糖尿病患者血浆减少α-突触核蛋白的磷酸化和寡聚化
2017-12-19郑凇杨杨巍巍李旭冉李旭颖于文娇
郑凇杨 李 昕,3,4 杨巍巍,3,4 李旭冉 李旭颖 于文娇 于 顺,3,4*
(1.首都医科大学宣武医院神经生物学研究室,北京市老年病医疗研究中心,北京 100053;2.首都医科大学帕金森病临床诊疗与研究中心,北京 100053;3.帕金森病北京市重点实验室和教育部神经变性病重点实验室,北京 100053;4.国家老年疾病临床医学研究中心,北京 100053)
·Alpha-突触核蛋白的致病机制·
糖尿病患者血浆减少α-突触核蛋白的磷酸化和寡聚化
郑凇杨1,2李 昕1,2,3,4杨巍巍1,2,3,4李旭冉1,2李旭颖1,2于文娇1,2于 顺1,2,3,4*
(1.首都医科大学宣武医院神经生物学研究室,北京市老年病医疗研究中心,北京 100053;2.首都医科大学帕金森病临床诊疗与研究中心,北京 100053;3.帕金森病北京市重点实验室和教育部神经变性病重点实验室,北京 100053;4.国家老年疾病临床医学研究中心,北京 100053)
目的研究2型糖尿病(type 2 diabetes,T2D)患者血浆对α-突触核蛋白(α-synuclein,α-Syn)磷酸化和寡聚化聚集的影响。方法收集首都医科大学宣武医院内分泌科T2D住院患者70例,另收集年龄和性别与之匹配的健康志愿者70例作为对照组。采集抗凝血,并分离血浆。将基因重组人α-Syn在患者和对照志愿者血浆中振荡孵育,ELISA法检测各组人群血浆中寡聚化和磷酸化α-Syn形成量。结果T2D患者血浆中寡聚化和磷酸化α-Syn形成量较对照组均有显著降低(P<0.05),且其与年龄有相关性。结论T2D患者血浆以年龄依赖的方式减少寡聚化和磷酸化α-Syn的形成。
α-突触核蛋白;2型糖尿病;血浆;磷酸化;寡聚化
2型糖尿病(type 2 diabetes,T2D)是糖尿病的主要类型,占糖尿病患者的90%以上。胰岛素抵抗(insulin resistance,IR)通常指胰岛素介导的葡萄糖利用率降低,又称胰岛素敏感性下降。目前认为,IR在糖尿病发病机制中起重要作用,并伴随着糖尿病发生、发展的全过程。
α-突触核蛋白(α-synuclein,α-Syn)是一个由140个氨基酸构成的蛋白质,主要表达于神经元的突触前末梢。目前认为,异常聚集的α-Syn对神经元具有毒性作用,并在神经退行性疾病尤其是帕金森病(Parkinson’s disease,PD)中起关键作用[1-3]。已知α-Syn的聚集受磷酸化修饰的影响,且磷酸化修饰的α-Syn聚集体是PD标志性病理变化路易体(Lewy body,LB)的主要成分。有研究[4]显示,在上千例患者血液样本的研究中,随着患者血清内源性α-Syn水平的降低,IR指标升高。此外,在对α-Syn缺乏的小鼠模型进行IR的饮食诱导过程中,小鼠机体表现为葡萄糖代谢障碍。利用葡萄糖钳夹实验[5-6]显示,α-Syn基因敲除小鼠在高脂饮食喂养过程中,脂肪组织和骨骼肌表现为严重的胰岛素抵抗。鉴于上述研究发现,笔者推测糖尿病机体由于IR造成的内环境改变可能不利于α-Syn的磷酸化和聚集,这一内环境变化也可能反映到患者的血浆中。因此,本研究观察T2D患者血浆对α-Syn寡聚化和磷酸化的影响及分析这一作用与糖尿病指标的相关性。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
从2015年7月至10月首都医科大学宣武医院内分泌科住院的T2D患者,诊断标准采用世界卫生组织(World Health Organization,WHO)(1999年)糖尿病诊断标准[7]。选取70例T2D患者,其中男40例,女30例,年龄46 ~ 70岁。另选取年龄、性别相匹配的70例健康志愿者作为对照组,其中男40例,女30例,年龄44 ~ 70岁。所有的受试者均接受综合生化检测项目,所有数据均进行正态性检验,数据以均数±标准差表示,两组比较采用t检验,详见表1。本研究经医院伦理委员会同意批准进行。所有受试者在进行抽血前均被告知实验研究目的与研究方案,并签署知情同意书。
表1 两组研究对象资料比较Tab.1 Detailed data with control group and type 2 diabetes group
1.2 材料
重组人α-Syn、抗α-Syn单克隆抗体(3D5)由本室制备;抗Ser129抗体(Santa Cruz公司,美国);生物素化的3D5(康为世纪标记);亲和素标记的碱性磷酸酶(Vector公司,美国);4-硝基磷酸二钠盐(pNPP)(Sigma公司,美国);ELISA 96孔酶标板(Corning公司,美国);酶标仪(Tecan公司,瑞士)。
1.3 方法
1) 血浆中α-Syn寡聚体形成量的ELISA检测[8]:向血浆中加入重组人α-Syn,使其浓度为100 μmol/L,37 ℃ 280 r/min恒温震荡48 h。用终浓度为1 μg/mL的3D5单抗包被96孔酶标板,100 μL/孔,37 ℃孵育2 h,4 ℃过夜,PBST洗板。10%(质量分数)BSA封闭,200 μL/孔,37 ℃孵育2 h,PBST洗板。加入倍比稀释的重组人α-Syn(0.5、0.25、0.125、 0.062 5、0.031 25、0 mol/L)和待测样品,100 μL/孔,37 ℃孵育2 h,PBST洗板。加入生物素化的3D5(1 μg/mL)100 μL/孔,37 ℃孵育2 h,PBST洗板。再加入亲和素标记的碱性磷酸酶(1: 5 000),37 ℃孵育1 h,PBST洗板,最后加入pNPP 100 μL/孔,37 ℃显色30 min,405 nm处测定吸光度值。每次每个样品重复3孔,重复3次。
2)血浆中磷酸化α-Syn形成量的ELISA检测:用终浓度为0.1 μg/mL的抗Ser129抗体包被96孔酶标板,其余步骤同上。
1.4 统计学方法

2 结果
2.1 血浆中寡聚化和磷酸化α-Syn形成量检测
如图1所示,T2D组血浆中寡聚化和磷酸化α-Syn形成量均较对照组显著降低,差异均有统计学意义(n=70,P<0.05)。
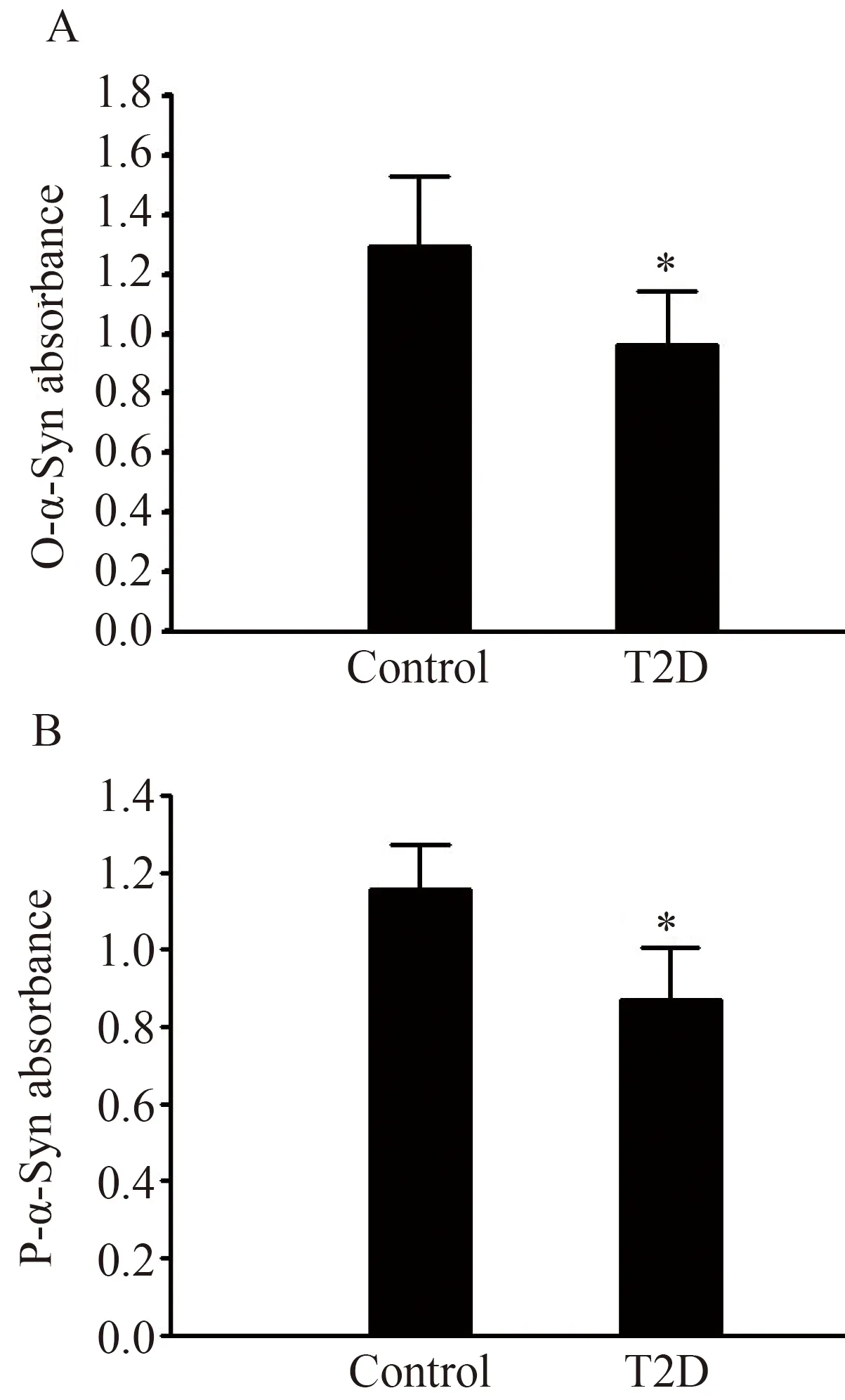
图1 2型糖尿病患者与对照者血浆中寡聚化和磷酸化α-Syn形成量比较Fig.1 Formation of oligomeric and phosphorylatedα-syn in plasmas of type 2 diabetes and control subjects
Statistical analysis of oligomeric α-Syn (A) and phosphorylated α-Syn (B) formation in plasma of type 2 diabetes and control subjects.*P<0.05vscontrol.n=70;T2D: type 2 diabetes;O-α-Syn: α-synuclein oligomers;P-α-Syn: phosphorylated α-synuclein.
2.2 T2D血浆中寡聚化和磷酸化α-Syn形成量与糖尿病指标的相关性分析
如图2所示,T2D血浆中磷酸化α-Syn水平与年龄有相关性(图2B)(r=0.261,P=0.029);寡聚化α-Syn水平与年龄没有相关性(图2A)(r=0.114,P=0.380);糖尿病病程分别与T2D血浆中寡聚化和磷酸化α-Syn水平(图2C,D)无明显相关性(r值分别为0.126和0.122,P值分别为0.318和0.278);空腹血糖分别与T2D血浆中寡聚化和磷酸化α-Syn水平(图2E,F)无明显相关性(r值分别为0.002和0.105,P值分别为0.985和0.485);糖化血红蛋白分别与T2D血浆中寡聚化和磷酸化α-Syn水平(图2G,H)无明显相关性(r值分别为0.045和0.084,P值分别为0.734和0.491)。
3 讨论
该研究利用本实验室建立的ELISA方法检测受试者血浆中寡聚化和磷酸化α-Syn的形成量,研究显示T2D患者血浆中上述两指标的水平较对照组明显降低,其降低机制尚不明确。蛋白磷酸酶2A(protein phosphatase 2A,PP2A)是一种促进α-Syn去磷酸化的酶[9],有文献[10-11]指出,游离脂肪酸可以提高其活性,加速α-Syn去磷酸化,从而降低磷酸化α-Syn形成量,并进一步影响α-Syn寡聚体的形成。
本实验还显示,T2D患者血浆中磷酸化α-Syn的形成量与年龄呈正相关。有文献[12-15]报道,代谢类疾病的发病率随着年龄增加显著增长,并且老化伴随着各种各样的生理改变,例如线粒体功能障碍、炎性反应发生和胰岛素敏感性的下降,这些改变最终加剧神经退行性疾病的进展。尽管上述相关性机制尚不清楚,但本课题组推测,年龄是影响T2D患者血浆中磷酸化α-Syn形成的重要因素,且具有增龄性。相比之下,α-Syn寡聚体的形成量与年龄的相关性不明显。已知α-Syn蛋白磷酸化修饰参与了α-Syn聚集形成寡聚体的过程[16],且α-Syn的聚集也受磷酸化修饰的影响[17-18],因此本室推测寡聚体形成较磷酸化α-Syn滞后可能是其与年龄相关性不明显的原因。此外,其余糖尿病指标与本实验测试的两指标无相关性,即其余糖尿病指标对T2D血浆中寡聚化和磷酸化α-Syn形成量的改变影响不大。
总之,本研究显示T2D患者血浆中寡聚化和磷酸化α-Syn的形成量较健康者明显降低。这不但反映了T2D患者血浆对寡聚化和磷酸化α-Syn形成的影响,也为T2D对神经元退变的影响提供了新的线索。
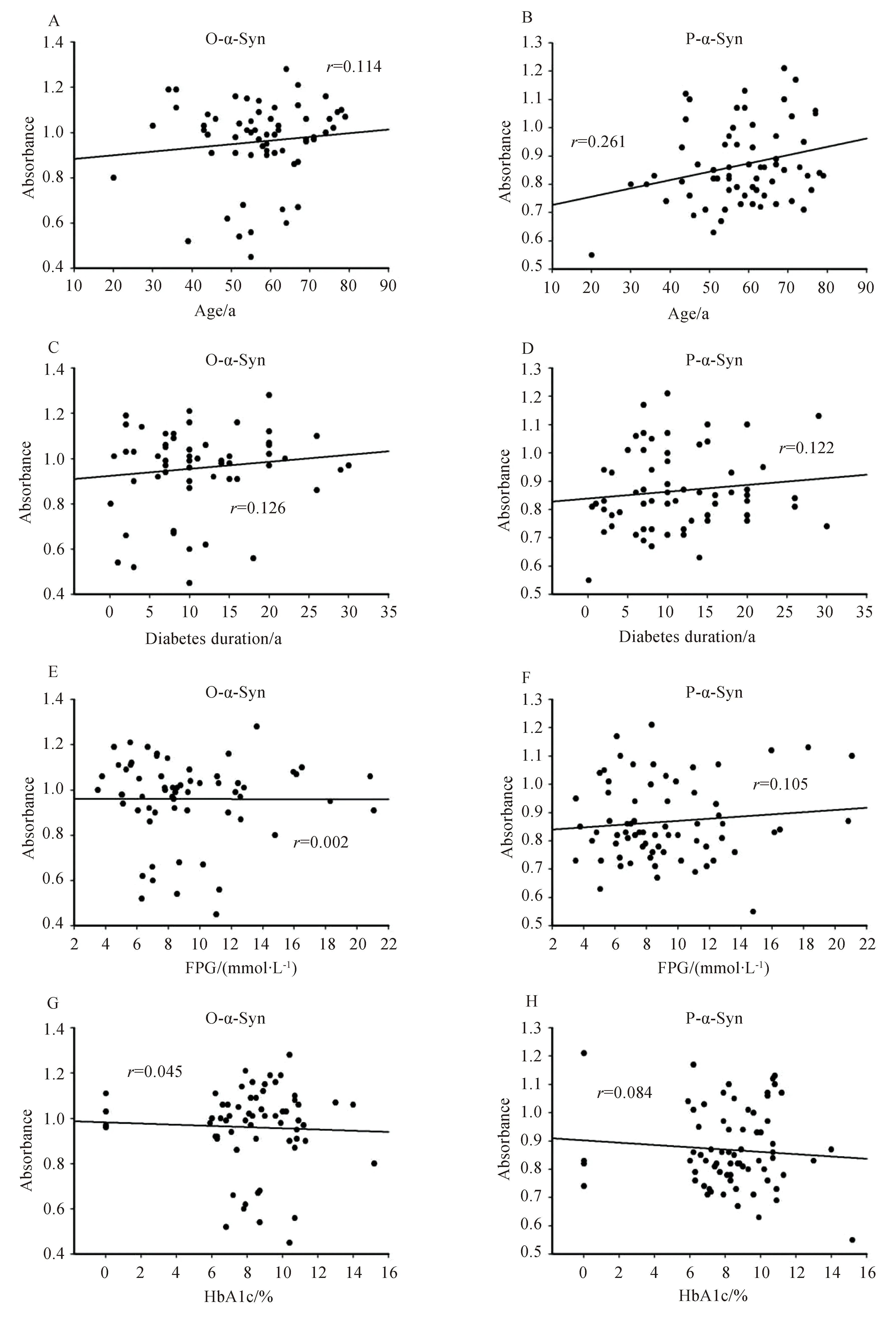
图2 2型糖尿病患者血浆中寡聚化和磷酸化α-Syn形成量与糖尿病指标的相关性分析Fig.2 Correlation analysis between formations of oligomeric and phosphorylated α-Syn and diabetic indexes
Correlation between formations of oligomeric α-Syn and phosphorylated α-Syn and age (A,B),diabetes duration (C,D),FPG (E,F),HbA1c (G,H).P-α-Syn in T2D patients was positively correlated with age.Other parameters and the formations of o-α-Syn and p-α-Syn in T2D patient plasma were not explicitly linked to each other.T2D: type 2 diabetes;O-α-Syn: α-synuclein oligomers;P-α-Syn: phosphorylated α-synuclein;FPG: fasting plasma glucose;HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c.
[1] Kruger R,Kuhn W,Muller T,et al.Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in parkinson’s disease [J].Nat Genet,1998,18(2): 106-108.
[2] International Parkinson Disease Genomics Consortium,Nalls M A,Plagnol V,et al.Imputation of sequence variants for identification of genetic risks for Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies [J].Lancet,2011,377(9766): 641-649.
[3] Polymeropoulos M H,Lavedan C,Leroy E,et al.Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease [J].Science,1997,276(5321): 2045-2047.
[4] Rodriguez-Araujo G,Nakagami H,Takami Y,et al.Low alpha-synuclein levels in the blood are associated with insulin resistance [J].Sci Rep,2015,5: 12081.
[5] Shiuchi T,Haque M S,Okamoto S,et al.Hypothalamic orexin stimulates feeding-associated glucose utilization in skeletal muscle via sympathetic nervous system[J].Cell Metab,2009,10 (6): 466-480.
[6] Ayala J E,Bracy D P,Malabanan C,et al.Hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps in conscious,unrestrained mice[J].J Vis Exp,2011(57)pii: 3188.
[7] Alberti K G,Zimmet P Z.Definition,diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications.Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation[J].Diabet Med,1998,15(7):539-553.
[8] 陈予东,尹娜,李昕,等.脑卒中患者血浆中α-突触核蛋白及其寡聚体形成量变化的研究[J].首都医科大学学报,2013,34(6): 826-829.
[9] Liu G,Chen M,Mi N,et al.Increased oligomerization and phosphorylation of α-synuclein are associated with decreased activity of glucocerebrosidase and protein phosphatase 2A in aging monkey brains [J].Neurobiol Aging,2015,36 (9): 2649-2659.
[10] Galbo T,Olsen G S,Quistorff B,et al.Free fatty acid-induced PP2A hyperactivity selectively impairs hepatic insulin action on glucose metabolism [J].PLoS One,2011,6 (11): e27424.
[11] Højlund K,Poulsen M,Staehr P,et al.Effect of insulin on protein phosphatase 2A expression in muscle in type 2 diabetes [J].Eur J Clin Invest,2002,32 (12): 918-923.
[12] Dillin A,Hsu A L,Arantes-Oliveira N,et al.Rates of behavior and aging specified by mitochondrial function during development [J].Science,2002,298(5602): 2398-2401.
[13] Lee S S,Lee R Y,Fraser A G,et al.A systematic RNAi screen identifies a critical role for mitochondria in C.elegans longevity [J].Nat Genet,2003,33(1): 40-48.
[14] Short K R,Bigelow M L,Kahl J,et al.Decline in skeletal muscle mitochondrial function with aging in humans [J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2005,102(15): 5618-5623.
[15] Riera C E,Dillin A.Tipping the metabolic scales towards increased longevity in mammals [J].Nat Cell Biol,2015,17(3): 196-203.
[16] Fujiwara H,Hasegawa M,Dohmae N,et al.alpha-Synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions [J].Nat Cell Biol,2002,4(2): 160-164.
[17] Arawaka S,Wada M,Goto S,et al.The role of G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 in pathogenesis of sporadic Parkinson’s disease [J].J Neurosci,2006,26(36): 9227-9238.
[18] Kragh C L,Lund L B,Febbraro F,et al.Alpha-synuclein aggregation and Ser-129 phosphorylation-dependent cell death in oligodendroglial cells [J].J Biol Chem,2009,284: 10211-10222.
Decreasedα-synucleinphosphorylationandoligomerizationintheplasmaofpatientswithtype2diabetes
Zheng Songyang1,2,Li Xin1,2,3,4,Yang Weiwei1,2,3,4,Li Xuran1,2,Li Xuying1,2,Yu Wenjiao1,2,Yu Shun1,2,3,4*
(1.DepartmentofNeurobiology,XuanwuHospital,CapitalMedicalUniversity,BeijingInstituteofGeriatrics,Beijing100053,China;2.ClinicalCenterforParkinson’sDisease,CapitalMedicalUniversity,Beijing100053,China;3.BeijingKeyLaboratoryforParkinson’sDiseaseandKeyLaboratoryofNeurodegenerativeDiseases,MinistryofEducation,Beijing100053,China;4.NationalClinicalResearchCenterforGeriatricDisorders,Beijing100053,China)
ObjectiveTo investigate the effect of the plasma of patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) patient on the formation of oligomeric and phosphorylated α-synuclein (α-Syn).MethodsA total of 70 hospitalized patients with T2D and 70 age-and sex-matched healthy control subjects were recruited.Blood plasmas were collected and recombinant human α-Syn was incubated with the plasma.ELISA was used to measure the levels of oligomeric and phosphorylated α-syn formed in the plasma.ResultsThe levels of oligomeric and phosphorylated α-syn in the plasma of T2D patients were significantly lower than those in the plasma of healthy controls (P<0.05),which was positively correlated with age.ConclusionCompared with control plasma,the plasma from T2D patients decreases α-syn oligomerization and phosphorylation in an age-dependent manner.
α-synuclein;type 2 diabetes;plasma;phosphorylation;oligomerization
国家自然科学基金(81371200,81071014,81401042),北京市医院管理局“使命”计划专项经费资助(SML20150803);北京市科学技术委员会资助(Z161100005116011,Z171100000117013);北京市卫生和计划生育委员会“老年重大疾病关键技术研究”(PXM2017_026283_000002)。This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81371200,81071014,81401042);Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals’ Mission Plan (SML20150803);Beijing Municipal Science &Technology Commission (Z161100005116011,Z171100000117013);Beijing Municipal commission of Health and Family Planning (PXM2017_026283_000002).
*Corresponding author,E-mail:yushun103@163.com
时间:2017-12-13 20∶53
http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3662.R.20171213.2053.012.html
10.3969/j.issn.1006-7795.2017.06.020]
R338
2017-10-23)
编辑 陈瑞芳
