基于仿真的博弈系统优化策略研究
2017-11-13,
,
(上海理工大学 理学院,上海 200093)
基于仿真的博弈系统优化策略研究
田伟,刘懿芳
(上海理工大学 理学院,上海200093)
以石头剪刀布博弈系统为例,提出一种新的理论方法优化该系统,目的是在不受其他因素影响下最大化玩家获得的收益,这种新方法即凸优化.引入非零和矩阵建立凸优化算法模型,定量地创建了石头剪刀布博弈系统收益方程,这种方法前人鲜有研究.创新地提出了博弈系统最优值的临界方程即鞍点方程,并用强对偶理论证明了该方程的正确性.重点研究凸优化中的Newton算法对石头剪刀布博弈系统进行数据仿真和最大化玩家获得的收益.仿真结果表明,数值结果与理论假设相一致,验证了该方法的可行性和正确性.该研究对于理解博弈系统和应用凸优化具有十分重要的意义.
仿真; 凸优化; 博弈系统; 鞍点
石头剪刀布(rock-paper-scissors,RPS)作为一个基本的非合作博弈系统[1],已广泛用于研究生物学中的竞争现象,如生态系统中物种的多样性[2-7].纳什均衡理论[8-10]在研究经典博弈论和进化博弈论中起着重要的作用,该理论假设玩家足够理性,目的是为了确保玩家能够了解对手的战略,从而优化自身的策略[1,11-13].很多研究致力于在博弈系统中建立模型获得系统最优,如石头剪刀布博弈系统动力学模型[14-15]、无标度网络记忆模型[16]和循环占优模型[17-19].此外,由于凸优化具有较好的可扩展性和广泛的应用性,常用于解决电子技术[20-21]和软件工程[22-25]等方面的优化问题.
目前,对凸优化的研究越来越受到重视,但将其应用于最优化博弈系统的研究鲜有报道.本文提出用凸优化优化博弈系统中玩家的收益,通过在凸优化模型中设定不同的值进行仿真,使系统最大收益处鞍点方程成立,从而证明凸优化的可行性,这在理论研究和实际应用中具有一定的创新性和前瞻性.
1 模 型
本文以2人非零和石头剪刀布为例研究非合作博弈系统,系统中每个玩家进行多次回合,每轮玩家可以选择石头(rock,R)、剪刀(scissors,S)、布(paper,P)中的任意一个动作,如图1所示.收益g(g>1)被定义为决定胜负的唯一参数[1],玩家根据g的大小决定选择的动作,如图2所示.当两个玩家(X和Y)选择相同的动作时,玩家X和玩家Y同时取得单位为1的收益;当玩家X击败玩家Y时,玩家X的收益为g,玩家Y的收益为0,反之亦然.

图1 收益树状图Fig.1 Payoff trees

图2 收益矩阵Fig.2 Payoff matrix
2 RPS博弈系统的凸优化
2.1凸优化方程的引入
玩家X和玩家Y每轮收益的期望值分别为
WX=XTAY
(1)
WY=YTAX
(2)

与传统的收益方程相比,本文的收益方程是严格凸的.以下为凸优化问题
XR+XP+XS=1;YR+YP+YS=1
(3)
(4)

式中:玩家X的策略i∈{1,2,3};玩家Y的策略j∈{1,2,3}.
如上所述,式(1)~(4)具有凸性,因此所有最优解是全局最优解.Boyd等[26]表示凸优化是一个基本属性,任何局部优化鞍点都是(全局)最优的.进一步假设,式(5)和式(6)严格可行.
2人非零和博弈系统的矩阵形式表示为YTAX+XTAY≠0.为定量研究该系统,假设玩家X先作选择,然后玩家Y根据玩家X的选择再作决定.玩家X想最小化收益WY,而玩家Y想最大化收益WY.同理,玩家X想最大化收益WX,而玩家Y想最小化收益WX.
玩家X最佳策略是利用变量X最小化收益YTAX
(7)
而玩家Y利用变量Y最大化收益
(8)
YRXR+YPXP+YSXS+g(YRXS+YPXR+YSXP)=
(YR+gYP)XR+(YP+gYS)XP+(YS+gYR)XS
(9)
假设χ=YR+gYP,ξ=YP+gYS,μ=YS+gYR.XR,XP,XS表示收益概率,χ,ξ,μ表示收益值.


(10)
式中:i为确定性策略;ei为第i个位置为1,其他位置全为零的矩阵.
凸优化函数标准形式为
(11)
引入变量α表示内部最小化的值
(12)
矩阵向量表示为
(13)

2.2鞍点方程

相当于
(14)

式(13)和式(14)分别为玩家X和Y的收益,两式为对偶关系(在博弈系统中玩家Y和玩家X是对偶关系).
最初假设玩家X和Y有先后顺序,实际上是玩家X和Y同时作决定.在此基础上,结合式(13)和式(14),有
(15)
式(15)称为鞍点方程,用于描述玩家获得最大收益时的鞍点.式(13)和式(14)分别为式(15)的两边.
同理,玩家X的收益用鞍点方程表示为
(16)
用于描述系统收益最大值.其中式(16)的两边分别用式(17)和式(18)表示.
(17)
(18)
3 算 法
3.1Newton算法
本文提出的鞍点方程是用于表示系统收益最优的临界方程,为验证其正确性,利用Newton算法证明.
对于z∈domf,称向量
Δznt=-2f(z)-1f(z)
(19)
为(f在z处的)Newton步径[26].由2f(z)的正定性可知,除非f(z)=0,否则就有
(20)
因此Newton步径为下降方向.

(21)
这是ν的二次凸函数,在ν=Δznt处达到最小值.因此,将z加上Newton步径Δznt能够极小化f在z处的二阶近似[26].
凸优化问题
(22)
(23)
可将Newton方向Δznt及其相关向量w解释为最优性条件
Cz*=D,f(z*)+CTz*=
ATy+CTν*=0
(24)
的线性近似方程组的解.用z+Δznt代替z*,用w代替ν*,并将第二个方程中的梯度项换成其在z附近的线性近似,从而得到
C(z+Δznt)=D,f(z+Δznt)+
CTw≈ATy+0+CTw=0
(25)
利用CX=D,以上方程变为
CΔznt=0,CTw≈-ATy
(26)
Newton方向Δznt由以下方程确定
(27)
式中,w是该二次问题的最优对偶向量.
Newton方向Δznt和Newton减量λ(z)分别为
(28)
3.2验证理论

图3 WX为玩家X获得的最大回报值,WY为玩家Y获得的最大回报值(单位为g1).Fig.3 Biggest gain of player X isWX,the biggest gain of player Y is WY (in units of g1).
4 结 论
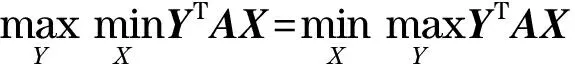
[1] WANG Z J,XU B,ZHOU H J.Social cycling and conditional responses in the rock-paper-scissors game[J].Scientific Reports,2014,4:5830.
[2] BIERNASKIE J M,GARDNER A,WEST S A.Multicoloured greenbeards,bacteriocin diversity and the rock-paper-scissors game[J].Journal of Evolutionary Biology,2013,26(10):2081-2094.
[3] LAIRD R A.Population interaction structure and the coexistence of bacterial strains playing ‘rock-paper-scissors’[J].Oikos,2014,123(4):472-480.
[4] LOERTSCHER S.Rock-scissors-paper and evolutionarily stable strategies[J].Economics Letters,2013,118(3):473-474.
[5] HE Q,MOBILIA M,TäUBER U C.Spatial rock-paper-scissors models with in homogeneous reaction rates[J].Physical Review E,2010,82(5):051909.
[6] SINERVO B,HEULIN B,SURGET-GROBA Y,et al.Models of density-dependent genic selection and a new rock-paper-scissors social system[J].The American Naturalist,2007,170(5):663-680.
[7] KERR B,RILEY M A,FELDMAN M W,et al.Local dispersal promotes biodiversity in a real-life game of rock-paper-scissors[J].Nature,2002,418(6894):171-174.
[8] BI Z D,ZHOU H J.Optimal cooperation-trap strategies for the iterated rock-paper-scissors game[J].PLoS One,2014,9(10):e111278.
[9] ZHOU H J.The rock-paper-scissors game[J].Contemporary Physics,2016,57(2):151-163.
[10] AUMANN R J,BRANDENBURGER A.Epistemic conditions for Nash equilibrium[J].Econometrica,1995,63(5):1161-1180.
[11] 汪筱阳,吴德伟,戴传金.基于纳什博弈论的功率控制策略及其牛顿迭代算法[J].电子设计工程,2013,21(1):74-76.
[12] BAHEL E,HALLER H.Cycles with undistinguished actions and extended rock-paper-scissors games[J].Economics Letters,2013,120(3):588-591.
[13] BAHEL E.Rock-paper-scissors and cycle-based games[J].Economics Letters,2012,115(3):401-403.
[14] WESSON E,RAND R.Hopf bifurcations in delayed rock-paper-scissors replicator dynamics[J].Dynamic Games and Applications,2016,6(1):139-156.
[15] SEMMANN D,KRAMBECK H J,MILINSKI M.Volunteering leads to rock-paper-scissors dynamics in a public goods game[J].Nature,2003,425(6956):390-393.
[16] LUBASHEVSKY I,KANEMOTO S.Scale-free memory model for multiagent reinforcement learning.Mean field approximation and rock-paper-scissors dynamics[J].The European Physical Journal B,2010,76(1):69-85.
[17] MOBILIA M.Oscillatory dynamics in rock-paper-scissors games with mutations[J].Journal of Theoretical Biology,2010,264(1):1-10.
[18] VERMA G,CHAN K,SWAMI A.Zealotry promotes coexistence in the rock-paper-scissors model of cyclic dominance[J].Physical Review E,2015,92(5):052807.
[19] SZOLNOKI A,PERC M.Zealots tame oscillations in the spatial rock-paper-scissors game[J].Physical Review E,2016,93(6):062307.
[20] 曾勇.基于博弈论的无线通信抗干扰关键技术研究[D].成都:电子科技大学,2014.
[21] JOSHI S,BOYD S.Sensor selection via convex optimization[J].IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,2009,57(2):451-462.
[22] 唐璜,毛璐.基于博弈论的软件动态调控策略的研究与实现[J].信息与电脑,2012(2):50-51.
[23] MATTINGLEY J,BOYD S.Cvxgen:a code generator for embedded convex optimization[J].Optimization and Engineering,2012,13(1):1-27.
[24] WANG T,JOBREDEAUX R,PANTEL M,et al.Credible autocoding of convex optimization algorithms[J].Optimization and Engineering,2016,17(4):781-812.
[25] 刘海姣,赵书田.一种关联博弈的软件调度线性规划控制算法[J].微电子学与计算机,2016,33(7):121-124.
[26] BOYD S,VANDENBERGHE L.Convex optimization[J].IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,2006,51(11):1859-1859.
OptimizingStrategyforGameTheorySystemBasedontheConvexOptimizationMethod
TIAN Wei,LIUYifang
(CollageofScience,UniversityofShanghaiforScienceandTechnology,Shanghai200093,China)
The convex optimization,which serves as a new optimized method,can be fully applied to the game theory system,aiming at maximizing the payoff of the game systems (for all players).The two-person non-zero-sum matrix was introduced to describe the equivalent of payoff in the hypothetical game theory system for making quantitative analyses and getting maximal payoff of the system.A saddle point equation was created to be the critical equation of the optimal value of the game theory system and Newton’s algorithm was used to simulate the game model.The simulation results show that,the results are consistent with the theoretical hypothesis values.The method was tested and verified to be feasible and accurate.The work is helpful for deeply understanding the game theory system and reasonably applying the convex optimization.
simulation;convexoptimization;gametheorysystem;saddlepoint
1007-6735(2017)05-0420-05
10.13255/j.cnki.jusst.2017.05.003
2017-05-21
国家自然科学基金资助项目(10874118)
田 伟(1977-),男,讲师.研究方向:系统分析与集成.E-mail:tianwei@usst.edu.cn
O174.13
A
(编辑:丁红艺)
