2008—2017年上海市朱泾镇水痘流行病学特征分析
2018-01-13李俊王胜马亚飞
李俊 王胜 马亚飞
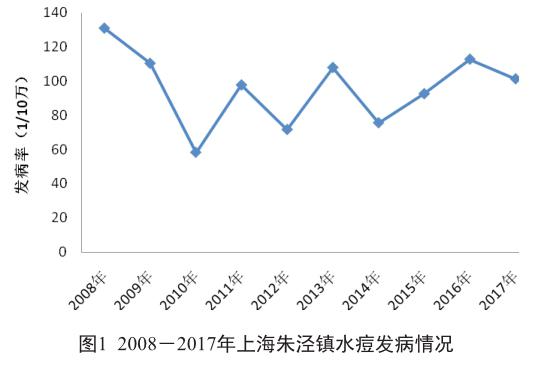
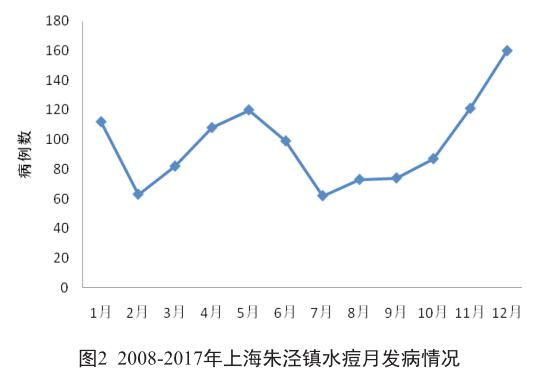
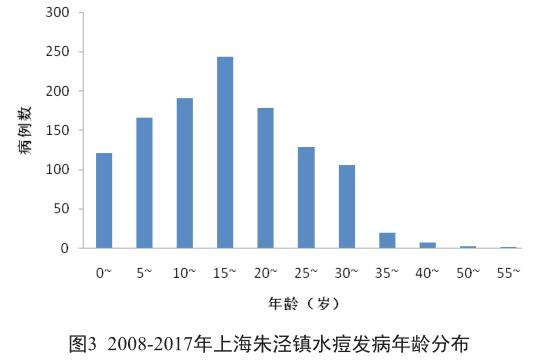
摘 要 目的:分析上海金山區朱泾镇2008-2017年水痘流行特征,为社区水痘防控工作提供科学依据。方法:通过中国疾病预防控制信息系统收集2008-2017年上海金山区朱泾镇水痘发病情况,采用描述性流行病学方法进行统计分析。结果:2008-2017年上海金山区朱泾镇共报告水痘病例1 161例,年平均发病率95.86/10万;男性发病563例,女性发病598例,男女发病性别比为0.94∶1;发病高发年龄段为25岁以下人群,占发病总数的88.46%(1 027/1 161);职业主要为学生,其次为托幼儿童和工人,分别占发病总数的48.58%(564/1 161)、9.91%(115 /1 161)和9.73%(113/1 161);发病呈现2个明显高发时间段,主发病高峰为11月至次年1月,占发病总数的33.85%(393/1 161),其次为4至6月,占发病总数的28.17%(327/1 161);本地居民发病率(108.85/10万)显著高于外来流动人员(61.44/10万),差异有统计学意义(χ2=56.57,P<0.05)。结论:2008-2017年上海金山区朱泾镇水痘发病率总体水平较高。需根据水痘发病的周期性和聚集性特征,加强针对重点人群和重点单位的宣传力度,落实水痘疫苗的查漏补种工作,从而降低水痘发病。
关键词 水痘;流行病学;特征分析
中图分类号:R511.5 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1006-1533(2018)24-0053-03
Analysis of epidemiological characteristics of varicella in Zhujing Town of Shanghai in 2008-2017
LI Jun, WANG Sheng, MA Yafei(Prevention and Health Care Department of Zhujing Community Health Service Center of Jinshan District, Shanghai 201599, China)
ABSTRACT Objective: To analyze the epidemiological characteristics of varicella in Zhujing Town, Jinshan District, Shanghai in 2008 - 2017 for providing scientific basis for the prevention and control of varicella in the community. Methods: The incidence of varicella in Zhujing Town, Jinshan District, Shanghai, in 2008 - 2017 was collected through the China Disease Prevention and Control Information System and descriptive epidemiology was used for statistical analysis. Results: In 2008 - 2017, a total of 1 161 cases of varicella were reported in Zhujing Town, Jinshan District, Shanghai, and the annual average incidence rate was 95.86/100,000; there were 563 male cases and 598 female cases, and the sex ratio of male to female was 0.94: 1; the highest incidence age group was below 25 years old, accounting for 88.46%(1 027/1 161) of the total number of cases; the occupations were mainly students, followed by nursery children and workers, accounting for 48.58%(564/1 161), 9.91%(115/1 161) and 9.73%(113/1 161) of the total number of cases, respectively; the incidence showed 2 periods of high incidence, the main incidence peaked from November to January, accounting for 33.85%(393/1 161) of the total number of cases, the second peak was from April to June, accounting for 28.17%(327 /1 161); the incidence of local residents(108.85/100,000) was significantly higher than that of migrant people(61.44/100,000), and the difference was statistically significant(c2=56.57, P<0.05). Conclusion: In 2008-2017, the overall incidence of varicella in Zhujing Town of Jinshan District, Shanghai was relatively high. According to the periodicity and aggregation characteristics of varicella, it is necessary to strengthen the propaganda of key populations and key units, and implement the investigation and re-inoculation of varicella vaccine to reduce the incidence of varicella.
