基于红外传感的高精度运动体质智能检测系统设计
2018-05-15刘丽
刘丽
摘 要: 普通运动体质智能检测系统检测精度较低,且需要较长的检测等待时间,为了解决此问题,引入红外传感技术,设计基于红外传感的高精度运动体质智能检测系统。在红外传感技术支持下,通过客户端设计、后台管理系统设计、用户管理模块设计,完成智能检测系统硬件设计;在高精度手段约束下,通过数据库设计、检测流程设计、业务流程设计,完成智能检测系统软件设计。对比应用普通系统与改进后系统的检测结果可知,基于红外传感的高精度运动体质智能检测系统可提高检测精度、缩短检测等待时间。
关键词: 红外传感; 运动体质; 智能检测; 硬件设计; 软件设计; 检测流程
中图分类号: TN219?34; TP399 文献标识码: A 文章编号: 1004?373X(2018)10?0051?04
Abstract: Since the ordinary intelligent detection system for sports physique has low detection precision and needs relatively long detection waiting time, a high?precision intelligent sports physique detection system based on infrared sensing was designed by introducing the infrared sensing technology. With the support of infrared sensing technology, the hardware design of intelligent detection system was accomplished by means of the design of client, background management system, and user management module. Relying on high?precision means, the software design of intelligent detection system was accomplished by means of the design of database, detection process, and business process. It is found, by comparing the detection results of the ordinary system and the improved system, that the high?precision intelligent sports physique detection system based on infrared sensing can improve the detection precision and shorten the detection waiting time.
Keywords: infrared sensing; sports physique; intelligent detection; hardware design; software design; detection process
普通运动体质智能检测系统引入加速度传感器技术,用于检测人体在运动状态下,体质的变化情况。加速度传感器技术的应用,不仅增加了能耗计算结果的可行性,也解决了传统能耗算法,在数据预处理方面存在的问题。但普通运动体质智能检测系统的应用,需要依附智能手机的实时运动强度识别算法,在采集人体特征指数、计算耗能参数等方面,需要进行大量的数据运算,不仅降低了系统的检测精度,也大大增加了检测等待时间[1?2]。为了在现有研究水平基础上,增加运动体质智能检测系统的实用性,引入红外传感技术,简化复杂的计算步骤,提升系统的检测精度。红外传感技术的应用需设置多个红外射线采集点,可满足不同射管阵列对于间距与数量的选取需求[3]。通过引入红外传感技术,将普通运动体质智能检测系统改进为基于红外传感的高精度运动体质智能检测系统,提升检测精度,缩短检测等待时间,提高系统的实用价值。
1 智能检测系统硬件设计
1.1 基于红外传感技术的系统客户端设计
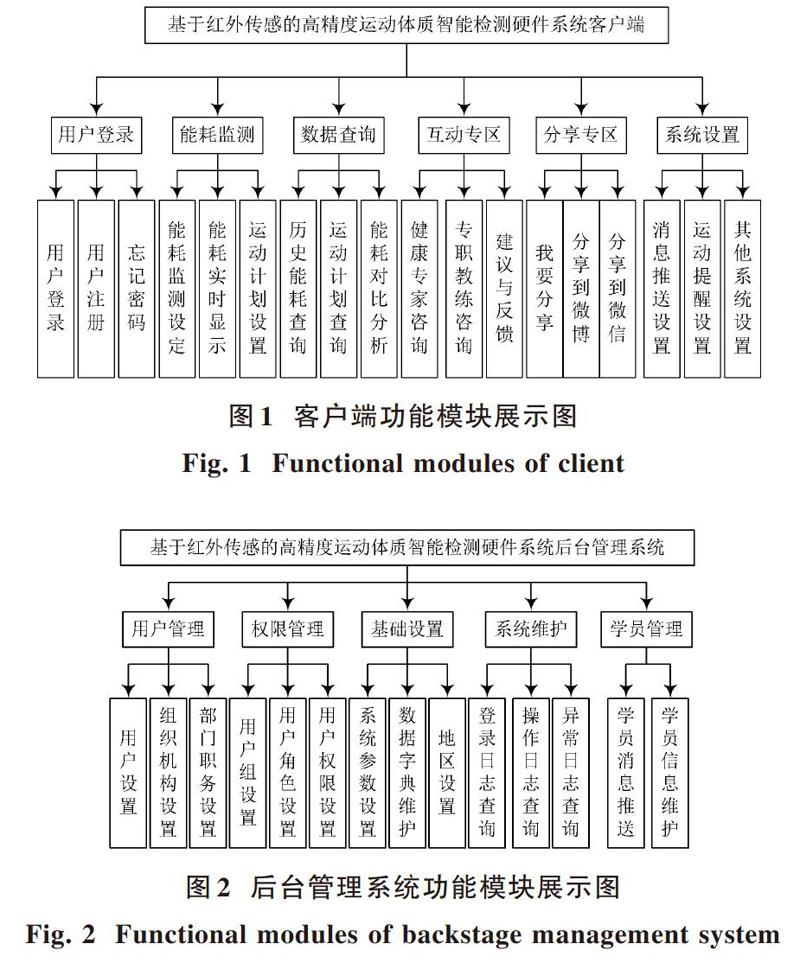
基于红外传感的高精度运动体质智能检测硬件系统客户端,运行在使用者的中心计算机上,主要用于记录用户的体质情况[4]。智能检测系统硬件客户端,具有历史数据查询以及专业数据分析的作用,在进行使用者体质情况检测的同时,也可提供数据分析查询、数据共享、用户间的互动等功能[5?6]。具体功能模块展示如图1所示。
1.2 基于红外传感技术的后台管理系统设计
基于红外传感的高精度运动体质智能检测硬件系统的后台管理系统,对客户端采集到的用户数据进行整合管理[7]。将基础用户数据和用户能耗数据分离,并对它们进行持久化保存处理。智能检测硬件系统的后台管理系统,主要为主机端提供用户管理、能耗查询、数据分析、消息推送等服务,具体功能模块如图2所示。
1.3 基于红外传感技术的用户管理模块设计
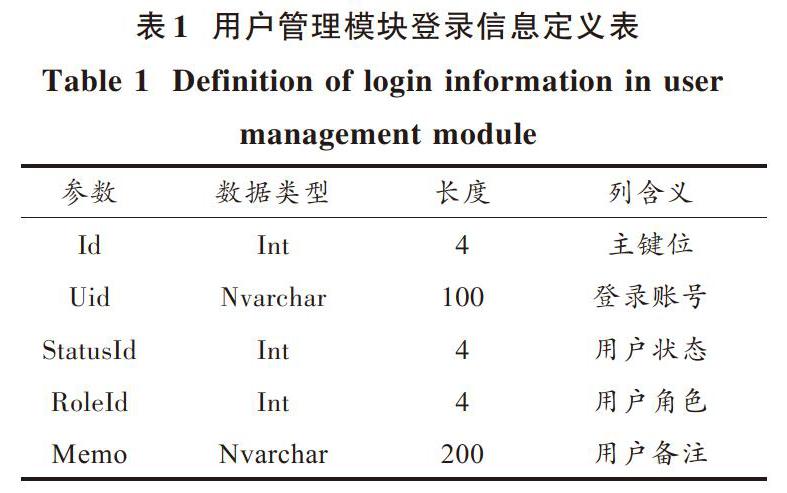
基于红外传感的高精度运动体质智能检测硬件系统的用户管理模块,采用红外传感技术,存储用户运动体质状态信息。完成登录操作后的用户信息,可按照表1进行具体定义。
2 智能检测系统软件设计
2.1 高精度运动体质智能检测系统数据库设计
基于红外传感的高精度运动体质智能检测系统数据库,具备根据后台表格或图表内容,查询所有回传至中心服务器数据损耗情况的功能[8]。通常情况下,运动计划可以反应使用者的体质健康情况,若某使用者可保持长时间、高强度的体育运动,则系统可根据运动的瞬时能耗以及运动总能耗,判定该名使用者体质良好。也可根据使用者的真实年龄、身高、体重、性别、从事行业等相关信息,对使用者的具体体质情况进行多维度的查询、分析。
2.2 高精度运动体质智能检测系统检测流程设计
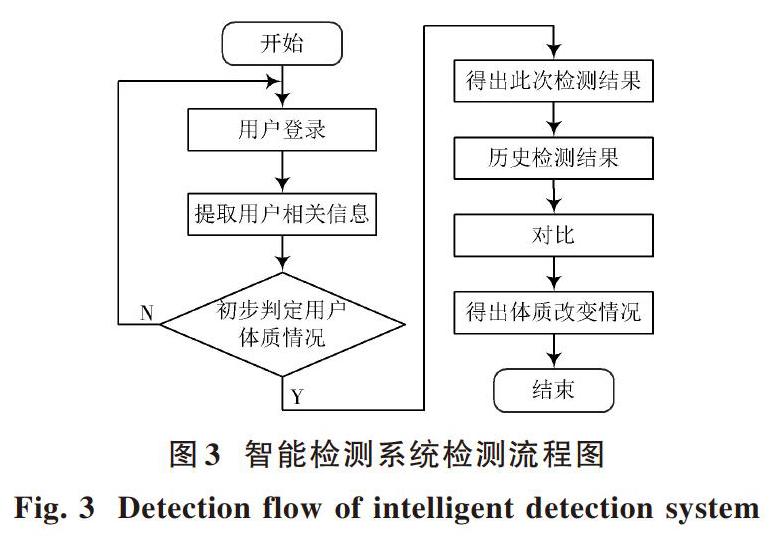
智能检测系统检测流程起始于用户登录模块,所有用户身份的合法性必须经过登录模块的验证,方可生效[9]。具体检测流程如图3所示。
2.3 高精度运动体质智能检测系统业务流程设计
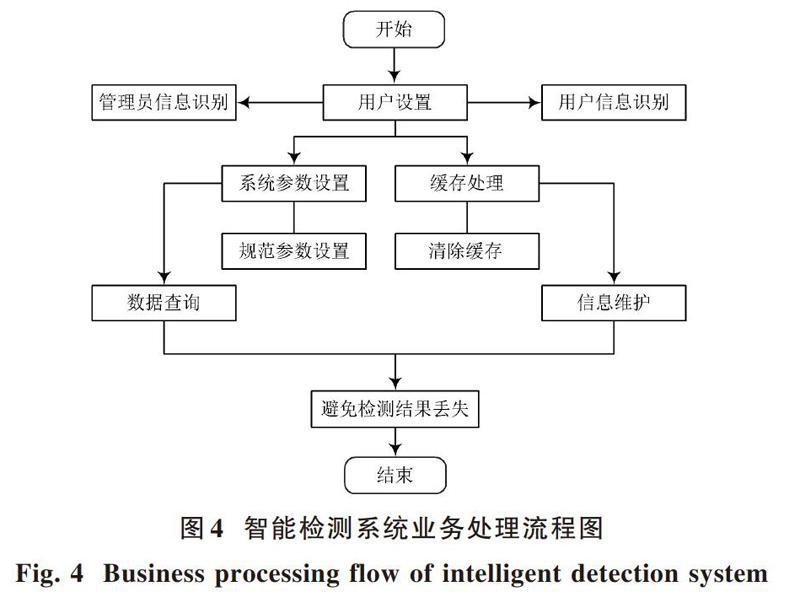
基于红外传感高精度运动体质智能检测系统的功能,与传统Web网站类似,通过数据库对后台数据的分析、处理,实现前端检测结果的展示[10]。系统参数设置及缓存管理,为系统的中段操作提供可能,具体业务处理流程如图4所示。
3 实验结果与分析
3.1 实验参数设置
表2中参数依次代表红外波动系数、检测精度等级、检测准确率、体质指标范围、系统响应时间、精度极限。其中传统系统的检测精度等级为Ⅲ级,改进后系统检测精度等级为Ⅳ级,代表两种系统的检测结果均为真实可靠的[11]。
3.2 检测精度对比
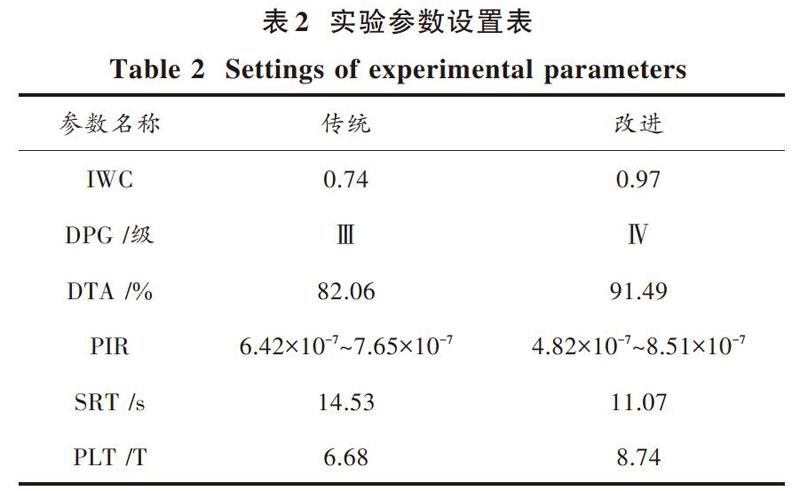
完成参数设置后,令运动员保持180 s的疾跑状态。在此过程中,检测该名运动员的体质改变情况,完成检测后,对比两种方法得到结果的检测精度。检测精度结果与GBH曲线存在反比关系,GBH曲线上下限间差值越大,则检测精度越低;GBH曲线上下限间差值越小,则检测精度越高。具体检测结果对比如图5所示。

分析图5可知,应用传统方法对运动体质进行智能检测,GBH曲线的最大值为6.68 T,最小值为0.97 T,二者间差值为5.71 T;应用基于红外传感高精度运动体质智能检测系统,对运动体质进行智能检测,GBH曲线的最大值为8.74 T,最小值为4.92 T,二者间差值[12]为3.82 T; 3.82 T<5.71 T。所以,可证明应用基于红外传感高精度运动体质智能检测系统后,运动体质智能检测精度明显提升。
3.3 检测等待时间对比
完成检测精度对比后,分别检测第30 s,60 s,90 s,120 s运动员的体质情况,对比应用普通方法和应用基于红外传感高精度运动体质智能检测系统各自的检测等待时间。
具体所需检测等待时间对比情况如图6所示。
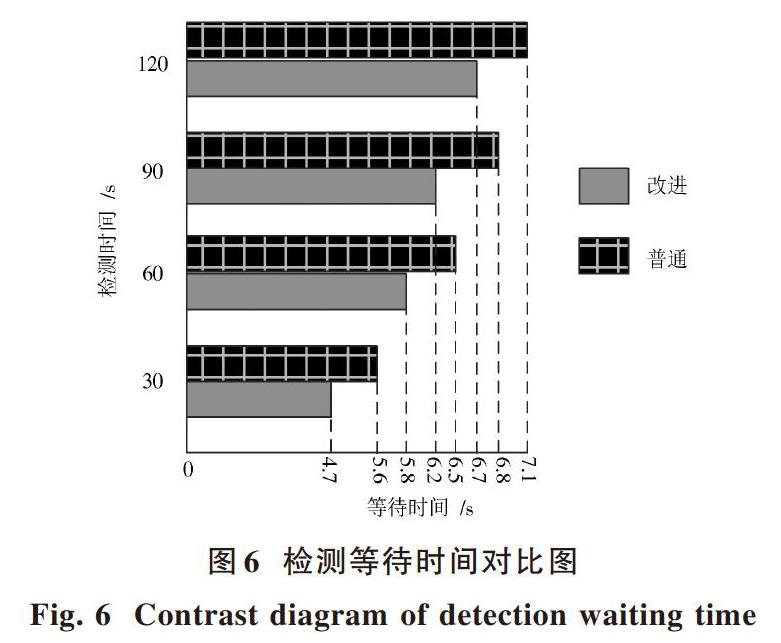
分析圖6可知,应用普通方法检测第30 s, 60 s,90 s,120 s运动员的体质情况,分别需要5.6 s,6.5 s,6.8 s,7.1 s;应用基于红外传感高精度运动体质智能检测系统,检测第30 s,60 s,90 s,120 s运动员的体质情况,分别需要4.7 s,5.8 s,6.2 s,6.7 s,明显低于应用普通方法所需的检测等待时间[13]。所以,可证明应用基于红外传感高精度运动体质智能检测系统后,运动体质智能检测等待时间明显缩短。
4 结 语
综上,本文完成了基于红外传感的高精度运动体质智能检测系统的搭建。通过对比实验的方法,证明该系统确实具备极高的实用价值。
参考文献
[1] 冯恒振,石云波,秦丽,等.基于热释电红外传感器的动作检测系统设计[J].压电与声光,2017,39(4):610?613.
FENG Hengzhen, SHI Yunbo, QIN Li, et al. Design of the motion detection system based on pyroelectric infrared sensor [J]. Piezoelectrics & acoustooptics, 2017, 39(4): 610?613.
[2] 姜晶,张宪,修威国,等.基于手机APP的便携式智能无线FDR传感器系统的设计[J].环境技术,2017,35(2):70?72.
JIANG Jing, ZHANG Xian, XIU Weiguo, et al. Design of portable intelligent wireless FDR sensor system based on mobile phone APP [J]. Environmental technology, 2017, 35(2): 70?72.
[3] 文冠祺,王忠,陈柏松.基于ARM的红外气体传感系统的设计与实现[J].计算机技术与发展,2017,27(4):180?183.
WEN Guanqi, WANG Zhong, CHEN Baisong. Design and implementation of infrared gas sensor system with ARM [J]. Computer technology and development, 2017, 27(4): 180?183.
[4] 张燕君,刘文哲,付兴虎,等.基于TTDF和CNS算法的多路BOTDR散射谱信息高精度分析研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析,2015,35(7):1802?1807.
ZHANG Yanjun, LIU Wenzhe, FU Xinghu, et al. The high precision analysis research of multichannel BOTDR scattering spectral information based on the TTDF and CNS algorithm [J]. Spectroscopy and spectral analysis, 2015, 35(7):1802?1807.
[5] 蒲洪玲,杨丹.“体智能”和“趣味田径”课程对幼儿身体素质影响的实验研究[J].沈阳体育学院学报,2017,36(1):124?128.
PU Hongling, YANG Dan. Experimental study on physical development of children through physical intelligent and kids′ athletics courses [J]. Journal of Shenyang Sport University, 2017, 36(1): 124?128.
[6] 李爽,张慧妍,王立,等.多属性皮肤指标的中医体质模糊优化分类模型[J].计算机科学与探索,2016,10(7):995?1002.
LI Shuang, ZHANG Huiyan, WANG Li, et al. Fuzzy optimization classification model in Chinese medicine constitution of multi?attribute skin indexes [J]. Journal of frontiers of computer science & technology, 2016, 10(7): 995?1002.
[7] 易金桥,黄勇,廖红华,等.热释电红外传感器及其在人员计数系统中的应用[J].红外与激光工程,2015,44(4):1186?1192.
YI Jinqiao, HUANG Yong, LIAO Honghua, et al. Pyroelectric infrared sensor and its application in people counting system [J]. Infrared and laser engineering, 2015, 44(4): 1186?1192.
[8] 田冉,陈梅香,董大明,等.红外传感器与机器视觉融合的果树害虫识别及计数方法[J].农业工程学报,2016,32(20):195?201.
TIAN Ran, CHEN Meixiang, DONG Daming, et al. Identification and counting method of orchard pests based on fusion method of infrared sensor and machine vision [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(20): 195?201.
[9] 李玉柱,宋建成,耿蒲龙,等.基于红外传感器的高压柜隔离开关触头温度在线监测系统研究[J].测控技术,2015,34(2):1?4.LI Yuzhu, SONG Jiancheng, GENG Pulong, et al. Online monitoring system of temperature of isolator contacts in high?voltage switchgear cabinet based on infrared sensor [J]. Measurement & control technology, 2015, 34(2): 1?4.
[10] 高莲弟,陶帅,季长清,等.基于屋顶二值红外传感器网络的人体定位和行为识别系统设计[J].计算机测量与控制,2017,25(1):163?166.
GAO Liandi, TAO Shuai, JI Changqing, et al. Design for human body localization and activities recognition system based on binary ceiling infrared sensor network [J]. Computer measurement & control, 2017, 25(1): 163?166.
[11] FENG H, SHI Y, QIN L, et al. Design of the motion detection system based on pyroelectric infrared sensor [J]. Piezoelectrics & acoustooptics, 2017, 39(4): 610?613.
[12] ZHENG Y. Characterization of a traffic management system using pyroelectric infrared sensors [J]. Instrumentation science & technology, 2015, 43(3): 319?333.
[13] ACKERMANN M, AJELLO M, ATWOOD W, et al. The third catalog of active galactic nuclei detected by the Fermi large area telescope [J]. Astrophysical journal, 2015, 223(1): 429?457.
