Expression of aquaporins in human larynx*
2018-05-21,,,,,△
, , ,, , △
(1.Department of Genetics and Biochemistry,Basic Medical School of Jiamusi University,2.Clinical Laboratory,Department of Infectious Diseases,Hospital of Jiamusi,Jiamusi 154007,China)
The larynx,an important part of the respiratory system (RS),is the vocal organ and the basis of vocalization and vocalism in humans[1].Fluid secretion and hydration equilibrium are necessary for laryngeal function[2].The larynx is a complicated organ that includes the supraglottic,glottic,and infraglottic portions.The upper margin of the supraglottic portion lies between the vocal fold down to the arytenoid cartilage and includes the ventricular band and laryngeal ventricle[3].The surface of the laryngeal cavity is covered by a mucous membrane,similar to that of the throat and trachea; only the composition and thickness differ.Most parts of the larynx,such as the vocal fold and aryepiglottic plicae,are covered with stratified squamous epithelium,and stratified columnar ciliated epithelium occurs on the other surface of the laryngeal cavity,below the laryngeal side of the epiglottis.The entire larynx has mucus glands except for the vocal fold,where the laryngeal ventricle secretes abundant mucus to lubricate the vocal fold.Furthermore,there are plenty of nervous and vascular tissues in the larynx for nutrition and controlling its movement[3-4].
Aquaporins (AQPs) are a family of small integral membrane proteins that function as water channels and are widely expressed on mammalian and plant cellular membranes.AQPs are involved in various cellular functions,such as migration,differentiation,adhesion,and secretion[5].In mammals,13 members have been identified thus far,of which 4 are found in the RS,including AQP1,AQP3,AQP4,and AQP5 and are distributed in the nasopharynx,larynx,trachea,and lung[5-6].AQPs play important roles in maintaining the dynamic equilibrium of the RS[6].AQPs seem to be localized throughout the human respiratory tract.AQPs seem to be localized throughout the human respiratory tract,but AQP expression has not been reported in the human larynx before,except for a report on AQP3 expression in adult vocal cords[6].Of note,however,Guan et al.reported AQP1 and AQP4 expression in laryngeal carcinoma patients.As the points,AQP1 was located mainly on capillary endothelia and laryngeal mucous glands of normal tissues,part of the tumor cells and cancer nests of laryngeal carcinoma tissues,however,AQP4 expressed mainly on squamous epithelial,pseu-dostratified ciliated columnar epithelia and laryngeal mucous glands of normal laryngeal tissues and on tumor cell membrane and cancer nests of laryngeal carcinoma tissues.But we questioned the pictures quality in the articles[7-8].
The aim of this study was to identify the tissue localization of AQPs in the larynx,which will help in understanding their function in the larynx and for maintaining vocalization.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Materials
Human larynx tissues were collected from laryngeal cancer patients after surgery at the First Affiliated Hospital of Jiamusi University.These tissues were divided into 3 parts:for RNA extraction,for protein detection,and for immunohistochemistry (IHC).The Histostain-SP IHC kit was obtained from Invitrogen (95-9643,Burlington,ONT,CA).
1.2 RT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from the larynx using TRIzol.Next,mRNA was purified from the total RNA using the Oligotex Direct mRNA Mini kit (Qiagen,72022,Valencia,CA,USA).cDNA synthesis was catalyzed by SuperScriptTMⅡ kit (Invitrogen,18064-014),and the first strand acted as the template for AQP gene amplification using the primers listed in Table 1,which were designed by crossing at least 1 intron junction.The primers were partly similar to those from our earlier publications[9].The PCR products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis and purified with a PCR purification kit (Qiagen,28104) for DNA sequencing.All primers cross intron junctions according to the mRNA and gene sequences.

Tab 1 Primers for aquaporin identification
1.3 Western blotting
Laryngeal tissue was homogenized and sonicated in lysis buffer (0.1% SDS,0.1% NP-40,0.5% sodium deoxycholate,1 mmol/L PMSF,1μg/ml aprotinin,2μg/ml leupeptin) from larynx tissue with additional centrifugation (16,000g,10min),and the supernatant was collected as total protein.Protein concentrations were quantified using a BCA protein reagent kit (23225,Pierce,Rockford,IL,USA).Protein (50μg) from each tissue was subjected to SDS-PAGE and transferred to PVDF membranes.Unbound sites were blocked for 1h at room temperature with 5% (w/v) skim milk powder in TBST (10mmol/L Tris (pH 8.0),150 mmol/L NaCl,0.05% Tween 20).Blots were incubated with AQP antibodies (1∶500; AQP1,sc-20810,AQP3,sc-20811,AQP4,sc-20812; Santa Cruz) at room temperature for 1h.The blots were then washed thrice for 10min each with TBST and incubated for 1h with 2μg/ml horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (1∶5000; Sigma,AP307P,Darmstadt,German) in TBST with 10% fetal bovine serum,followed by 3 TBST washes.Samples were incubated with ECL Plus Western blotting detection reagents (RPN2132,GE,Piscotoway,NJ,USA) and then exposed to X-ray film (Eastman Kodak Co.).
1.4 Immunohistochemical staining
Laryngeal tissues were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde,followed by paraffin embedding and sectioning.After incubation with 10% H2O2for 10min and microwave antigen retrieval,the streptavidin peroxidase (SP) method was employed for detecting AQP expression as follows:specimens were blocked with 10% goat serum and incubated with AQP primary antibodies (AQP1,AQP3,and S100; 1∶100,Santa Cruz) for 1h,and whole-molecule rabbit IgG was used as the negative control in parallel with the primary antibodies.This was followed by 3 washes with wash buffer (PBS with 0.5% bovine serum albumin and 0.15% glycine,pH 7.4),and subsequent incubation with horseradish peroxidase-labeled secondary antibodies (1∶500; AP307P) for 30min.The slides were subjected to washing and staining with DAB,counterstaining with hematoxylin,dehydration in graded ethanol,clearing in xylene,mounting,and microscopy.
2 Results
2.1 AQP1 and AQP3 expressed in human larynx
RT-PCR products of AQP1,AQP3,AQP11,and AQP12 were found on agarose gels,and the bands were cut and purified for DNA sequencing.Only AQP1 and AQP3 corresponded to the correct sequences,whereas AQP11 and AQP12 were found to be nonspecific products (Figure 1A).
Western blotting was employed by using AQP1,AQP3,AQP4,and AQP5 as the first primary antibodies according to the PCR results and previous reports (Figure 1B).In line with the PCR results,Western blotting also detected only AQP1 and AQP3 proteins.

Fig 1 Identification of AQPs in the larynx
A: AQPs were detected by RT-PCR.Total RNA was extracted from the larynx after surgery.After purification,about 300 ng mRNA was used as the template for retrotranscription of cDNA.The cDNA served as the template for PCR with the AQP primers shown in Table 1.Bands were found for AQP1,AQP3,AQP11,and AQP12.By DNA sequencing,AQP1 and AQP3 corresponded to the correct fragments,and AQP11 and AQP12 were found to be nonspecific bands.B: AQP1 and AQP3 proteins were detected in the larynx by Western blotting.L: larynx tissue; LN: adjacent tissues; C: kidney tissue of an AQP1 and AQP3 double knockout mouse as the negative control; K: kidney.
2.2 Localization of AQP1 and AQP3 in human larynx
Localization of AQPs in the larynx analyzed by S-P IHC staining revealed that AQP1 was located on the cilia of the pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium (PCCE),in the vascular endothelial cells of the lamina propria mucosae,and in glial cells of nerve fibers and ganglia (Figure 2A,D,and Figure 3A).
Furthermore,AQP3 was distributed on the membrane of squamous epithelial cells and lamina propria glandular cells of the laryngeal mucosa,as well as on the basal lateral membrane of the PCCE (Figure 3B,C,D).Corresponding to the RT-PCR and Western blotting findings,no AQP4 or AQP5 was found by IHC staining (data not shown).
3 Discussion
3.1 Localization of AQPs in the larynx is important for understanding respiratory AQPs
AQPs,small integral water channels,widely exist in the cell membranes of mammals,and thus far,13 AQPs have been identified (AQP0-12).These molecules are selectively located in tissues associated with the absorption or secretion of liquid,which is important for the tissues’ liquid reabsorption,secretion,and extra- and intracellular water equilibrium[5].In the RS,AQPs play a vital role in maintaining the water balance.Until now,4 AQPs were reported to be localized in the RS:AQP1,AQP3,AQP4,and AQP5.AQP1 is mainly expressed on vascular endothelial cells and pleural cells.AQP3 is mainly expressed in the basolateral membrane of basal cells in airways and in the lamina propria mucosae of true adult vocal cords[6,10].AQP4 expression is localized in the basolateral membrane of columnar ciliary epithelial cells of the trachea and bronchi,whereas AQP5 is expressed in columnar cells,glandular cells in bronchi,and the apical membrane of type I alveolar cells[6].Until now,it appeared that the localization of AQPs in the human RS was clarified.In fact,except for the vocal fold,no report on AQP localization in the human larynx has been published.In other words,the localization of AQPs in the RS remains incomplete.In the literature,AQP expression has been reported in the larynx of other animals:AQP1 and AQP4 expression has been found in the rat larynx[8],and AQP1-8 expression has been detected in the mouse larynx[11].However,our report on human samples demonstrated only AQP1 and AQP3 expression using RT-PCR,Western blotting,and IHC.It is different from the reports of Guan et al.that AQP4 was not found in our research[7].More researches needed to identify if AQP4 expresses in the larynx.
3.2 AQPs might play important roles in laryngeal function
According to our results,AQP1 expression sites are markedly different from AQP3 expression sites in the larynx.Corresponding to previous reports[6],in this study,AQP1 was expressed on the cilia of the PCCE,in the vascular endothelial cells of the lamina propria mucosae,and in glial cells of nerve fibers and nodes.AQP1 is the first identified AQP that is widely distributed throughout the body.Here,for the first time,AQP1 expression was detected on the cilia of the PCCE of the laryngeal ventricle.Hydration of the cilia is vital for ciliary movement and vibration[12].The capillary endothelium is the barrier for water transport.Bai et al.found that permeability between alveoli and capillaries decreased by about 50% in AQP1-knockout mice,which proved that AQP1 was the main transporting pathway for water passing through the capillaries[12].High expression of AQP1 in the laryngeal capillary endothelium ensures quick water transport into peripheral tissues to regulate the hydrodynamic pressure and alternatively expensive pressure of intercellular liquid volume and vascular volume to guarantee laryngeal metabolism.Consistent with previous reports,AQP3 expression was located in squamous epithelial cells and lamina propria glandular cells of the laryngeal mucosa[13].Water has been found to be transported by AQP3 to dilute sticky mucus,thereby making mucus secretion smoother[14].Moreover,AQP1 expression was detected in glial cells of recurrent laryngeal nerve ganglia and nerve fascicles,confirming our previous report[15].AQP1,2,and 4 have been reported to be expressed in the peripheral nervous system with differential expression[16].The main function of recurrent nerve ganglia is algesia regulation,and Zhang et al found that sensitivity to pain decreased dramatically in dorsal root ganglia of AQP1-null mice.Verifying if AQP1 is involved in pain regulation was beyond the scope of the present experiments; however,the likely role of AQP1 in pain regulation has been demonstrated[17].
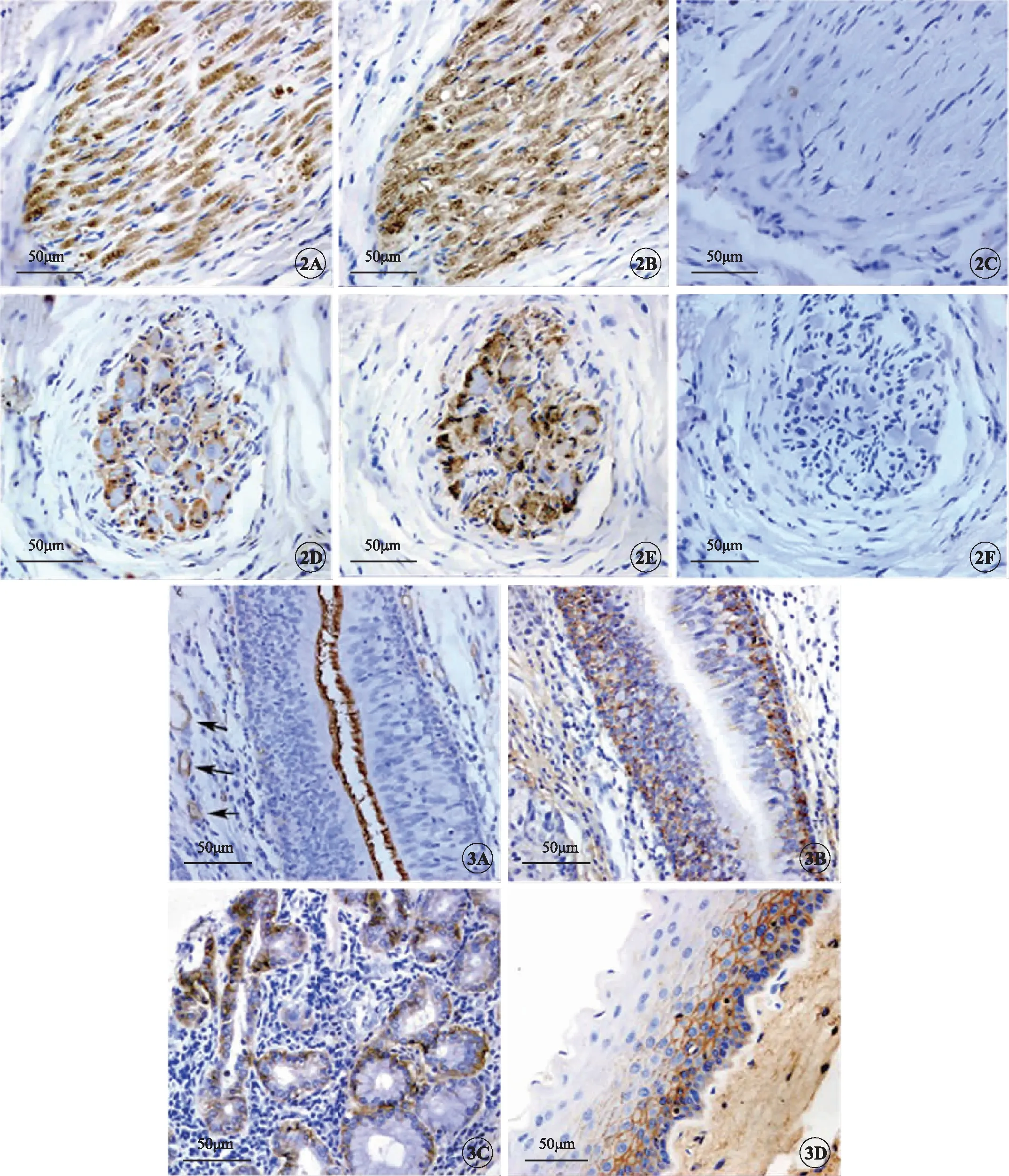
Fig 2 Immune staining of AQP1 in laryngeal ganglia.Bar=50μm.A-C:serial longitudinal sections of the ganglia.D-F:serial cross sections.AQP1 expression was found in glial cells (A,B) and was identified with marker S100 (D,E).AQP1 and S100 had similar localization in glial cells.C and F were the negative controls (rabbit IgG as the primary antibody).
Fig 3 Immune staining of AQP1 and AQP3 in the larynx.Bar=50μm.A,B:Serial sections of the ventricle were stained by using AQP1 and AQP3 antibodies.AQP1 was located on the cilia of the pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium (PCCE) (A) and the membrane of vascular endothelial cells (arrowheads).AQP3 was localized on the basolateral membrane of the PCCE (B),lamina propria glandular cells of the laryngeal mucus gland (C),and membrane of squamous epithelial cells (D).
It is noteworthy that our research confirmed the importance of AQPs in preserving the function of the human “sound box” or the laryngeal ventricle.A pleasant voice in humans arises by resonance[18].Vocal resonances include resonance of the head cavity,nasal cavity,and oral cavity.The oral cavity is shaped like a flared pipe.The oral and nasal cavities lie above the vocal cord,the outlets of which include the nasal and oral cavities.The ventricle or pharyngeal cavity,whose chamber forms the “sound box” of the “horn” which is the first cavity for resonance after sound is produced by the vocal cord.Resonance from the sound box is produced by internal cilia and the wall of the ventricle together[19].AQP1 expression is found on the cilia of the PCCE in the ventricle of the larynx,and AQP3 is expressed in the squamous epithelial cells of the ventricle and lamina propria glandular cells of the laryngeal mucosa.AQP1 secretes water to the surface of the cilia,and AQP3 facilitates mucus secretion.The hydration of the ventricle is beneficial for resonance,which in turn is very important for vocalization,especially for vocalism.However,there has been no report on AQP1-null persons having obvious speech impairments,implying that the role of AQP1 may be subtle.However,most of the earlier reports only focused on changes in the Colton antigen system rather than on sound quality[20-21].Furthermore,AQP1 might have an important role in laryngeal nerve nutrition and message transduction (Zhang et al.2015).
In conclusion,the localization of AQP expression in the human larynx was determined in this study.The distribution of AQP1 and AQP3 expression was as follows:AQP1 expression was localized on the cilia of the PCCE,in the vascular endothelial cells of the lamina propria mucosae,and in glial cells of nerve fibers and ganglia.AQP3 expression was detected in squamous epithelial cells and lamina propria glandular cells of the laryngeal mucosa.Thus,AQP1 and AQP3 might be playing important roles in the proper functioning of the larynx.
References
[1] Lieberman P.The evolution of language and thought[J].J Anthropol Sci,2016,94:127-146.
[2] Leydon C,Sivasankar M,Falciglia D L,et al.Vocal fold surface hydration:a review[J].J Voice,2009,23(6):658-665.
[3] Morris I R.Functional anatomy of the upper airway[J].Emerg Med Clin North Am,1988,6(4):639-669.
[4] Nakashima T,Komiyama S,Makishima K,et al.Immunopathological study of the larynx.IgA distribution and secretory activity[J].Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol,1980,89(4 Pt 1):359-365.
[5] Verkman A S.Aquaporins in clinical medicine[J].Ann Rev Med,2012,63:303-316.
[6] Verkman A S.Role of aquaporins in lung liquid physiology[J].Respir Physiol Neurobiol,2007,159(3):324-330.
[7] 关兵,孙丽光,董震,等.水通道蛋白1及4在喉癌组织中的分布及意义[J].中国肿瘤临床,2005,21(6):269-272.
[8] 关兵,张庆丰,董震,等.水通道蛋白1及4在大鼠喉组织中的表达[J].临床耳鼻咽喉科杂志,2006,20(3):132-134.
[9] Su W,Guan X,Zhang D,et al.Occurrence of multi-oocyte follicles in aquaporin 8-deficient mice[J].Reprod Biol Endocrinol,2013,11(88):1-6.
[10] Goodier M A,Goodier A P,Brown A S,et al.Immunohistochemical analysis of aquaporins in the fetal and adult vocal fold[J].Laryngoscope,2010,120 (Suppl 4):S195.
[11] Ahmed Mel-R,Bando H,Hirota R,et al.Localization and regulation of aquaporins in the murine larynx[J].Acta Otolaryngol,2012,132(4):439-446.
[12] Bai C,Fukuda N,Song Y,Ma T,et al.Lung fluid transport in aquaporin-1 and aquaporin-4 knockout mice[J].J Clin Invest,1999,103(4):555-561.
[13] Vesterdorf K,Blache D,Maloney S K.Immunolocalization of aquaporins 1,3,and 5 in the nasal respiratory mucosa of a panting species,the sheep[J].J Therm Biol,2014,43:61-69.
[14] Tsang K W,Leung J C,Tipoe G L,et al.Down-regulation of aquaporin 3 in bronchiectatic airways in vivo[J].Respir Med,2003,97(1):59-64.
[15] Gao H,He C,Fang X,et al.Localization of aquaporin-1 water channel in glial cells of the human peripheral nervous system[J].Glia,2006,53(7):783-787.
[16] Ma T,Gao H,Fang X,et al.Water channel proteins in the peripheral nervous system in health and disease[J].Mol Aspects Med,2012,33(5-6):605-611
[17] Zhang H,Verkman A S.Aquaporin-1 water permeability as a novel determinant of axonal regeneration in dorsal root ganglion neurons[J].Exp Neurol,2015,265:152-159.
[18] Vos R R,Daffern H,Howard D M.Resonance tuning in three girl choristers[J].J Voice,2017,31(1):e1-e7.
[19] Siyahhan B,Knobloch V,de Zélicourt D,et al.Flow induced by ependymal cilia dominates near-wall cerebrospinal fluid dynamics in the lateral ventricles[J].J R Soc Interface,2014,11(94):20131189.
[20] Saison C,Peyrard T,Landre C,et al.A new AQP1 null allele identified in a Gypsy woman who developed an anti-CO3during her first pregnancy[J].Vox Sang,2012,103(2):137-144.
[21] Arnaud L,Peyrard T,Landre C,et al.A functional AQP1 allele producing a Co(a-b-) phenotype revises and extends the Colton blood group system[J].Transfusion,2010,50(10):2106-2116
(编辑:冀凯宏)
摘要目的:探讨水通道在喉组织中的分布及可能的功能。方法:通过RT-PCR、免疫印迹分别在RNA和蛋白水平明确喉组织中水通道的种类;采用免疫组织化学法对喉组织中的水通道蛋白进行定位分析。结果:水通道AQP1和AQP3在喉组织中表达:水通道蛋白AQP1在喉室黏膜假复层纤毛柱状上皮的纤毛、黏膜固有层的血管内皮及喉部神经纤维和神经节中表达;AQP3在喉黏膜鳞状上皮和固有层腺体上有表达。结论:喉组织中的水通道蛋白AQP1和AQP3在维持喉正常生理功能特别是发声中可能具有重要的作用。
关键词喉; 喉室; 水通道蛋白1; 水通道蛋白3; 发声