3-乙基-2-乙酰吡嗪缩4-苯基氨基脲Agガ配合物的合成、结构和DNA结合性质
2018-06-06康瑞芳吴伟娜
吴 浩 王 元 张 玲 康瑞芳 吴伟娜
(河南理工大学化学化工学院,河南省煤炭绿色转化重点实验室,焦作 454000)
In recent years,semicarbazones have become increasingly important as fine chemicalintermediates[1-3],which could also form complexes with the transition metal ions,producing amazing biological activities,such as anti-bacterial,antitumor,antivirus[4-6].
On the other hand,as one of the most important heterocycles,pyrazine is of significant interest in the pharmacological field[7].Our previous work has shown that several Cuギ/Znギ complexes with semicarbazones bearing pyrazine unit have potential antitumor activities[8-10].However,the investigation on the Agガcomplexes of such type of ligands are relatively scarce[11].In fact,Agガcomplexes have been known for centuries,especially with respect to medical properties[12].Meanwhile,the polynuclear metal complexes are highly desired,because they usually possess higherbiologicalactivitiesthan themononuclear ones[13-15].As the continuation of our work,the complex[Ag2(HL)(NO3)2]n(1)derived from 1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene-4-phenylsemicarbazide (HL)has been synthesized and structuraldetermined by singlecrystal X-ray diffraction。In addition,the interactions of HL and 1 with ct-DNA have been studied by ethidium bromide(EB)fluorescence probe.
1 Experimental
1.1 Materials and measurements
Solvents and starting materials for synthesis were purchased commercially and used as received.The ligand HL was synthesized according to the reference[10].Elemental analysis was carried out on an Elemental Vario EL analyzer.The IR spectra(ν=4 000~400 cm-1)were determined by the KBr pressed disc method on a Bruker V70 FT-IR spectrophotometer.The UV spectra were recorded on a PurkinjeGeneralTU-1800 spectrophotometer.The interactions between the compounds and ct-DNA are measured using literature method[9]via emission spectra on a Varian CARY Eclipse spectrophotometer.
1.2 Preparation of complex 1
The complex 1 was generated by reaction of the ligand HL (5 mmol)with AgNO3(molar ratio 1∶2)in methanol solution(10 mL).Crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis were obtained by evaporating the corresponding reaction solutions at room temperature.Colorless blocks.Anal.Calcd.for C15H17Ag2N7O7(%):C 27.86,H 2.67,N 15.59;Found(%):C 28.91,H 2.75,N 15.73.FT-IR(cm-1):ν(C=O)1 685,ν(C=N)1 600,ν(C=N)pyrazine1 537,ν1(NO3)1 498,ν4(NO3)1 382 and 1 311.
1.3 X-ray crystallography
The X-ray diffraction measurement for HL and complex 1 was performed on a Bruker SMART APEXⅡ CCD diffractometer equipped with a graphite monochromatized Mo Kα radiation(λ=0.071 073 nm)by using φ-ω scan mode.Semi-empirical absorption correction was applied to the intensity data using the SADABS program[16].The structures were solved by direct methods and refined by full matrix least-square on F2using the SHELXTL-97 program[17].All nonhydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically.All the H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model.Details of the crystal parameters,data collection and refinements forcomplex is summarized in Table 1.
CCDC:1588866,HL;1588867,1.
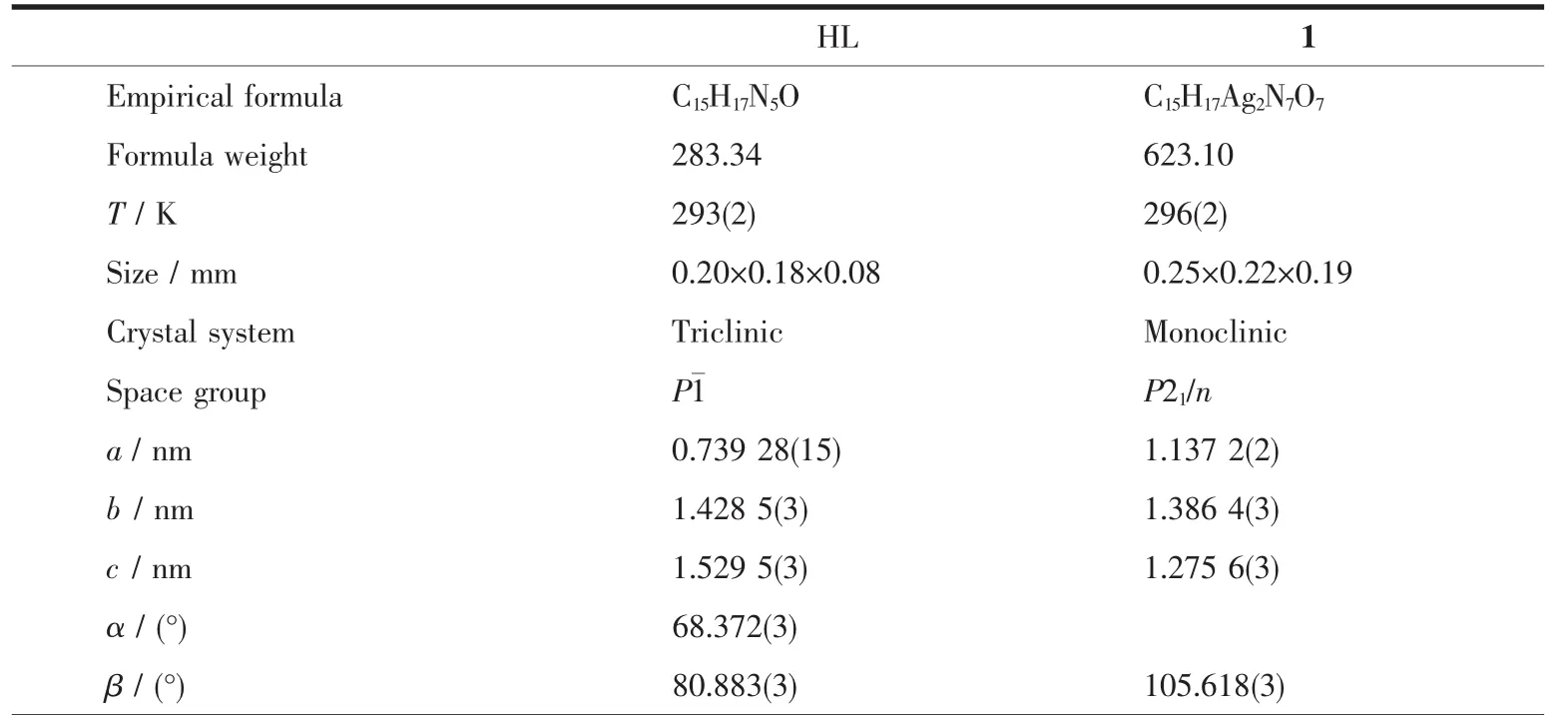
Table 1 Crystal data and structure refinement for HL and complex 1
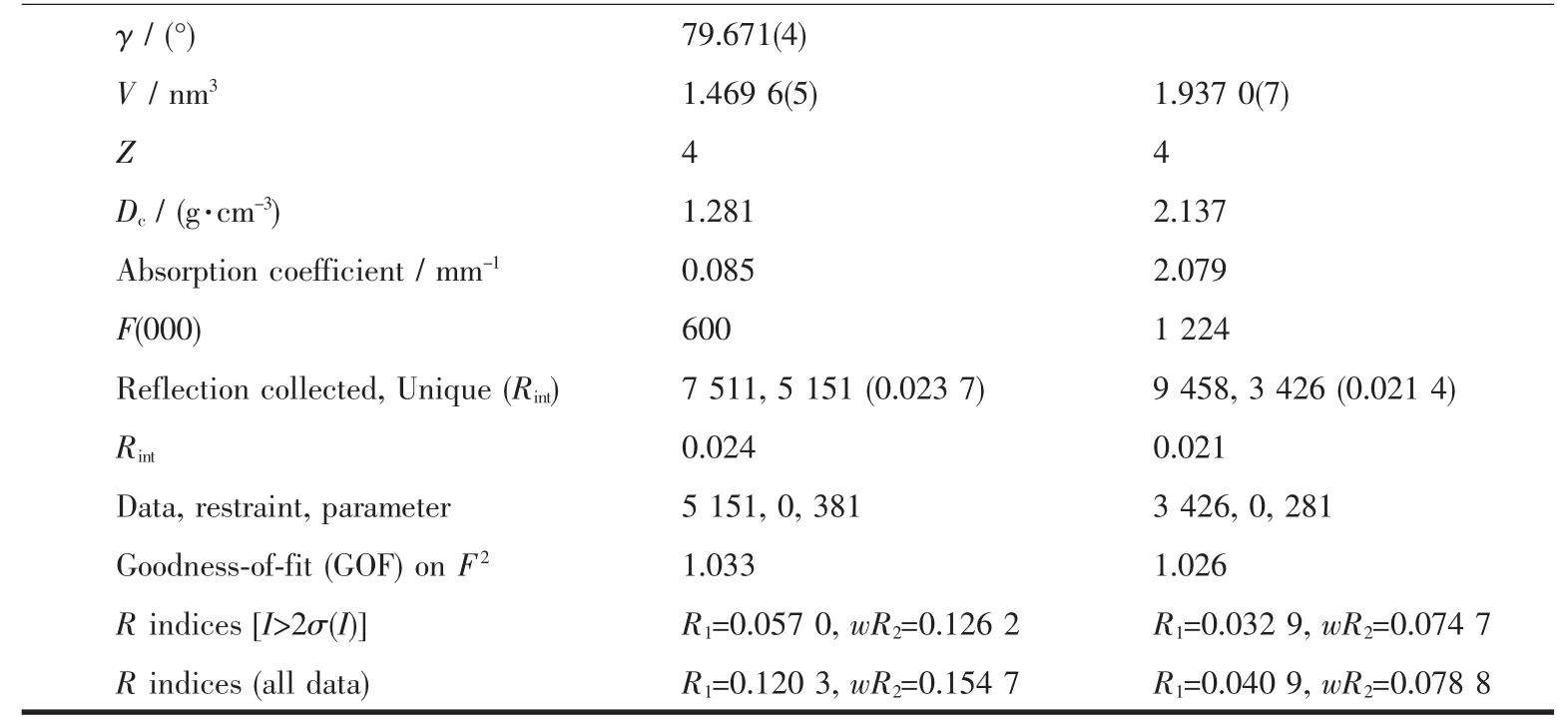
Continued Table 1
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Crystal structure description
Selected bond distances and angles of HL and complex 1 are listed in Table 2.As shown in Fig.1a,there are two independent molecules in the asymmetry unit of HL,in which the bond lengths of C9-O1(0.122 6(3)nm)and C24-O2(0.122 6(3)nm)are comparable to those of some reported semicarbazone ligands[18].Pairs of intermolecular N-H…O hydrogen bonds link two molecules into a centrosymmetry dimer in the solid state (N4-H4…O2,with D…A distance being 0.286 9(3)nm,D-H…A angle being 162.0°;N9-H9…O1,with D…A distance being 0.294 0(3)nm,D-H…A angle being 162.0°).
As illustrated in Fig.1b,the asymmetry unit of complex 1 contains two independent Agガions.One of them is surrounded by one HL ligand with ON2donor set,two O atoms from two nitrate anions,giving a distorted square pyramid coordination geometry;while its counterpart with a planar square coordination geometry is coordinated with three O atoms from two adjacent nitrate anions and terminal pyrazine N4 atom of HL.It is worth noting that O4 and O6 atoms also participate coordination,since the bond lengths of Ag1-O6(0.266 7(3)nm)and Ag2-O4(0.279 9(4)nm)are within the scope of normal inspection and matches with the Ag-O bond in some Agガcomplexes in the literature[19].The neighboring Agガions are linked by two types of nitrate ions into a 1D chain along a axis(in the case of N7/O5-O7,Fig.1c),and a 1D zig-zag chain along c axis(in the case of N6/O2-O4,Fig.1d),respectively,thus giving a 2D framework paralleling to(101)plane(Fig.1e).In the crystal,intermolecular N-H…O hydrogen bonds between the semicarbazone ligands and nitrate anions are also presented(N5-H5…O7iv,with D…A distance being 0.289 5(5)nm,DH…A angle being 162.0°;N4-H4…O6iv,with D…A distance being 0.307 1(5)nm,D-H…A angle being 165.0°,Symmetry codes:ivx,y,z+1).

Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and angles(°)of HL and complex 1

Fig.1 Diamond drawing of HL(a)and 1(b)with 30%thermal ellipsoids;(c)Chain-like structure along a axis in complex 1;(d)Zig-zag chain-like structure along c axis in complex 1;(e)Extended 2D framework structure in complex 1
2.2 IR spectra
The infrared spectral bands most useful for determining the mode of coordination of the semicarbazone ligand are the ν(C=O), ν(C=N),and ν(C=N)pyrizinevibrations.As our previous work shows,such three bands of the ligand HL are at 1 705,1 609 and 1 595 cm-1[10],while they shift to 1 685,1 600 and 1 537 cm-1in the complex 1,respectively,indicating that the carbonyl O,imine N and pyrizine N atoms take part in the coordination[8].In addition,the intense absorption bands in the spectra of complex 1 associated with the asymmetric stretching appear at 1 382,1 311 cm-1(ν4)and 1 498 cm-1(ν1),clearly establishing the existence of monodentate and bidentate NO3-ligands[8,10,20].It is in accordance with the crystal structure study.
2.3 UV spectra

Fig.2 UV spectra of the ligand HL and complex 1 in the methanol solution at room temperature
The UV spectra of complex 1 in methanol solution(concentration:10 μmol·L-1)were measured at room temperature (Fig.2).The spectra of HL features one main band located around 275 nm(ε=6 929 L·mol-1·cm-1)and a shoulder at 282 nm(ε=6 567 L·mol-1·cm-1),which could be assigned to characteristic π-π*transition of benzene and pyrazine units,respectively[10].In complex 1,such two peaks are merged to 291 nm(ε=3 813 L·mol-1·cm-1)with concomitant hypochromic effect,confirming the coordination of ligand HL in complex 1.
2.4 EB-DNA binding study by fluorescence spectrum
It is well known that EB can intercalate nonspecifically into DNA,which causes it to fluoresce strongly.Competitive binding of other drugs to DNA and EB will result in displacement of bound EB and a decrease in the fluorescence intensity[9].As shown in Fig.3,the fluorescence intensities of EB bound to ct-DNA at about 600 nm show remarkable decreasing trends with the increasing concentration of the tested samples,indicating that some EB molecules are exchanged by the tested compounds.The quenching of EB bound to DNA by the compounds is in agreement with the linear Stern-Volmer equation:I0/I=1+Ksqr[8],where I0and I represent the fluorescence intensities in the absence and presence of quencher,respectively,Ksqis the linear Stern-Volmer quenching constant,r is the ratio of the concentration of quencher and DNA.In the quenching plots of I0/I versus r,Ksqvalues are given by the slopes.The Ksqvalues of complex 1 is tested to be 0.781,which is much higher than that of the ligand HL(0.363).The results indicate that interactions of the complex 1 with DNA are stronger than that of the ligand HL.This is probably due to the structure rigidity and metal-ligand synergism effect of the complex 1[8-9].In addition,2D framework structure of the complex 1 may be also responsible for its DNA interaction ability in some content.
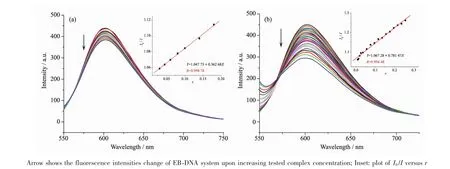
Fig.3 Emission spectra of EB-DNA system in the presence of HL(a)and complex 1(b),respectively
[1]Farhadi S,Mahmoudi F,Dusek M,et al.J.Mol.Struct.,2017,1130:592-602
[2]Enyedy A,Bognár G M,Nagy N V,et al.Polyhedron,2014,67:242-252
[3]Salem N M H,Rashad A R,Sayed L E,et al.Inorg.Chim.Acta,2015,432:231-242
[4]Farhadi S,Mahmoudi F,Dusek M,et al.Polyhedron,2017,122:247-256
[5]Venkatachalam T K,Bernhardt P V,Noble C J,et al.J.Inorg.Biochem.,2016,162:295-308
[6]Todorovic T R,Vukasinovic J,Portalone G,etal.MedChemComm,2017,8:103-111
[7]Patil S R,Asrondkar A,Patil V,et al.Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett.,2017,27:3845-3850
[8]MAO Pan-Dong(毛盼东),ZHAO Xiao-Lei(赵晓雷),SHAO Zhi-Peng(邵志鹏),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(无机化学学报),2017,33:890-896
[9]LIN Long(林龙),LI Xian-Hong(李先宏),ZHANG Bo(张波),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(无机化学学报),2017,33:143-148
[10]MAO Xian-Jie(毛献杰),ZHOU Li-Hua(周利华),FU Si-Lian(伏思连),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(无机化学学报),2017,33:163-168
[11]Alisir S H,Sariboga B,Caglar S,et al.J.Mol.Struct.,2017,1130:156-164
[12]MovahediE,RezvaniAR.J.Mol.Struct.,2017,1139:407-417
[13]Ahmar S,Mac Donald D G,Vijayaratnam N,et al.Angew.Chem.,2010,122:4524
[14]Sun D,Liu F J,Huang R B,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2011,50:12393
[15]Bosch E,Barnes C L.Inorg.Chem.,2002,41:2543-2547
[16]Sheldrick G M.SADABS,University of Göttingen,Germany,1996.
[17]Sheldrick G M.SHELX-97,Program for the Solution and the Refinement of Crystal Structures,University of Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[18]Sheremetev A B,Yudin I L.Russ.Chem.Rev.,2003,72:87-100
[19]Kan W Q,Wen S Z,Kan Y H,et al.Polyhedron,2015,85:246-254
[20]Nakamoto K.Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds.4th Ed.New York:Wiley,1986:257
