基于注意力机制的双向LSTM模型在中文商品评论情感分类中的研究
2018-01-05成璐
成璐
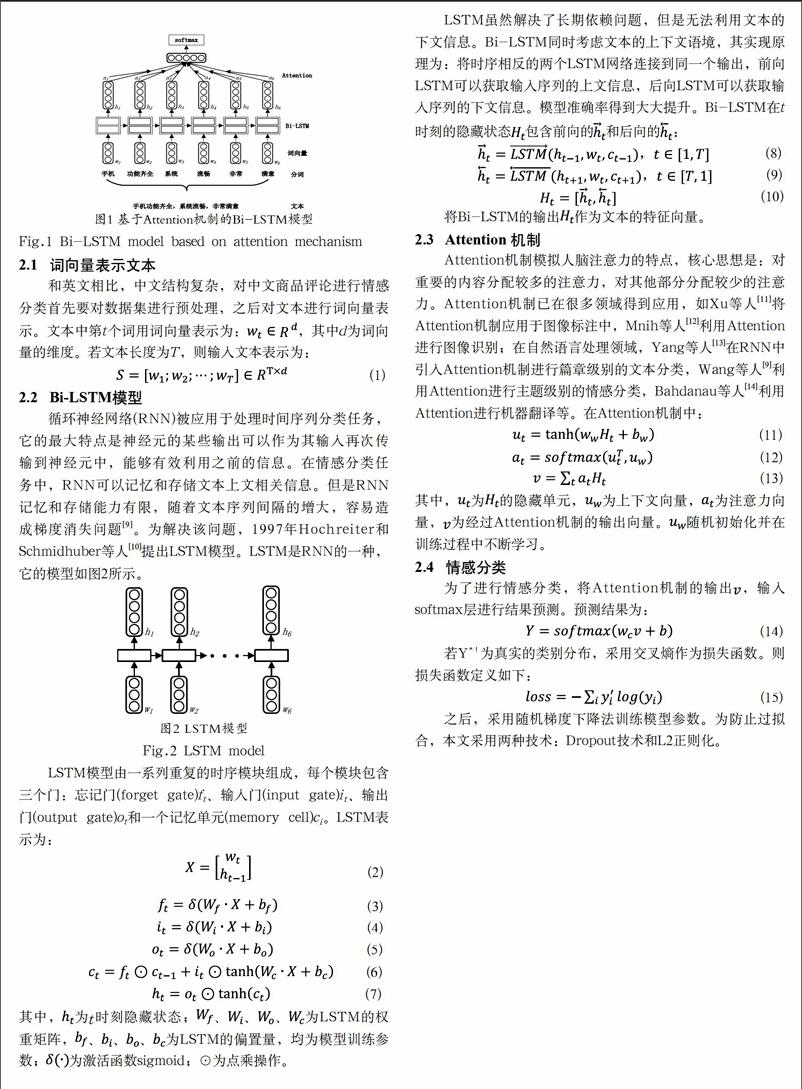
摘 要:国内电商网站的快速发展促使产生大量的中文商品评论信息。对这些评论进行情感分类有利于获取其中的有用信息,具有重要的应用意义。目前,情感分类的研究主要基于情感词典或者传统机器学习。这些方法通常需要人工选取特征,费事费力,分类效果不好。针对这些不足,本文提出一种基于注意力机制的双向LSTM模型,对中文商品评论进行情感分类。实验结果表明,该模型在中文商品评论二分类任务和三分类任务中均获得了较好的准确率、召回率、F1值。
关键词:中文商品评论;情感分类;注意力机制;双向LSTM
中图分类号:TP391 文献标识码:A
Abstract:With the rapid development of domestic E-commerce websites,there are lots of Chinese product reviews.The sentiment classification of Chinese product reviews is helpful to obtain useful information,with great application significance.Currently,most sentiment classification studies are based on the sentiment dictionary or traditional machine learning methods.These methods usually need artificial selection of features,with low classification efficiency and effectiveness.In view of all these deficiencies,the paper proposes an attention mechanism-based bidirectional LSTM model for the sentiment classification of Chinese product reviews.The experimental results show that the proposed model has better precision rate,recall rate and F1 score in binary classification tasks and three classification tasks in Chinese product reviews.
Keywords:Chinese product reviews;sentiment classification;attention mechanism;bidirectional LSTM
1 引言(Introduction)
随着国内电商网站的迅猛发展,越来越多的人选择网上购物,随之产生大量的中文商品评论信息。对这些信息进行情感分类,不仅可以挖掘用户对商品的喜好程度,给潜在用户提供购买建议,同时有利于商家及时改善产品及服务,从而提高商业价值。因此,对中文商品评论进行情感分类变得非常必要。
传统的情感分类研究方法主要有两种:(1)基于情感词典的方法;(2)基于传统机器学习的方法[1]。前者需要人工创建情感词典,费事费力。后者通常采用朴素贝叶斯(NB)、最大熵(ME)、支持向量机(SVM)等进行分类,这些方法容易丢失文本语法语义信息,很难有效捕获文本中的情感。
随着深度神经网络在自然语言处理领域的应用,2003年Bengio等人[2]通过神经网络训练词向量来表示文本。词向量不仅可以有效获取语义信息[3],同时避免了数据稀疏性问题。利用词向量表示文本,并采用深度学习模型,如递归神经网络[4,5]、卷积神经网络(CNN)[6,7]、循环神经网络(RNN)[8]等,进行情感分类可以获得比传统机器学习方法更优的效果。
考虑到在对商品评论进行情感分类时,文本对上下文有较强的依赖性,而标准的神经网络模型不能很好地解决该问题,本文采用双向的长短时记忆神经网络(Bidirectional Long Sort Term Memory,Bi-LSTM)进行情感分类。另外,考虑到不同的词对文本的贡献不相同,引入Attention机制。基于此,本文提出了一种基于Attention机制的Bi-LSTM模型对中文商品评论进行情感分类。为了验证模型的有效性,本文采用某电商网站的手机评论数据集对模型进行实验。实验结果表明,该模型取得了较好的效果。
2 基于Attention机制的Bi-LSTM模型(Bi-LSTM
model based on attention mechanism)
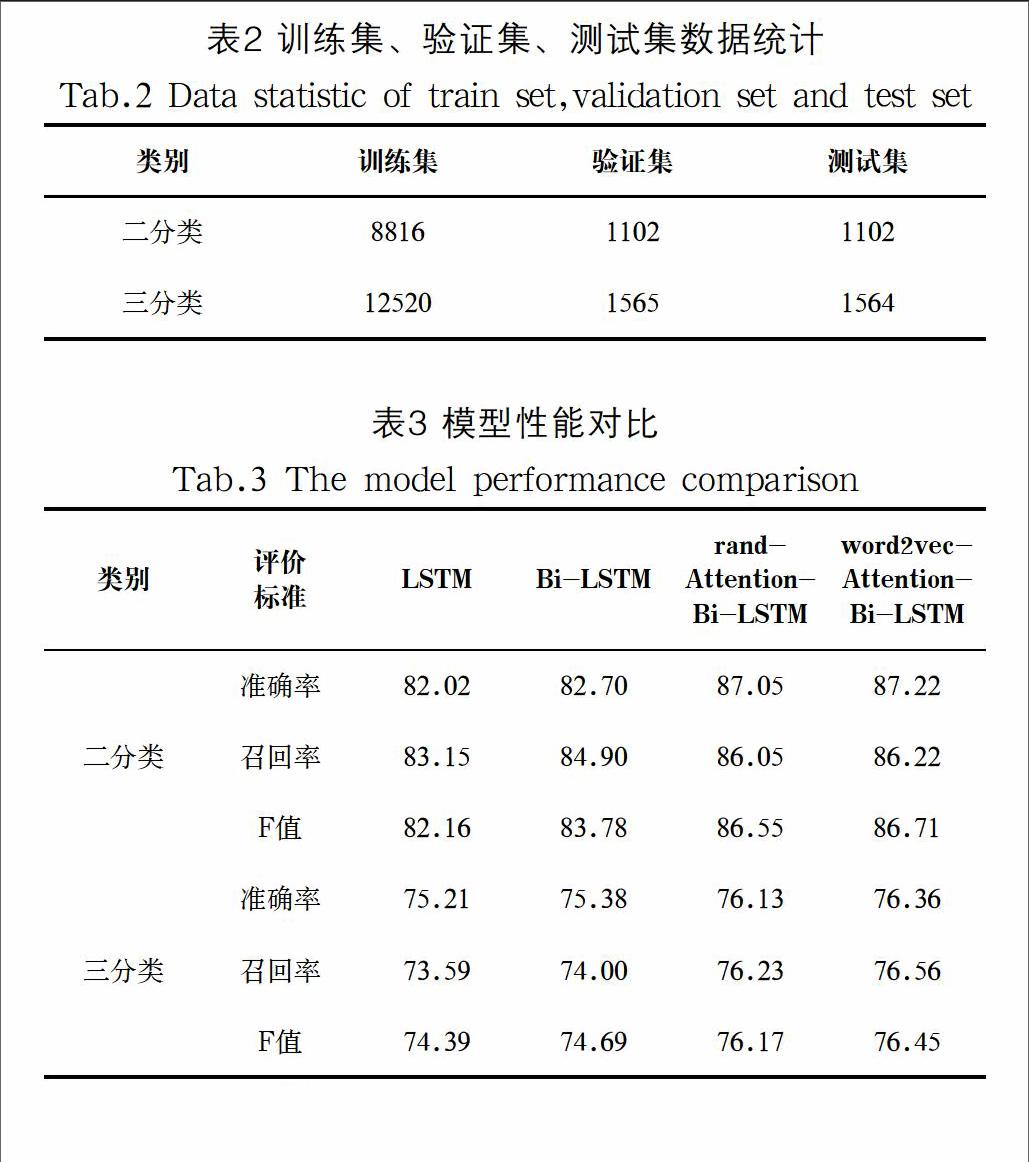
基于Attention机制的Bi-LSTM模型如图1所示。该模型主要由四部分组成:
(1)采用词向量表示文本;
(2)利用Bi-LSTM模型获取文本特征;
(3)引入Attention机制表示不同特征的重要性;
(4)最后利用分类器进行情感分类。
3 实验(Experiment)
3.1 数据集
为了验证模型,采取某电商网站的手机评论作为数据集。该数据集共15649篇评论,根据评论星级划分为:好评(4星、5星)4373篇评论,中评(3星)4629篇评论,差评(1星、2星)6647篇评论。数据集样例见表1。
本文选取好评、差评进行二分类;选择好评、中评、差评进行三分类。所有的分类任務重,按照80%、10%、10%的比例将数据集随机分为训练集、验证集、测试集,见表2。endprint
3.2 數据预处理
本文采用jieba分词工具对评论文本进行分词并去除分词列表中的停用词和标点符号。处理之后文本最大长度为281。为了构建特征向量,词向量的维度为100,采用两种方式初始化词向量:
(1)随机初始化:所有的词均随机初始化,并在训练过程中词向量动态更新。
(2)使用word2vec工具:使用2013年Google提出的开源工具word2vec训练词向量,同时对于未出现的词随机初始化,训练过程中词向量动态更新。
3.3 实验参数设置
为了训练一个较优的模型,模型参数的设置非常关键。模型中主要参数设置为:学习率为0.01,批处理文件数为50,Bi-LSTM中隐藏单元数为200,Dropout值为0.75,L2正则化参数为0.0001。
3.4 实验结果及分析
为了验证模型的有效性,将本文提出的模型rand-Attention-Bi-LSTM、word2vec-Attention-Bi-LSTM与LSTM、Bi-LSTM进行比较。模型评价指标为准确率、召回率、F值。实验结果见表3。
通过表3可以看出:
(1)Bi-LSTM和LSTM相比,准确率、召回率、F值均有所提升,这是因为Bi-LSTM同时考虑文本的上下文,说明Bi-LSTM的分类效果优于LSTM。
(2)由于引入Attention机制,本文的模型准确率、召回率、F值均高于LSTM和Bi-LSTM,说明Attention机制能够较好地反映文本中词的重要性。
(3)通过word2vec-Attention-Bi-LSTM和rand-Attention-Bi-LSTM对比发现,采用word2vec初始化词向量更有效,有利于提高情感分类精度。
4 结论(Conclusion)
本文提出了一种基于Attention机制的Bi-LSTM模型对中文商品评论进行情感分类。将商品评论用词向量表示,通过Bi-LSTM获取文本的上下文关系,同时引入Attention机制表示不同特征的重要性,并进一步优化模型。最后,运用该模型在某电商网站的手机评论集上进行情感分类,实验结果验证了该模型的可行性和有效性。
由于中文商品评论中包含对商品多个属性的评价,下一步工作将寻找更优的深度学习模型,对商品评论中的不同属性进行情感倾向性研究。
参考文献(References)
[1] 杜昌顺,黄磊.分段卷积神经网络在文本情感分析中的应用[J].计算机工程与科学,2017,39(01):173-179.
[2] Yoshua Bengio,Holger Schwenk,Jean-Sébastien Senécal,et al.A Neural Probabilistic Language Model[J].Journal of Machine Learning Research,2003,3:1137-1155.
[3] Mikolov Tomas,Yih Wen-tau,Zweig Geoffrey.Linguistic regularities in continuous space word representations[C].The Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics(NAACL-HLT), 2013:746-751.
[4] Richard Socher,Brody Huval,Christopher D.Manning,et al.Semantic compositionality through recursive matrix vector spaces[C].Proceedings of the 2012 Joint Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning(EMNLP-CoNLL),2012:1201-1211.
[5] Richard Socher,Alex Perelygin,Jean Wu,et al.Recursive deep models for semantic compositionality over a sentiment Treebank[C].Proceedings of 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing(EMNLP),2013:1631-1642.
[6] Yoon Kim.Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification[C].Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing(EMNLP),2014:1746-1751.
[7] Nal Kalchbrenner,Edward Grefenstette,Phil Blunsom.A convolutional neural network for modelling sentences[C].Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics(ACL),2014:655-665.endprint
[8] Siwei Lai,Liheng Xu,Kang Liu,et al.Recurrent convolutional neural networks for text classification[C].Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence,2015:2267-2273.
[9] Yequan Wang,Minlie Huang,Xiaoyan Zhu,et al.Attention-based LSTM for Aspect-level Sentiment Classification[J].Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing(EMNL),2016:606-615.
[10] Sepp Hochreiter,Jürgen Schmidhuber.Long short-term memory[J].Neural computation,1997,9(8):1735-1780.
[11] Kelvin Xu,Jimmy Ba,Ryan Kiros,et al.Show,attend and tell:Neural image caption generation with visual attention[C].Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning(ICML),2015:2048-2057.
[12] Volodymyr Mnih,Nicolas Heess,Alex Graves,et al.Recurrent models of visual attention[C].Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27(NIPS),2014:2204-2212.
[13] Zichao Yang,Diyi Yang,Chris Dyer,et al.Hierarchical Attention Networks for Document Classification[C].Proceedings of Human Language Technologies.The Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics(NAACL-HLT),2016:1480-489.
[14] Dzmitry Bahdanau,Kyunghyun Cho,Yoshua Bengio.Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate[C].International Conference on Learning Representations(ICLR),2015.
作者簡介:
成 璐(1988-),女,硕士,助教.研究领域:人工智能,自然语言处理,无线传感网络.endprint
