中医情志的现代神经心理学观点*
2018-05-10顾思梦荆莉媛高梦丹王福顺
顾思梦,荆莉媛,高梦丹,王福顺
(1.江苏大学医学院医学心理学系 镇江 212013;2.南京中医药大学心理学院 南京 210023)
Introduction
Major depressive disorder(MDD)is a prevalent mental disorder characterized by anhedonia,depressed mood,helplessness,loss of interest or pleasure.It has been identified as a leading cause of disability,and affects about~17%of the populations worldwide,making it one of the most prevalent health-related causes of human suffering1,2.Recently,compelling evidences from genetic studies and pharmacological studies point to dysfunction of the central catecholamine network.The most widely accepted theory about the mechanism of MDD and the effects of antidepressant action point to the monoamine neurotransmitters,including serotonin(5-HT),norepinephrine(NE)and dopamine(DA)3,4.Current antidepressants such as 5-HT and NE reuptake inhibitors and selective 5-HT reuptake inhibitors are considered to be the first choice of treatment for MDD.These neuromodulators can affect the neural network or astrocytes,like what we reported before5,6.However,many adverse effects lead the patients stop using the drugs.For example,the 5-HT toxicity,also named 5-HT syndrome,including emotional lability,mania,restlessness,insomnia,has been experienced in almost all the drugs with 5-HT regulations.Therefore,alternative medicines are needed in treating these patients.Interestingly,many ways of treatment from Chinese Medicine,including herbal medicine,acupuncture,Tai Chi,qigong,yoga,and massage,have been widely used around the world,and have been proved to be effective in treating depression.There is another kind of emotional therapy from Chinese medicine,named Yiqing Shengqing(using events to induce one kind of emotion in order to relieve another kind of emotion that bothers the patients,such as using joy to treat depression),which has been proved to be effective by a lot of clinical evidences7,and has been widely used in Traditional Chinese medicine,but seldom known to the west medicine.Most interestingly,this kind of ancient emotional therapy can be explained perfectly with the current monoamine mechanism of the emotions8,9.Here we want to introduce this kind of therapy to our peers who are interested in emotional study and/or in depression studies,which might shed light in depression treatment.

Figure 1 Schematic draft shows the relationship between the Five Element theory and the five basic emotions:fear(water,kidney),anger(wood,liver),joy(fire,heart),missing(soil,spleen),and sadness(metal,lung).They can interact with each other by inducing or blocking.The inducing pathway is:fear→anger→joy →missing→sadness;and the blocking pathway is:fear–joy–sadness–anger-missing.Depression can block anger(liver),while anger can induce joy,therefore anger can be used in the treatment for depression.
1 Five Elements theory in Chinese Medicine
Depression is one of the prevalent causes of healthrelated human suffering and is,first and foremost,a disorder of one of the least-studied biological phenomena:emotion10.Therefore,it is critically important to understand emotion,in order to understand depression9.Chinese medicine textbook Huangdi Neijing(Huangdi's Canon of Medicine),which was published 2000 years ago,is the oldest textbook about emotion,which has developed a theory about basic emotions and their interactions,and also their roles in cause and therapy in almost all of human diseases.The emotion theory in this book and later studies in Chinese medicine are so well-developed that Gardner Murphy said that,“The home of psychology is China”11.The emotion theory in Chinese medicine derived from the"Five Elements"theory,which is an important philosophy in ancient China to explain various physiological and pathological phenomena.The five elements—water,wood,fire,earth,and metal— are held by the ancients to compose the physical universe and are believed to be the fundamental elements of everything in the universe,including the basic emotions(fear,anger,joy,sadness and missing).The theory about the interactions between these emotions are also called Qingzhi theory in Chinese medicine(Figure 1),which was originally booked in Huangdi Neijing(Huangdi's Canon of Medicine)2000 years ago.In this book,it is proposed that all human diseases are due to two major factors:inside emotional factors,and outside environment factors.The inside emotional factors are the seven emotions(Qiqing):Happiness,anger,worrying,missing,sadness,fear,panic.Because of the similarities between fear and panic,worrying and missing,the several emotions can be further collected into five basic emotions(Wuzhi):fear,anger,joy,sadness and missing.Their relationship with the Five elements and also the five major organs is that:anger is related to liver,and sadness can block it;Joy is related to heart,and fear can block it;missing is related to spleen,and anger can block it;worry(sadness)is related to lung,and joy can block it(Figure 1).Many centuries of clinical practices have proved their usefulness in treating emotional disorders ever since,including depression.For example,there are more than 5000 papers about emotional problems treated with Chinese e since 198912,and it is reported that most of the depressive patients are due to blocking of anger in live(Ganqi Yujie,or Ganyu)13,and the treatment is using expressing of anger in liver(Shu gan)14,15.From figure 1,we can see that ancient Chinese medicine already found that depression can block anger(liver),while anger can induce joy.So anger can be used in the treatment of depression,we will explain it in detail in the following text.
2 Basic emotions
Chinese medicine is the first to introduce basic emotions and benefits from the basic emotion theory,similarly the emotional study in modern psychology also benefits from basic emotion theory16.The central idea of basic emotion theory is that human nature constitute a group of qualitatively distinct emotions17.The best way of studying basic emotions is put them in dimensions of emotion.Russell and Barrett has done a lot of experiments,referred to many theoretical approaches,and concluded that all basic emotions can be arranged in a circumplex18,19.They introduced the circumplex model of emotions to present the most general structure of basic emotions20.The circumplex is defined as a circular arrangement of basic emotions around two independent,bipolar dimensions:hedonic(pleasure-displeasure)and arousal(rest-activated)(Figure 2).Both the horizontal dimension,named hedonic valence and the vertical dimension,named arousal,are independent from each other8,21.
Ever since Wundt's dimension model of emotions was first proposed,there was almost no controversy about the valence of the horizontal dimension,even though many similar names have been given:valence,hedonic dimension,hedonic tone,liking and other identical items8.The second dimension addresses whether something happened in an unexpected way or not,which is related the arousal state of the body,so it is called arousal dimension.Like Barrett proposed that“Arousal is associated with the uncertainty regarding whether a stimulus will predict threat of reward,the need to pay more attention to a stimulus of importance,or urgency to engage in active coping”22.The interesting thing of traditional Chinese Medicine is that the five basic emotions(fear,anger,joy,sadness and missing),can be easily located in the two-dimensional circumplex(compare Figure 1 and Figure 2).
3 Neuromodulator and Basic Emotions
As shown in figure 2,monoamine neuromodulators have the advantages to work as the substrate for the basic emotions in that they affect both the periphery nervous system and the central nervous system.Since the 50s-60s in last century,catecholamine and 5-HT have been regarded as the neural substrate for emotion.Consistently,decades of research have clearly established that monoamine neuromodulators contribute to MDD.As shown in figure 2,monoamine neuromodulators are substrates for the basic emotions:dopamine-pleasant,5-HT-displeasant and norepinephrine-arousal24-26,like 3 basic colors(Figure 2).
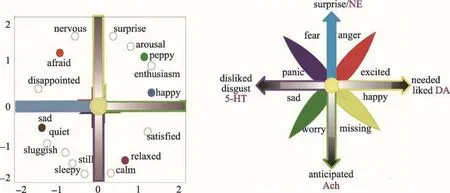
Fig.2 Circumplex model of emotions.A.One example of self-report datum about circumplex model modified from Russell and Barrett23,all emotions,including the basic emotions can find their locations in the circle of the circumplex.B.Basic emotions can be arranged in a two-dimension coordinate plane adopted from our previous paper9.Emotions can be induced by two affective qualities of things:the valence of the stimulus and the way the stimulus occur.Horizontal dimension shows the valence of the stimulus,which means the hedonic quality of the objects or situations when they fit into personal needs(pleasant-unpleasant).Vertical dimension shows how the way the objects or situations occur,which means unexpected or uncertainty.
3.1 Dopamine
Dopamine has been strongly regarded as the rewarding processes in the brain ever since 1980,when Wise proposed the Hedonic Hypothesis of dopamine27,28:dopamine signals stimulus salience,inducing happy and rewarding feelings.Dopamine is a rewarding signal for salient stimuli such as sex,food and other needs29.
3.2 5-HT
More than 20 years have passed since Deakin and Graeff hypothesized that 5-HT pathways are related to aversive stimuli,and dysfunction of these pathways contributes to the pathophysiology of anxiety and affective disorders30.Even though 5-HT acts as a neuromodulator in the central nervous system(CNS),about 90%of 5-HT in the body is secreted by the gut enterochromaffin cells in response to noxious substance in the food,where 5-HT causes diarrhea or vomiting by making the gut moves faster31,therefore,5-HT give a stimulus a unpleasant marker.A plant with 5-HT exploits this reaction to make the passage of seeds fast through the digestive system.Animals such as scorpion and wasp sting use 5-HT in their venom to induce pain25.5-HT in the CNS is mostly produced by neurons in raphe neclei,and released into extracellular space between neurons in CNS32.In all,serotonergic systems are implicated in physiological responses to aversive stimuli,and dysfunction of this system is involved in the pathophysiology of stress-related psychiatric disorders33.
However,5-HT is the most elusive neuromodulators,and it is reported to be related to sleep,appetite and emotion34.These functions are also changing,for example,it was thought that 5-HT induced sleep,but it is currently found that 5-HT functions predominantly to induce wakefulness,and only under some circumstance did it induce sleep propensity35,and act as a tranquilizer.Because of its behavioral suppression function,it inhibits avoidance behaviors at punishments,or inhibit exploration behaviors at aversive stimulations36,its aversive marker function is often neglected.Actually,5-HT is mostly involved in punishment and threats and is correlated negatively with rewards37.Indeed,depleting 5-HT reduces the suppression behavior at aversive events38,and intraventricular injection of 5-HT increase punishment sensitivity.Finally,5-HT also opposes the rewarding behavior of dopamine directly via the suppression activity of 5-HT2Creceptors upon the dopaminergic neurons39.And it is found that drugs which block 5-HT2Creceptors make the human unable to shut off appetite,and these drugs are related to increased weight gain.In addition,5-HT dramatically inhibits the hyper-locomotion elicited by dopamine.In all,5-HT is mostly involved in punishment.
3.3 Norepinephrine
Dopamine and 5-HT respond to the hedonic value of the objects/situations around us,but safety is more important than the hedonic value9.For example,we will worry about whether it will induce threat at a new situation,especially for our ancestors exploring in an environment of many kinds of variability40,41.Therefore,our ancestors evolved an adaptive mechanism to first have a safety check for everything in the world.If it happens unexpectedly,the first reaction would be scared.The safety check will induce the emotion“fear or anger”and the behavior“flight or fight”9.Therefore,fear and anger are not directly resulted from the valence quality of objects/situations;instead they are due to unexpected ways these things happen(Figure 2).
Norepinephrine(NE)together with adrenaline and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal(HPA)acts as stress or threat hormones,and underlies the“fight-or-flight”responses42,43.Interactions among the brain areas,such as Locus Coeruleus,amygdala,hypothalamus and prefrontal cortex facilitate activation of HPA to process fear responses.Then at hypothalamus,fear-signaling impulses activate both the sympathetic nervous system and the HPA axis.The adrenal gland is the major endocrine system that is related to stress and regulates many physiological processes and also emotions processes.Amygdala is the central part of the nervous circuitry for fear reactions and memory.In the presence of threatening stimuli,the amygdala secrets neurotransmitters that induce fear and aggression and then hypothalamus may elicit hormone release into the body to induce a state of alertness.This defensive response is generally referred as the"fight-or-flight"behavioral response regulated by the hypothalamus in physiology,and also fear or anger emotions24.The interesting thing is that Fear has been found to be related to adrenal systems(which involved more than kidney proper itself,and also the adrenal gland)in Chinese medicine 2000 years ago(Figure 1 and 3).

Figure 3 HPA axis.Hypothalamus-pituary-adrenal axis constitutes the HPA axis,which controls reactions to stress and threats.It is a common mechanism for interactions among the midbrain and glands to mediate the general adaptation syndrome(GAS).Interactions among the brain areas,such as Locus Coeruleus,amygdala,prefrontal cortex and hypothalamus facilitate activation of HPA to process fear responses.The adrenal gland is a major endocrine system that is involved with fear.Similarly,the interesting thing is that Fear has been found to be related to adrenal systems in Chinese medicine 2000 years ago(refer to figure 1).
4 Emotion flow
From Figure 2,we can find that fear and anger share the same neuromodulator NE,whose major function is to induce"fight or flight"behavior.It is really the case that fear and anger related to each other like twins,and anyone who tried to differentiate anger from fear will be confused by their similarities24.Lazarus proposed that fear and anger are:“opposite but interdependent sides of the same adaptation coin”44,45.Experiencing fear and anger usually induces high epinephrine levels in the body,which raises the physical strength and endurance levels of the person.Imaging studies reported that fear and anger elicits similar neural activities in amygdala and frontal cortices46.Frijda tried to differentiate fear and anger by proposing that:fear is the urgency to remove oneself from an aversive event,and anger is the urgency to attack47.But some studies reported that a fear situation,defined by the presence of threat(e.g.,a predator),is associated with different behaviors(e.g.,vigilance,freezing,flight,attack)depending on the functional demands of that specific situation48.Indeed,fear also induces attack sometimes,when there is no ways to flight.The somatic substrates for both fear and anger are almost the same;in addition to the characteristic behavior"fight or flight",this response includes increases in blood stress hormones that are reminiscent of responses to fear and stress in humans and are controlled by HPA axis.Therefore it is so easy to switch from one to another,just like flipping a coin9.
Indeed,there are many situations that fear changed to anger so fast that it is hard to differentiate one from another.Animals sense the environmental threat that challenge their survival and respond with behavioral and physiological responses to eliminate the challenge by removing oneself from it(flight)or throw it away(fight).Facing stressful events,people will first feel scared(fear),and then they will try to cope with the stressful event after fear is gone.And afterwards they will feel happy after coping with the stressful stimuli successfully or feel sad if they failed to cope with stressful event.Finally,the stressful events go away,and people calm down.This kind of emotional flow constitutes our everyday emotions.So“fear--anger--happiness--sadness”constitute the emotional rainbow in our everyday life(Figure 4).Therefore,fear is the origin of all the emotions in our everyday life.It is smart enough for Traditional Chinese Medicine to mention that kidney(The meaning of kidney has a broad meaning,which might include adrenal gland,therefore,we call it adrenal system)being the congenital origin of human life,so it is with the fear,which is part of the characteristics of kidney(adrenal system).Furthermore,it is even smarter for Chinese medicine to mention that fear leads to anger(Figure 1),anger leads to joy.All the basic emotions can be arranged in a rainbow,just like the seven basic emotions in Chinese medicine.
Fear is the scariness at the stressful event,due to its uncertainty,unpleasantness,and situational un-control;anger,by contrast,will be associated with the tendency to control the new situations.And fear and anger occur in a tandem,with fear coming first and anger following next.Fear is the scariness from the uncertainty about the upcoming of stressful events,and anger is the coping with the stressful events after fear is gone."Fear and anger are the double edges of the same sword,which functions to keep a distance between the subject and the threat.Fear is to move the subject himself away from the threat,while anger is to thwart the threat away."9So fear and anger can be differentiated with time sequences:anger always comes after fear.

Figure 4 Emotion flow.At stressful events or threatening events,people get the fear and anger reactions.Fear is the scariness at the stressful events,and anger is coping with the stressful events.Stress--Fear--Response(anger)--Consequences(happiness or sadness)constitute the emotional flow in our everyday lives.Therefore,fear and anger occur in a tandem,with fear coming first and anger following next.So fear is the start of all the emotions in our everyday lives.The interest thing is that adrenal system(named kidney)was regarded as the origin of our lives in Chinese Medicine,and even more interesting is that Chinese Medicine already found the emotion flow pathway:fear--anger--joy--missing--sadness.All basic emotions can be arranged in a rainbow,the seven colors in the rainbow is just like the seven basic emotions(Qiqing)proposed in old Chinese medicine,which might happen in a series from a stressful event like a rainbow.
5 Depression is due to disturbance of 5-HT
Stressful events will not always induce depression,only uncontrolled stresses can induce depression,especially repeated failure induced helplessness at coping with the stressful events.Long term helplessness makes the person accept the failure without trying to cope(anger)with the situation(Figure 4).Therefore,lacking anger emotion is a characteristic of depression.From this point of view,anger is good,for anger is the vent of fear,and can activate the energy in the body to cope with stressful situations.This is consistent with the data of recent studies in Chinese Medicine:most depression is due to suppression of liver,whose emotion in the Five elements is anger49.Uncontrollable stressful events activate serotonergic neurons in the mid-rostrocaudal to caudal raphe nucleus,as measured by increases in extracellular 5-HT and c-Fos expression in 5-HT neurons50.Exposure to unpredictable noise stress,but not sham noise stress,increases in vivo 5-HT activity selectively,within the raphe nucleus51.In the elevated T-maze,a behavioral test used to measure escape behavior,inhibitory avoidance increased the expression of c-Fos in serotonergic neurons of the raphe nucleus,whereas the one-way escape equipment,which was used to measure panic behavior does not change the c-Fos expression52.Other more ethologicallyrelevant stressors such as social defeat also result in activation of raphe nucleus serotonergic neurons53.
5.1 Dearkin and Graeff’s hypothesis
Lacking of anger in depressive patient can also be evidenced by Deakin and Graeff’s hypothesis that the raphe nucleus produces active defensive responses in the presence of a proximal threat,and that 5-HT normally restrains these innate fight-or-flight responses54.The learned helplessness is also associated with marked activation of raphe nucleus neurons55,and with large increases in extracellular 5-HT from DRN projections to the amygdala.To reconcile the anxiogenic effect of 5-HT in conflict tasks with the 5-HT,Deakin proposed the different types of aversive stimuli activate different 5-HT pathways that send unique patterns of efferent to specific forebrain and brainstem structure.5-HT is thought to mediate its effects through activation of a myriad of postsynaptic 5-HT receptors,including:5-HT1A,5-HT2A,5-HT2c,5-HT3,5-HT4,5-HT5,5-HT6 and 5-HT7 receptors56.5-HT receptors consist of at least 14 different subtypes that predominantly belong to the family of G-protein coupled receptors(GPCR),except for the 5-HT3 receptors,which are ligand-gated ion channels57.It was proposed that the first serotonergic pathway,consisting of the dorsal raphe periventricular tract,restrains fight-or-flight behavior in response to either(a)stimulation of the DPAG or(b)exposure to acute unconditioned aversive stimuli(e.g.predator exposure,pain or aversive interoceptive stress),resulting in freezing/quiescence30.This is consistent with theory of Chinese medicine that sadness can inhibit anger.The inhibitory action of 5-HT in the raphe nucleus is thought to be mediated by stimulation of 5-HT1Aand/or 5-HT2Areceptors.It was hypothesized that dysfunction of this serotonergic pathway results in unrestrained bouts of sympathetic and behavioral arousal reminiscent of panic disorder(PD).It was proposed that a second pathway(consisting mostly of forebrain bundle tract in the dorsal raphe)is recruited by exposure to acute aversive stimuli to direct the organism away from the danger.In this pathway,5-HT was thought to work through 5-HT2A/2Cand 5-HT3 receptors pathways.It was hypothesized that abnormalities in this pathway is related to anxiety disorders like Generalized Anxiety Disorder(GAD)58.Finally,the third serotonergic pathway consists of the median raphe,which is activated by chronic stimuli.It was hypothesized that dysfunction of this serotonergic pathway,and consequently failure to adapt to chronic stress,is relevant to depression.The experimental evidence that led to the evidence generated since their proposal have been reviewed extensively59.
5.2 An alternative way for treatment of depression
Chinese medicine found that most of the depressions are due to inhibition of liver(named Ganyu),therefore there are several ways to treat depression,such as using herbs to relieve the stress in the liver,or using events to induce other emotions,such as joy or anger to relieve depression,which can be called Yiqing Shengqing.
5.2.1 Yiqing Shengqing
According to the Five element theory,Joy can block sadness,and sadness can block anger.The depression patients usually have no joy and also inhibited anger.Therefore,it is better to have the patients experience happy emotion,and also to have anger to release the sad experience.It has been a long history in Chinese medicine to use this method in treating depression.For example,we checked recent publications in Chinese medicine,and found 141 reports using Yiqing Shengqing treating many kinds of depression,including postpartum depression.There are two ways for the Yiqing Shengqing:blocking and anti-blocking7.For example,happiness can block the sadness,we can use happy emotion to block sadness;sadness can block anger,and anger can be used to antiblock sadness60.
5.2.2 Shugan Herbs
Many Chinese herbs have been proved to be effective in treating depression,for example,we recently reported a kind of Chinese herb Yueju(Cyperusrotundus L.(CR),Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort.(LC),Gardenia jasminoides Ellis.(GJ),Atractylodeslancea(Thunb.)DC.(AL)and Massa Fermentata(MF).)can be used to cure depression patients very quickly2.The major etiology for depression is due to Ganyu(or inhibition of liver,whose major emotion is anger).Therefore the major function of the herbs to treat depression is to relieve liver,for example,Chaihu Shugan San(which includes several herbs:Radix Bupleurum,Paeonia Lactiflora).The major gradient paeoniflorin has been proved to be effective in the treatment61.
6 Conclusion
Major depressive disorder(MDD)is one of the prevalent causes of health-related human suffering10.Here we introduced the interactions between five basic emotions(fear-anger-joy-missing-sad).The facilitating pathway is:fear--anger--joy--missing--sadness,which can be called Emotion flow.The blocking pathway is:fearjoy-sadness-anger-missing.Most depression is due to suppression of liver,whose emotion is anger.For depressive patients,repeated failure in coping with stressful situations led them to accept the situation sadly without coping(anger).Therefore,lacking anger is a characteristic for depression patients.From this point of view,anger is good in that anger is the vent of fear,and can activate the energy in the body to cope with stressful situations.This is consistent with the data of recent studies in Chinese Medicine:most depression is due to suppression of liver(Ganyu),whose emotion is anger.
This work was supported,in part,Jiangsu University Science Research Project(17KJD310001,S.G.),National Science Foundation in China 816280007(J.H.H.and F.W.),Jiangsu Specially Appointed Professorship Foundation (F.W.), Jiangsu Nature Science Foundation BK20151565(F.W.),Jiangsu Traditional Chinese Medicine Foundation ZD201501(F.W.),Jiangsu Six Talent Peak project 2015YY006(F.W.),and the priority academic program development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institute(Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine).
Competing financial interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
1 Wang,H.et al.Norbin ablation results in defective adult hippocampal neurogenesis and depressive-like behavior in mice.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 112,9745-9750,doi:10.1073/pnas.1510291112(2015).
2 Xue,Wenda et al.PKA-CREB-BDNF signaling regulated long lasting antidepressant activities of Yueju but not ketamine.Scientific Report 6,1-8(2016).
3 Moeller,S.J.et al.Monoamine polygenic liability in health and cocaine dependence:imaging genetics study of aversive processing and associations with depression symptomatology.Drug Alcohol Depend 140,17-24,doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.04.019(2014).
4 Hamon,M.&Blier,P.Monoamine neurocircuitry in depression and strategies for new treatments.Progress in neuro-psychopharmacology&biological psychiatry 45,54-63,doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.04.009(2013).
5 Wang,F.et al.Astrocytes modulate neural network activity by Ca2+-dependent uptake of extracellular k+.Sci Signal 5,ra26,doi:10.1126/scisignal.2002334(2012).
6 Wang,F.,Xu,Q.,Wang,W.,Takano,T.&Nedergaard,M.Bergmann glia modulate cerebellar Purkinje cell bistability via Ca2+-dependent K+uptake.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109,7911-7916,doi:10.1073/pnas.1120380109(2012).
7 Zhong,B.On the psychological therapis in ancient China.Psychological Science 27,175-176(2004).
8 Gu,S.,Wang,F.,Yuan,T.,Guo,B.&Huang,H.Differentiation of primary emotions through neuromodulators:review of literature.International journal of neurology research 1,43-50(2015).
9 Zheng,Z.et al.Safety Needs Mediate Stressful Events Induced Mental Disorders.Neural plasticity 2016,8058093,doi:10.1155/2016/8058093(2016).
10 Damasio,A.R.Neuropsychology.Towards a neuropathology of emotion and mood.Nature 386,769-770,doi:10.1038/386769a0(1997).
11 Murphy,G.Histrorical Introduction to Modern Psychology.(Beijing Business Publisher,1980).
12 ZHang,H.,Wang,T.,Guo,W.,Tian,Y.&Ma,Y.Analysis of papers of 10 years about depression treated with Chinese Medicine.Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 28,79-82(2005).
13 An,C.&Cheng,W.Rencet studis about etiology and symptoms of depression from Chinese Medicine.Informtiona about Traditional Chinese Medicine 24,12-15(2007).
14 Jiang,Y.Analysis of studies about antidepressant in Chinese Herbs.Journal of Yunnan Chinese Medicine and Chinese Herbs 31,76-79(2010).
15 Wang,H.,Liang,H.&Qiu,Q.The trend of depression studies in Chinese Medicine.Journal of Liaoning University of TCM 94(2007).
16 Russell,J.A.Core affect and the psychological construction of emotion.Psychol Rev 110,145-172(2003).
17 Russell,J.A.Emotions are not modules.Canadian Journal of Philosophy Supplement volume 32,53-71(2006).
18 Weierich,M.R.,Wright,C.I.,Negreira,A.,Dickerson,B.C.&Barrett,L.F.Novelty as a dimension in the affective brain.NeuroImage 49,2871-2878,doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.09.047(2010).
19 Russell,J.A.&Barrett,L.F.Core affect,prototypical emotional episodes,and other things called emotion:dissecting the elephant.Journal of personality and social psychology 76,805-819(1999).
20 Russell,P.S.&Giner-Sorolla,R.Bodily moral disgust:what it is,how it is different from anger,and why it is an unreasoned emotion.Psychological bulletin 139,328-351,doi:10.1037/a0029319(2013).
21 Barrett,L.F.,Mesquita,B.,Ochsner,K.N.&Gross,J.J.The experience of emotion.Annual review of psychology 58,373-403,doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.58.110405.085709(2007).
22 Barrett,L.F.Solving the emotion paradox:categorization and the experience of emotion.Personality and social psychology review:an official journal of the Society for Personality and Social Psychology,Inc 10,20-46,doi:10.1207/s15327957pspr1001_2(2006).
23 Barrett,L.F.&Russell,J.A.Structure of current affect:Controversies and Emerging consensus.Current directions in the psychological sciences 8,10-14(1999).
24 Gu,S.,Wang,W.,Wang,F.&Huang,J.H.Neuromodulator and Emotion Biomarker for Stress Induced Mental Disorders.Neural plasticity 2016,2609128,doi:10.1155/2016/2609128(2016).
25 Wang,F.&Pereira,A.Neuromodulation,Emotional Feelings and Affective Disorders.Mens sana monographs 14,5-29,doi:10.4103/0973-1229.154533(2016).
26 Lovheim,H.A new three-dimensional model for emotions and monoamine neurotransmitters.Medican Hypotheses 78,doi:doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2011.11.016.(2011).
27 Corbett,D.&Wise,R.A.Intracranial self-stimulation in relation to the ascending dopaminergic systems of the midbrain:a moveable electrode mapping study.Brain research 185,1-15(1980).
28 van Berckel,B.N.et al.Modulation of amphetamine-induced dopamine release by group II metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist LY354740 in non-human primates studied with positron emission tomography.Neuropsychopharmacology:official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology 31,967-977,doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1300902(2006).
29 Arias,B.et al.Analysis of COMT gene(Val 158 Met polymorphism)in the clinical response to SSRIs in depressive patients of European origin.Journal of affective disorders 90,251-256,doi:10.1016/j.jad.2005.11.008(2006).
30 Morris,J.S.,DeGelder,B.,Weiskrantz,L.&Dolan,R.J.Differential extrageniculostriate and amygdala responses to presentation of emotional faces in a cortically blind field.Brain 124,1241-1252(2001).
31 Young,R.L.,Lumsden,A.L.&Keating,D.J.Gut Serotonin Is a Regulator of Obesity and Metabolism.Gastroenterology 149,253-255,doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.05.020(2015).
32 Amo,R.et al.The habenulo-raphe serotonergic circuit encodes an aversive expectation value essential for adaptive active avoidance of danger.Neuron 84,1034-1048,doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2014.10.035(2014).
33 Hayashi,K.,Nakao,K.&Nakamura,K.Appetitive and aversive information coding in the primate dorsal raphe nucleus.The Journal of neuroscience:the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 35,6195-6208,doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2860-14.2015(2015).
34 Pakalnis,A.,Splaingard,M.,Splaingard,D.,Kring,D.&Colvin,A.Serotonin effects on sleep and emotional disorders in adolescent migraine.Headache 49,1486-1492,doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2009.01392.x(2009).
35 Monti,J.M.Serotonin control of sleep-wake behavior.Sleep medicine reviews 15,269-281,doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2010.11.003(2011).
36 Silva,K.,Carvalho,M.C.&Padovan,C.M.Tolerance to repeated stress in rats with lesions of the serotoninergic neurons of the Median Raphe Nucleus and chronically treated with imipramine.Behavioural brain research 302,220-227,doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2016.01.025(2016).
37 Crockett,M.J.et al.Dissociable Effects of Serotonin and Dopamine on the Valuation of Harm in Moral Decision Making.Current biology:CB 25,1852-1859,doi:10.1016/j.cub.2015.05.021(2015).
38 Rygula,R.et al.Role of Central Serotonin in Anticipation of Rewarding and Punishing Outcomes:Effects of Selective Amygdala or Orbitofrontal 5-HT Depletion.Cerebral cortex 25,3064-3076,doi:10.1093/cercor/bhu102(2015).
39 Fossat,P.,Bacque-Cazenave,J.,De Deurwaerdere,P.,Cattaert,D.&Delbecque,J.P.Serotonin,but not dopamine,controls the stress response and anxiety-like behavior in the crayfish Procambarus clarkii.The Journal of experimental biology 218,2745-2752,doi:10.1242/jeb.120550(2015).
40 Yu,A.J.&Dayan,P.Uncertainty,neuromodulation,and attention.Neuron 46,681-692,doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2005.04.026(2005).
41 Daw,N.D.,Niv,Y.&Dayan,P.Uncertainty-based competition between prefrontal and dorsolateral striatal systems for behavioral control.Nature neuroscience 8,1704-1711,doi:10.1038/nn1560(2005).
42 Hu,H.et al.Emotion enhances learning via norepinephrine regulation of AMPA-receptor trafficking.Cell 131,160-173,doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.09.017(2007).
43 Johnson,L.R.,Hou,M.,Prager,E.M.&Ledoux,J.E.Regulation of the Fear Network by Mediators of Stress:Norepinephrine Alters the Balance between Cortical and Subcortical Afferent Excitation of the Lateral Amygdala.Frontiers in behavioral neuroscience 5,23,doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2011.00023(2011).
44 Lazarus,R.S.Progress on a cognitive-motivational-relational theory of emotion.The American psychologist 46,819-834(1991).
45 Lazarus,R.S.The Emotional Brain:the mysterous underpinnings of emotional life.(1991).
46 Pichon,S.,de Gelder,B.&Grezes,J.Two different faces of threat.Comparing the neural systems for recognizing fear and anger in dynamic body expressions.NeuroImage 47,1873-1883,doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.03.084(2009).
47 Frijda,N.The Emotions.(1986).
48 Bouton,M.E.,Garcia-Gutierrez,A.,Zilski,J.&Moody,E.W.Extinction in multiple contexts does not necessarily make extinction less vulnerable to relapse.Behaviour research and therapy 44,983-994,doi:10.1016/j.brat.2005.07.007(2006).
49 Shen,H.,Tang,Q.&ZHao,J.Treatment of depression of liver-qi stagnation and spleen-deficiency type with therapy of soothing liver and invigorating spleen.Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 31,856-858(2008).
50 Amat,J.et al.Medial prefrontal cortex determines how stressor controllability affects behavior and dorsal raphe nucleus.Nature neuroscience 8,365-371,doi:10.1038/nn1399(2005).
51 Evans,K.C.et al.Modulation of spontaneous breathing via limbic/paralimbic-bulbar circuitry:an event-related fMRI study.NeuroImage 47,961-971,doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.05.025(2009).
52 Adamec,R.,Toth,M.,Haller,J.,Halasz,J.&Blundell,J.Activation patterns of cells in selected brain stem nuclei of more and less stress responsive rats in two animal models of PTSD-predator exposure and submersion stress.Neuropharmacology 62,725-736,doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.11.018(2012).
53 Gardner,K.L.,Thrivikraman,K.V.,Lightman,S.L.,Plotsky,P.M.&Lowry,C.A.Early life experience alters behavior during social defeat:focus on serotonergic systems.Neuroscience 136,181-191,doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.07.042(2005).
54 Johnston,B.A.et al.Failure of hippocampal deactivation during loss events in treatment-resistant depression.Brain:a journal of neurology 138,2766-2776,doi:10.1093/brain/awv177(2015).
55 Andrade,T.G.,Zangrossi,H.,Jr.&Graeff,F.G.The median raphe nucleus in anxiety revisited.Journal of psychopharmacology 27,1107-1115,doi:10.1177/0269881113499208(2013).
56 Hariri,A.R.&Holmes,A.Genetics of emotional regulation:the role of the serotonin transporter in neural function.Trends Cogn Sci 10,182-191,doi:10.1016/j.tics.2006.02.011(2006).
57 Brindley,R.L.,Bauer,M.B.,Blakely,R.D.&Currie,K.P.An interplay between the serotonin transporter(SERT)and 5-HT receptors controls stimulus-secretion coupling in sympathoadrenal chromaffin cells.Neuropharmacology 110,438-448,doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.08.015(2016).
58 Orsolini,L.et al.New advances in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder:the multimodal antidepressant vortioxetine.Expert review of neurotherapeutics 16,483-495,doi:10.1586/14737175.2016.1173545(2016).
59 Paul,E.D.,Johnson,P.L.,Shekhar,A.&Lowry,C.A.The Deakin/Graeff hypothesis:focus on serotonergic inhibition of panic.Neuroscience and biobehavioral reviews 46 Pt 3,379-396,doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.03.010(2014).
60 Li,Y.&Wang,F.Behavioral studies about emotional control.Emotion Readings,17-20(2015).
61 Asai,M.et al.Protective effect of a molecular chaperone injucer,paeoniflorin,on the HCl-and ethanole-triggered gastric mucosal injury.Life Science 88,350-357(2011).
