H2O2稳定性的密度泛函研究
2018-06-01程学礼
程 学 礼
(泰山学院 化学化工学院,山东 泰安 271000)
1 前言
双氧水(H2O2)是一种清洁氧化剂而被广泛用于造纸和化学合成[1],能够参与多种氧化还原反应[2-4].H2O2还常被用于有机污染物的降解[5-7],著名的芬顿反应就是用H2O2和Fe2+的混合溶液氧化有机化合物,特别是难降解有机污染物[8-9].
H2O2可以通过氢气和氧气直接反应或氧气电还原等方法低成本合成[10-11].然而,无论在气相还是溶液中H2O2均不稳定,易分解释放氧气(ΔH=-98.23 kJ/mol);H2O2对光照敏感,双氧水在λ= 275-366nm下均可分解[12-13].在金属阳离子、碘离子和金属氧化物催化下,H2O2能够快速分解[14-17].一般情况下,H2O2分解为2个羟基自由基参与反应,因此,O-O键长的变化在H2O2分解过程中将扮演重要角色.
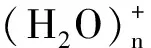
2 计算方法

3 结果与讨论
3.1 基态结构


图1 B3LYP和M06-2X方法结合得到的分子结构(键长的单位是nm,括号内为气相键长)
3.2 发射光谱

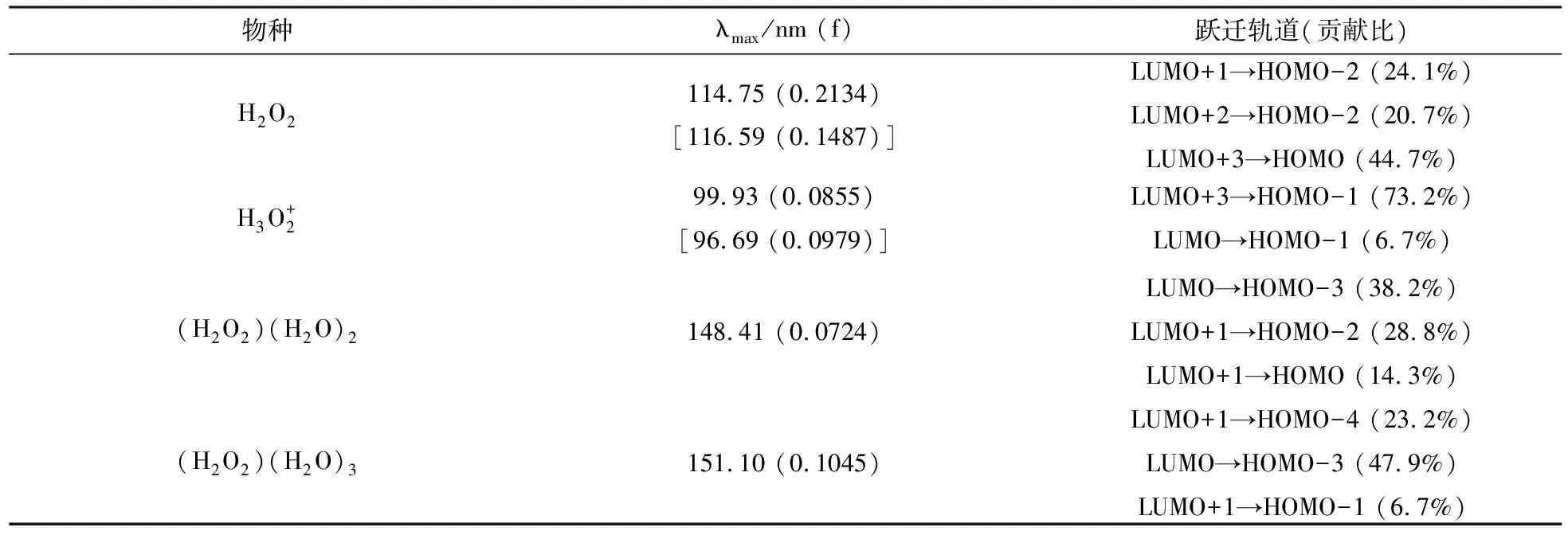
表1 TD-M062X模拟得到的4种结构发射光谱的最大发射波长λmax(振子强度f)和跃迁轨道(跃迁贡献比). λmax以nm为单位.方括号内数据为气相数据
3.3 激发态结构


图2 T1态优化结构参数
4 结论
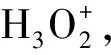
[参考文献]
[1]Kim S., Moon G., Kim H., Mun Y., Zhang P., Lee J., Choi W. Selective charge transfer to dioxygen on KPF6-modified carbon nitride for photocatalytic synthesis of H2O2under visible light[J]. J.Catal.,2018(357):51-58.
[2]Yin G.,Ni Y. Mechanism of the ClO2generation from the H2O2-HClO3reaction[J].Can.J.Chem.Eng.,2000,78(4):827-833.
[3]Jena N. R.,Mishra P. C. Mechanisms of formation of 8-oxoguanine due to reactions of one and two OHradicals and the H2O2molecule with guanine: A quantum computational study[J].J.Phys.Chem.B,2005,109(29):14205-14218.
[4]Das S., Bhattacharyya J.,Mukhopadhyay S. Mechanistic studies on oxidation of hydrogen peroxide by an oxo-bridged diiron complex in aqueous acidic media[J].Dalton Trans.,2008(46):6634-6640.
[5]Gain S., Mishra R., Mukhopadhyay S., Banerjee R. Mechanistic studies on oxidation of hydrogen peroxide and hydrazine by a metal-bound superoxide[J].Inorg.Chim.Acta,2011(373):311-314.
[6]朱承驻,秦艳,周元祥,董文博,侯惠奇.266 nm光照下水溶液中氯苯与H2O2的反应机理研究 [J].化学学报,2007,65(5):451-458.
[7]Merényi G, Lind J., Naumov S.,von Sonntag C. Reaction of ozone with hydrogen peroxide (peroxone process): A revision of current mechanistic concepts based on thermokinetic and quantum-chemical consideration[J].Environ.Sci.Technol.,2010,44(9):3505-3507.
[8]Perez-Benito J.F. Iron(III)-hydrogen peroxide reaction: Kinetic evidence of a hydroxyl-mediated chainmechanism[J].J.Phys.Chem.A,2004,108(22):4853-4858.
[9]Navalon S., Dhakshinamoorthy A., Alvaro M., Garcia H. Heterogeneous Fenton catalysts based on activatedcarbon and related materials[J].ChemSusChem,2011,4(12):1712-1730.
[10]Zhao K., Su Y.,QuanX., Liu Y.,ChenS.,YuH. Enhanced H2O2production by selective electrochemical reduction of O2on fluorine-doped hierarchically porous carbon[J].J.Catal.,2018(357):118-126.
[11]Wilson N.M.,Priyadarshini P.,Kunz S.,Flaherty D.W. Direct synthesis of H2O2on Pd and AuxPd1clusters: Understanding the effects of alloying Pd with Au[J].J.Catal.,2018(357):163-175.
[12]Odochian L., Iancu L., Humelnicu I., Mocanu A.M., Baiceanu A. Contributions to the reaction mechanism of photochemicaldecomposition of hydrogen peroxide in aqueous solution[J]. Rev. Chim. (Bucharest),2011,62(10):1012-1016.
[13]Nedrygailov I.I., Lee C., Moon S.Y., Lee H., Park J.Y. Hot electrons at solid liquid interfaces: A large chemoelectriceffect during the catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide[J].Angew.Chem.Int. Ed.,2016,55(36):10859-10862.
[14]Dalmázio I., Moura F.C. C., Ara jo M.H., Alves T.M. A., Lago R.M., de Lima G.F., Duarte H.A.,R.Augusti. The iodide-catalyzed decomposition of hydrogen peroxide: Mechanistic details of an oldreaction as revealed by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry monitoring[J].J. Braz. Chem. Soc., 2008,19(6):1105-1110.
[15]Voloshin Y., Manganaro J., Lawal A. Kinetics and mechanism of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide over Pd/SiO2catalyst[J]. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.,2008,47(21):8119-8125.
[16]Do S.-H.,Batchelor B.,Lee H.-K.,Kong S.-H. Hydrogen peroxide decomposition on manganese oxide (pyrolusite): Kinetics, intermediates, and mechanism[J].Chemosphere,2009(75):8-12.
[17]Zhao Y., Chen Z., Shen X., Zhang X. Kinetics and mechanisms of heterogeneous reaction of gaseoushydrogen peroxide on mineral oxide particles[J].Environ. Sci. Technol.,2011,45(8):3317-3324.
[18]Verlet J. R. R., Bragg A. E., Kammrath A., Cheshnovsky O., Neumark D. M. Observation of largewater-cluster anions withsurface-bound excess electrons[J].Science,2005,307(5706):93-96.
[19]Turi L., Sheu W., Rossky P.J. Characterization of excesselectrons in water-cluster anions by quantum simulations[J].Science,2005,309(5736):914-917.
[20]Tsai C. J.,Jordan K. D. Theoretical study of the (H2O)6cluster[J].Chem.Phys.Lett.,1993(213):181-188.
[21]Pedulla J. M., Vila F., Jordan K. D. Binding energy of the ring form of (H2O)6: Comparison of the predictions of conventional and localized-orbital MP2 calculations[J].J.Chem.Phys.,1996,105(24):11091-11099.
[22]Pedulla J. M., Kim K., Jordan K. D. Theoretical study of the n-body interaction energies of the ring, cage and prism forms of (H2O)6[J].Chem.Phys.Lett.,1998(291):78-84.
[23]Balasubramanian K. Nonrigid group theory, tunneling splittings, and nuclear spin statistics of waterpentamer: (H2O)5[J].J.Phys.Chem.A,2004,108(26):5527-5536.
[24]Jiang J., Wang Y., Chang H., Lin S.H., Lee Y.T., Niedner-Schatteburg G., Chang H. Infrared spectra of H+(H2O)5-8clusters: Evidence for symmetricproton hydration[J].J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2000,122(7):1398-1410.
[25]Dahms F., Costard R., Pines E., Fingerhut B.P., Nibbering E.T. J., Elsaesser T. The hydrated excess proton in the Zundel cation H5O2+: The role of ultrafast solvent fluctuations[J].Angew.Chem.Int. Ed.,2016,55(36):10600-10605.
[26]Arias C., Mata F., Perez-Benit J.F. Kinetics and mechanism of oxidation of iodide ion by the molybdenum(VI)-hydrogen peroxide system[J].O.Can.J.Chem.,1990,68(9):1499-1503.
[27] Moin S.T., Hofer T.S., Randolf B.R., Rode B.M. An ab initioquantum mechanical charge eld molecular dynamics simulation of hydrogen peroxide in water[J].Comput.Theor.Chem.,2012(980):15-22.

