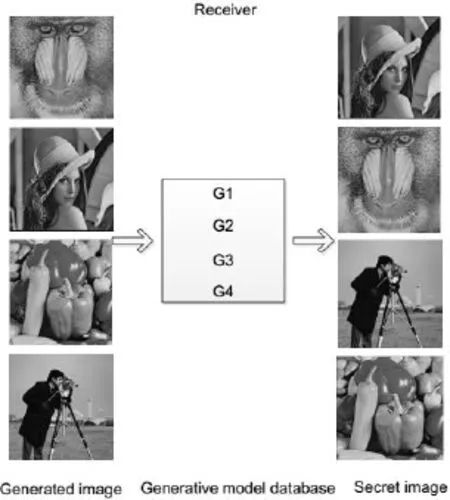
Figure 7: Training generative model database for receiver
As shown above, when the sender wants to transmit the secret imageLena, the generated imageBabooncan be transmitted to the receiver to generate a generated image visually the same as the secret imageLena, similarly, if you want to transmitBaboon, you can transmit the generated imageLena, if you want to transmitCameraman, you can transmit the generated imagePeppers, if you want to transmitPeppers, you can transmit the generated imageCameraman. In this experiment, we have successfully achieved theeffect of coverless image steganographic scheme based on a generative model by feeding a secret image to generate a meaning-normal and independent image which is not related to the secret image we want to transmit, and when the secret image is given, the transmitted image is unique and specific. Consequently, the image steganographic scheme proposed in this paper is feasible. In practical application, we are more concerned with the content of the image rather than the pixels in addition to professional image workers, this scheme can produce a meaning-normal and independent image which is not related to the secret image we want to transmit, which can satisfy most requirements,thereby, we suppose that if you want to send a secret image, you only need to transmit a meaning-normal and independent image to the receiver, the receiver only need to feed transmitted image to the generative model database, generate an image visually the same as the secret one, no needing direct transmission of the secret image. Besides, the transmitted image does not embed any information of the secret image, so it does not give visual cues to attackers, and the image steganography analysis does not work. This scheme can resist detection of all the existing steganalysis tools, and improve the security of the image.
The experimental results show that the image is completely different from the secret image based on the method of generative model. The attacker cannot know what the secret image to be transmitted is, and the generated image is visually the same as the secret image, which meet the practical application standard, In addition to the visually qualitative analysis, the histogram of Fig. 8 can also obtain the same quantitative analysis results.
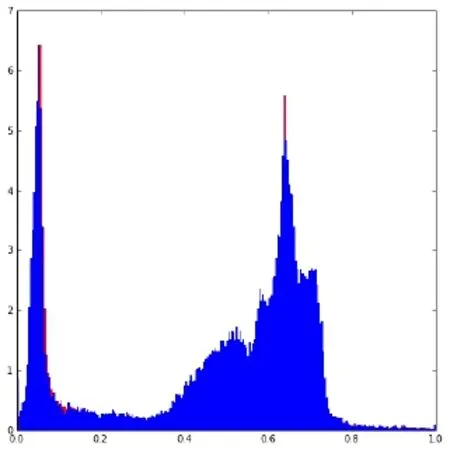
Figure 8: The histogram of the generated image and secret image distribution
As shown in Fig. 8, the red portion represents the secret image, and the blue portion represents the generated image. It can be seen from this histogram that the distribution of the generated images and the secret images are almost identical, and the small differences are almost negligible.
5 Conclusion
To sum up, the paper proposed the coverless image steganographic scheme based on a generative model. An image visually the same as the secret image is generated by transmitting a normal-meaningful image to the receiver. A fed image corresponds uniquely to a secret image. This method is practical. Therefore, it can be applied to image steganography and image protection.
Acknowledgement: This paper was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1204606), the Key Programs for Science and Technology Development of Henan Province (No. 172102210335), Key Scientific Research Projects in Henan Universities (No. 16A520058).
杂志排行
Computers Materials&Continua的其它文章
- Biodegradation of Medicinal Plants Waste in an Anaerobic Digestion Reactor for Biogas Production
- Molecular Structure and Electronic Spectra of CoS under the Radiation Fields
- Feature Selection Method Based on Class Discriminative Degree for Intelligent Medical Diagnosis
- A Spark Scheduling Strategy for Heterogeneous Cluster
- Rare Bird Sparse Recognition via Part-Based Gist Feature Fusion and Regularized Intraclass Dictionary Learning
- Event-Based Anomaly Detection for Non-Public Industrial Communication Protocols in SDN-Based Control Systems
