沈阳市高校离退休老年人抑郁现状及其与身体活动关系分析
2017-12-29宁静刘蕾
宁静,刘蕾
(1.山东省武城县人民医院护理部,山东 德州 253300;2.沈阳医学院护理学院)
沈阳市高校离退休老年人抑郁现状及其与身体活动关系分析
宁静1,刘蕾2*
(1.山东省武城县人民医院护理部,山东 德州 253300;2.沈阳医学院护理学院)
目的:分析沈阳市高校离退休老年人的抑郁现状,并分析其抑郁程度与身体活动的相关性。方法:对沈阳市两所高校的离退休老年人132名采用横断面调查的方法,使用社会学资料调查表、老年人抑郁量表和老年人身体活动量表来收集高校离退休老年人的人口社会学资料,抑郁程度和身体活动的数据。结果:132名高校离退休老年人的抑郁得分为6.69±5.14,抑郁的发生率为20.46%。收入越高,抑郁得分越低(P<0.05),不同年龄、性别、受教育程度、婚姻状况、工作状况、职称之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。离退休老年人的身体活动水平与抑郁程度呈负相关(P<0.05)。结论:高校离退休老年人身体活动和经济收入是抑郁的保护因素,因此,我们在今后应基于提高离退休老年人的身体活动和社会保障的基础上制定干预措施,减少其抑郁的发生。
高校;离退休老年人;抑郁;身体活动;相关性
全球已逐渐进入老龄化社会,老年人口迅速增多,其身心健康已引起社会关注。抑郁是老年人群中普遍存在的一种心理问题,与身体疾病共存,可引起生活质量降低和失能[1-2],国外有研究显示,大约15%老年人都会伴有抑郁症状[3]。国内有研究指出,85%的中国老年人存在不同程度的心理问题,其中27%有明显的抑郁症[4]。
高校教师离退休以后,社会联系减少、社会地位改变、生活内容和方式改变,加上老年人自然发生的生理功能衰退,使得他们产生无用或被遗落感,易产生抑郁的情绪[5-7]。抑郁症使得老年人丧失生活的乐趣,影响他们的记忆力和注意力。还能引起疼痛,严重者会自杀[8]。国外有研究证明,规律的身体活动能减少抑郁症的发生[9-10],本研究以实证调查的方式来探究沈阳市高校离退休老年人的抑郁现状,身体活动与抑郁之间的关系,以期为高校离退休老年人的心理健康干预提供参考和依据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象 本研究采用便利抽样的方法,以沈阳市2所高校的离退休老年人132名为样本,年龄≥60岁,其中女65例,男67例;大专及以下文化程度88例,本科及以上44例;配偶健在112例;丧偶20例;未从事任何工作123例,仍从事工作9例;初级职称32例,中级47例,高级53例,收入3 000元以下30例,3 000元以上102例。
1.2 入选和排除标准 入选标准:正规本科院校的离退休老年人;具备读写能力;无认知障碍;自愿参与调查。排除标准:疾病晚期。
1.3 调查工具
1.3.1 离退休老年人一般资料 一般资料调查表由研究者自行设计。主要包括老年人的性别、年龄、婚姻状况、文化程度、经济收入等。
1.3.2 老年人抑郁量表(Geriatric Depression Scale-30,GDS-30) GDS-30是由Brink研制的,包括30个条目,答案选项为“是”或“否”,每题1分,满分为30分,其中1、5、7、9、15、19、21、27、29、30反序计分,其余20条正序计分,0~10分为正常,11~20分轻度抑郁,21~30分中重度抑郁。该量表克朗巴赫α系数为0.94,重测信度为0.85[11-12]。
1.3.3 老年人身体活动问卷(Physical Activity Scale for Elderly,PASE) PASE 由 Washburn 等[13]于1993年研发,包含12个条目,分数范围0~360,克朗巴赫α系数为0.69,重测信度为0.75。于洪军等[14]将该问卷引入中国,在中国老年人群中进行信效度检验,重测信度为0.897,Armband能量代谢测试仪与PASE量表测试结果之间的相关系数为0.442。
1.4 研究过程 调查员进行统一培训,在同一地点发放问卷,20 min收回,提供笔和老花镜,问卷由被研究者自行填写,对于书写困难者可帮助记录。对于老年人的疑惑耐心解释。最后发放问卷150份,回收146份,有效问卷132份。
1.5 统计学方法 数据录入EpiData3.1软件进行管理,使用SPSS进行分析,计量资料使用均数±标准差、百分位数、中位数来表示,计数资料使用频数、百分比来表示,统计显著性水平α=0.05。
2 结果
2.1 离退休老年人抑郁得分情况 132名离退休老年人的抑郁得分为6.69±5.14,无抑郁者105人,轻度抑郁23人,重度抑郁4人,抑郁的发生率20.46%。
2.2 不同人口学特征的离退休老年人抑郁状况分析及比较 沈阳市离退休老人收入越高,抑郁得分越低(P<0.05)。而不同年龄、性别、受教育程度、婚姻状况、工作状况、职称之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表1。
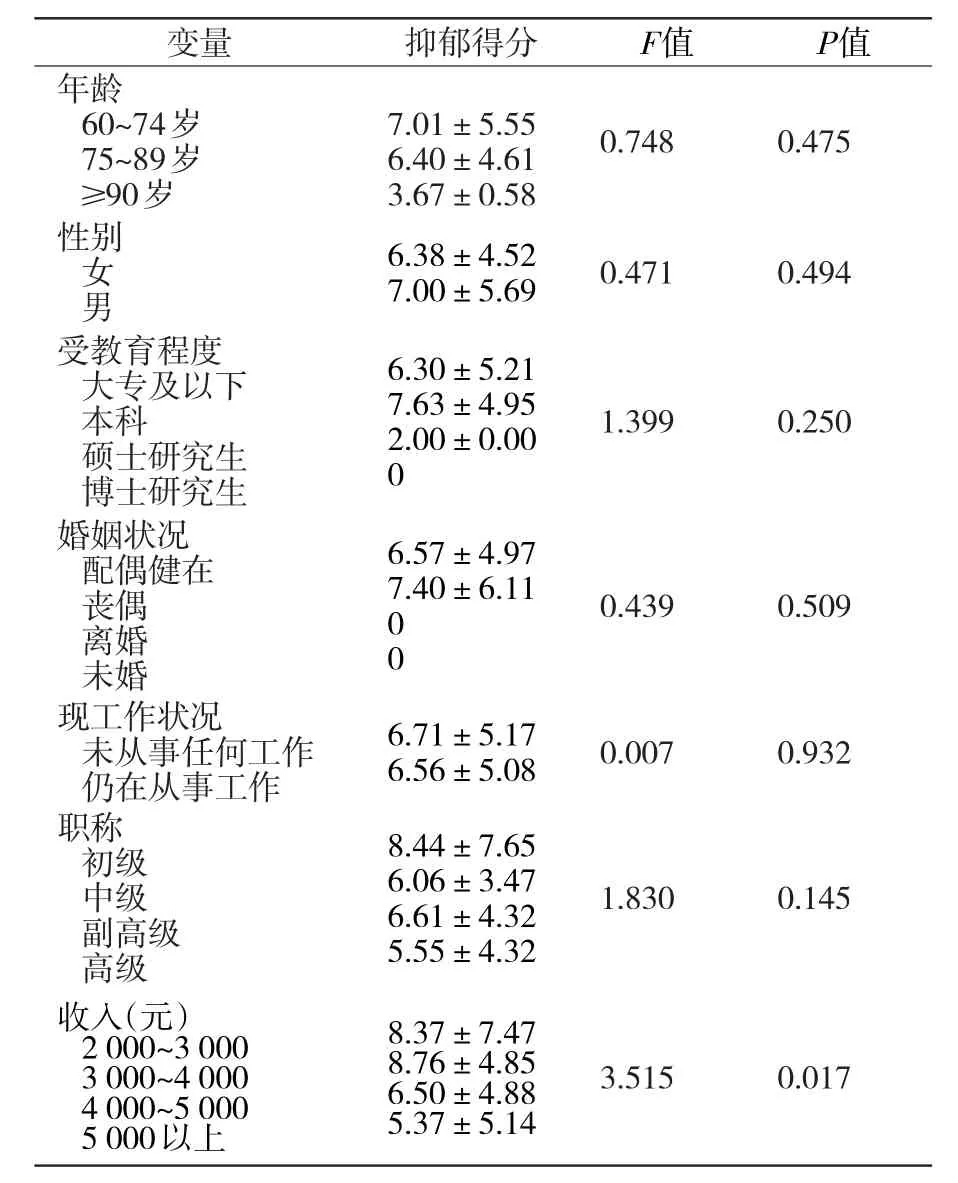
表1 不同人口学特征的离退休老年人的抑郁状况分析与比较
2.3 离退休老年人身体活动与抑郁评分的相关性分析 沈阳市离退休老年人的身体活动水平与抑郁程度呈负相关(P<0.05),见表2。
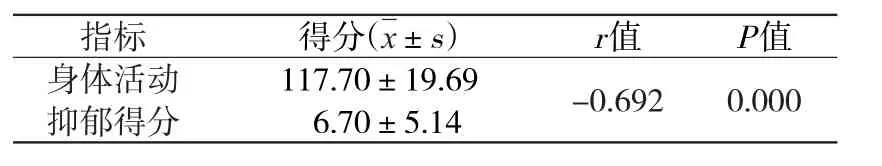
表2 离退休老年人身体活动水平与抑郁评分的Pearson分析
3 讨论
抑郁已成为世界普遍存在的精神疾病以及增加疾病负担的主要因素[15]。一项研究结果显示[16-20],老年人抑郁的发生率为11%~25.35%,孟琛等[21]的研究结果显示,北京市老年人约有13.7%会有明确的抑郁症状。本研究中,沈阳市高校离退休老年人抑郁的发生率为20.46%低于赵新爽 等[22]报 道 的 32.31%,杨 本 付 等[24]报 道 的29.39%,杨雪莹等[23]报道的37.01%。高校离退休老年人经济收入有保障,生活条件相对较好,因此其抑郁情绪的发生率相比社区老年人低一些,但发生率还是偏高,应予以重视。
本研究结果显示,老年人收入越高,抑郁得分越低(P<0.05),经济水平高,能够保障老年人的衣食住行,减少因为经济为老人带来的担忧。不同年龄、性别、受教育程度、婚姻状况、工作状况、职称之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。沈阳市离退休老年人的身体活动水平与抑郁程度呈负相关的(P<0.05),即身体活动越多,抑郁程度越低,这与肖存利等[25]的研究结果一致。参加规律身体活动的人,大脑会分泌一种叫做“内啡肽“的物质,这种物质能够让人产生积极的情绪[26]。近年来身体活动在国际上越来越被重视,身体活动带来的身心益处也被大众意识到。因此,应该为老年人制定适当的锻炼计划,以促进其身心健康。
综上所述,经济水平和身体活动是沈阳市高校离退休老年人心理健康的保护因素,因此,在今后的干预措施中,应注重促进老年人的身体活动,不断完善社会保障体系,提高离退休老年人的心理健康水平。
[1] Knol MJ,Twisk JW,Beekman AT,Heine RJ,Snoek FJ,et al.Depression as a risk factor for the onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus.A meta-analysis[J].Diabetologia,2006,49:837-845.
[2] Wulsin LR,Singal BM.Do depressive symptoms increase the risk for the onset of coronary disease?a systematic quantitative review[J].Psychosomatic Medicine,2003,65:201-210.
[3] Covinsky KE,Yaffe K, Lindquist K, Cherkasova E, et al.Depressive symptoms in middle age and the development of laterlife functional limitations:the long-term effect of depressive symptoms[J].J Am Geriatr Soc,2010,58:551-556.
[4]闫玉美.老年人的社区护理服务需求及对策[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2011,19(3):486.
[5]明兴建,朱鹏,王琪琪.高校离退休老人心理健康与社会支持实证研究[J].重庆大学学报(社会科学版),2015,21(3):189-195.
[6] Cotten SR,Ford G,Ford S,et al.Internet Use and Depression Among Retired Older Adults in the United States:A Longitudinal Analysis[J].The Journals of Gerontology Series B:Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences,2014,69(5):763-771.
[7] Dickens AP, Richards SH, Greaves CJ.et al.Interventions targeting social isolation in older people: a systematic review[J].BMC Public Health, 2011,(11):1-22.
[8] Alexopoulos GS,Katz IR,Ross RW.Depression in older adults[J].Journal of Psychiatric Practice,2001,7(6):441-446.
[9] Nosrat S,Whitworth JW,SantaBarbara NJ,et al.Association between physical activity and depression:The exercise for persons who are immunocompromised (EPIC)study[J].Med Sci Sports Exerc,2016,48(5):610.
[10] Birch K,Ten Hope M, Malek-Ahmadi M,et al.Cognitive function as a mediator in the relationship between physical activity and depression status in older adults[J].J Aging Phys Act,2016,24(4):540-546.
[11] Yesavage JA, Brink TL, Rose TL, et al.Development and validation ofa geriatric depression screening scale: a preliminary report[J].J Psychiatr Res.1982,17(1):37-49.
[12]汪向东,王希林,马弘,等.心理卫生评定量表手册(增订版)[J].中国心理卫生杂志,1999,13(增刊):185-186.
[13] Washburn RA, Smith KW,Jette AM,et al.The Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly(PASE): development and evaluation[J].J Clin Epidemiol,1993,46(2):153-162.
[14]于洪军,仇军.运用PASE量表测量中国老年人体力活动的信效度验证[J].上海体育学院学报,2014,38(5):45-49.
[15] GA Wells BS,D O′Connell,J Peterson,et al The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS)for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses.Ottawa:Ottawa Health Research Institute.http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.htm.
[16]Mezuk B,Lohman M,Dumenci L,Lapane KL.Are depression and frailty overlapping syndromes in mid-and late-life?A latent variable analysis[J].Am J Geriatr Psychiatry,2013,21 (6):560-569.
[17]Sánchez-García S,Sánchez-Arenas R,García-Peña C,et al.Frailty among community-dwelling elderly Mexican people:prevalence and association with sociodemographic characteristics, health state and the use of health services[J].Geriatr Gerontol Int,2014,14(2):395-402.
[18] Pegorari MS,Tavares DM.Factors associated with the frailty syndrome in elderly individuals living in the urban area[J].Rev Lat Am Enfermagem,2014,22(5):874-882.
[19] Lohman M, Dumenci L, Mezuk B.Sex differences in the construct overlap of frailty and depression:evidence from the Health and Retirement Study[J].J Am Geriatr Soc,2014,62(3):500-505.
[20] Lohman M,Dumenci L,Mezuk B.Depression and frailty in late life:evidence for a common vulnerability[J].J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci,2016,71(4):630-640.
[21]孟琛,项曼君.北京老年人的抑郁状况调查及CES-D的结构分析[J].中国心理卫生杂志,1997,11(1):55-58.
[22]赵新爽.社区老年人抑郁状况调查及与社会支持的相关性研究[J].河南科技大学学报(医学版),2015,33(3):215-217.
[23]杨本付,刘东光,邵光方.济宁市老年抑郁情绪的现况及其影响因素的探讨[J].中国老年学杂志,1999,19(4):195-196.
[24]杨雪莹,李永成,王淑惠.等.天津市老年人抑郁调查及其影响因素分析[J].中国老年学杂志,2007,27(19):1921-1924.
[25]肖存利,陈博.北京市西城社区老年人焦虑与抑郁现况调查[J].中国全科医学,2014,17(26):3113-3116.
[26]高龙喜.抑郁倾向大学生感觉门控和认知电位特点与运动参与状况研究[D].济南:山东师范大学2015.
Depression Status of Retired Teachers in Colleges and Universities in Shenyang and the Correlation between Depression and Physical Activity
NING Jing1,LIU Lei2*
(1.Nursing Department,The People′s Hospital of Wucheng County,Wucheng 253300,China;2.Shenyang Medical College)
Objective:To explore the depression status of retired teachers in colleges and universities in Shenyang,and to analyze the correlation between depression and physical activity.Methods:A total of 132 retired teachers from two universities in Shenyang were sampled by using the method of cross-sectional survey.The data were collected by self-designed general information questionnaire,GDS-30 and PASE.The data of demographic sociology,depression and physical activity of retired teachers were collected.Results:The depression score of 132 retired teachers was 6.69±5.14,105 without depression,23 with mild depression and 4 with severe depression.The incidence rate of depression was 20.46%.The higher the income,the lower the score of depression(P<0.05).There was no difference among different age,gender,educational level,marital status,working condition and title(P> 0.05).The level of physical activity of retired teachers was negatively correlated with the degree of depression (P<0.05).Conclusion:Physical activity and economic income are the protective factors of depression.Therefore,we should improve the physical activity and social security of retired teachers in the future.On the basis of the development of interventions to reduce the incidence of depression.
colloge;retired teachers;depression;physical activity;correlation
R749.4
A
1008-2344(2017)04-0353-03
10.16753/j.cnki.1008-2344.2017.04.018
刘蕾(1980—),女(汉),讲师,在读博士研究生.研究方向:护理学教学.E-mail:liulei0428@sina.com
2017-04-26
(杨秀梅编辑)
