关于调和Fibonacci数的一类特殊矩阵的谱范数
2018-06-20贺美美
贺美美
(西北大学 数学学院, 陕西 西安 710127)
矩阵作为一种基本的数学工具,在数值分析、优化领域和概率统计等众多学科都有着极其广泛的应用。而在矩阵的理论研究中,有关矩阵的欧几里得范数、谱范数的研究是非常重要的。近年来,多名学者针对Teoplitz矩阵、循环矩阵Hankel矩阵等一些特殊矩阵的谱范数作了相应的探究[1-10]。例如,文献[1]给出了一种包含Fibonacci和Lucas数的特殊矩阵的谱范数的上下界。文献[3]给出了包含Fibonacci和Lucas数的r-Teoplitz矩阵的谱范数的上下界。文献[5]给出了包含k-Fibonacci和k-Lucas数的r循环矩阵的谱范数的上下界。
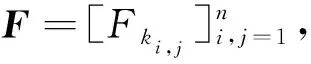
1 预备知识
定义1定义Fn为第n个Fibonacci数,对任意的非负整数n,Fibonacci数具有如下的递推公式
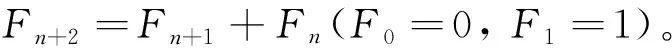
(1)
定义2[11]定义Fn为第n个调和Fibonacci数,即Fibonacci数的前n项倒数和。如下

(2)
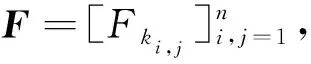
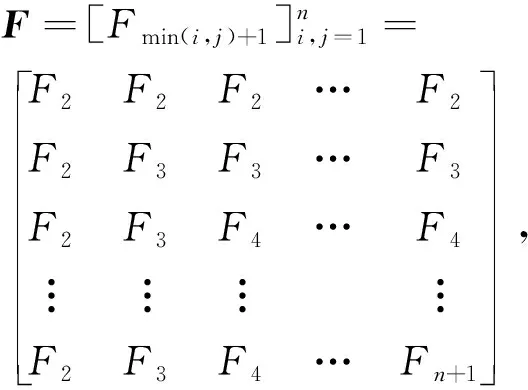
(3)
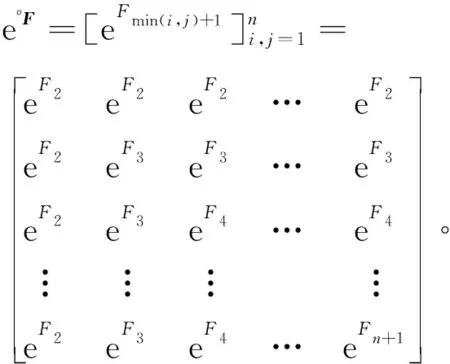
(4)
定义4设A=[aij]是一个n×n阶矩阵,AH表示A的共轭转置,λi表示AAH的特征值,则矩阵A的欧几里得范数和谱范数分别为
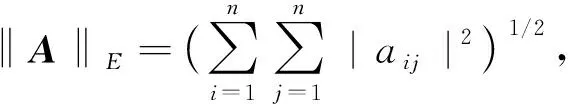
(5)
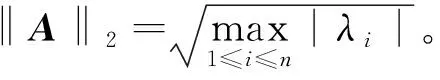
(6)
定义5定义矩阵A的最大行范数r1(A)和最大列范数c1(A)分别为
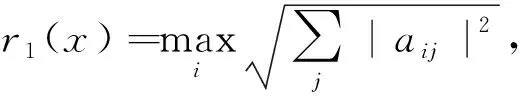
(7)
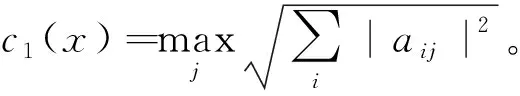
(8)
定义6[12]设B=[bij],C=[cij]都是n×n阶矩阵,定义矩阵B和C的Hadamard乘积为

(9)
性质1[13-14]u(x)的微分算子定义为Δu(x)=u(x+1)-u(x),则有
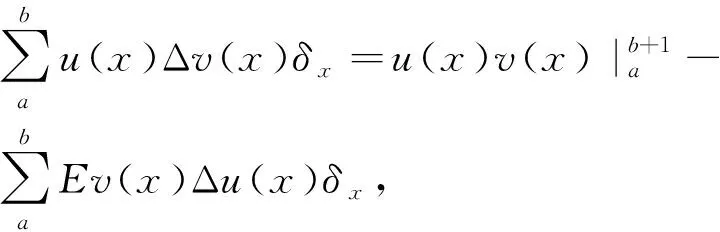
(10)
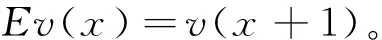
性质2[12,15]关于矩阵的两种范数有如下性质
‖A‖2≤r1(B)c1(C),
(11)
其中矩阵A,B,C满足A=B∘C,

(12)
2 主要结果及证明
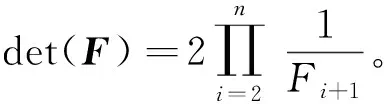
证明对式(3)作初等行变换得到
|F|=
于是
引理1设A是一个n×n阶可逆矩阵,B是一个n×1阶矩阵,c是任意实数。若
则M的逆是
其中λ=c-BTA-1B。
证明根据矩阵逆的定义,很容易验证MM-1=En+1。
定理2设F是形如式(3)的n×n阶矩阵,则F是可逆矩阵,并且它的逆是一个对称三角矩阵。矩阵F的逆为
F-1=
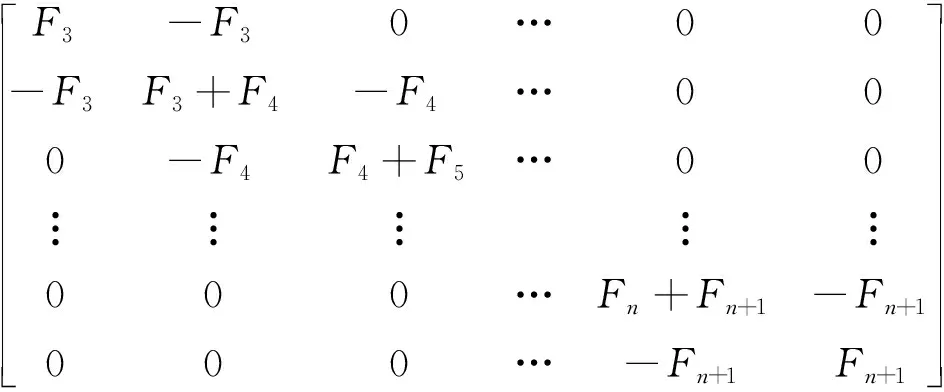
证明由定理1可知矩阵F是可逆的。为了证明这个定理,本文采用数学归纳法。当n=2时,结论成立;此时

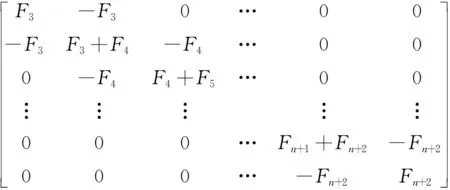
即对(n+1)×(n+1)阶矩阵结论仍成立,从而证明了定理。
定理3设F是形如式(3)的n×n阶矩阵,则矩阵F的欧几里得范数是
其中
证明由式(5)得到
其中
从而
定理4设F是形如式(3)的n×n阶矩阵,我们可以得到矩阵F谱范数的上下界,即

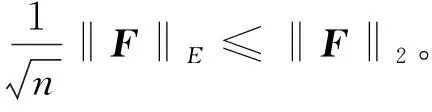
其中ki,j=min(i,j)+1,则有F=A∘B。
根据r1(A)和c1(B)的定义,得到

根据式(11)可得到
‖F‖2≤r1(A)c1(B)=

证明由定理1得到
则
从而结论(i)成立;由结论(i)得到
则结论(ii)成立;为了证明结论(iii),我们用数学归纳法。当n=2时,结论成立;此时
假设结论(iii)对n成立,即
则有
即结论(iii)对n+1也成立,从而证明了定理。
定理6设e°F是形如式(4)中的n×n阶矩阵,则有
证明对上述矩阵作初等行变换得到
det(e°F)=
从而
令式(10)中的u(i)=Fi且Δv(i)=1,便得到Δu(i)=1/Fi+1,v(i)=i和Ev(i)=i+1。于是有
从而便证明了定理。
定理7设e°F是形如式(4)中的n×n阶矩阵,则它的逆是
(e°F)-1=
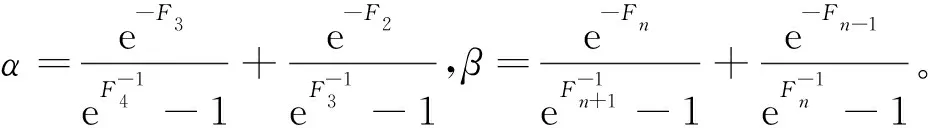
证明与定理2类似,用数学归纳法便可以证明结论。
定理8设e°F是形如式(4)中的n×n阶矩阵,则可以得到矩阵e°F的谱范数的上界是
证明设
则有e°F=A∘B。再根据r1(A)和c1(B)的定义,可以得到
最后根据式(11),有
‖e°F‖2≤r1(A)c1(B)=
定理9设e°F是形如式(4)的n×n阶矩阵,Dn表示矩阵e°F的顺序主子式。即
Dn=det(e°F)。
则有
证明由定理6可知
则
从而证明了结论。
参考文献:
[1] JAFARI-PETROUDI S H, PIROUZ M. On the bounds for the spectral norm of particular matrices with Fibonacci and Lucas numbers [J]. International Journal of Advances in Applieel Mathematics and Mechanics, 2016,3(4):82-90.
[2] AKBULAK M, BOZKURT D. On the norms of Toeplitz matrices involving Fibonacci and Lucas numbers [J]. Hacettepe Journal of Mathematics and Statistics, 2008, 37(2): 89-95.
[3] HASON G, RAMAZA T. On the norms ofr-Toeplitz matrices involving Fibonacci and Lucas numbers [J]. Advances in Linear Algebra & Matrix Theory, 2016, 6(2): 31-39.
[4] SOLAK S. On the norms of circulant matrices with the Fibonacci and Lucas numbers [J]. Applied Mathematics & Computation, 2005, 160(1): 125-132.
[5] SHEN Shou-qiang, CEN Jian-miao. On the spectral norms ofr-circulant matrices with thek-Fibonacci andk-Lucas numbers [J]. International Journal of Contemporary Mathematical Sciences, 2010, 5(12): 569-578.
[6] BAHSI M, SOLAK S. On the norms ofr-circulant matrices with the hyper-Fibonacci and Lucas numbers [J].Journal of Mathematical Inequalities, 2014, 8(4): 693-705.
[7] HASON G, RAMAZA T. On the spectral norm ofr-circulant matrices with the Pell and Pell-Lucas numbers [J]. Journal of Inequalities and Applications, 2016, 2(16): 65-71.
[8] AKBULAK M, BOZKURT D. On the norms of Hankel matrices involving Fibonacci and Lucas numbers [J].Selcuk Jourral of Applied Mathematics, 2008, 9(2): 45-52.
[9] GUNGOR A D. Lower bounds for the norms of Cauchy-Toeplitz and Cauchy-Hankel matrices [J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation,2004, 157(3): 599-604.
[10] SOLAK S, BOZKURT D. On the spectral norm of Cauchy-Toeplitz and Cauchy-Hankel matrices [J].Applied Mathematics and Computation,2003, 140(2-3): 231-238.
[11] RABINOWITZ S. Algorithmic summation of reciprocals of products of Fibonacci numbers [J].The Fibonacci Quarterly, 1999, 37(2): 122-127.
[12] HORN R A, JOHNSON C R. Topics in Matrix Analysis [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1991: 298-356.
[13] TUGLU N, CAN K, KESIM S. On the harmonic and hyperharmonic Fibonacci numbers [J]. Advances in Difference Equations,2015: 297.
[14] GRAHAM R L, KNUTH D E, PATASHNIK O. Concrete Mathematics [M].6nd ed.Boston: Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, 1989: 258-268.
[15] ZIELKE G. Some remarks on matrix norms, condition numbers and error estimates for linear equation [J]. Linear Algebra and its Applications, 1988, 110(11): 29-41.
