HBV/HCV重叠感染患者临床特点分析
2017-12-07薛红元赵彩彦
张 宁,薛红元,赵彩彦
HBV/HCV重叠感染患者临床特点分析
张 宁,薛红元,赵彩彦
目的由于两种病毒间存在相互干扰,HBV/HCV重叠感染患者临床表现及预后情况与单病毒感染不同。本文旨在探讨HBV/HCV重叠感染患者临床特点及其疾病转归情况,为优化其诊治方案提供依据。方法2002年11月~2013年12月河北医科大学第三医院住院的HBV/HCV重叠感染患者30例,2013年6月~2014年12月河北医科大学第三医院住院的慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)患者59例,慢性丙型肝炎(CHC)患者54例。对各组患者的临床资料进行回顾性分析。结果HBV/HCV重叠感染患者血清球蛋白水平为(32.12±6.76)g/L,显著高于CHB组【(28.69±7.16)g/L,P<0.05】,ALT 水平为(134.02±209.34)U/L,显著高于 CHB 组【(71.57±53.23)U/L,P<0.01】,TBIL 水平为(62.18±99.05)μmol/L,显著高于 CHB 组【(30.98±30.70)μmol/L,P<0.01】,GGT 水平为(71.60±51.92)U/L,显著高于 CHB 组【(50.28±47.23)U/L,P<0.05】,PTA 水平为(73.39±17.19)%,显著低于CHB组【(91.28±17.71)%,P<0.01】;HBV/HCV重叠感染患者HBeAg阴性占50.0%,与CHB组的45.0%比,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);HBV/HCV重叠感染组血清HBV DNA阳性率为50%,显著低于CHB组的79.7%(P<0.01);HBV/HCV重叠感染组血清病毒载量显著低于CHB组,差异有统计学意义(Z=-3.331,P<0.01);HBV/HCV重叠感染组慢性肝炎重度和肝硬化发生率为53.3%,显著高于CHB组的34.0%;重叠感染患者在疾病预后和转归方面与CHB 比,差异有统计学意义(Z=-3.121,P<0.01);HBV/HCV 重叠感染患者血清白蛋白水平为(37.78±6.74)g/L,显著低于 CHC 组【(43.07±4.48)g/L,P<0.01】,球蛋白水平显著高于 CHC 组【(28.83±5.84)g/L,P<0.05】,AST 水平为(71.07±48.72)U/L,显著高于 CHC 组【(51.29±38.61)U/L,P<0.05】,ALT水平显著高于 CHC 组【(52.91±29.71)U/L,P<0.01】,TBIL水平著高于 CHC 组【(16.71±7.65)μmol/L,P<0.01】,GGT 水平显著高于 CHC 组【(38.39±29.10)U/L,P<0.01】,PTA 水平显著低于 CHC 组【(104.62±16.10)%,P<0.01】;HBV/HCV 重叠感染组与CHC组比,血清病毒载量水平显著低下,差异有统计学意义(Z=-5.612,P<0.01);重叠感染组存在严重肝功能损害的发生率为53.3%,显著高于CHC组的13.0%,差异有统计学意义(Z=5.249,P<0.01)。结论与单病毒感染患者比,HBV/HCV重叠感染患者更易发生严重的肝功能损害,肝硬化发生率也显著升高,但血清病毒载量并不非常高,应注意甄别。
乙型肝炎;丙型肝炎;重叠感染;临床特点;疾病转归
乙型肝炎病毒(hepatitis B virus,HBV)和丙型肝炎病毒(hepatitis C virus,HCV)感染是导致全球慢性肝脏疾病的主要原因,可导致肝硬化和肝细胞癌(hepatocellular carcinoma,HCC)[1,2]。HBV 与 HCV传播途径相同,所以HBV/HCV重叠感染(HBV/HCV superinfection)并不少见。研究表明,HBV/HCV重叠感染者血清病毒间呈现“此消彼长”的特点,以HBV占主导[3],亦或以HCV占主导[4]。新近研究表明,HBV/HCV重叠感染时,何种病毒为优势病毒取决于优先感染何种病毒[5]。与慢性乙型肝炎(chronic hepatitis B,CHB)患者或慢性丙型肝炎(chronic hepatitis C,CHC)患者比,HBV/HCV 重叠感染时,虽病毒复制受到抑制,但这并不意味着肝脏炎症病变减轻,反而可能加速了肝脏疾病的进行性恶化,肝硬化和HCC的发生率也显著升高[6-10]。本研究旨在探讨HBV/HCV重叠感染患者的临床特点及预后情况,现将结果报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 病例来源 2002年11月~2013年12月在河北医科大学第三医院住院的HBV/HCV重叠感染患者30例,2013年6月~2014年12月在河北医科大学第三医院住院的CHB患者59例,CHC患者54例。所有患者诊断符合中华医学会感染病学分会和肝病学分会制订的丙型肝炎防治指南和慢性乙型肝炎防治指南[11,12]。排除甲、丁、戊型肝炎病毒、免疫缺陷病毒、巨细胞病毒、人类疱疹病毒感染以及酒精性、药物性和自身免疫性肝病,除外有严重心肺疾病、糖尿病、癫痫、精神疾病患者。
1.2 检测方法 采用荧光定量PCR法检测血清HBV DNA和HCV RNA载量(达安基因股份有限公司);采用ELISA法检测HBV标志物及抗HCV抗体(厦门英科新创科技有限公司);使用奥林巴斯AU5400全自动生化分析仪检测血生化指标;使用美国BECKMANCOULTER TOP700全自动血凝仪检测凝血酶原时间。
1.3 统计学分析 应用 SPSS 13.0软件进行统计处理。计量资料以(±s)表示,对符合正态分布且方差齐性资料采用t检验。对不符合正态分布和方差不齐资料采用秩和检验。计数资料采用x2检验。等级资料采用秩和检验。以 P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 三组基本资料比较 入选的慢性HBV/HCV重叠感染患者30例,男性23例(76.7%),女性7例(23.3%)。年龄 33~77岁,平均年龄(54.62±12.36)岁;CHB患者59例,男性40例(67.8%),女性19例(32.2%)。年龄25~81岁,平均年龄(48.24±14.53)岁;CHC患者54例,男性32例(59.3%),女性22例(40.7%)。年龄21~69岁,平均年龄(49.7±14.41)岁。CHB组或CHC组与HBV/HCV重叠感染组患者在年龄和性别方面差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
2.2 三组患者疾病临床分型比较 HBV/HCV重叠感染组失代偿期肝硬化(包括存在腹水、肝性脑病、肝肾综合征、肝细胞癌等并发症)的发生率显著高于CHB 组(Z=-3.121,P<0.01)或 CHC 组(Z=5.249,P<0.01,表 1)。
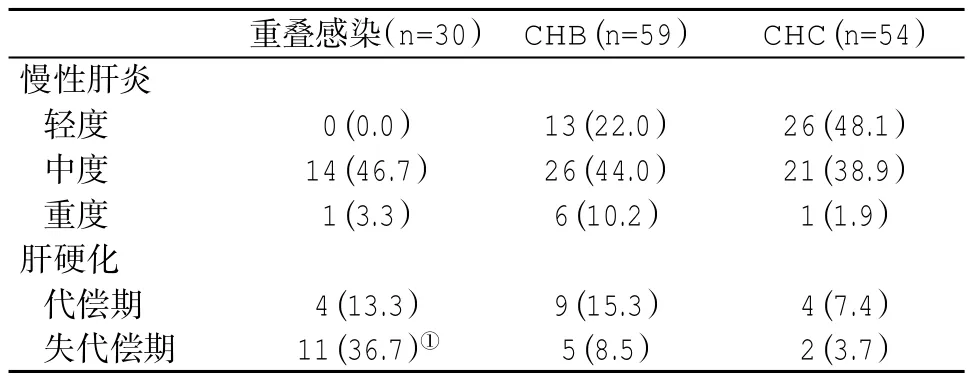
表1 三组临床分型(%)比较
2.3 三组血清生化和凝血功能指标比较 重叠感染组患者肝功能损害更明显,与其他两组比,有关指标差异显著(P<0.05,表 2)。
表2 三组血清肝功能指标(±s)比较
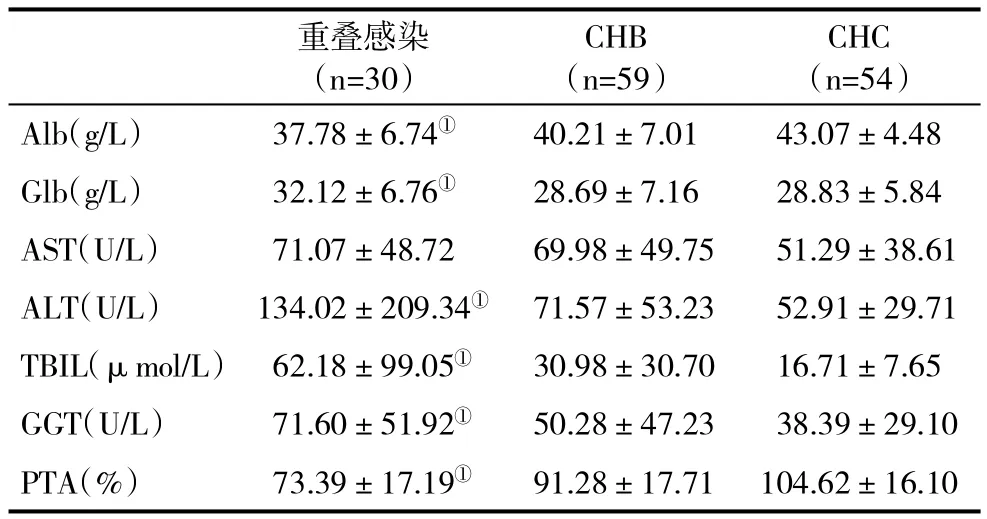
表2 三组血清肝功能指标(±s)比较
与CHB或CHC比,①P<0.05
CHC(n=54)Alb(g/L) 37.78±6.74① 40.21±7.01 43.07±4.48 Glb(g/L) 32.12±6.76① 28.69±7.16 28.83±5.84 AST(U/L) 71.07±48.72 69.98±49.75 51.29±38.61 ALT(U/L) 134.02±209.34① 71.57±53.23 52.91±29.71 TBIL(μmol/L) 62.18±99.05① 30.98±30.70 16.71±7.65 GGT(U/L) 71.60±51.92① 50.28±47.23 38.39±29.10 PTA(%) 73.39±17.19① 91.28±17.71 104.62±16.10重叠感染(n=30)CHB(n=59)
2.4 三组血清病毒载量比较 HBV/HCV重叠感染组血清HBV DNA水平显著低于CHB组,差异有统计学意义(Z=-3.331,P<0.01),HCV RNA 水平显著低于CHC组,差异有统计学意义(Z=-5.612,P<0.01,表 3)。
表3 三组血清病毒载量(±s)比较
与CHB或CHC比,①②P<0.01
HCV RNA(×105copies/ml)重叠感染 30 2.72±9.98① 1.05±3.74②乙型肝炎 59 40.00±100丙型肝炎 54 20.09±45.51例数 HBV DNA(×106copies/ml)
3 讨论
本研究显示,HBV DNA阳性/HCV RNA阳性者8例,HBV DNA阳性/HCV RNA阴性者7例,HBV DNA阴性/HCV RNA阳性者12例,HBV DNA阴性/HCV RNA阴性3例,以HBV DNA阴性/HCV RNA阳性表现形式为主,即以HCV感染占主导,HCV RNA可能抑制了HBV DNA复制,这与既往多数研究结论一致。关于HBV/HCV重叠感染的病毒学模式,已有大量的临床试验研究,多数研究支持HBV/HCV重叠感染者两种病毒载量在某一时期表现为以HCV占主导为主,即表现为HCV RNA高水平复制,HBV DNA低水平复制,进一步说明两种病毒间存在相互干扰。HCV对HBV产生抑制作用的机制可能是HCV的核心蛋白抑制了HBV的活动,影响了HBV的转录[13]。然而,也有研究发现两种病毒载量以HBV占主导[14],可能与病毒间的相互干扰作用,不同时期出现不同的病毒学模式,从而出现不同的“优势病毒株”。因此,在临床工作中,不同时期选择不同的优化治疗方案至关重要。
自90年代初,体外实验已经发现HCV核心蛋白可抑制HBV复制[13]。尽管是增强或抑制HBV复制的结论尚未明确,相关研究发现HCV NS5A蛋白可影响HBV活性[15,16]。HBV与HCV间存在相互干扰,可能为HCV可以刺激机体产生γ干扰素,从而对HBV复制产生抑制[17]。HCV核心蛋白可以抑制HBV增强子1和2,在转录水平上抑制了HBV复制,抑制作用的强弱与HCV基因型相关,HCV基因1b型抑制作用强于基因3a和1a型[13]。但体外研究所得结论却与之相反。研究发现,HCV NS5蛋白可促进HB sAg和HBeAg表达,并增加HBV DNA合成[16]。在HBV/HCV重叠感染时,低复制水平的HBV亦能干扰HCV的复制,抑制NS4的体液免疫应答[18]。
本组30例HBV/HCV重叠感染患者病毒载量虽低于单病毒感染者,但往往表现为更为严重的肝脏损害。与单独HBV感染组比,重叠感染组Glb、ALT、TBIL、GGT水平均显著增高,且PTA水平显著下降;与单独HCV感染组比,重叠感染组Alb水平明显下降,Glb、AST、ALT、TBIL、GGT 水平均显著增高,并且PTA水平显著下降。推测肝脏损伤加重的原因可能为:①HBV和HCV通过多种方式抑制了对方基因序列表达,使各自的病毒复制水平处于较低状态,此过程促进了肝细胞损害和疾病进展;②肝细胞的炎性坏死使机体免疫反应增强,机体免疫反应激活抑制了病毒的复制;③在疾病进展的某个阶段,肝细胞炎性坏死加重,病毒复制水平反而降低[19]。
重叠感染组较单独HCV感染组有更为严重的肝功能损害,包括慢性肝炎重度、肝硬化比例也显著升高。既往研究也表明,与单病毒感染的患者相比,HBV/HCV重叠感染的患者更易发生严重的肝脏损害,肝硬化和HCC的发生率也显著升高[10]。此外,本研究还发现,血清HBV DNA、HCV RNA水平越低,肝功能越差,预后也越差。既往多数研究显示HBV/HCV重叠感染可加重肝脏疾病的进展,增加HCC发生的风险,但Jamma[20]应用新的细胞生物模型检测两种病毒间的相互作用显示,HBV和HCV可在同一肝细胞内复制而互不影响,遗传特质和适应免疫共同决定了病毒的复制及疾病的结局,其具体机制有待进一步研究。
[1]Lok AS,McMahon BJ.Chronic hepatitis B:update 2009.Hepatology,2009,50(3):661-662.
[2]Ghany MG,Strader DB,Thomas DL,et al.Diagnosis,management,and treatmentofhepatitis C:an update.Hepatology,2009,49(4):1335-1374.
[3]Sagnelli E,Coppola N,Pisaturo M,et al.HBV superinfection in HCV chronic carriers:a disease that is frequently severe but associated with the eradication of HCV.Hepatology,2009,49(4):1090-1097.
[4]Wieland SF,Asabe S,Engle RE,et al.Limited hepatitis B virus replication space in the chronically hepatitis C virus-infected liver.J Virol,2014,88(9):5184-5188.
[5]Chen F,Zhang J,Wen B,et al.HBV/HCV dual infection impacts viral load,antibody response,and cytokine expression differently from HBV or HCV single infection.Sci Rep,2016,6:39409.
[6]Caccamo G,Saffioti F,Raimondo G.Hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus dual infection.World J Gastroenterol,2014,20(40):14559-14567.
[7]Liu CJ,Chen PJ,Chen DS.Dual chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection.Hepatol Int,2009,3(4):517-525.
[8]Amin J,Law MG,Bartlett M,et al.Causes of death after diagnosis of hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection:a large community-based linkage study.Lancet,2006,368(9539):938-945.
[9]El-Serag HB.Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma.Gastroenterology,2012,142(6):1264-1273.
[10]Sagnelli E,Coppola N,Messina V,et al.HBV superinfection in hepatitis C virus chronic carriers,viral interaction,and clinical course.Hepatology,2002,36(5):1285-1291.
[11]中华医学会肝病学分会、中华医学会感染病学分会.丙型肝炎防治指南(2015年更新版).实用肝脏病杂志,2016,19(4):IX-XXVI.
[12]中华医学会肝病学分会、中华医学会感染病学分会.慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2015 年版). 实用肝脏病杂志,2016,19(03):V-XVI.
[13]Schuttler CG,Fiedler N,Schmidt K,et al.Suppression of hepatitis B virus enhancer 1 and 2 by hepatitis C virus core protein.J Hepatol,2002,37(6):855-862.
[14]Nguyen LH,Ko S,Wong SS,et al.Ethnic differences in viral dominance patternsin patientswith hepatitisB virusand hepatitis C virus dual infection. Hepatology,2011,53:1839-1845.
[15]Guo H,Zhou T,Jiang D,et al.Regulation of hepatitis B virus replication by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-akt signal transduction pathway.J Virol,2007,81(18):10072-10080.
[16]Pan Y,Wei W,Kang L,et al.NS5A protein of HCV enhances HBV replication and resistance to interferon response.Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2007,359(1):70-75.
[17]Chisari FV.Viruses,immunity,and cancer:lessons from hepatitis B.Am J Pathol,2000,156(4):1117-1132.
[18]Chu CM,Sheen IS,Liaw YF.Low-level hepatitis C viremia and humoral immune response to NS4 in chronic hepatitis B virus-hepatitis C virus coinfection.Scand J Gastroenterol,2004,39(8):778-782.
[19]张卡,曹红,杨小安,等.乙型肝炎病毒和丙型肝炎病毒不同模式重叠感染患者临床特征分析.中华传染病杂志,2011,29(7):429-432.
[20]Jamma S,Hussain G,Lau DT.Current concepts of HBV/HCV coinfection:coexistence,butnotnecessarily in harmony.Curr Hepat Rep,2010,9(4):260-269.
(收稿:2017-02-21)
(本文编辑:陈从新)
Clinicalfeaturesand disease outcomesin patientswith HBV/HCV superinfection
Zhang Ning,Xue Hongyuan,Zhao Caiyan.Department of Infectious Disease,Third Hospital,Hebei Medical University,Shijiazhuang 050000,Hebei Province,China;Zhang Ning,XueHongyuan.Departmentof Ultrasound,Hebei General Hospital,Shijiazhuang 050000,Hebei Province,China
ObjectiveDue to the interference between two viruses,the clinical features and prognosis in patients with superinfection of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus(HBV/HCV)are usually different from the patients with single hepatotropic virus infection.The aim of this study is to investigate the characteristics of the mutual interference between the viruses and disease outcomes in patients with HBV/HCV superinfection,and provide evidence to help the diagnosis and treatment for the HBV/HCV superinfection patients.Methods30 patients with HBV/HCV superinfection were enrolled between November 2002 and December 2013 in the Third Hospital,Hebei Medical University,and 59 patients with chronic hepatitis B(CHB)and 54 patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC)between June 2013 and December 2014 in the Third Hospital,Hebei Medical University were also included in this study.All the patients in each group were retrospectively analyzed for the patient's general conditions and clinical data.ResultsSerum level of globulin in patients in HBV/HCV superinfection was(32.12±6.76)g/L,significantly higher than that in CHB patients【(28.69±7.16) g/L,P<0.05】,serum level of ALT was(134.02±209.34)U/L,significantly higher than that in CHB group【(71.57±53.23)U/L,P<0.01】,serum level of total bilirubin was(62.18±99.05)μmol/L,which was significantly higher than that in CHB group【(30.98±30.70)μmol/L,P<0.01】,serum level of GGT was(71.60±51.92)U/L,which was significantly higher than that in CHB group【(50.28±47.23)U/L,P<0.05】,and the level of prothrobin time activity(PTA)was(73.39±17.19)%,which was significantly lower than that in CHB group 【(91.28±17.71)%,P<0.01】;the negative rate of serum HBeAg in HBV/HCV superinfection group was 50.0%,not significantly different(P>0.05) as compared to 45.0%in HBV infection group;the positive rate of serum HBV DNA in HBV/HCV superinfection group was 50.0%,which was significantlylowerthan that in HBV infection group (79.7% ,P<0.01);the serum viral load in HBV/HCV superinfection group was significantly lower than that in CHB group,and the difference was significant(Z=-3.331,P<0.01);the incidence of severe chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis in HBV/HCV superinfection group was 53.3%,which was significantly higher than that in HBV infection group (34.0%,P<0.05),and there was an significant difference in terms of disease outcome (Z=-3.121,P<0.01);serum albumin level in patients with HBV/HCV superinfection was(37.78±6.74)g/L,which was significantly lower than that in CHC group【(43.07±4.48)g/L,P<0.01】,serum globulin level was significantly higher than that in CHC group 【(28.83±5.84)g/L,P<0.05】,serum level of AST was significantly higher than that in CHC group 【(51.29±38.61)U/L,P<0.05】,serum level of ALT was significantly higher than that in CHC group 【(52.91 ±29.71) U/L,P <0.01】,serum bilirubin level was significantly higher than that in CHC group【(16.71±7.65)μmol/L,P<0.01】,serum level of GGT was significantly higher than that in CHC group【(38.39±29.10)U/L,P<0.01】and PTA was significantly lower than that in CHC group 【(104.62 ±16.10)% ,P <0.01】;serum HCV RNA loadinpatientswithHBV/HCV superinfectionwas significantly lower than that in CHC group(Z=-5.612,P<0.01);the incidence of severe liver function damage in HBV/HCV superinfection group was 53.3%,which was higher than that in CHC group(13.0%,Z=-5.249,P<0.01).Conclusions HBV/HCV superinfection tends to lead to more severe liver damage,and the incidence of liver cirrhosis is also significantly increased,while the serum viral loads might be lower,which needs to take into consideration in clinical practice.
Hepatitis B;Hepatitis C;Superinfection;Clinical feature;Disease outcomes
10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2017.06.015
050000石家庄市 河北省人民医院超声科(张宁,薛红元);河北医科大学第三医院感染病科(张宁,赵彩彦)
张宁,女,30岁,2012级河北医科大学第三医院感染病科硕士研究生,现工作于河北省人民医院超声科。E-mail:zhangning19871027@126.com
赵彩彦,E-mail:zhaocy2005@163.com
