腹腔镜完全腹膜外疝无张力修补术对成人腹股沟疝的治疗效果研究
2018-01-06周志刚杨兵
周志刚,杨兵
(1.陆军军医大学西南医院门诊部,重庆 400038;2.重庆市长寿区中医院外科,重庆 401220)
腹腔镜完全腹膜外疝无张力修补术对成人腹股沟疝的治疗效果研究
周志刚1,杨兵2
(1.陆军军医大学西南医院门诊部,重庆 400038;2.重庆市长寿区中医院外科,重庆 401220)
目的分析腹腔镜完全腹膜外疝无张力修补术对成人腹股沟疝的临床疗效。方法125例手术治疗的腹股沟疝患者分为观察组(TEP,n=65)及对照组(开放疝无张力疝修补术,n=60)。比较两组手术时间、术后住院日、术后疼痛及术后1年复发率,并对比两组患者手术前后外周血炎症因子水平(CRP、IL-6及IL-10)变化情况。结果术后24 h,两组患者外周血CRP及IL-6水平均高于术前水平(P<0.05),但观察组低于对照组(P<0.05);观察组患者术后住院时间及术后24 h的VAS评分均低于对照组患者(P<0.05);两组患者手术时间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);两组患者术后1年疝累积复发率比较差异无统计学意义(3.08%vs. 5.00%;Log-rankχ2=0.282,P=0.595)。结论TEP对成人腹股沟疝的治疗效果理想。
腹股沟疝;腹腔镜完全腹膜外疝无张力修补术;炎症;术后复发
腹股沟疝是普通外科最为常见的良性疾病之一,腹股沟疝无张力修补术是目前腹股沟疝的最常用手术治疗方式[1]。疝的临床治疗得益于补片材料的长足进步,这使得传统的高位疝囊结扎手术基本废弃。随着微创外科的发展以及腹腔镜技术的不断普及,在腹股沟疝治疗领域不断涌现出新的手术方式和技巧[2]。腹腔镜全腹膜外无张力疝修补术(totally extraperitoneal prosthetics,TEP)是近年来不断发展和应用于临床的新术式[3]。与传统的开放式疝无张力修补术相比,TEP具有创伤更小、术后恢复更快等优势[4]。本研究尝试分析TEP对成人腹股沟疝的治疗效果,并与传统的开放手术进行对比,以期为此类疾病的诊疗提供参考。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
分析2014年1月至2017年1月在重庆西南医院接受手术治疗的125例腹股沟疝患者的临床资料。依据患者采用的手术方式不同分为观察组(TEP,n=65)及对照组(开放疝无张力疝修补术,n=60)。两组患者一般资料比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表1。所有患者均经临床及影像学检查明确诊断为腹股沟疝,并排除以下情况的患者:合并疝内容物嵌顿、绞窄等血运障碍;合并严重凝血功能障碍;合并活动性感染;合并严重肝肾功能障碍;合并自身免疫性疾病。
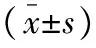
表1 两组患者一般资料比较
1.2 治疗及评估
两组患者均接受同一组医师所施行的手术治疗,观察组患者采用TEP[5]:全麻后取平卧位,常规消毒铺巾,选着脐孔作一10 mm切口置入腹腔镜,脐平面下病变对侧作2个5 mm腹直肌外侧缘腹膜外操作孔;剥离疝囊直至腹膜盆壁化,分离腹膜前间隙,暴露生殖血管,将聚丙烯补片裁剪至合适大小后覆盖在耻骨结节、联合肌腱、Cooper’s韧带及腹直肌背侧上。开放式疝无张力修补术在腰麻下完成[6]。分别于术前及术后24 h抽取患者外周血5 mL,检测如下指标:C-反应蛋白(C-reactive protein,CRP)、白介素-6(Interleukin-6,IL-6)及IL-10。记录手术时间、术后住院时间,并于术后24 h采用视觉模拟评分法(visnal analogue scale,VAS)评估两组患者疼痛情况。对每位患者进行为期1年的随访,记录术后1年累积复发率。
1.3 观察指标
比较两组患者手术前后外周血炎症指标的改变;比较两组患者手术时间、术后住院时间及术后疼痛情况;对比两组患者术后1年疝复发率。
1.4 统计学分析
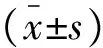
2 结果
2.1 两组患者手术前后外周血炎症指标的改变比较
两组患者术前各项指标比较均差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。术后24 h,两组患者外周血CRP及IL-6水平均高于术前水平,且观察组低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组患者手术前后外周血IL-10水平未见显著差异(P>0.05)。见表2。
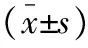
表2 两组患者手术前后外周血炎症指标的改变比较
*P<0.05,与组内术前比较;#P<0.05,与对照组比较。
2.2 组患者手术时间、术后住院时间及术后疼痛情况比较
观察组患者术后住院时间及术后24 h的VAS评分均低于对照组患者(P<0.01)。两组患者手术时间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表3。
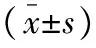
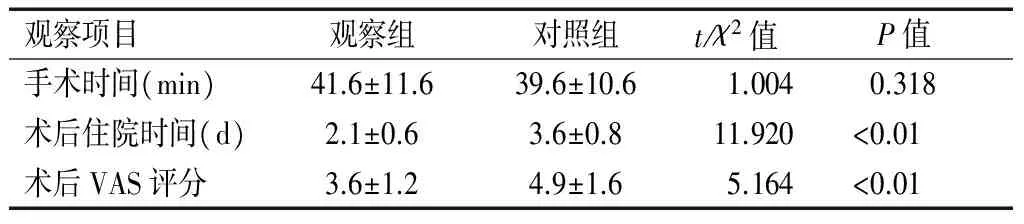
观察项目观察组对照组t/χ2值P值手术时间(min)41.6±11.639.6±10.61.0040.318术后住院时间(d)2.1±0.63.6±0.811.920<0.01术后VAS评分3.6±1.24.9±1.65.164<0.01
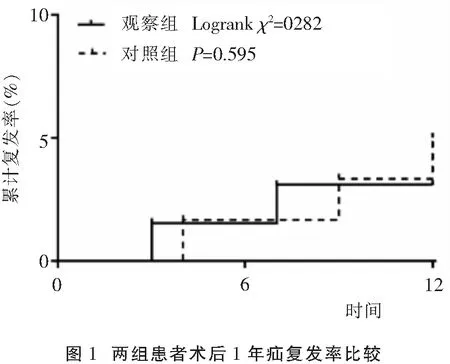
2.3 两组患者术后1年疝复发率比较
观察组患者术后有2例出现复发,对照组患者有3例。两组患者术后1年疝累积复发率比较差异无统计学意义(3.08%vs. 5.00%;Log-rankχ2=0.282,P=0.595)。见图1。
3 讨论
腹股沟疝是临床常见病、多发病,此病约占腹外疝的90%以上。医学界对腹股沟疝的治疗经历过漫长的发展,最早的有张力腹股沟疝修补手术曾经使用了约100年。但这种治疗方法存在复发率高、术后恢复时间长等缺点。近年来,腔镜技术在世界范围内迅速崛起,尤其是在中国的发展和普及的速度十分迅速。随着腔镜技术和设备的不断普及,越来越多的医院具备了腔镜手术的条件。而腹腔镜下疝无张力修补术开始逐步应用于临床,从最早的经腹膜修补逐步发展至TEP[7-8]。本研究以成人腹股沟疝患者为研究对象,以开放疝无张力修补术为对照,从术后恢复、术后炎症反应及术后复发等多个角度评估TEP的临床疗效。
研究结果显示,术后24 h,两组患者外周血CRP及IL-6水平均高于术前水平,但观察组低于对照组。CRP是一种非特异性急性期反应蛋白,是临床上用于评估应激水平及炎症反应程度的常用指标[9-10]。IL-6是一种促炎介质,其在感染、组织损伤等过程中表达升高,主要由单核巨噬细胞系统所分泌,是评估炎症及损伤的敏感指标[11-12]。事实上,无论何种等级的手术对患者来说均是一种医源性创伤,结果显示腔镜下的手术治疗显著降低了这种手术对患者造成的损伤,肯定了微创治疗的优势[13-14]。同时,结果数据显示观察组患者术后住院时间及术后24 h的VAS评分均低于对照组患者。腔镜下疝无张力修补术只需建立1个观察通道及2个操作通道,仅需做10 mm皮肤切口1个、5 mm皮肤切口2个,这应当是患者术后24 h疼痛程度较对照组轻的主要原因之一[15-16]。此外,由于患者无腹壁长切口,其术后恢复更为迅速。本研究未发现两组患者手术时间及术后1年疝累积复发率有显著差异,提示两组患者的操作耗时及远期疗效相当。手术主刀应当选择经验丰富的外科医师,主刀对局部解剖结构及腔镜的操作熟练程度直接影响手术时间和手术副损伤,而降低手术创伤是微创手术的主要目的。手术应当对适用患者做一定甄别,对于肥胖的患者来说,腔镜下建立腹膜外气腹较为困难;此外,对于合并有嵌顿及绞窄的患者也不应选择腔镜手术。
综上,TEP对成人腹股沟疝的治疗效果可靠。
[1] Shehata SM,Ei AAA,Attia MA,etal.Laparoscopic herniotomy in children:prospective assessment of tertiary center experience in a developing country[J].Hernia,2013,17(2):229-234.
[2] Li B,Zhang JY,Wang YB,etal.Laparoscope-assisted diagnosis and treatment for Amyand’s hernia in children-report of six cases[J].Pediatr Surg Int,2013,29(5):525-528.
[3] Carvalho GL,Loureiro MP,Bonin EA,etal.Minilaparoscopic technique for inguinal hernia repair combining transabdominal pre-peritoneal and totally extraperitoneal approaches[J].JSLS,2012,16(4):569-575.
[4] Caron JP.Incisional hernia repair in horses:a cadaveric study of endoscopic component separation[J].Vet Surg,2014,43(1):1-5.
[5] Zhou X,Qi X,Jiang B,etal.Transumbilical endoscopic technique for complete closure of inguinal hernias in female pediatric patients[J].Exp Ther Med,2017,13(1):41-44.
[6] 刘子文,孙蒙清,张立阳,等.开放式腹膜前间隙修补术与Lichtenstein无张力修补术治疗腹股沟疝的比较研究[J].中华外科杂志,2014,52(9):682-685.
[7] Li S,Liu L,Li M.Single-port laparoscopic percutaneous extraperitoneal closure using an innovative apparatus for pediatric inguinal hernia[J].J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A,2014, 24(3):188-193.
[8] Yilmaz E,Afsarlar CE,Senel E,etal.A novel technique for laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair in children:single-port laparoscopic percutaneous extraperitoneal closure assisted by an optical forceps[J].Pediatr Surg Int,2015,31(7):639-646.
[9] Fan S,Zhong JL,Chen WX,etal.Postoperative immune response and surgical stress in selective neck dissection:Comparison between endoscopically assisted dissection and open techniques in cT1-2N0 oral squamous cell carcinoma[J].J Craniomaxillofac Surg,2017,45(8):1112-1116.
[10] Janik S,Bekos C,Hacker P,etal.Elevated CRP levels predict poor outcome and tumor recurrence in patients with thymic epithelial tumors:A pro- and retrospective analysis[J].Oncotarget,2017,8(29):47090-47102.
[11] Sternby H,Hartman H,Johansen D,etal.IL-6 and CRP are superior in early differentiation between mild and non-mild acute pancreatitis[J].Pancreatology,2017,17(4):550-554.
[12] Kumar A,Torres ML,Cliby WA,etal.Inflammatory and Nutritional Serum Markers as Predictors of Peri-operative Morbidity and Survival in Ovarian Cancer[J].Anticancer Res,2017,37(7):3673-3677.
[13] Ordorica-Flores R,Figueroa-Portillo R,Pérez-Escamirosa F,etal.Pediatric inguinal hernia repair with a single-incision approach using an Endo Close suturing device[J].Surg Endosc,2016,30(11):5134-5135.
[14] Wang F,Zhong H,Chen Y,etal.Single-site laparoscopic percutaneous extraperitoneal closure of the internal ring using an epidural and spinal needle:excellent results in 1464 children with inguinal hernia/hydrocele[J].Surg Endosc,2017,31(7):2932-2938.
[15] Obata S,Ieiri S,Jimbo T,etal.Feasibility of Single-Incision Laparoscopic Percutaneous Extraperitoneal Closure for Inguinal Hernia by Inexperienced Pediatric Surgeons:Single-Incision Versus Multi-Incision Randomized Trial for 2 Years[J].J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A,2016,26(3):218-221.
[16] Murase N,Uchida H,Seki T,etal.A feasibility of single-incision laparoscopic percutaneous extraperitoneal closure for treatment of incarcerated inguinal hernia in children:our preliminary outcome and review of the literature[J].Nagoya J Med Sci,2016,78(1):19-25.
Studyontheclinicaleffectoftotallyextraperitonealprostheticsinthetreatmentofinguinalhernia
ZHOU Zhi-gang1,YANG Bing2
(1.DepartmentofOvtpatient,SouthwestHospitalofChongqing,Chongqing400038;2.DepartmentofSurqery,ChangshouDistrictHosptialofTraditonalChineseMedicine,Chongqing412200,China)
Objective:To analyze the clinical effect of totally extraperitoneal prosthetics(TEP) in the treatment of inguinal hernia.Methods125 cases of patients with inguinal hernia were divided into the observation group (TEP,n=65) and the control group (open tension free hernia repair,n=60).The operation time,postoperative hospital stay,postoperative pain and recurrence rate after 1 year in the two groups were compared,and the changes of peripheral inflammatory cytokines (CRP,IL-6 and IL-10) in the patients of the two groups were compared.Results24 hours after surgery,the levels of CRP and IL-6 in the peripheral blood of the two groups were higher than those of the preoperative level (P<0.05),but the levels in the observation were lower than those in the control group (P<0.05).The postoperative hospitalization time and the VAS score of 24 h after operation in the observation group were lower than those in the control group (P<0.05).There was no significant difference in the operation time between the two groups (P>0.05).There was no significant difference in the cumulative recurrence rate between the two groups after 1 year of operation (3.08%vs. 5.00%,Log-rankχ2=0.282,P=0.595).ConclusionTEP show an ideal clinical effect in treatment of inguinal hernia.
Inguinal hernia;Totally extraperitoneal prosthetics(TEP); Inflammation;Post-operation recurrence
10.3969/j.issn.1005-3697.2017.06.031
2017-06-29
周志刚(1979-),男,主治医生。E-mail:37931482@qq.com
时间: 2017-12-27 16∶44网络出版地址http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1254.R.20171227.1643.062.html
1005-3697(2017)06-0915-03
R656.2
A
(学术编辑:全信保)
