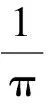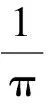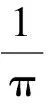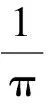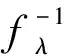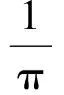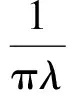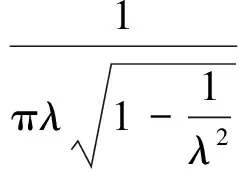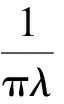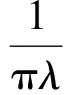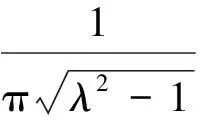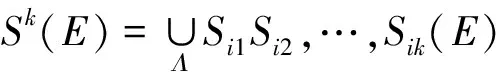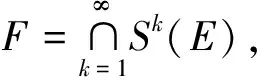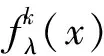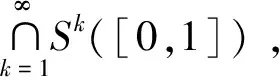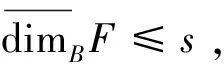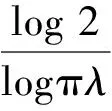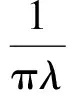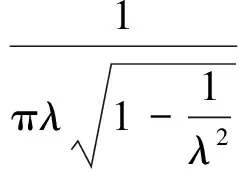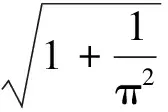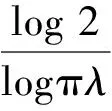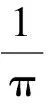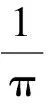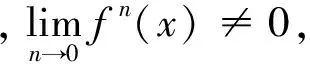某类生物种群模型的动力性研究*
2017-11-16黄华鹰
邓 迪,陈 阵,黄华鹰
(安徽大学 数学科学学院,合肥 230601)
某类生物种群模型的动力性研究*
邓 迪,陈 阵,黄华鹰
(安徽大学 数学科学学院,合肥 230601)
针对一类生物种群总量变化模型fλ(x)=λsinπx,提出了该模型中不同λ值下的动力性分析;该方法对λ的取值区间进行分类,分别通过两种方法分析其动力性,与传统方法相比,更容易被应用于不同的模型中;该研究结合离散动力系统,不变集,斥子和Hausdorff测度的定义和性质,将Lagrange中值定理应用到该模型逆映射的两个不同分支中,得到了有关fλ的逆映射的不等式,进而得到fλ存在唯一不变集的条件和不变集与斥子间的关系;最后,对较大的系数λ,估计了fλ(x)的斥子的Hausdorff维数;对于区间(0,1]上的系数λ,分别研究了fλ(x)迭代的动力性, 研究结论比传统方法更容易应用于相应的生物种群模型。
动力系统;不动点;不变集;吸引子;斥子;Hausdorff维数
映射fλ:0,1→R由fλ(x)=λSinπx给出,其中fλ为正常数[1],是作为某个物种总量变化的模型引入的。设在任一年末生物总量为x,则下一年末的总量为fλ(x)[2]。本文将研究fλ(x)迭代生成的一维动力系统。
1 基本概念
定义1[1]设D是Rn的一个子集,f:D→D是连续映射,fk表示f的k次迭代,因此f0(x)=x,f1(x)=f(x),f2(x)==f(f(x)),…。一个迭代序列{fk}通常称为一个离散的动力系统[3]。对任意x∈D,fk(x)可能收敛到一个不动点w,即使得w=f(w)∈D。更一般地,fk(x)可能收敛到周期为p的点{w,f(w),…,fp-1(w)}的轨道,这时p是使fp(w)=w的最小正整数,此时当k→∞,fk(x)-fi(x)→0,i=0,1,2,…,p-1。集合S称为一个动态系统的不变集, 如果从S中一个点出发的系统轨线永远停留在S中,重要的不变集有极限集、极限集、非游荡集和链回归集等[3]。
定义2[1]对于不变集F⊂0,1,若∀x∉F,∃k∈Z+,使得fk(x)∉[0,1],则称F为f的斥子。
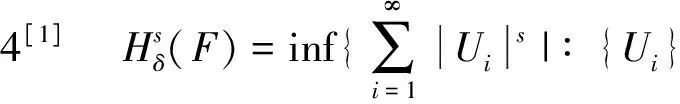
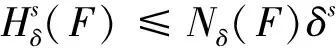
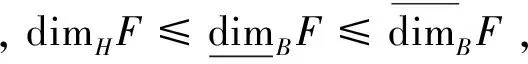
2 主要结果
定理1 当系数λ足够大时,fλ存在唯一不变集F⊂[0,1],且F为fλ的斥子。
定理2fλ(x) =λSin πx的逆映射有两个不同的分支S1(x),S2(x),且存在0 证明设λSin πx= 1,x∈[0,1]得两个根 由于fλ(x)=λsin πx在[0,a]与[1-a,1]上分别单调,因此[0,a]与[1-a,1]中每一点都被fλ一一地映入[0,1]中,记映射: S1:[0,1]→[0,a] S2:[0,1]→[1-a,1] 对∀x∈[0,1],有 对∀x,y∈[0,1],由Lagrange中值定理, 有 S1(x)-S1(y)=S1′(ξ)(x-y) S2(x)-S2(y)=S2′(η)(x-y) ξ,η介于x与y之间。 dx-y≤Si(x)-Si(y)≤cx-y,i=1,2 在估计斥子F的Hausdorff维数之前,需要以下引理。 引理1[4]设S1,S2:[0,1]→R, 且|Si(x)-Si(y)|≤c|x-y|,∀x,y∈[0,1],0 (1) 存在唯一非空紧子集F⊂[0,1],满足F=S1(F)∪S2(F); 证明先证存在性: 因为∀E∈J,S1(E)⊂E,S2(E)⊂E,所以有: S(E)=S1(E)∪S2(E)⊂E S2(E)=S(S1(E)∪S2(E))= S1(S1(E)∪S2(E))∪S2(S1(E)∪ S2(E))⊂S1(E)∪S2(E)=S(E) 由数学归纳法: 再证唯一性: 设A,B∈J,定义 diam(A,B)=min{x-y:x∈A,y∈B} diam(S(A),S(B))=diam(S1(A)∪S2(A),S1(B)∪S2(B))≤max{diam(S1(A),S1(B)),diam(S2(A),S2(B))}≤max{c1diam(A,B),c2diam(A,B)}=max{c1,c2}diam(A,B)。 若S(A)=A,S(B)=B,则 diam(A,B)≤max{c1,c2}diam(A,B) 因为0 S1(x)-S1(y)=S2(x)-S2(y)≤cx-y 0 证明由于fλ(S1(F))=F,fλ(S2(F))=F,由引理中的(2),可得fλ(F)=fλ(S1(F)∪S2(F))=F,定理3得证。 以下估计斥子F的Hausdorff维数。 引理2[1]设S1,S2,…,Sm是Rn的闭子集D上的压缩映射,满足 Si(x)-Si(y)≤cix-y(x,y∈D) 引理3[9]设S1,S2,…,Sm是Rn的闭子集D上的压缩映射,使 bix-y≤Si(x)-Si(y) (x,y∈D) 对每个i,0 上面的并是不交并,则dimHF≥s,其中 证明由于 以下讨论系数λ∈(0,1]的fλ(x)=λSin πx迭代的动力性。 命题1 当0<λ<1时,0为fλ(x)=λSin πx的吸引不动点。 命题2 当λ=1时,x0为fλ(x)=λSin πx的吸引不动点。 (f(x)-x)′=λπCos πx-1>0 所以x很接近0时,f(x)-x≥0,即在0附近,fn(x)≥fn-1(x) [1] 肯尼思·法尔科内. 分形几何:数学基础及其应用[M]. 沈阳:东北大学出版社, 1991 FALCONER K J. Fractal Geometry:Mathe-matical Foundations and Applications[M]. Shenyang:North-eastern University Press,1991 [2] 吕敬亮. 几类随机生物种群模型性质的研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2011 LU J L. Analysis on Properyies of Some Stochastic Population Models[D]. Harbin:Harbin Institute of Technology,2011 [3] 何思谦. 数学辞海[M]. 太原:山西敎育出版社, 2002 HE S Q . Mathematics Dictionary [M].Taiyuan :Shanxi Education Press,2002 [4] 张雪. 若干类生物动力系统的复杂性研究[D]. 沈阳:东北大学,2010 ZHANG X. Researches on Complexity for Some Classes of Biological Dynamical Systems[D]. Shengyang: Nor-theaster University,2010 [5] 霍胜进. 拟圆周的Hausdorff维数[D].北京:北京大学,2013 HUO S J. Hausdorff Dimensions of Quasicircles[D]. Beijing: P-eking University, 2013. [6] 杨玉莲. 几类分形集的Hausdorff维数[D].海口:海南大学,2011 YANG Y L. The Hausdorff Dimension of a Few Kinds of Fractal Sets [D]. Haikou:Hainan University, 2011. [7] 王艳. 自相似集的Hausdorff维数与测度及其计算机实现[D].淮北:淮北师范大学,2010. WANG Y.The Hausdorff Dimension and Measure of Self-similar Sets and Its Computer Implementation[D].Huaibei:Huaibei Normal University,2010 [8] 张光云. 基于动力系统理论的一类金融混沌系统的定性分析[J]. 重庆工商大学学报(自然科学版),2017(2):37-40 ZHANG G Y. Qualitative Analysis of a Class of Financial Chaotic System Based on Dynamical System Theory [J]. Journal of Chongqing Technology and Business University(Natural Science Edition),2017(2):37-40 [9] 董丽. 几类生物种群动力系统动力学行为的研究[D].厦门:集美大学,2012. DONG L.The Study for The Dynamics Behaviors of Several Dynamical Populations [D]. Xiamen:Jimei Uni-versity,2012. [10] 李宁. 若干类生物动力系统的复杂性分析与控制[D].沈阳:东北大学,2010 LI N.Complexity Analysis and Control for Some Kinds of Biological Dynamical Systems [D]. Shenyang: Northeaster University,2010 The Study on Dynamics of a Class of Biological Population Model DENGDi,CHENZhen,HUANGHua-ying (School of Mathematical Sciences, Anhui University, Hefei 230601, China) For a total change model of a class of biological population:fλ(x)=λsinπx, dynamic analysis of differentλvalue in the model is proposed. Firstly, the method classifies the range ofλ, then the dynamical properties offλ(x)are analyzed from two points. Compared with traditional methods, it is more easily applied to different models. Lagrange Mean Value Theorem is applied to the two different branches of the inverse mapping of the model, and the inequality of the inverse mapping aboutfλis obtained by combining the definitions and properties of the discrete dynamical system, invariant set, repellers and Hausdorff dimension. Then the condition of existence of a unique invariant set and the relationship between the invariant set and the repellers are obtained. Finally, for a larger coefficientλ, the Hausdorff dimension offλ(x) repellers is estimated. For the coefficientλon interval(0,1], the dynamical properties offλ(x)iteration are studied respectively. The conclusion of the study is more likely to be applied to the corresponding biological population model than the traditional method. dynamic system; fixed point; invariant set; attractor; repellors; Hausdorff dimension O417 A 2016-11-28; 2017-01-17. 安徽大学大学生创新创业训练计划项目(201510357346). 邓迪(1995-),女,安徽滁州人,硕士研究生,从事分形几何研究. 责任编辑:代小红