Treatment of refractory H.pylori by Chai Ping Decoction:two case reports
2018-04-23HeqingChenYaweiDuXiaoyiTangShuoFengXiaoliWangXinyiLiYeyinHuYoupingLiGuihuaTianBoLi
Heqing Chen ,Yawei Du ,Xiaoyi Tang,Shuo Feng,Xiaoli Wang,Xinyi Li,Yeyin Hu,Youping Li,Guihua Tian,*,Bo Li*
1Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Capital Medical University,Beijing Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Beijing 100010,China. 2Dongzhimen Hospital,Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Beijing,100700,China.3Chinese Cochrane Center,West China Hospital,Sichuan University,Chengdu,Sichuan,610041,China.
#Heqing Chen and Ya-Wei Du contributed equally to this study.
Introduction
H.pylori(Helicobacter pylori)is one of the most common infections in humans.Its prevalence can reach 50%of the world’s population[1],and its infection is correlated with gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, and extra-digestive diseases [2, 3]. H. pylori is also considered a human carcinogen [4], and which is closely related to the occurrence and development of gastric cancer.A mature series of clinical treatments,including quadruple therapy and sequential therapy,have been used to treat the infection.These therapies usually have high eradication rate.However,some patients still suffer from repeated failed treatments.For these patients,using only antibiotic treatment may not completely resolve their condition. But traditional Chinese medicine(TCM)may help to improve these problems.TCM treatment may play a role in protecting the gastric mucosa and enhancing the function of the stomach,instead of eradicating the bacteria directly.Chai Ping Tang,a Chinese fomula based on TCM theory, may work for it. Chai Ping Decoction is composed of Radix Ginseng (Renshen), Radix Scutellariae (Huangqin), Bupleurum (Chaihu),Rhizoma pinelliae (Banxia), Mangnolia officinalis(Houpo),Rhizoma Chuanxiong(Chuanxiong),Fructus tsaoko (Caoguo), Glycyrrhiza Uralensis (Gancao),Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae (Chenpi) and Atractylodes (Chaocangzhu). Through the treatment combined Chai Ping Decoction and sequential therapy,we aimed to provide a good strategy to eradicate H.pylori infection.
Case presentation
This article reports two cases of refractory H.pylori infection treated with Chai Ping Decoction combined with sequential therapy.One case is a 60-year-old Chinese woman with stomach pain, anorexia,unnormal urination and defecations for more than 30 years.She came to the Digestive Department for the first time on May 14,2015.We found that her tongue was red with white coating and her pulse was smooth.Besides,the results of electronic gastroscopy showed that she had chronic atrophic gastritis(CAG)and H.pylori infection.According to the Chinese medicine,she had spleen qi deficiency and dampness syndrome.Subsequently,we treated her with a 28-day Chinese herbs.We instructed the patient to have the herbs daily(twice a day,0.5 h after breakfast and dinner and about 200 ml each time).The Chai Ping Decoction includes Roasted Astragalus (Zhihuangqi, 30 g), Coptis(Huanglian,6 g),Bupleurum(Chaihu,10 g),Cassia twig (Guizhi,10 g),Rhizoma Zingiberis Preparata(Paojiang,10 g),Atractylodes(Chaocangzhu,45 g),Folium Nelumbinis(Heye,10 g),Amomum(Sharen,6 g), Concha Ostreae (Shengmuli, 30 g), Os Draconis (Shenglonggu, 30 g), Trichosanthin(Tianhuafen, 10 g), Parched Fructus Crataegi(Jiaoshanzha, 30 g), Parched Fructus Hordei Germinatus(Jiaomaiya,30 g),Massa Medicata Fermentata (Jiaoshenqu, 30g), Glycyrrhiza Uralensis(Shenggancao,10 g),Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae (Chenpi, 10 g), and Ophiopogon Japonicus (Maidong, 12 g). (Xiyuan Hospital Pharmacy provided the above Chinese herbals.)
Because the patient had dyssomnia,we also prescribed a bottle of compound jujube seed paste(25 g Po tid).On June 12,she visited the doctor again and said she felt a little better.Following that, we continued to prescribe the herbs,combining them with some drugs, including rabeprazole sodium enteric-coated capsules (20 mg Po bid), clarithromycin dispersible tablets(0.50 g Po bid),potassium citrate capsule(0.3 g Po bid),and tinidazole tablets(1 g Po bid).After taking the medicine,the patient's symptoms were relieved.On September 25,the patient said the uncomfortable symptoms had been greatly relieved.The patient took a 13C-Urea Breath Test again that day,showing the H.pylori was 0.3‰(normal reference value is below 2.4‰).
The other patient is a Vietnamese woman aged 46.She came to the clinic on July 6,2015.The patient had abdominal pain for 11 years that had been intermittent,steady at night,and resolved in the morning.Eating spicy or greasy foods could cause the pain. In addition, the patient was constipated, and her abdominal pain might be improved after passing gas.Gastroscopy showed that the patient had chronic superficial gastritis with erosion, accompanied with H. pylori infection (+++). The related pathologic examination showed that the gastric angle had mild chronic superficial gastritis, mild active inflammation,and mucosal hyperemia,while the gastric antrum mastoideum showed mild chronic atrophic gastritis with mild active inflammation.We gave a TCM diagnosis of spleen qi deficiency and dampness syndrome,following her reports of symptoms of tongue and pulse.After diagnosis,we also gave the patient a 28-day Chai Ping Decoction.
We also prescribed her amoxicillin capsules(1 g Po bid), rabeprazole sodium enteric-coated capsules (20 mg Po bid), clarithromycin dispersible tablets(0.5 g Po bid),potassium citrate capsules(0.3 g Po bid),and tinidazole tablets(0.5 g Po bid)for combination therapy.During the treatment,we instructed the patient to follow a diet with low salt and fat and to avoid raw,cold,or spicy food.The patient also needed to avoid cold,keep a regular life,and reasonable diet.After10 weeks,the patient returned for further consultation.The pain had relieved well.We then tested for H.pylori again,with a result of 0‰.(All these relevant examination results and the treatment datas are shown in Table 1 and Table 2).
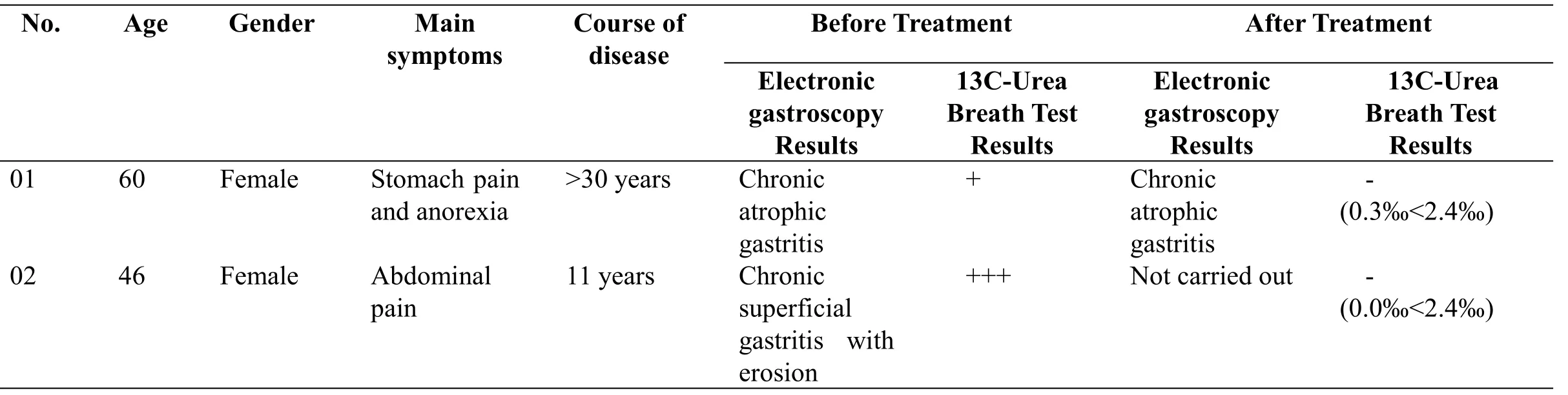
Table 1 Basic characteristics of patients before and after treatment

Table 2 Details of combine treatment for patients
During the treatment,these two patients reported no significant adverse events and any uncomfortable feelings due to the treatment.After the treatment,they were advised to keep the follow-up electronic gastroscopy and pathologic examination.At the latest follow-up,which was 1 year after treatment,these two patients were kept in good condition.
Discussion
H.pylori infection is closely related to chronic gastritis, gastric ulcer, and gastric cancer.Therefore,the treatment of H.pylori infection has played an important role in curing H.pylori-related disease.According to the latest Maastricht guidelines,clarithromycin-containing treatments are recommended for first-line empirical treatment in regions of low clarithromycin resistance[5].In regions of high resistance, quadruple treatment, including bismuth,has been proposed as the first-line treatment.While these therapies are unavailable, nonbismuth quadruple therapy and sequential therapy have been recommended [6]. These strategies have been continuously improved, and the therapeutic effects have been greatly enhanced.
However,it is often difficult to completely eradicate infection and solve related symptoms for patients suffering from refractory H. pylori infection. The resistance to antibiotics may be the chief reason,which is widely recognized[6,7].Using TCM may generally not cause such problems.Because the mechanism of TCM therapy does not focus on killing H.pylori.It inhibits the bacterium and protects the gastric mucosa.TCM may also enhance the repairing ability of the mucous membrane.Therefore,TCM treatment may confer comprehensive effects on patients.
Refractory H. pylori infection usually can be distinguished as spleen qi deficiency and dampness,according to its symptoms and signs. Spleen qi deficiency is a syndrome in TCM theory,including loss of appetite,abdominal distension,abdominal pain,and loose stool.The patient may has abdominal pain after eating cold or spicy food. For the pathogenic mechanism,spleen qi deficiency means that the organ cannot protect itself well so that the stomach mucus barrier could be easily damaged and H.pylori in the stomach can become parasitic and multiply.In this circumstance,H.pylori can decompose the urea to produce ammonia,enzymes,cell toxin,protein,and free radicals,etc.These productions could continue causing gastric irritation,forming inflammation and leading to gastritis and other related diseases.
Further,spleen qi deficiency means the disability of transportation and transformation of water and food,according to TCM theory.Those substances in the stomach, unable to spread out, would accumulate,forming dampness. When such foods stay in the stomach for a long time after being digested, the gastric juice may have been consumed and the pH would be at a higher level than in an empty stomach.At this time,the gastric microecologic condition may be different from the normal one.While Wroblewski et al.[8]support that the gastric microecologic condition,of which the gastric bacteria play an important part,are important in keeping the balance of the gastric-internal environment.But after the gastric emptying function is affected,the normal gastric bacteria would stay mixed with gastric juice and chime for a long time so that its activity would also be affected.Besides,according to Mowat et al.[9],the sufferers have more bacteria but not H. pylori in the stomach than uninfected people.Hence,after being infected,the gastric microecologic condition may be somewhat different.
Therefore,spleen qi deficiency may help the H.pylori settle in the stomach and weaken the digestive function,which may induce a dampness condition and may be a good breeding ground for the bacteria.H.pylori infection can also induce apoptosis of gastric mucosal cells and cause inflammation and immune response in gastric mucosa, while the inflammation and immune response can induce gastric mucosal atrophy and intestinal metaplasia of gastric mucosa.Thus,the function is damaged and the transportation of food,from stomach into intestine, works improperly.This is the so-called spleen qi deficiency and dampness syndrome.
For treatment,we will strengthen and replenish the spleen Qi in TCM theory.We may also choose to clear the dampness.The Chai Ping Decoction is based on this therapy.The decoction can relieve the congestion, edema, and erosion in gastric mucosa,and can increase the epidermal growth factor and trefoil factor to promote gastric mucosa injury repair by the expression of Astragaloside IV and Astragalus astragaloside in Astragalus membranaceus [10]. It may also have perfect effects in regulating the immune function and enhancing the antioxidant effect by using Atractylodes,enhancing the organism to clear the radical[11].Licorice has the effect of anti-ulcer and inhibiting gastric acid secretion,and it can also alleviate the gastric mucosal damage caused by H.pylori infection[12].The total alkaloids of coptis chinensis can affect the gastric mucosal inflammation and epithelial cell apoptosis caused by H.pylori infection by balancing the expression of nitric oxide synthase in gastric mucosa[13].Thus,the mucous membrane may be protected and repaired,while its function may be also improved.At the same time,licorice can promote secretion of pancreatic juice and digestion of food and improve gastric distension[14].Fried hawthorn can increase the secretion of digestive enzymes in the stomach.Volatile oil,from Amomum villosum,can increase gastrointestinal function and the secretion of digestive juice[15].These show that Chai Ping Decoction may enhance the Qi of spleen and promote the transformation.When the function can be repaired,the stomach may digest and empty the food faster, after which the symptoms can be relieved.Therefore,dampness can be transformed and cleared up.
The combined therapy, including Chai Ping Decoction and sequential therapy, may work together in various aspects. Sequential therapy may play a role in improving the efficacy of sterilization and bacteriostasis and TCM treatment contributes to protect the gastric mucosa,restore the function of the stomach,and promote gastrointestinal peristalsis.Thus,the pathogenic factors are expelled and patients are cured.
Conclusion
Chai Ping Decoction combined with sequential therapy may treat refractory H.pylori infection well.Based on this,it is possible to carry out further clinical studies to investigate the specific improvement and efficiency of Chai Ping Decoction in the treatment of H.pylori infection.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of these case reports and any accompanying images.
Availability of data and materials
This paper is a patient case reports.Data sharing is not applicable to this article because no datasets besides those reported in the article were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Competing interests
All authors declare that they have no competing interests and no support from any organization for the submitted work;no financial relationships with any organization that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Funding
This case report was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81774146) and Beijing Nova Program(No.xxjh2015A093 and No.Z1511000003150125).
Authors’contributions
YD and HC are joint first authors.GT and BL designed the report.XT,SF,XW and XL collected the patient’s clinical data.YH made the follow-up data collection.HC and YD drafted the paper.GT,YL and BL guided revising the manuscript.All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.GT and BL are the study guarantors.
Acknowledgement
We would like to thank Rison RA and his team.We used the CARE checklist when writing our reports[16].
1. Hunt RH, Xiao SD, Megraud F, et al.Helicobacter pylori in developing countries.World Gastroenterology Organisation Global Guideline.J Gastrointestin Liver Dis,2011,20:299.
2. Ghotaslou R, Milani M,Akhi MT,et al.Relationship Between Drug Resistance and cagA Gene in Helicobacter pylori.Jundishapur J Microb,2013,6:463-468.
3. Ghotaslou R, Milani M,Akhi MT,et al.Diversity of Helicobacter Pylori cagA and vacA Genes and Its Relationship with Clinical Outcomes in Azerbaijan,Iran.Adv Pharm Bull,2013,3:57.
4. P Malfertheiner,F Megraud,C O'Morain,et al.Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection:the Maastricht III Consensus Report.Gut,2007,56:772-781.
5. Cammarota G, Ianiro G, Bibbò S, et al.Culture-guided treatment approach for Helicobacter pylori infection:Review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol, 2014,20:5205-5211.
6. Di MF, Cavallaro LG, Scarpignato C.'Rescue' therapies for the management of Helicobacter pylori infection.Dig Dis,2006,24:113.
7. Rafeey M,Ghotaslou R,Nikvash S,et al.Primary resistance in Helicobacter pylori isolated in children from Iran. J Infect Chemother,2007,13:291-295.
8. Wroblewski LE, Jr PR, Wilson KT.Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer:factors that modulate disease risk. Clin Microbiol Rev,2010,23:713-739.
9. Mowat C, Williams C, Gillen D, et al.Omeprazole,Helicobacter pylori status,and alterations in the intragastric milieu facilitating bacterial N-nitrosation.Gastroenterology,2000,119:339.
10. Huang KE, Zhao M, Wang JH. The pharmacological research progress of astragalus alpinus.Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology(Chin),2005,16:461-463.
11. Wang HX,Liu WJ.The pharmacological and clinical application of rhizoma atractylodis macrocephalae in gastrointestinal diseases.Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research(Chin),2007,18:2847-2848.
12. Zeng PL. Clinical study of treatment and protective effect of Huangqi Guizhi Ten Junzi Soup Decoction on gastric mucosal injury Specialty:Clinical with combination of TCM and Western Medicine. M.Med. thesis, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine,2015.
13. Lu JS,Liu YQ,Li M.Research on protective effects and mechanism research of total alkaloids from coptidis rhizome for gastric mucosal lesion of Rats.China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica(Chin),2007,32:1333-1336.
14. Liu JL,Xu XY.The pharmacological research progress of hawthorn. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs(Chin),2009,1:63-66.
15. Yan Y.Research progress of Amomum villosum.Chinese Journal of Traditional Medical Science and Technology(Chin),2009,14(4):304-304.
16. Rison RA, Kidd MR, Koch CA. The CARE(CAse REport)guidelines and the standardization of case reports.J Med Case Rep,2013,7:261.
杂志排行
Clinical Research Communications的其它文章
- Fabry disease combined with acute interstitial nephritis:one case and literature review
- A protocol for the reporting and methodological quality of robotic surgery case reports
- Research progress of microRNA in prevention and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head
- Research progress of continuous nursing care in patients with percutaneous coronary intervention
