节能日光温室蓄热技术研究进展
2018-04-16鲍恩财曹晏飞邹志荣申婷婷
鲍恩财,曹晏飞,邹志荣,申婷婷,张 勇
(西北农林科技大学园艺学院,农业部西北设施园艺工程重点实验室,杨凌 712100)
0 引 言
日光温室在中国设施园艺的发展过程中起到了重要的作用。从上世纪初即开始初期发展,实现了冬春季节北方栽培的突破,80年代进入大规模发展阶段,2015年日光温室总面积为97.42万hm2,全国占比从2010年的20 %提高到25.2%,目前技术日臻完善,其意义及优越性进一步显现[1-4]。中国 2/3的日光温室集中在北方寒区,成为北方乃至全国“菜篮子工程”供应的重要手段、农民增收的重要途径和农业产业结构调整、农业现代化和新农村建设的重要内容,其节能减排效果显著,为提高城乡居民的生活水平、稳定社会做出了历史性贡献[5-6]。其优越性也受到国外的高度关注,2017年4月12日,荷兰的第 1座中国节能型日光温室正式开放,该日光温室位于瓦格宁根大学研究基地,结合应用了荷兰先进的生产管理技术[7]。
日光温室的研究内容主要集中于保温蓄热机理与实现方式[1],其中,节能日光温室的蓄热技术一直是国内外学者研究日光温室最重要、最集中的内容之一。本文分析了日光温室的研究现状,综述了国内外关于节能日光温室蓄热技术的相关研究,进行总结并展望其未来发展方向,以期为国内开展节能日光温室蓄热技术研究提供参考。
1 节能日光温室研究现状
节能日光温室起源于中国辽南地区,具有完全的自主知识产权,但作为一种温室形式,日光温室并不属中国独有。从2 000多年前开始的世界范围内的温室形式演变史来看,早期依墙而建的单屋面温室就是目前日光温室的雏形[1,8],国外学者对该类温室的光热环境、覆盖材料开展了部分研究[9-11]。随着欧美日等发达国家的经济发展,这种土地使用率较低的温室类型逐渐被淘汰,并转向全光型温室[1]。近年来,中国节能日光温室的发展迅速,其优良的保温蓄热性能得到国外学者的高度关注和研究,印度学者Sethi等[12]总结温室蓄热性能时,从节能角度考虑,借鉴了日光温室的蓄热原理,在温室北面砌墙并采用厚重材料作为蓄热体从而减少热量损失;Nayak等[13]进行光伏/光热与温室结合的试验时,采用的温室即为带后墙的类似中国日光温室的结构形式。土耳其学者Ucar等[14]分析了建筑物外墙采用4种不同绝热材料的效果,并认为可以作为温室外墙使用。伊朗学者 Mobtaker等[15]从能源需求的角度对当地6种温室类型进行了比较,分析计算了维持植物理想温度所需的总能量并建立了数学模型,结果表明,东西走向、北侧为砖墙的温室中所需的额外能量最低,可节能31.7%。加拿大学者为降低冬季温室加温的能源消耗,早在2005年就引入了中国日光温室建造于Manitoba地区(50° N,97° W),并测试该温室在冬季的保温情况,结果表明在当地最冷的 2月份,室外平均气温为–13.1 ℃,室内夜间平均气温为2.4 ℃,后墙的日均蓄、放热量分别为166、159 MJ,为维持室内不低于10 ℃的气温,日均加温时长为19 h[16];Mahmood等[17]在日光温室内采用地下卵石床蓄热,并将猪舍的废气通过净化后通往室内供应 CO2,以促进植物生长;Ahamed等[18]建立了日光温室的热环境数学模型。日本学者畔柳武司[19]提出了日光温室热环境模型的研究。韩国学者 Kwon等[20]针对沿海地区风载较大的问题,设计了类似日光温室结构形式的塑料大棚。中国学者总结了日光温室的发展由来、建筑结构形式、光热环境与气候适应性、历史性贡献、存在问题及产业前景,认为日光温室作为具有典型中国特色、规模巨大的设施类型,一直是中国温室园艺装备升级的重点[6,21-22],并对日光温室的覆盖材料[23-25]、建筑结构及材料[8,26-28]、设施与装备[29-32]、保温蓄热性能[33-36]、环境监测及控制系统[37-40]等进行了详细的研究。
2 蓄热技术研究现状
节能日光温室的蓄放热示意图如图 1所示,可实现白天蓄热、夜间放热功能的结构有土壤、墙体和骨架,但普通骨架结构自身的储热量很小,一般忽略不计。节能日光温室的蓄热是通过结构、材料、设备的单一或协同应用来最大化利用太阳能为室内提供热能。蓄热有被动蓄热和主动蓄热 2种形式,主动蓄热是以太阳能为能量来源,以机械动力设备为手段,利用室内土壤、墙体、骨架结构以及相变材料为热量吸收介质的一种热量蓄积方式;反之则为被动蓄热。主动蓄热与被动蓄热的能量均来源于太阳,利用途径有 2种,一是最大化利用室内截获的太阳能或室内富余热量,一是利用室外的太阳能。
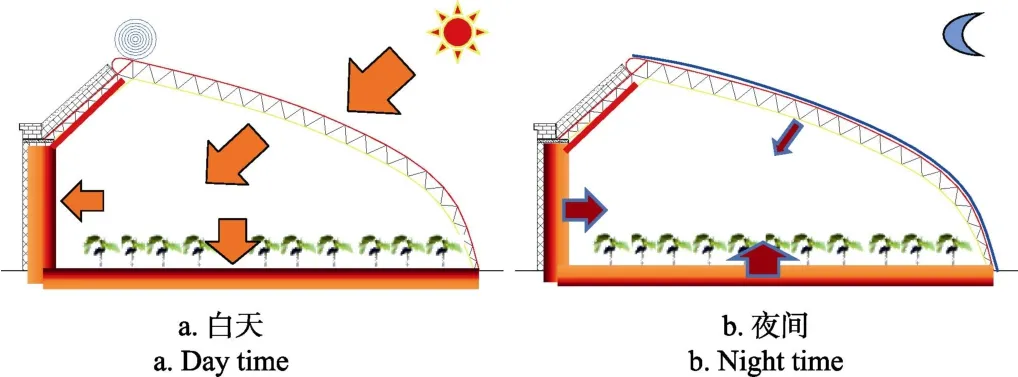
图1 日光温室蓄放热示意图Fig.1 Schematic diagram of heat storage-release in solar greenhouse
2.1 主动采光蓄热
日光温室的前屋面以平面为最佳,采光量最大,而且光照分布最均匀[41]。为了使日光温室室内获得更多的能量,张真和[42]通过综合分析农业气象学和光学的研究成果,确定了冬至日正午时太阳光线投射角度为50°时的采光屋面角度是合理的采光屋面角度。陈端生等[43]利用数学方法模拟温室的采光屋面,得出了温室的采光屋面最佳的坡度并不是一个定值,而应该随太阳高度角的变化进行调整。
基于上述研究,张勇等[44-46]设计了一种可变采光倾角日光温室实现主动采光蓄热(如图2所示),并对其温光性能进行了研究,与固定采光倾角日光温室相比,典型晴、阴天时可变采光倾角日光温室内的平均光照度分别提高29.00%、22.27%,平均温度分别提高4.3、2.9 ℃;与传统8、9 m跨的弧形采光屋面日光温室分别进行对比分析,在晴天和多云采光天气条件下,倾转屋面日光温室室内的整体采光率分别较传统8、9 m跨固定采光面日光温室提高41.75%、25.05%,对应的室内辐照度平均增加69.54、38.99 W/m2,故表现为室内气温整体水平提高。张勇等[47]还从经典光学理论出发,结合理论计算和试验测试的方法,详细分析了温室采光面在小幅调整条件下自然光的透过率以及温室采光面角度调整与室内光照强度透过率的增加之间的定量关系。

图2 主动采光蓄热日光温室结构[46]Fig.2 Structure of active lighting and heating storage type solar greenhouse
上述研究表明通过主动地改变日光温室前屋面倾角的形式可以提高采光面透光率,进而提高室内光辐射照度,解决了能量“多进”的问题。但室内墙体和土壤等蓄热体仍然为被动蓄热,被动蓄热的墙体和土壤的蓄热深度有限,未得到利用的室内富余热量仍会随着冷风渗透、地中传热、通风等途径被释放至室外,未实现能量在室内“多存”。因此,主动采光蓄热需要和其他室内主动蓄热设备或材料联合使用才能更好的发挥其效果。
2.2 空气循环蓄热
2.2.1地下空气循环蓄热
地下空气循环蓄热在园艺设施的土壤中应用较早,马承伟[48-49]研究了塑料大棚的地-气热交换系统,结果表明,该系统可有效地贮存太阳能并用于夜间加温,能使塑料大棚在不加温条件下在夜间维持 10 ℃左右的棚内外气温差。孙忠富[50]的研究结果表明,地-气热交换系统可使塑料大棚白天降温 2.5~6.5 ℃,夜间升温 2.0~4.4 ℃。袁巧霞[51-52]设计了一种半被动式塑料大棚地下热交换系统,试验表明,该系统可在夜间维持8~9 ℃的棚内外气温差,同时棚内地温可提高10 ℃左右。Santamouris等[53]利用地下热交换系统对1 000 m2的玻璃温室进行蓄热,结果表明具有良好的白天降温、夜间增温的效果。吴德让等[54-55]运用传热学的基本理论,建立了日光温室地下热交换系统土壤温度场的数学模型,同时通过试验研究了日光温室采用地下热交换系统在冬季生产喜温蔬菜的可行性和实用性,结果显示,300 m2的日光温室采用地下热交换系统的整个冬季放热量为1.575×106kJ、节煤量达1 950 kg。孙周平等[56]在彩钢板保温装配式节能日光温室室内地下 0.5 m位置设计安装了空气—地中热交换系统进行蓄热,整个冬季的试验结果表明,该系统具有良好的蓄热效果,与温室水循环蓄热系统结合可确保试验温室内热环境满足番茄生长所需。
2.2.2墙体空气循环蓄热
张勇等[57-58]设计了一种能够将白天富余能量进行有效存储的日光温室空气循环式主动蓄热后墙(如图 2所示的后墙结构),在墙体内部分层安装蓄热风道,墙体表面安装有轴流风机,风机将室内热空气抽入后墙蓄热风道,经过热交换,热量蓄积入墙体内蓄热体中,与传统9 m跨的普通砖墙日光温室进行了对比分析表明,在晴天、多云天夜间保温时段(16:00~次日 09:00),主动蓄热后墙日光温室温度较 9 m跨普通砖墙日光温室分别提高1.8~2.8、1.6~4.2 ℃。鲍恩财等[59]改进了原有的后墙空气循环蓄热系统,将原有进风口和出风口之间的距离由80 m缩短至40 m,并利用试验地(内蒙古乌海地区)丰富的沙土作为后墙蓄热体的一部分,实测结果表明,典型晴天条件下,固化沙主动蓄热后墙日光温室室内日平均气温较固化沙被动蓄热后墙日光温室和普通砖墙日光温室分别高3.3、3.6 ℃,典型阴天的夜间气温分别高3.2、3.8 ℃;固化沙主动蓄热后墙温室的墙体内部恒定温度区域处于740~1 000 mm之间,蓄热体厚度超过740 mm,其中固化沙蓄热厚度超过620 mm,蓄热风道上下表面各200 mm的高度范围内均属于蓄热体。王昭等[60]测试了基于太阳能光伏板提供电能的后墙主动蓄热日光温室,与当地普通日光温室对比发现,后墙主动蓄热日光温室较普通日光温室晴、阴天夜间平均温度分别高2.1、0.9 ℃,试验温室蓄热体厚度为320~520 mm,番茄采收期产量提高17.8%。
王庆荣等[61]设计了一种中空墙体,该墙体可实现与室内空气的自然对流循环蓄热,通过测试及 Fluent软件模拟分析,发现墙体构造所形成的循环气流可以在一定程度上扰动室内空气,进而在温室内走道和作物栽培行间等位置形成气流,其中温室跨中栽培行间的下部平均气流速度可达0.25 m/s,对日光温室冬季封闭栽培条件下的气流环境有一定的改善作用。任晓萌等[62]测试了该墙体的蓄放热效果,在晴天白天,内部中空层两侧墙体表面的温度高于相邻实心构造部分,但比中空层空气温度的19.2 ℃分别低2.2、3.7 ℃,表明墙体深处处于蓄热状态;清晨,中空层两侧表面温度分别比其中空层空气温度的11.7 ℃高1.3、0.8 ℃,表明墙体内部直至清晨仍处于放热阶段。
上述研究表明可以通过强迫对流或自然对流的方式将室内富余热量蓄积进入较深层的土壤或墙体内储存起来,对室内气温的提高具有一定的效果。强迫对流需要增加通风管道、风机等设备投入,且运行过程消耗电能,因此,在安装制作之前,需要计算土壤或墙体可蓄积的能量与电能消耗量,并确定是否具有节能性;自然对流依靠温差形成气流,故气流速度较小,为最大化利用墙体的蓄放热潜力,可通过增加变频风机继续研究不同流速对蓄放热量的影响,进而分析得到最佳风速及其控制策略。气流运动对室内温度场、湿度场、气体浓度场均会产生影响,今后在气流运动均匀性方面需加强研究。
2.3 水循环蓄热
水的比热容较大且易于流动,适于作为热能的贮存和传递介质,国内外学者均有将水作为蓄热体为温室供热的研究报道[63-65]。Zaragoza等[66]介绍了热水供暖在农业建筑(包含温室)上的应用前景及趋势;Sethi等[67]采用地下水(24 ℃)对温室开展冬季供暖及夏季降温试验研究,发现冬季可提高室内气温 7~9 ℃;Attar等[68-69]使用太阳能热水加温系统对温室加热,将毛细热交换管布置在地下作物根部附近,并使用TRNSYS软件模拟了毛细热交换管的适宜长度和水流速度。
2.3.1水幕帘蓄放热系统
张义等[70]设计了一种水幕帘蓄放热系统,该系统以日光温室墙体结构为依托,以水为介质进行热量的蓄积与释放,白天利用水循环通过水幕帘吸收太阳能,同时将能量储存在水池中,夜晚利用水循环通过水幕帘释放热量,该水幕帘蓄放热系统可使温室内夜间气温提高5.4℃以上,作物根际温度提高1.6 ℃以上。Fang等[71-74]利用不同材质和颜色的封装膜改进了该水幕帘蓄放热系统,如图 3所示。测试结果表明,晴、阴天时采用双黑膜封装的蓄放热装置能将温室夜间平均气温分别提高4.6、4.5 ℃,与电加热方式相比该系统的节能率超过51.1%;采用金属膜封装的蓄放热装置集热效率达到了83%,对太阳辐射的吸收率为0.81,优于双黑膜封装的蓄放热装置。孙维拓等[75-78]进一步拓展了水幕帘蓄放热系统的应用,或将其与热泵结合使用提高蓄放热性能,或应用于大跨度日光温室中。
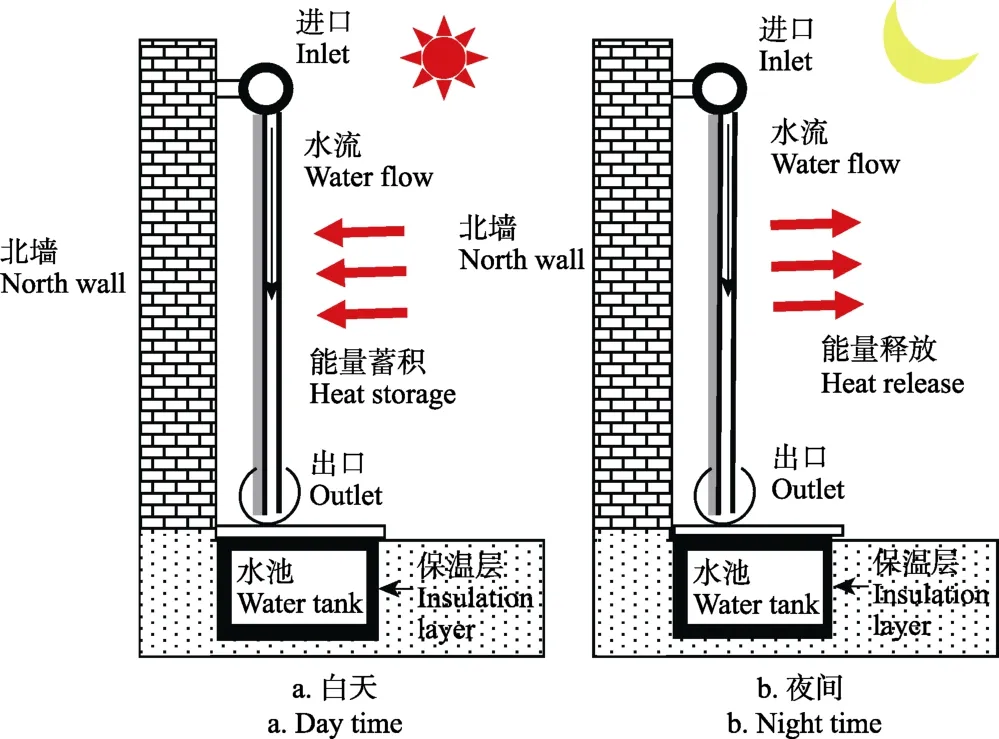
图3 水幕帘系统示意图[73]Fig.3 Schematic diagram of water curtain system
2.3.2管道水循环蓄热
一些学者将太阳能热水系统引入日光温室中,如方慧等[79]以温室浅层土壤为蓄热体,白天将后墙集热器获得的热量收集并储存到温室浅层土壤中,夜间通过土壤的自然放热将热量释放到温室中,与对照相比夜间平均气温差为4.0 ℃;王双喜等[80-81]在日光温室的后墙顶部安装太阳能热水器,热水管道埋置于室内土壤中;余学江[82]将加热盘管在靠近地面位置进行迂回铺设;于威等[83-84]利用 ANSYS软件分析了日光温室地中埋热水管对土壤加温效果的影响,结果表明,水温对地表温度影响显著,管道内水流速≥0.10 m/s时地表温度变化不大,在长期平稳条件下,埋管深度、管径对地表温度影响不大,而管间距对土壤温度分布影响显著,筛选出适宜管间距200 mm、管径25 mm。
佟雪姣等[85-86]采用聚乙烯(polyethylene,PE)软管为输水管道,以聚碳酸酯(polycarbonate,PC)板为集/散热装置,研究日光温室太阳能水循环系统冬季的蓄热增温效果,对PC板的不同颜色、厚度、黑膜添加方式及水的不同流量开展了研究,试验结果表明,同等条件下褐色、8 mm厚的PC板的蓄热量最多,透明阳光板内外侧均添加黑膜后蓄热量增加20%,当流量为4.4~4.5 L/h时,8 mm的透明阳光板蓄热效果最好;冬季晴天,日光温室内光照条件好,水循环系统日蓄热量为 159.8 MJ,可将温室内夜间温度提高3~5 ℃,集热效率为54.5%,蓄热增温效果明显。马承伟等[87]研究了日光温室钢管屋架管网水循环集放热系统(图4),理论计算表明,在屋架间距为1 m,上、下弦杆件均为外径33.5 mm的圆管时,系统的太阳能截获率可达7%~8%;测试结果表明,与对照日光温室相比,平均提高夜间室内最低气温2.4 ℃,容积为8.6 m3的蓄热水体白昼日平均蓄热温升4.7 ℃,平均蓄热量为149 MJ,夜间水体日平均放热温降2.5 ℃,平均放热量为78.9 MJ。
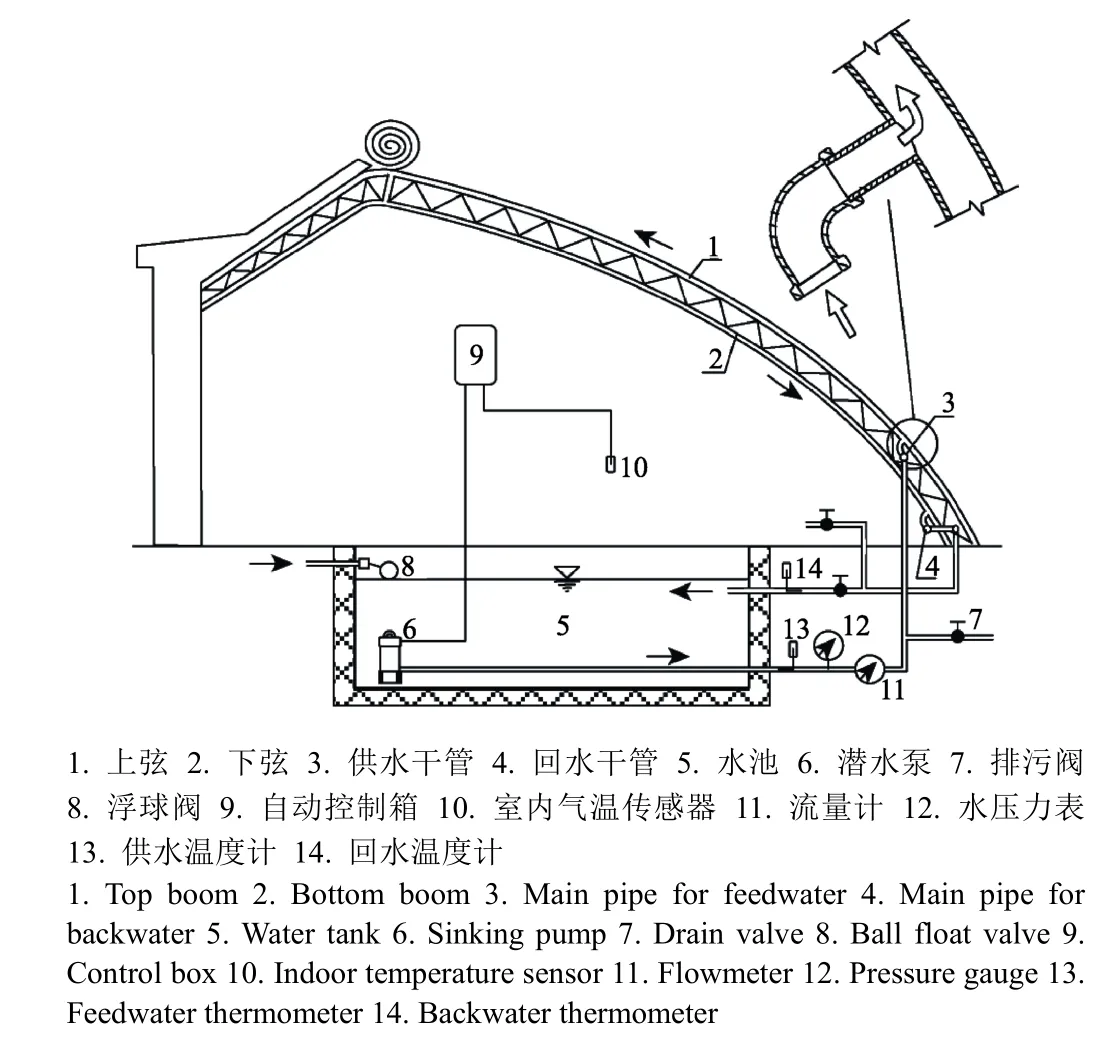
图4 钢管屋架管网水循环集放热系统[87]Fig.4 Water circulation system of steel pipe network formed by roof truss for heat collection and release
水循环蓄热的效果较为明显,水流的均匀性较好,但缺点也较为明显,即对循环管道的密闭性和抗腐蚀性要求较为严格,且施工过程增加了水池、管道、水泵等设备,故施工工艺要求较高。在原有后墙南侧安装水循环蓄热的集/放热装置会削减后墙的蓄放热效果,应分析水循环蓄热与原有墙体蓄热之间的“竞争”关系并量化,在维持室内作物生产适宜热环境的基础上,可适当降低后墙蓄热结构部分的厚度或减少水循环蓄热的投入以达到最佳投入。
2.4 相变材料蓄热
相变材料在日光温室中具有白天“削峰”、夜间“填谷”的作用,国内外学者主要从相变材料的筛选制备[88-97]、封装[89-90,93-98]、与温室的结合方式[92,98-101]等方面进行了大量研究。主要筛选的材料有石蜡[89,93]、芒硝 基[89]、 Na2SO4·10H2O[90,93-94]、 CaCl2·6H2O[91-92]、Na2HPO4·12H2O[95,97]、脂肪酸类[96]等。采用的封装方式有共混浸泡[93]、砌块封装[93]、稻壳吸附[94,98]、石墨吸附[96]等,制备成微胶囊[89]、板材[90,93,95-97]、砌块[93-94,98]。与温室的结合方式主要是将封装之后的相变材料放置在温室的北墙[92,99],或利用板材或砌块直接砌筑在日光温室后墙内侧[98,100-101]。
近年来,也有学者[91,102-104]将相变材料与太阳能集热器结合应用于温室中,并取得了一定的效果,如 Benli等[91]利用相变材料与太阳能平板集热器为温室供热,测试发现该系统为试验温室提供了每日热能需求量的 18~23%,闫彦涛[104]分析得到太阳能相变蓄热器单位面积放热量为4.05 MJ/m2;凌浩恕等[105-107]将多曲面槽式空气集热器结合相变材料应用于带竖向风道的日光温室后墙 (图 5),研究发现,当墙体内竖向空气通道间距为400 mm、空气通道内空气速度为0.26 m/s、空气流动方向为上进下出时,相变蓄热墙体换热效率为66.2%,主动蓄热量约为9.43 MJ/m3。
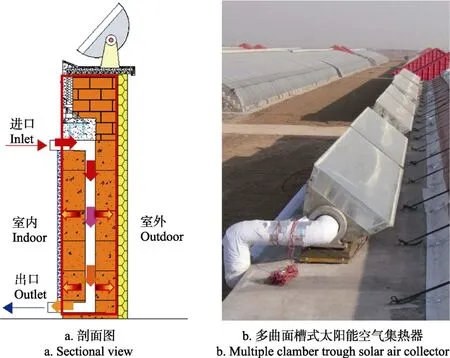
图5 带竖向空气通道的太阳能相变蓄热墙体体系[105]Fig.5 Phase change material wall with vertical air channels integrating solar concentrators
相变材料种类繁多,但真正被研究者系统研究过的种类却屈指可数,且需要契合日光温室冬季室内温度环境;相变材料在使用过程中体积变化率大,对封装密闭性的要求较高,目前的封装方式都有不同程度的泄露问题,有一定的环境污染风险。因此,需要进一步筛选适宜日光温室使用的材料种类及混合配比,并在封装技术上加强研究。
2.5 卵石蓄热
卵石是良好的显热储能材料,国外一般在温室中部的地下土壤中埋置卵石床,Öztürk等[108]利用卵石床结合太阳能空气集热器为120 m2的塑料大棚供热,卵石床面积为6 m×2 m,深0.6 m,研究发现卵石床的平均日蓄热量为1 242 W,夜间放热量为601.3 W,可提供室内总需热量的18.9%;Kürklü等[109]以2座面积均为15 m2的塑料大棚为试验对象,其中1座埋置有卵石床,PVC管道穿过卵石床,采用流量1 100 m3/h的风机强制将室内空气通过管道流经卵石床,测试发现试验温室夜间气温比对照温室提高约10 ℃,卵石蓄热系统的能量吸收及释放效率均超过 80%。国内将卵石作为日光温室蓄热材料有 2种形式,一种是直接作为墙体材料;一种是作为蓄热床。张洁等[110]以铅丝网笼装填卵石作为墙体主要材料,认为卵石之间的缝隙可以加强热空气的流动,从而增强墙体的蓄热性能,与普通砖墙日光温室相比,卵石墙体温室内平均气温在典型晴天高4.0 ℃。Chen等[111]将卵石床铺在室内土壤表面,研究发现卵石孔隙率一定时,应适当增大卵石床的粒径,当卵石粒径大于一定值时,适当增加卵石床孔隙率可以增强卵石床与温室气流,以及卵石床内部的对流换热。张峰等[112]测试发现卵石床地下蓄热系统的蓄热功率约为 94 W/m2,大于地下埋管蓄热系统(蓄热功率约为76 W/m2),该日光温室的夜间最低温度比无蓄热装置的对照温室提高了5~8 ℃。
卵石的传热速率较快,卵石之间的孔隙也有利于对流传热,但在冬季夜间卵石放热过快会导致前半夜室内气温较高、后半夜室内气温偏低。因此,需要研究如何减缓卵石所蓄积热量的释放,或将卵石所蓄积热量传导至其他材料中储存起来。
2.6 热泵蓄热
热泵根据所利用热源的不同主要分为水源热泵、空气源热泵和土壤源热泵 3类。国外学者将热泵应用到温室中较早,Marsh等[113]采用生命周期成本分析法(life cycle costing,LCC)分析了利用热泵将矿井中的恒温空气作为空气源对温室进行加温的可行性;Bot等[114]分析了利用热泵夏季储热为冬季供热的温室节能模式,预计节能率超过 60%;Ozgener等[115]测试得到土壤源热泵为温室供热的性能系数(coefficient of performance,COP)为 2.13(多云天)~2.84(晴天);Yang等[116-117]利用空气源热泵对温室进行冬季加温、夏季降温,均取得了良好的节能效果。
进入21世纪,国内学者开始探索热泵在日光温室上的应用,柴立龙等[118-119]采用地下水作为热源的热泵系统对北京地区日光温室进行了供暖试验研究,结果表明,整个供暖期(2007-10-15~2008-03-10)热泵的 COP为3.83,与燃煤热水采暖相比,可节约42%的能源消耗。孙维拓等[75,120]设计了一套日光温室水循环主动蓄放热与热泵联合加温系统(如图 6所示),主动蓄放热系统为热泵机组提供热源,与对照温室相比,试验温室夜间气温高出 5.26~6.64 ℃,系统集热效率达到了 72.32%~83.62%,总体 COP值达 5.59,而单纯使用热泵制热的COP为4.38~5.17。孙维拓等[121]还设计了一套日光温室空气余热热泵加温系统,白天适时运行系统,将日光温室内富余空气热能泵取并储存于蓄热水池中;夜间室内气温较低时,首先开启风机和水泵,当蓄热水池水温降至一定温度,逆向运行热泵系统强制放热;与对照温室相比,试验温室白天平均气温降低 3.7~5.2 ℃,相对湿度降低12.3%~16.5%;夜间平均气温高出2.8~4.4 ℃,相对湿度降低8.0%~11.5%。孙先鹏等[122-123]采用太阳能联合空气源热泵供热系统为日光温室供热,在西安地区-6~10 ℃冬季气温条件下开展了试验研究,结果表明,在试验天气条件下,热泵单独供热时系统的 COP在2.09~2.45之间,太阳能联合空气源热泵供热时系统的COP在3.45~5.56之间,具有显著的节能减排效果。
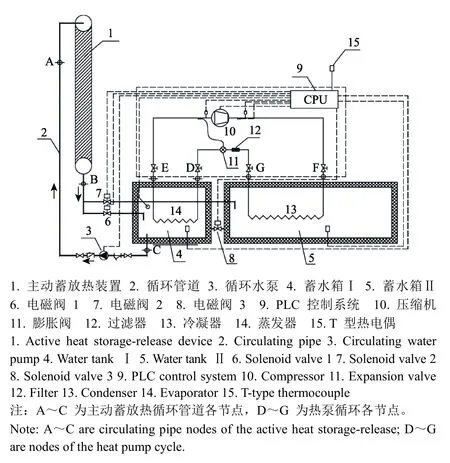
图6 温室主动蓄放热-热泵联合加温系统原理图[120]Fig.6 Principle diagram of active heat storage-release associated with heat pump heating system in greenhouse
热泵系统具有节能环保、供热稳定的优点,但设备投资较高、运行耗电量较大,在日光温室中的应用研究还处于初级阶段,其系统参数配置、加工工艺等还有待优化。在使用热泵蓄热时,对日光温室的蓄热性能要求降低,因此可适当减少温室蓄热墙体结构的投入,同时在运行时间上与峰谷电价相结合,可降低部分运行成本。
2.7 联合方式蓄热
为了提高蓄热技术的应用效果,部分学者将 2项或以上蓄热方式结合应用到日光温室中,如Benli[124]将地源热泵与相变材料蓄热技术结合应用于温室采暖;孙周平等[56]在大跨度日光温室中将空气—地中热交换系统与水循环蓄热系统结合使用可代替传统土墙的蓄热能力,经过整个冬季的测试发现,该联合系统可以确保日光温室冬季的热环境满足作物所需;凌浩恕等[105-107]将相变材料、带空气通道的后墙与太阳能空气集热器结合构建带竖向空气通道的太阳能相变蓄热墙体体系;Kürklü等[109]将卵石蓄热与地下空气循环蓄热结合应用;孙维拓等[120]将水循环主动蓄放热系统与热泵机组联合使用,测试发现,联合系统的效果大于单一使用热泵的效果,也远高于传统太阳能热水系统以及地源热泵,节能效果显著;高文波等[125]将主动采光与墙体空气循环主动蓄热结合,典型晴天、多云天主动采光蓄热型日光温室室内平均光照度分别提高了21.28%、11.73%,平均气温分别提高了5.6、2.1 ℃。
除此之外,部分学者还就温室蓄热相关技术做了前言探索性研究,如Liu等[126]开发了一种新型的由乙烯—四氟乙烯(ETFE)膜和相变材料RT28组成的温室薄膜,对该薄膜的光学性能进行了试验研究,结果表明,相变材料在液态下,薄膜的透射率高于固态,此外,透光率与相变材料的温度有关。Anifantis等[127]结合光伏制氢技术与地源热泵技术为温室供暖,白天通过光伏板电解产生H2,然后将其储存在压力罐中,夜间H2通过燃料电池转化为电力,为地源热泵供电,从而为温室供暖。
上述研究表明,从目前联合方式蓄热的发展现状来看,国内较国外的技术更加成熟和丰富,尽管国外的前沿性研究较多,但仍处于初期阶段。要实现蓄热技术在日光温室上的推广应用,除技术先进、符合科技发展趋势外,也要满足市场现状。因此,应加强对蓄热技术的技术经济性指标分析。
3 讨 论
本文总结了目前节能日光温室蓄热技术的主要形式,包括主动采光蓄热、空气循环蓄热、水循环蓄热、相变材料蓄热、卵石蓄热、热泵蓄热、联合方式蓄热,均为结构、材料、设备 3个方面的单一或协同应用,如主动采光蓄热通过温室前屋面结构的角度转变实现光能的主动利用,但蓄热体未变;空气循环蓄热通过空气循环将室内多余热量存储进入地下土壤或墙体内;水循环蓄热是通过设备将水循环蓄热,以水为主要蓄热体;相变材料蓄热与卵石蓄热严格意义来说包括主动蓄热和被动蓄热 2种形式,如与太阳能集热器结合应用的相变材料蓄热属于主动蓄热,而单纯的利用材料改变来蓄热集热是被动的热量蓄积;热泵蓄热通过消耗电能提取空气、水或土壤中的低温热源的热能将其转移到室内;联合方式蓄热通过以上2种或以上蓄热技术结合应用。
3.1 主要技术问题
国外对现代日光温室的研究较少,中国在日光温室节能设计基础理论及应用上始终处于领先地位[128]。日光温室蓄热技术亦属于节能设计之一,国内学者对此做了大量的研究与改进。这些技术对改善室内环境均具有一定的效果,但也存在一些缺点与不足之处,因此研发应用蓄热技术为日光温室供热时需要重点考虑以下问题:1)主动采光蓄热具有明显提高室内光温环境的效果,但是没有良好的蓄热系统,热量得不到存储,白天过多的热量易对作物形成热害,只能随着通风被排出去造成热量浪费;2)强迫对流式空气循环蓄热主要是将传热风道埋置于日光温室的墙体或土壤中,建成后整个系统只有风机消耗电能,对温室增温具有一定的效果,在安装制作之前,需要计算墙体或土壤可蓄积的能量与电能消耗量,并确定是否具有节能性。自然对流式空气循环蓄热依靠温差形成气流,故气流速度较小;3)水循环蓄热和相变材料蓄热都是因其热容较大,可尽量多的将热量存储起来,但是水和相变材料的封装均需要良好的封闭性,否则容易泄露;4)卵石的传热速率较快,往往前半夜放热量较多,导致温室内后半夜的温度较低;5)热泵蓄热的COP一般都在2以上,避免了环境污染、节能效果显著,但该系统结构复杂,初始投资较高,系统性能的可靠性、稳定性有待于进一步验证[129];6)通过结合2项或以上蓄热方式联合应用于日光温室中,效果具有累加效应,但成本更高。
3.2 研究重点
基于以上节能日光温室蓄热技术存在的问题,当前研究的重点是:1)将主动采光技术与其他蓄热技术结合应用,形成主动采光—蓄热联合技术,实现温室内太阳能的“多进多存”;2)除管道连接处的密闭性外,强迫对流式空气循环蓄热应考虑风机的风速、流量与管道的直径、材质、长度等条件耦合,不同地区还应结合土壤的蓄热系数来合理布置管道,在墙体中埋置时还应考虑适当的分层及施工工艺的简易化。自然对流式空气循环蓄热可与强迫对流相结合,研究适宜的风速指标及气流运动的调控以实现最大化蓄热;3)水在蓄放热的过程中需要流动,而相变材料在蓄放热的过程中会部分发生相变,因此,水循环蓄热和相变材料蓄热的循环管道、封装材料应做到密闭、抗腐蚀;4)卵石的传热较快,可增加热阻帘人为地延缓放热时间,也可与其他储热介质结合应用,如作为墙体的吸热层,或在其孔隙内填充储热材料;5)热泵蓄热结合其他蓄热方式应用较单一应用的效果会有所提高,冬季供暖中具有良好的应用前景,如何进一步合理利用、合理配置温室地源热泵系统,完善相关技术,降低其建设费用、运行能耗和费用,也是今后应着重研究解决的问题;6)从蓄热的2种热量利用途径来看,因日光温室原本就具有土壤和墙体蓄热的优势,在利用室内截获的太阳能进行主动蓄热时应避免主动蓄热系统与室内原有蓄热体之间形成太阳能的“争夺”。在利用室外太阳能转化为室内所需热能的同时应尽量减少太阳能多级转化过程中的损耗;7)部分蓄热技术在日光温室应用的传机理尚不明确,有待进一步研究,如墙体空气循环蓄热过程中传热的动力学原理,再如卵石墙体对室内的传热机理。计算流体力学(computational fluid dynamics,CFD)拥有各种数值算法,有助于研究流体流动、传热等,可借助CFD模拟与试验结合的方式开展蓄热技术的传热机理研究。
4 结论与展望
节能日光温室经过近 1个世纪的发展,蓄热技术日臻完善、节能减排效果显著,为中国设施园艺的发展做出了历史性贡献。本文概述了有关日光温室的研究现状,总结了当前节能日光温室蓄热技术的主要形式并综述了国内外相关研究进展,分析主要技术问题及研究重点。展望未来节能日光温室蓄热技术的发展方向与研究内容主要包括:
1)利用蓄热技术对传统日光温室进行节能化改造。随着设施园艺的快速发展,目前有部分传统日光温室因为保温蓄热性能不足、环境调控能力差、劳动强度高等原因处于闲置或半闲置状态,造成土地资源的浪费。同时,随着人口增长与土地资源有限的矛盾不断突出,亟需对这部分日光温室从结构上进行升级改造,从而满足日益增长的园艺产品供应需求。节能日光温室蓄热技术成为传统日光温室更新换代的重点内容,通过蓄热技术可将日光温室的土壤、墙体甚至是骨架结构的蓄热潜力发挥出来。
2)蓄热技术随着节能日光温室新结构的发展而继续完善。墙体(特别是后墙)是节能日光温室与其他园艺设施的最大区别所在,也是传统日光温室节能化改造的重点对象。当前,设施园艺朝着大型化、机械化、智能化方向发展,日光温室也不例外,从提高土地利用率的角度出发,出现了墙体被部分或全部替代的日光温室类型,墙体的减少意味着日光温室内蓄热体的减少,这就更需要通过蓄热技术为室内提供更多的热能来弥补墙体减少的损失。因此,蓄热技术在现代节能日光温室的发展中将会起到越来越重要的作用。
3)运用跨学科、多方法集成的手段深入研究蓄热技术。当前主要从日光温室的结构或材料的改变来开展蓄热技术的效果研究,研究对象主要是室内温湿环境,而对室内气流场、空气成分浓度场的分析较少,且对应蓄热技术的蓄放热机理缺乏深入研究。因此,应加强跨学科综合研究,从满足作物生长发育过程需求的角度出发,运用理论分析、软件模拟、试验测试的集成方法来分析温室内综合环境,从而对现有蓄热技术进行优化,以进一步提高蓄热性能、改善室内环境、降低劳动强度,这也对新型节能日光温室的推广应用具有重要作用。
4)节能日光温室蓄热技术市场化应用前景广阔。中国幅员辽阔,在华北、东北、西北、青藏高寒区、环渤海及黄淮海地区的日光温室面积巨大,蓄热技术的市场化前景广阔。蓄热技术应在满足预期效果的前提下尽可能降低应用投入,随着软硬件技术的不断发展,可选用价格较低、性能较高的构件及材料来完善蓄热技术。并对技术成熟、参数齐备的蓄热技术形成标准规范的施工工艺,加强市场化推广应用。
[参考文献]
[1] 陈青云. 日光温室的实践与理论[J]. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版),2008,26(5): 343-350.Chen Qingyun. Progress of practice and theory in sunlight greenhouse[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University(Agricultural Science), 2008, 26(5): 343-350. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 喻景权. “十一五”我国设施蔬菜生产和科技进展及其展望[J]. 中国蔬菜,2011(2): 11-23.Yu Jingquan. Progress in protected vegetable production and research during‘The Eleventh Five-year Plan’in China[J]. China Vegetables, 2011(2): 11-23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 张真和. 农用塑料技术在设施园艺产业中的应用与发展[J]. 中国蔬菜,2015(7): 1-5.Zhang Zhenhe. Application and development of agricultural plastic technology in horticultural industry[J]. China Vegetables, 2015(7): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 汪懋华. 物联网技术支撑蔬菜日光温室转型创新发展的探索[R]. 沈阳:全国日光温室发展学术论坛,2015.
[5] 方虹. 国内外日光温室技术装备的研究与应用分析[J].农业科技与装备,2014(5): 40-41.Fang Hong. Analysis of research and application of solar greenhouse technology and equipment at home and abroad[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology and Equipment, 2014(5): 40-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 李天来. 我国日光温室产业发展现状与前景[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报,2005, 36(2): 131-138.Li Tianlai. Current situation and prospects of green house industry development in China[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural, 2005, 36(2): 131-138. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 全球果蔬网. 中国式日光温室在荷兰开放[DB/OL]. http://www. freshplaza. cn/article/6549#,2017-04-13.
[8] Tong G, Christopher D M, Li T, et al. Passive solar energy utilization: A review of cross-section building parameter selection for Chinese solar greenhouses[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2013, 26: 540-548.
[9] Miguel A F, Silva A M, Rosa R. Solar irradiation inside a single-span greenhouse with shading screens[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1994, 59(1): 61-72.
[10] Pieters J G, Deltour J M. Performances of greenhouses with the presence of condensation on cladding materials[J].Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1997, 68(2):125-137.
[11] Pieters J G, Deltour J M. Modelling solar energy input in greenhouses[J]. Solar Energy, 1999, 67(1): 119-130.
[12] Sethi V P, Sharma S K. Survey and evaluation of heating technologies for worldwide agricultural greenhouse applications[J]. Solar Energy, 2008, 82(9): 832-859.
[13] Nayak S, Tiwari G N. Energy and exergy analysis of photovoltaic/thermal integrated with a solar greenhouse[J].Energy and Buildings, 2008, 40(11): 2015-2021.
[14] Ucar A, Balo F. Determination of the energy savings and the optimum insulation thickness in the four different insulated exterior walls[J]. Renewable Energy, 2010, 35(1):88-94.
[15] Mobtaker H G, Ajabshirchi Y, Ranjbar S F, et al. Solar energy conservation in greenhouse: Thermal analysis and experimental validation[J]. Renewable Energy, 2016, 96:509-519.
[16] Beshada E, Zhang Q, Boris R. Winter performance of a solar energy greenhouse in southern Manitoba[J]. Canadian Biosystems Engineering, 2006, 48(5): 1-8.
[17] Mahmood K, Mann D D, Zhang Q, et al. A perpetual harvest greenhouse system: Integrating barn, biofilter, and greenhouse[J]. Agricultural Engineering International:CIGR Journal, 2009, 6:1-24.
[18] Ahamed M S, Guo H, Tanino K K. Modeling of heating requirement in Chinese solar greenhouse[C]//2016 ASABE Annual International Meeting. American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, 2016, (1): 2-14.
[19] 畔柳武司. 日光温室の熱環境形成機構に関する基礎的研究[D]. 日本茨城: 筑波大学,2003.
[20] Kwon K, Kim D, Kim R, et al. Evaluation of wind pressure coefficients of single-span greenhouses built on reclaimed coastal land using a large-sized wind tunnel[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2016, 141: 58-81.
[21] 陈端生. 中国节能型日光温室建筑与环境研究进展[J].农业工程学报,1994,10(1):123-129.Chen Duansheng. Advance of the research on the architecture and environment of the Chinese energe-saving sunlight greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE),1994, 10(1): 123-129. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 魏晓明,周长吉,曹楠,等. 中国日光温室结构及性能的演变[J]. 江苏农业学报,2012,28(4): 855-860.Wei Xiaoming, Zhou Changji, Cao Nan, et al. Evolution of structure and performance of Chinese solar greenhouse[J].Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 28(4): 855-860. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 丁敏,施旭栋,李密密,等.薄膜承载力及其对日光温室结构稳定性能的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(12):194-202.Ding Min, Shi Xudong, Li Mimi, et al. Load-bearing capacity of films and its effect on structure stability of Chinese solar greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(12): 194-202. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 刘晨霞,马承伟,王平智,等. 日光温室保温被传热的理论解析及验证[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(2):170-176.Liu Chenxia, Ma Chengwei, Wang Pingzhi, et al.Theoretical analysis and experimental verification of heat transfer through thick covering materials of solar greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015,31(2): 170-176. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 刘晨霞,马承伟,王平智,等. 日光温室保温被保温性能影响因素的分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(20):186-193.Liu Chenxia, Ma Chengwei, Wang Pingzhi, et al. Analysis on affecting factors of heat preservation properties for thermal insulation covers[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(20): 186-193. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 白义奎,李天来,张文基. 日光温室地基温度场数学模型及试验分析[J]. 北方园艺,2010(13): 49-53.Bai Yikui, Li Tianlai, Zhang Wenji. Experimental analysis and mathematical model on temperature field of the solar greenhouse's foundation[J]. Northern Horticulture,2010(13): 49-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 宋丹, 王宏丽, 李凯,等. 日光温室钢架组合墙体结构研究[J]. 北方园艺, 2013(3): 52-55.Song Dan, Wang Hongli, Li Kai, et al. Mechanical analysis of the steel-frame wall of solar greenhouse[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2013(3): 52-55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 杨小龙. 砖苯复合墙体日光温室热环境测试与模拟[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2014.Yang Xiaolong. Thermal Environment Testing and Simulation of Chinese Solar Greenhouse with Brick-Polystyrene Board Compound Wall[D]. Yangling:Northwest A & F University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 张国祥,傅泽田,李鑫星,等. 改进型日光温室后置固定式卷帘装置设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(12): 299-308.Zhang Guoxiang, Fu Zetian, Li Xinxing, et al. Design and experiment of rear fixed type rolling shutter device in solar greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(12): 299-308. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 王春野. 日光温室除湿技术的试验研究[D]. 长春:吉林农业大学,2016.Wang Chunye. The Experimental Study on Dehumidifying of Solar Greenhouse[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] Zhou B, Zhang Y, Yang Q, et al. Dehumidification in a Chinese solar greenhouse using dry outdoor air heated by an active heat storage-release system[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture. 2016,32(4): 447-456.
[32] 马文娟,塔娜,五十六,等. 冷风挡帘对日光温室内气温影响的数值模拟及其结构优化[J]. 中国农业大学学报,2017,22(5): 108-117.Ma Wenjuan, Ta Na, Wu Shiliu, et al. Numerical simulation and verification for the effect of keep-off shade on temperature field in solar greenhouse[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2017,22(5): 108-117. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 刘在民. 节能日光温室温光性能优化及其应用效果研究[D]. 哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2007.Liu Zaimin. The Performance Optimization on the Temperature and Light of the Greenhouse and the Research on Its Application Effectiveness[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 张亚红,包长征,曹云娥. 宁夏两种结构日光温室墙体与地面传热特性分析[J]. 农业现代化研究,2011,32(4):509-512.Zhang Yahong, Bao Changzheng, Cao Yune. Analysis on measurement of heat absorption and release of wall and ground in two different solar greenhouses[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 2001, 32(4): 509-512. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 封美琦. 宁夏银川地区日光温室土质后墙环境变化特征研究[D]. 银川:宁夏大学,2013.Feng Meiqi. The Research on Environment Variation Characteristics of Solar Greenhouses’ Soil Back Wall in Ningxia Yinchuan[D]. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2013.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] 安巧霞,孙三民,陈浩,等. 北疆地区冬季半地下式日光温室模拟设计[J]. 农机化研究,2017,39(7): 66-70.An Qiaoxia, Sun Sanmin, Chen Hao, et al. Sunken solar greenhouse simulation design in the winter in north of Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research. 2017,39(7): 66-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[37] 徐凡,马承伟. 温室环境分析中冬季室外气温日变化及数学表达[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(12):203-209.Xu Fan, Ma Chengwei. Daily change and math-expression method of outside temperature in winter for greenhouse environmental analysis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(12): 203-209. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] 袁洪波. 日光温室封闭式栽培系统关键技术研究[D]. 北京:中国农业大学, 2015.Yuan Hongbo. Study on Key Technologies for Closed Cultivation Systems in Solar Greenhouses[D]. Beijing:China Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[39] Yu H, Chen Y, Hassan S G, et al. Prediction of the temperature in a Chinese solar greenhouse based on LSSVM optimized by improved PSO[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2016, 122: 94-102.
[40] Li M, Chen S, Liu F, et al. A risk management system for meteorological disasters of solar greenhouse vegetables[J].Precision Agriculture, 2017, 18(6): 997-1010.
[41] 刘建,周长吉. 日光温室结构优化的研究进展与发展方向[J]. 内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版),2007,28(3):264-268.Liu Jian, Zhou Changji. The present and development of sunlight greenhousestructureoptimization[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agriculture University (Nature Science Edition), 2007, 28(3): 264-268. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[42] 张真和. 高效节能型日光温室的开发进展及问题讨论[J].中国蔬菜,1992(5): 1-10.Zhang Zhenhe. Development and discussion of energy efficient solar greenhouse[J]. China Vegetables, 1992(5): 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[43] 陈端生,郑海山,张建国,等. 日光温室气象环境综合研究(三):几种弧型采光屋面温室内直射光量的比较研究[J]. 农业工程学报,1992,8(4):78-82.Chen Duansheng, Zheng Haishan, Zhang Jianguo, et al. A comprehensive research on the meteorological environment in sun-light greenhouse ()Ⅲ: A comparative research on the total amount of direct radiation in the greenhouse with different arc lighting surfaces[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 1992, 8(4): 78-82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[44] 张勇,邹志荣. 一种可变倾角采光面的日光温室:101116408[P]. 2008-02-06.
[45] 张勇,邹志荣. 高效可变采光倾角日光温室的结构及其性能研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2013,41(11): 113-118,124.Zhang Yong, Zou Zhirong. Structure and properties of solar-greenhouse with variable incidence angle[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University(Natural Science Edition),2013, 41(11): 113-118, 124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[46] 张勇,邹志荣,李建明. 倾转屋面日光温室的采光及蓄热性能试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(1):129-137.Zhang Yong, Zou Zhirong, LI Jianming. Performance experiment on lighting and thermal storage in tilting roof solar-greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014,30(1): 129-137. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[47] 张勇,邹志荣. 日光温室主动采光机理与透光率优化试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(11):178-186.Zhang Yong, Zou Zhirong. Optimization experiment of light transmittance and active lighting mechanism of solar greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017,33(11): 178-186. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[48] 马承伟. 塑料大棚地下热交换系统的试验研究[J]. 北京农业机械化学院学报,1984,4:69-78.Ma Chengwei. Experimental study on underground heat exchange system in plastic greenhouse [J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Agricultural Mechanization Technology,1984, 4: 69-78. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[49] 马承伟. 塑料大棚地下热交换系统的研究[J]. 农业工程学报,1985,1(1):54-65.Ma Chengwei. Studys on the vinyl-house house heating by the underground heat exchange system [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 1985, 1(1): 54-65(in Chinese with English abstract)
[50] 孙忠富. 地—气热交换塑料大棚中热量平衡的研究[J].农业工程学报,1989,5(2):35-46.Sun Zhongfu. Studies on the heat balance of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) greenhouse with an earth-air heat exchanger[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 1989,5(2): 35-46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[51] 袁巧霞. 塑料大棚太阳能地下热交换系统的增温效应[J].华中农业大学学报,1995,14(3):297-302.Yuan Qiaoxia. Plastic greenhouse solar underground heat exchange system warming effect[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agriculture University, 1995, 14(3): 297-302. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[52] 袁巧霞. 塑料大棚地下热交换系统的应用问题探讨[J].湖北农业科学,1997(1):38-40.Yuan Qiaoxia. Application of underground heat exchange system in plastic greenhouse [J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 1997(1): 38-40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[53] Santamouris M, Mihalakakou G, Balaras C A, et al. Energy conservation in greenhouses with buried pipes[J]. Energy,1996, 21(5): 353-360.
[54] 吴德让,李元哲,于竹. 日光温室地下热交换系统的理论研究[J]. 农业工程学报,1994,10(1):137-143.Wu Derang, Li Yuanzhe, Yu Zhu. Theory research on earth tube heat exchangers in a sun-light greenhouse[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 1994, 10(1): 137-143. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[55] 吴德让,李元哲,于竹. 日光温室地下热交换系统的实验和优化设计研究[J]. 农业工程学报,1994,10(1):144-149.Wu Derang, Li Yuanzhe, Yu Zhu. Optimal design and test research of earth tube heat exchangers in a sun-light greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 1994,10(1): 144-149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[56] 孙周平,黄文永,李天来,等. 彩钢板保温装配式节能日光温室的温光性能[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(19):159-167.Sun Zhouping, Huang Wenyong, Li Tianlai, et al. Light and temperature performance of energy-saving solar greenhouse assembled with color plate[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(19): 159-167. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[57] 张勇,邹志荣. 一种蓄热后墙的日光温室:102630526[P].2012-08-15.
[58] 张勇,高文波,邹志荣. 主动蓄热后墙日光温室传热CFD模拟及性能试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(5): 203-211.Zhang Yong, Gao Wenbo, Zou Zhirong. Performance experiment and CFD simulation of heat exchange in solar greenhouse with active thermal storage back-wall[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(5): 203- 211. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[59] 鲍恩财,朱超,曹晏飞,等. 固化沙蓄热后墙日光温室热工性能试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(9): 187-194.Bao Encai, Zhu Chao, Cao Yanfei, et al. Thermal performance test of solidified sand heat storage wall in Chinese solar greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(9): 187-194. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[60] 王昭, 陈振东, 邹志荣, 等. 青海型主动蓄热日光温室应用性能分析[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2017, 22(8): 116-123.Wang Zhao, Chen Zhendong, Zou Zhirong, et al.Application performance analysis on active heating storage greenhouse of Qinghai style[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2017, 22(8): 116-123. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[61] 王庆荣,程杰宇,崔文慧,等. 日光温室对流循环蓄热墙体构造对室内气流场的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学,2016,53(7): 1319-1328.Wang Qingrong, Cheng Jieyu, Cui Wenhui, et al. Impact on indoor air distribution with the convective circulation thermal storage wall of Chinese solar greenhouse[J].Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 53(7): 1319-1328.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[62] 任晓萌,程杰宇,夏楠,等. 日光温室自然对流蓄热中空墙体蓄放热效果研究[J]. 中国农业大学学报,2017,22(2): 115-122.Ren Xiaomeng, Cheng Jieyu, Xia Nan, et al. Study on the effect of natural convective hollow wall on thermal storage/release in solar greenhouse[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University,2017,22(2): 115-122. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[63] Boulard T, Razafinjohany E, BaillE A. Heat and water vapour transfer in a greenhouse with an underground heat storage system part I. Experimental results[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 1989, 45(3-4): 175-184.
[64] Boulard T, Razafinjohany E, Baille A. Heat and water vapour transfer in a greenhouse with an underground heat storage system part II. Model[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 1989, 45(3/4): 185-194.
[65] 刘圣勇,张杰,张百良,等. 太阳能蓄热系统提高温室地温的试验研究[J]. 太阳能学报,2003, (4): 461-465.Liu Shengyong, Zhang Jie, Zhang Bailiang, et al.Experimental study of solar thermal storage for increasing the earth temperature of greenhouse[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2003, (4): 461-465. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[66] Zaragoza G, Buchholz M, Jochum P, et al. Watergy project:Towards a rational use of water in greenhouse agriculture and sustainable architecture[J]. Desalination, 2007, 211(1/3):296-303.
[67] Sethi V P, Sharma S K. Experimental and economic study of a greenhouse thermal control system using aquifer water[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2007, 48(1):306-319.
[68] Attar I, Naili N, Khalifa N, et al. Parametric and numerical study of a solar system for heating a greenhouse equipped with a buried exchanger[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2013, 70: 163-173.
[69] Attar I, Farhat A. Efficiency evaluation of a solar water heating system applied to the greenhouse climate[J]. Solar Energy, 2015, 119: 212-224.
[70] 张义,杨其长,方慧. 日光温室水幕帘蓄放热系统增温效应试验研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(4):188-193.Zhang Yi, Yang Qichang, Fang Hui. Research on warming effect of water curtain system in Chinese solar greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012,28(4): 188-193. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[71] Fang H, Yang Q, Zhang Y, et al. Performance of a solar heat collection and release system for improving night temperature in a Chinese solar greenhouse[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2015, 31(2): 283-289.
[72] 李文,杨其长,张义,等. 日光温室主动蓄放热系统应用效果研究[J]. 中国农业气象,2013,34(5): 557-562.Li Wen, Yang Qichang, Zhang Yi, et al. Application effects of active heat storage and release system in a Chinese solar greenhouse[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2013,34(5): 557-562. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[73] 梁浩,方慧,杨其长,等. 日光温室后墙蓄放热帘增温效果的性能测试[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(12): 187-193.Liang Hao, Fang Hui, Yang Qichang, et al. Performance testing on warming effect of heat storage-release curtain of back wall in Chinese solar greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(12): 187-193. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[74] 方慧,张义,杨其长,等. 日光温室金属膜集放热装置增温效果的性能测试[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(15):177-182.Fang Hui, Zhang Yi, Yang Qichang, et al. Performance testing on warming effect of heat storage-release metal film in Chinese solar greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(15): 177-182. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[75] 孙维拓,杨其长,方慧,等. 主动蓄放热-热泵联合加温系统在日光温室的应用[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(19):168-177.Sun Weituo, Yang Qichang, Fang Hui, et al. Application of heating system with active heat storage-release and heat pump in solar greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(19): 168-177. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[76] 周升,张义,程瑞锋,等. 大跨度主动蓄能型温室温湿环境监测及节能保温性能评价[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(6): 218-225.Zhou Sheng, Zhang Yi, Cheng Ruifeng, et al. Evaluation on heat preservation effects in micro environment of large scale greenhouse with active heat storage system[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(6): 218-225. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[77] Zhou S,Zhang Y,Yang Q C,et al. Performance of active heat storage-release unit assisted with a heat pump in a new type of Chinese solar greenhouse[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture,2016,32(5): 641-650.
[78] Lu W, Zhang Y, Fang H, et al. Modelling and experimental verification of the thermal performance of an active solar heat storage-release system in a Chinese solar greenhouse[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2017, 160: 12-24.
[79] 方慧,杨其长,梁浩,等. 日光温室浅层土壤水媒蓄放热增温效果[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,27(5): 258-263.Fang Hui, Yang Qichang, Liang Hao, et al. Experiment of temperature rising effect by heat release and storage with shallow water in solar greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(5): 258-263. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[80] 王双喜,马春生,张静,等. 节能温室太阳能土壤蓄热加温系统的研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2003, 19(5): 197-203.Wang Shuangxi, Ma Chunsheng, Zhang Jing, et al.Substrate heating system with solar energy for greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2003,19(5): 197-203. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[81] 王顺生,马承伟,柴力龙,等. 日光温室内置式太阳能集热调温装置试验研究[J]. 农机化研究,2007, 30(2): 130-133.Wang Shunsheng, Ma Chengwei, Chai Lilong, et al.Equipment in sunlight greenhouse for collecting heat and adjusting temperature[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research. 2007, 30(2): 130-133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[82] 余学江. 严寒地区日光温室主动太阳能供暖系统研究[D]大庆:东北石油大学,2011.Yu Xuejiang. Research on the Active Solar Heating System of Greenhouse in Intense Cold Area[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[83] 于威,王铁良,刘文合,等. 日光温室地中热水管加温对土壤温度的影响[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2014, 45(3):321-325.Yu Wei, Wang Tieliang, Liu Wenhe, et al. Soil temperature in solar greenhouse with buried hot water pipes[J].Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2014, 45(3): 321-325. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[84] 杨英英. 生态温室墙挂式太阳能辅助加温系统研究[D].沈阳:沈阳农业大学,2016.Yang Yingying. Study on Wall Hung Solar Assisted Heating System of Ecological Greenhouse[D]. Shenyang:Shenyang Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[85] 佟雪姣,孙周平,李天来,等. 日光温室太阳能水循环系统冬季与夏季试验效果[J]. 太阳能学报, 2016, 37(9):2306-2313.Tong Xuejiao, Sun Zhouping, Li Tianlai, et al.Experimental effects of solar energy water-cycling system for solar greenhouse in winter and summer[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2016, 37(9): 2306-2313. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[86] 佟雪姣, 孙周平, 李天来, 等. 温室太阳能水循环集热装置的蓄热性能研究[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2016, 47(1):92-96.Tong Xuejiao, Sun Zhouping, Li Tianlai, et al. Heating performance of heating device of the solar energy water-cycling system in greenhouse[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University. 2016, 47(1): 92-96. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[87] 马承伟,姜宜琛,程杰宇,等. 日光温室钢管屋架管网水循环集放热系统的性能分析与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(21):209-216.Ma Chengwei, Jiang Yichen, Cheng Jieyu, et al. Analysis and experiment of performance on water circulation system of steel pipe network formed by roof truss for heat collection and release in Chinese solar greenhouse[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(21): 209-216. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[88] 王宇欣, 刘爽, 王平智, 等. 温室蓄热微胶囊相变材料制备筛选与性能表征[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(9): 348-358.Wang Yuxin, Liu Shuang, Wang Pingzhi, et al. Preparation and characterization of microencapsulated phase change materials for greenhouse application[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(9):348- 358. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[89] 蒋自鹏, 铁生年. 芒硝基相变材料性能及其在简易温室中升温效果试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(20): 209-216.Jiang Zipeng, Tie Shengnian. Property and heat storage performances of Glauber's salt-based phase change materials for solar greenhouse in Qinghai-Tibet plateau[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(20): 209-216. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[90] 韩丽蓉. 相变蓄热材料十水硫酸钠的改性及应用研究[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2014.Han Lirong. Modification and Application of Sodium Sulfate Decahydrate as Phase Change Thermal Storage Material[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2014.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[91] Benli H, Durmuş A. Performance analysis of a latent heat storage system with phase change material for new designed solar collectors in greenhouse heating[J]. Solar Energy, 2009, 83(12): 2109-2119.
[92] Berroug F, Lakhal E K, Elomari M, et al. Thermal performance of a greenhouse with a phase change material north wall[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2011, 43(11): 3027-3035.
[93] 张立明. 温室墙体复合相变材料的制备与蓄热机理研究[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2008.Zhang Liming. The Preparation of Greenhouse Wall Composite PCM Materials and Research on Heat Storage Principle[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2008.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[94] 孙心心. 日光温室新型保温墙体材料的制备及应用效果的研究[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2010.Sun Xinxin. Study on the Preparation of New Thermal Insulation Greenhouse Wall Materials and Effect of Application[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University,2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[95] 许红军. 日光温室相变蓄热墙板制备及性能研究[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2013.Xu Hongjun. Preparation and Study on the Greenhouse Thermal Storage Wallboard with PCM[D]. Yangling:Northwest A&F University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[96] 张庆. 脂肪酸复合相变材料的制备及其在日光温室中的应用[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2015.Zhang Qing. Preparation of Fatty Acid Composite Phase Change Material and Its Application in Solar Greenhouse[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University,2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[97] 杨小龙, 王宏丽, 许红军, 等. 磷酸氢二钠相变墙板在温室中的应用效果[J]. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版),2014, 32(4): 88-94.Yang Xiaolong, Wang Hongli, Xu Hongjun, et al.Performance of phase change thermal storage wallboard of disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate in solar greenhouses[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University(Agricultural Science), 2014, 32(4): 88-94. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[98] 王宏丽,李晓野,邹志荣. 相变蓄热砌块墙体在日光温室中的应用效果[J]. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(5): 253-257.Wang Hongli, Li Xiaoye, Zou Zhirong. Application of brick wall with phase change rice husk in solar greenhouse[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(5): 253-257. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[99] Boulard T, Razafinjohany E, Baille A, et al. Performance of a greenhouse heating system with a phase change material[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 1990,52(3-4): 303-318.
[100] 管勇,陈超,李琢,等. 相变蓄热墙体对日光温室热环境的改善[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(10): 194-201.Guan Yong, Chen Chao, Li Zhuo, et al. Improving thermal environment in solar greenhouse with phase-change thermal storage wall[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012,28(10): 194-201. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[101] 管勇,陈超,凌浩恕,等. 日光温室三重结构相变蓄热墙体传热特性分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(21): 166-173.Guan Yong, Chen Chao, Ling Haoshu, et al. Analysis of heat transfer properties of three-layer wall with phase-change heat storage in solar greenhouse[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(21): 166-173. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[102]Öztürk H H. Experimental evaluation of energy and exergy efficiency of a seasonal latent heat storage system for greenhouse heating[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2005, 46(9): 1523-1542.
[103] 李晓野. 温室太阳能空气集热—相变蓄热装置设计及性能研究[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2012.Li Xiaoye. Design and Study on the Solar Air Heating System with Phase Change Materials Energy Storage in Greenhouse[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University,2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[104] 闫彦涛. 温室平板太阳能相变蓄热系统的设计及应用研究[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2016.Yan Yantao. Design and Application of Greenhouse Solar Panel Phase Change Thermal Storage System[D]. Yangling:Northwest A&F University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[105] 凌浩恕,陈超,陈紫光,等. 日光温室带竖向空气通道的太阳能相变蓄热墙体体系[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(3): 336-343.Ling Haosu, Chen Chao, Chen Ziguang, et al. Performance of phase change material wall with vertical air channels integrating solar concentrators[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(3):336 -343. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[106] 陈紫光. 基于相变蓄热墙体的太阳能空气集热器传热性能研究[D]. 北京:北京工业大学,2014.Chen Ziguang. Heat Transfer Performance of Solar Air Collector Based on Phase Change Thermal Storage Wall[D].Beijing: Beijing Industry University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[107] 陈超,张明星,郑宏飞,等. 日光温室用双集热管多曲面槽式空气集热器性能试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(15):245-252.Chen Chao, Zhang Mingxing, Zheng Hongfei, et al.Thermal performance experiment for multiple clamber trough solar air collector with dual collector tubes for solar greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017,33(15): 245-252. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[108]Öztürk H H, Başçetinçelik A. Energy and exergy efficiency of a packed-bed heat storage unit for greenhouse heating[J].Biosystems Engineering, 2003, 86(2): 231-245.
[109] Kürklü A, Bilgin S, Özkan B. A study on the solar energy storing rock-bed to heat a polyethylene tunnel type greenhouse[J]. Renewable Energy, 2003, 28(5): 683-697.
[110] 张洁,邹志荣,张勇,等. 新型砾石蓄热墙体日光温室性能初探[J]. 北方园艺,2016(2): 46-50.Zhang Jie, Zou Zhirong, Zhang Yong, et al. Performance of heating storage gravel wall solar greenhouse[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2016(2): 46-50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[111] Chen W, Liu W. Numerical and experimental analysis of convection heat transfer in passive solar heating room with greenhouse and heat storage[J]. Solar Energy, 2004, 76(5):623-633.
[112] 张峰,张林华,刘文波,等. 带地下卵石床蓄热装置的日光温室增温实验研究[J]. 可再生能源,2009,27(6): 7-9.Zhang Feng, Zhang Linhua, Liu Wenbo, et al. Experimental study on temperature increasing in solar greenhouse with underground pebble bed thermal storage[J]. Renewable Energy, 2009, 27(6): 7-9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[113] Marsh L S, Singh S. Economics of greenhouse heating with a mine air-assisted heat pump[J]. Transactions of the ASAE,1994, 37(6): 1959-1963.
[114] Bot G P A, Braak N J van de, Challa H, et al. The solar greenhouse: State of the art in energy saving and sustainable energy supply[J]. Acta Horticulturae, 2005,691(2): 501-508.
[115] Ozgener O, Hepbasli A. Experimental investigation of the performance of a solar-assisted ground-source heat pump system for greenhouse heating[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2005, 29(3): 217-231.
[116] Yang S H, Rhee J Y. Utilization and performance evaluation of a surplus air heat pump system for greenhouse cooling and heating[J]. Applied Energy, 2013, 105: 244-251.
[117] Attar I, Naili n, Khalifa N, et al. Experimental study of an air conditioning system to control a greenhouse microclimate[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,2014, 79: 543-553.
[118] 柴立龙,马承伟,张义,等. 北京地区温室地源热泵供暖能耗及经济性分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2010,26(3):249-254.Chai Lilong, Ma Chengwei, Zhang Yi, et al. Energy consumption and economic analysis of ground source heat pump used in greenhouse in Beijing[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(3): 249-254. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[119] Chai L, Ma C, Ni J Q. Performance evaluation of ground source heat pump system for greenhouse heating in northern China[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2012, 111(1): 107-117.
[120] 孙维拓,张义,杨其长,等. 温室主动蓄放热-热泵联合加温系统热力学分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(14):179-188.Sun Weituo, Zhang Yi, Yang Qichang, et al.Thermodynamic analysis of active heat storage-release associated with heat pump heating system in greenhouse[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(14): 179-188 (in Chinese with English abstract)
[121] 孙维拓,郭文忠,徐凡,等. 日光温室空气余热热泵加温系统应用效果[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(17):235-243.Sun Weituo, Guo Wenzhong, Xu Fan, et al. Application effect of surplus air heat pump heating system in Chinese solar greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015,31(17): 235-243 (in Chinese with English abstract)
[122] 孙先鹏,邹志荣,赵康,等. 太阳能蓄热联合空气源热泵的温室加热试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(22):215-221.Sun Xianpeng, Zou Zhirong, Zhao Kang, et al. Experiment on heating effect in greenhouse by solar combined with air-source heat pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE),2015, 31(22): 215-221. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[123] 孙先鹏,郭康权,邹志荣,等. 太阳能联合空气源热泵系统温室供热实验研究[J]. 太阳能学报,2016,37(3): 658-665.Sun Xianpeng, Guo Kangquan, Zou Zhirong, et al. System investigation of a solar combined with air-source heat pump system for greenhouse heating[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2016, 37(3): 658-665. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[124] Benli H. Energetic performance analysis of a groundsource heat pump system with latent heat storage for a greenhouse heating[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2011, 52(1): 581-589.
[125] 高文波,张勇,邹志荣,等. 主动采光蓄热型日光温室性能初探[J]. 农机化研究,2015, 37(7): 181-186.Gao Wenbo, Zhang Yong, Zou Zhirong, et al. Preliminary study on performance in an active lighting and heating storage type solar greenhouse[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2015, 37(7): 181-186. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[126] Liu X, Gao H, Sun Y, et al. Thermal and optical analysis of a passive heat recovery and storage system for greenhouse skin[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2016, 155: 472-478.
[127] Anifantis A S, Colantoni A, Pascuzzi S. Thermal energy assessment of a small scale photovoltaic, hydrogen and geothermal stand-alone system for greenhouse heating[J].Renewable Energy, 2017, 103: 115-127.
[128] 白义奎,周东升,曹刚,等. 北方寒区节能日光温室建筑设计理论与方法研究[J]. 新疆农业科学,2014,51(6):990-998.Bai Yikui, Zhou Dongsheng, Cao Gang, et al. Research on solar greenhouse architectural design theory and method during winter time in northern cold regions of China[J].Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 51(6): 990-998. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[129] 郭长城,石惠娴,朱洪光,等. 太阳能-地源热泵联合供能系统研究现状[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,27(14): 356-362.Guo Changcheng, Shi Huixian, Zhu Hongguang, et al.Review of solar-assisted ground source heat pump system[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011,27(14): 356-362. (in Chinese with English abstract)
