基于3-吡唑-5吡啶-1,2,4-三唑和均苯四甲酸构筑的两个同构配位聚合物的晶体结构和磁性
2018-06-06王玉芳太军慧颜小伟赵梦云王利亚
王玉芳 太军慧 颜小伟 赵梦云 王利亚*,
(1洛阳师范学院化学化工学院,功能导向多孔材料重点实验室,洛阳 471934)(2南阳师范学院化学与制药工程学院,南阳 473000)
0 Introduction
The keen interest in the design and fabrication of coordination polymers (CPs)has flourished as an emerging area of research because of their impressive structural topologies and promising application in guest molecule inclusion,gas and vapor storage,chemical sensing,magnetism,heterogeneous catalysis,etc[1-5].Over the past decades,numerous CPs have been successfully constructed,and crystal engineering has reached a relatively mature level that some CPs with specific topologies can be designed by the judicious selection of metal ions and organic ligands[6-7].In this regard,a very promising approach is the use of mixed ligands such as N-donor heterocyclic ligands together with polycarboxylate organic co-linkers in the same system[8-11].N-donor heterocyclic ligands,particularly pyrazole-based flexible or rigid linkers,are acclaimed for theirhigh thermalstability and interesting structural topologies[12-14].Aromatic polycarboxylates are used extensively as organic co-linkers since they often produce inherently rigid structures which have potential application in gas adsorption and storages[15].Keeping this in mind,in this contribution,we report the syntheses and characterization of two new 2D isomorphic coordination polymers with 3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazole and 1,2,4,5-benzenetetracarboxylic acid(Scheme 1).The compounds are formulated as[Co(btec)0.5(H2L)]n(1),[Cu(btec)0.5(H2L)]n(2).
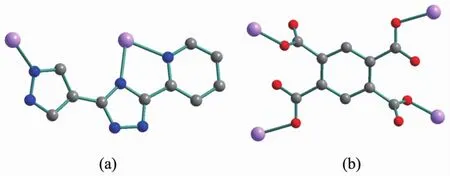
Scheme 1 Coordination modes of H2L and btec4-
1 Experimental
1.1 General
All reagents used in the syntheses were of analyticalgrade.Elementalanalyses forcarbon,hydrogen and nitrogen were performed on a Vario ELⅢelemental analyzer.The infrared spectra (4 000~600 cm-1)were recorded by using KBr pellet on an AvatarTM360 E.S.P.IR spectrometer.The powder X-ray diffraction patterns(PXRDs)were recorded with a Bruker AXS D8 Advance diffractometer using monochromated Cu Kα radiation (λ=0.154 18 nm,2θ=5°~50°),in which the X-ray tube was operated at 40 kV and 40 mA.Magnetic measurements were carried out with a Quantum Design MPMS XL-7 SQUID-VSM magnetometer.Pascal′sconstantswere used to determine the diamagnetic corrections.
1.2 Preparation of compounds 1 and 2
A mixture of Co(NO3)2·4H2O(0.30 mmol,87.3 mg),H2L(0.1 mmol,21.2 mg),and H4btec(0.2 mmol,50.8 mg)was dissolved in 8 mL mixed solvent of CH3CN/H2O (1∶4,V/V),then sealed in a 25 mL Teflonlined stainless steel vessel and heated at 160℃for 72 h.After cooling to room temperature,the dark red block crystals were obtained and then washed with alcohol for several times and filtered to give pure crystals of 1.Anal.Calcd.for C15H9CoN6O4(%):C 45.47,H 2.29,N 21.21.Found(%):C 45.51,H 2.25,N 21.18.IR(KBr,cm-1):2 973,2 901,2 352,1 745,1 694w,1 551,1 458,1 361,1 053,884 808,732,673.Compound 2 was obtained by hydrothermal procedure as that for the preparation of compound 1 only using Cu(OAc)2·H2O(0.1 mmol,19.9 mg),distilled water and 125 ℃ instead of Co(NO3)2·4H2O,mixed solvent of CH3CN/H2O and 150℃.Green block crystals of 2 were collected.Anal.Calcd.for C15H9CuN6O4(%):C 44.95,H 2.26,N 20.96.Found(%):C 44.89,H 2.23,N 20.91.IR(KBr,cm-1):2 985,2 905,2 366,1 746,1 709,1 556,1 513,1 466,1 350,1 046,883,805,733,679.
1.3 X-ray crystallography
Diffraction intensity data of the single crystals of 1 and 2 were collected on a Rigaku oxford diffraction equipped with a graphite monochromated Mo Kα radiation (λ=0.071 073 nm)by using the X-scan technique at 293(2)K.The structures were solved by direct methods and refined on F2by full matrix least squares using SHELXTL[16].All non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically.The hydrogen atoms were located by geometrically calculations,and their thermal parameters were fixed during the structure refinement.Crystallographic data and details of refinement for compounds 1 and 2 are reported in Table 1.Selected bond distances and angles are given in Table 2.
CCDC:1559405,1;1559419,2.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Crystal structure description
Single crystal X-ray analysis reveals that compounds 1 and 2 are isomorphic,and hence only the structure of 1 is given in the ensuing discussion.The asymmetry unit contains one Coギion,half btec4-ligand,and one H2L ligand(Fig.1a).Each Coギcenter is penta-coordinated by three N atoms from two different H2L ligands(Co(1)-N(1)0.212 6(2)nm,Co(1)-N(3)#2 0.216 50(19)nm,and Co(1)-N(6)#2 0.212 1(2)nm)and two O atoms from two different btec4-ligands(Co(1)-O(1)0.204 06(16)nm,Co(1)-O(4)#1 0.203 03(17)nm)showing a distorted trigonal bipyramid coordination geometry.The O-Co-N bond angles vary from 87.28(7)°to 133.90(7)°.The O-Co-O bond angle is 112.77(7)°matching those ofpreviously reported cobaltギcompounds[17].
Table 1 Crystal data and structure refinement for compounds 1 and 2
Table 2 Seclected bond lengths (nm)and bond angles (°)for compounds 1 and 2
It is noteworthy that the H4btec is completely deprotonated in the formation of the compound 1.The four carboxyl groups of btec4-ligand in compound 1 exhibit the same coordination modes( μ1-η1∶η0,μ1-η1∶η0,μ1-η1∶η0,μ1-η1∶η0)(Scheme 1b)and link neighboring four Coギions forming two-dimensional[Co4(btec)]4+structure with the Co…Co separations of 0.637 5 and 0.920 0 nm,respectively(Fig.1b).On the other hand,H2L ligands adopt the μ3-bridging+chelating modes(Scheme 1a)to bind two Coギions forming 1D helix chain with the Co…Co separations of 0.637 5 nm(Fig.1c).The H2L ligands link the two-dimensional[Co4(btec)]4+plane through Co-N coordination interactions to give a two-dimensional network as illustrated in Fig.1d.In the crystal packing,there are H-bonding interactions between triazole nitrogen atom and carboxyl groups of btec4-ligand(N(2)-H(2)…O(2):0.172(3)nm,dN…O=0.262 5(3)nm,∠N-H…O=173(3)°;N(5)-H(5)…O(3)#1:dH…O=0.199 nm,dN…O=0.281 8(3)nm,∠N-H…O=159.9°,Symmetry codes:#1:3/2-x,1/2+y,z).Analysis of the crystal packing also reveals the presence of face to face π…π stacking contacts between the neighbouring 2D layers.The triazole ring(C4-N3-C5-N4-N5)and pyridyl ring(C6-C7-C8-C9-C10-N6)of the neighbouring layers are almost parallel to each other with the dihedral angle of 1.028°.The perpendicular distance between the involved pyridyl and coordinated triazole ring is 0.338 6 nm.The centroid-to-centroid distance between the involved pyridyl and coordinated triazole ring is 0.355 2 nm.As a result,these coordination layers are further extended along the c-axis via such secondary interactions to form a 3D supramolecular lattice.
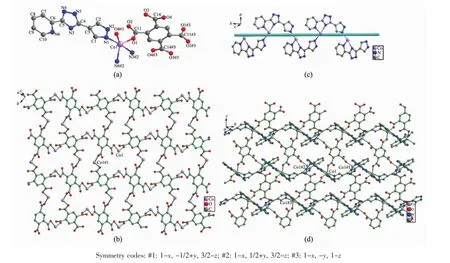
Fig.1 (a)Coordination geometry of the Coギion in 1;(b)2D layer[Co4(btec)]4+in 1;(c)1D chain[Co(H2L)]2+in 1;(d)2D network of 1
2.2 PXRD study
Phase purities of the materials of 1 and 2 were confirmed by powder X-ray diffraction(PXRD)patterns(Fig.2).The experimental and simulated PXRD patterns agree well with each other,confirming the good phase purity.The slight difference in intensity may arise from the preferred orientation of crystalline powder samples.

Fig.2 PXRD patterns of 1 and 2
2.3 Magnetic properties of the compounds
According to the structural data,compound 1 contains Coギchain interlinked by the H2L and btec4-ligands.Considering the interchain Co…Co distance(0.637 5 nm)with Co-O-C-C-C-C-O-Co pathway,the system could be treated as magnetically isolated 1D chain.Variable-temperature magnetic susceptibility of 1 was carried out at 2 000 Oe and from 2.0 to 300 K on a polycrystalline sample.As shown in Fig.3,the χMT value at 300 K is 1.86 cm3·mol-1·K,which is slightly lower than the expected value(1.88 cm3·mol-1·K)of one magnetically isolated spin-only Coギ ion.As T is lowered,χMT continuously increases and reaches a local maximum of 5.02 cm3·mol-1·K at 14 K,and then dropping quickly to 1.69 cm3·mol-1·K at 2.0 K.This behaviour may indicate the occurrence ofa weak ferromagnetic interaction.
The magnetic susceptibility in the range of 21~300 K obeys the Curie-Weiss law with a Curie constant C=3.01 cm3·mol-1·K,which is close to the experimental value 3.39 cm3·mol-1·K for an octahedral Coギion,and a positive Weiss constant θ of 3.39 K.The Curie constant for spin-only Coギion is 1.875 cm3·mol-1·K;the relatively bigger C value for 1 should arise from the significant spin-orbit coupling of Coギion.The positive θ value indicates dominating ferromagnetic interactions between the neighbouring Coギions via the Co-O-C-C-C-C-O-Co pathway.In order to understand quantitatively the magnitude of magnetic interaction,a 1D chain model has been utilized to simulate the experimental magnetic behavior.Then the interaction(J)can be expressed by the spin Hamiltonian H=-J∑SiSi+1.In the classical-spin approximation,the following expression(Eq.1)of magnetic susceptibility was deduced by Fisher[18].
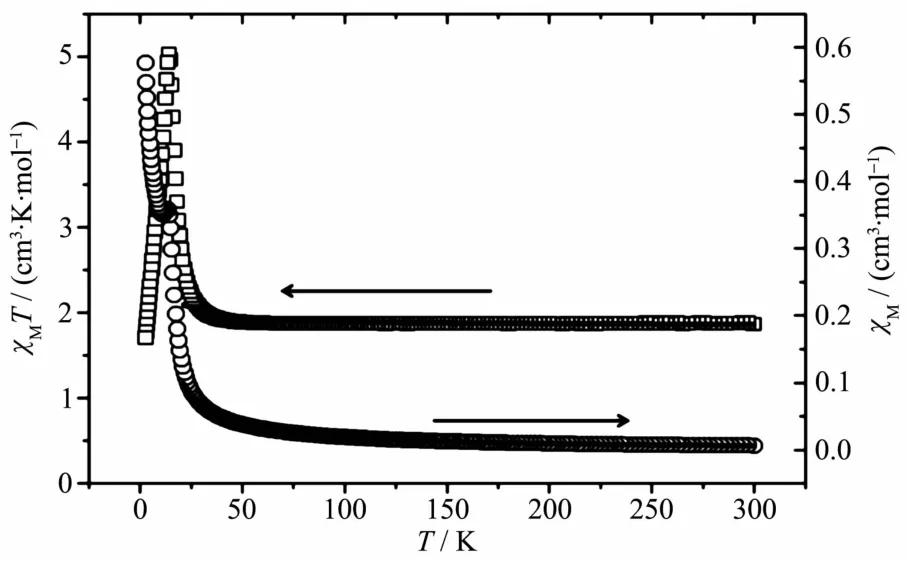
Fig.3 Plots ofand χM(○)versus T for 1
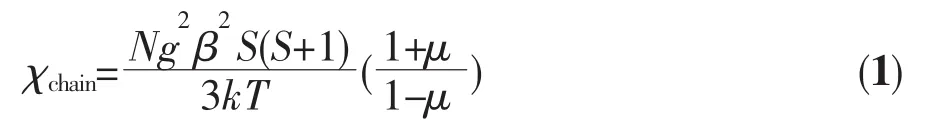
where μ is the Langevin function,μ=coth[JS(S+1)/(kT)]-kT/[JS(S+1)],with S=3/2.The best simulation of the experimental data of 1 lead to J=0.72 cm-1,g=1.99 with an agreement factor(defined asof 8.5×10-3.The solid lines in Fig.3 show that the data in the 21~300 K rang are accommodated by Eq.1.The result indicates that there is a weak ferromagnetic interaction between Coギions in 1.
Similar to structural analysis of compound 1,there are 1D Cuギ chains with the Cu…Cu distance of 0.625 1 nm in compound 2.Magnetic susceptibility of 2 was measured at 2 000 Oe and from 2.0 to 300 K on a polycrystalline sample.As shown in Fig.4,the χMT value at room temperature is 0.374 cm3·mol-1·K,which is very close to the expected value for one uncoupled spin(C=0.374 cm3·mol-1·K,S=1/2,g=2)of Cuギ.As the temperature is lowered to 2 K,the χMT products decrease first slowly and then rapidly.This behavior suggests that antiferromagnetic interaction is operative in 2.To simulate the experimental magnetic interactions in the system,we used the analytical expression for a one-dimensional Heisenberg chain of classical spins(S=1/2)[19]:
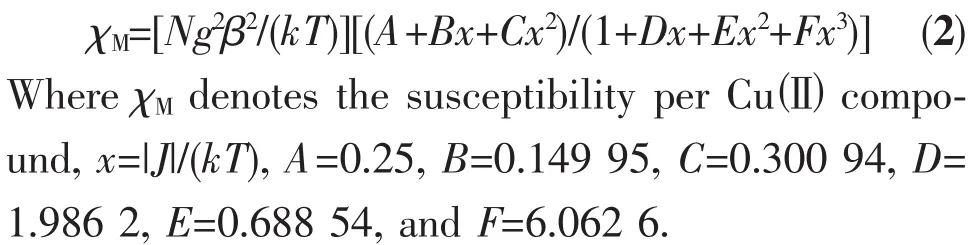
The least-squares analysis of the magnetic susceptibility data led to J=-0.23 cm-1,g=2.00,and R=1.1×10-3.The result indicates the typical feature of paramagnetic behavior in compound 2.
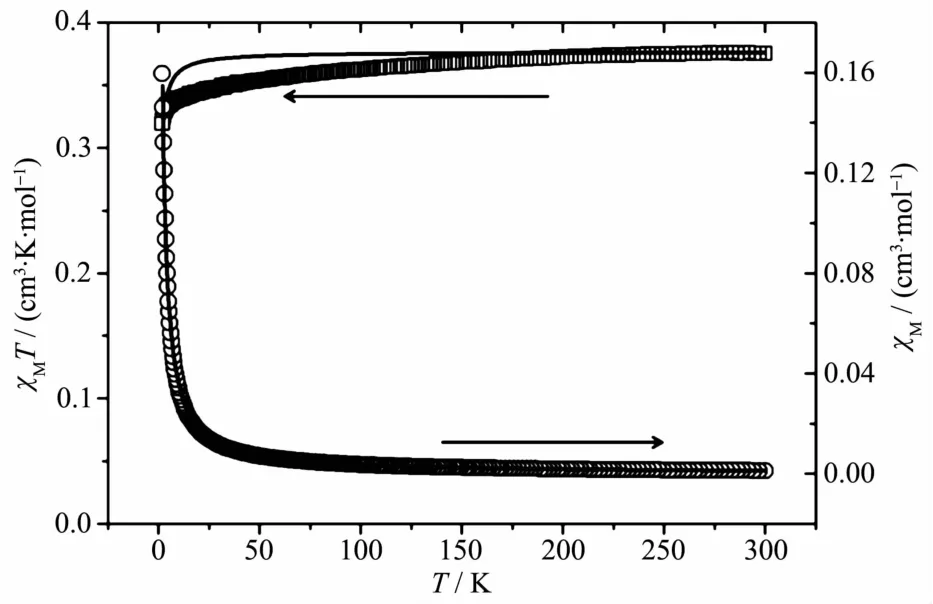
Fig.4 Plots of χMT(□)and χM(○)versus T for 2
3 Conclusions
In summary,two isomorphic compounds have been generated from mixed-ligands system of the 3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazole and aromatic carboxylic acid ligands,which display the same 2D net.Aromatic carboxylic acids are introduced not only to balance the charge but also to coordinate with metal ions,with the aim of obtaining novel products.Accordingly,our present findings will further enrich the crystal engineering strategy and offer the possibility of controlling the formation of the desired network structures.Magnetic studies reveal weak ferromagnetic and paramagnetic behavior in 1 and 2,respectively.
[1]Cowan M G,Miller R G,Southon P D,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2014,53:12076-12083
[2]Goswami S,Adhikary A,Jena H S,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2013,52:12064-12069
[3]Zhang X,Sun M L,Huang Y Y,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun.,201,37:155-157
[4]Feng X,Liu J,Chen J L,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun.,2014,50:42-47
[5]Feng X,Chen J L,Li R F,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun.,2016,66:41-46
[6]Huang Y M,Zhang B G,Duan J G,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2014,14:2866-2872
[7]Ward M D,Raithby P R.Chem.Soc.Rev.,2013,42:1619-1636
[8]Du M,Li C P,Liu C S,et al.Coord.Chem.Rev.,2013,257:1282-1305
[9]TANG Hui(唐辉),GUO Yan-Hong(郭艳红),SHENG Jun-Feng(盛俊峰),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(无机化学学报),2017,33(1):134-142
[10]Wang Y F,Li S H,Ma L F,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun.,2015,62:42-46
[11]Guo X G,Yang W,Wu X,et al.Dalton Trans.,2013,42:15106-15112
[12]Colombo V,Galli S,Choi H J,et al.Chem.Sci.,2011,2:1311-1319
[13]Ganguly S,Mondal R.Cryst.Growth Des.,2015,15:2211-2222
[14]Ma L,Yu N Q,Chen S S,et al.CrystEngComm,2013,15:1352-1364
[15]Chen K J,Lin R B,Liao P Q,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2013,13:2118-2123
[16]Sheldrick G M.Acta Crystallogr.Sect.A:Found.Crystallogr.,2008,A64:112-122
[17]Wang Y F,Li Z,Sun Y C,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun.,2014,44:25-28
[18]Fisher M E.Am.J.Phys.,1964,32:343-346
[19]Ma L F,Wang Y Y,Wang L Y,et al.Eur.J.Inorg.Chem.,2008:693-703
