基于柔性三齿配体的镉和锌配合物的合成、结构和荧光性质
2017-11-01王红艳董益利胡炯圣刘冬菊刘红科
吴 琪 苏 志 王红艳董益利 胡炯圣刘冬菊 吴 昶 徐 芸 应 翱 方 敏*, 刘红科*,,2
吴 琪1苏 志1王红艳1董益利1胡炯圣1刘冬菊1吴 昶1徐 芸1应 翱1方 敏*,1刘红科*,1,2
(1南京师范大学化学与材料科学学院,江苏生物功能材料重点实验室,南京 210023)
(2南京大学配位化学国家重点实验室,南京 210023)
柔性三齿配体 1,3,5-tris(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylbenzene(TITMB)和 1,3,5-tris(triazol-1-ylmethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylbenzene(TTTMB)与金属镉和锌分别反应,合成了配合物{[Cd3(SO4)4(TITMB)2(H2O)4][Cd(H2O)6]·2CH3OH}n(1)和{[Zn(TTTMB)(HCOO)2]·CH3OH}n(2)。配合物1和2均采用单晶X射线衍射、红外光谱、固态荧光、热重分析和元素分析进行了表征。在配合物1中,存在着由硫酸根离子和Cd构成的一维链,其再与配体TITMB配位形成二维层状结构,[Cd(H2O)6]2+位于层与层中间平衡电荷。配合物2具有典型的63二维蜂窝状拓扑结构。配合物1和2中的二维层状结构,均通过氢键作用延伸成为三维结构。配合物1和2均具有较高的热稳定性,并且在固态下释放蓝色荧光。
柔性三齿配体;配位聚合物;荧光性质
In recent years,the rational design and assembly of metal organic frameworks(MOFs)have attracted great attention due to their intriguing framework structures and potential applications in optical,gas storage,catalysis,and so on[1-8].In general,the resulted structures of MOFs could be influenced by several factors,such as the selection of metal centers,organic ligands and the reaction pathways[9].In contrast to the rigid ligands with fixed conformations,flexible ligands may adopt variable conformations to satisfy the requirement of the center metal ions[10-11].In previous work,the utilization of flexible tripodal nitrogen-including ligands have been proved to be effective candidates to build MOF structures,such as 1,3,5-tris(4-pyridylmethyl)benzene[12],1,3,5-tris(pyrazol-1-ylmethyl)-2,4,6-triethylbenzene[13], 1,3,5-tris(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene[14],and 1,3,5-tris(benzimidazole-1-ylmethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylbenzen[15].Herein,the structures and properties of two two-dimensional(2D)coordination polymers based on the 1,3,5-tris(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylbenzene (TITMB)and 1,3,5-tris(triazol-1-ylmethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylbenzene(TTTMB)have been synthesized and characterized,where both TITMB and TTTMB ligands have adopted cis,cis,trans-configuration(Scheme 1)[16-18].
1 Experimental
1.1 Materials and measurements
All commercially available chemicals are of reagent grade and were used as received without further purification.TITMB and TTTMB were prepared according to the literature methods[19].The C,H and N analyses were performed on a Perkin-Elmer 240C elemental analyzer.Infrared (IR)spectra were recorded on a NEXUS670 spectrophotometer by using KBr pellets.Thermogravimetric analyses(TGA)were performed on a Perkin Elmer instruments Diamond Thermogravimetric/Differential Thermal Anal-yzer under nitrogen with a heating rate of 10℃·min-1.The luminescence spectra were measured at room temperature on PEKIN ELMER Luminescence Spectrometer LS50B.
1.2 Synthesis of complex{[Cd3(SO4)4(TITMB)2(H2O)4][Cd(H2O)6]·2CH3OH}n(1)
A mixture of CdSO4·8/3H2O (8.54 mg,0.041 mmol),ligand TITMB(16.6 mg,0.046 mmol),and 1,4-bis(trazol-1-ylmethyl)-2,3,5,6-tetramethylbenzene(p-BTTMB)(12.4 mg,0.042 mmol)was suspended in 4 mL mixed solvents of methanol and H2O (1∶3,V/V),and heated in a Teflon-lined steel bomb at 120℃for 2 d.After the mixture was slowly cooled to room temperature,colorless crystals of 1 were obtained.Anal.Calcd.for C44H76Cd4N12O28S4(%):C,29.37;H,4.25;N,9.34.Found(%):C,29.28;H,3.88;N,9.00.IR(KBr,cm-1):3 381(s),1 621(m),1 520(m),1 457(w),1 400(w),1 319(m),1 246(m),1 237(m),1 118(s),980(w),935(w),760(m),660(m).
1.3 Synthesis of{[Zn(TTTMB)(HCOO)2]·CH3OH}n(2)
A mixture of Zn(CH3COO)2·2H2O(87.2 mg,0.4 mmol),TTTMB (145.6 mg,0.4 mmol),1,3-bis(1-imidazo)-1-ylmethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylbenzen(m-BITMB)(112.0 mg,0.4 mmol),3 mL methanol and 1 mL ethanol was placed in a 10 mL glass vial and dissolved by ultrasound.Methanoic acid was added to adjust pH value to 4.The glass vial was transferred into a 30 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel vessel and heated at 80℃for 3 d.After the mixture was slowly cooled to the room temperature,colorless crystals of 2 were obtained.Anal.Calcd.for C21H27N9O5Zn(%):C,45.74;H,4.90;N,22.87.Found(%):C,45.00;H,4.80;N,22.58.IR(KBr,cm-1):3 398(m),3 087(m),3 005(m),2 821(m),2 744(w),1 712(w),1 611(s),1 524(m),1 448(m),1 339(s),1 280(s),1 221(w),1 201(w),1 132(s),1 033(w),1 013(w),1 005(w),994(s),875(w),773(m),674(s).
1.4 X-ray crystal structure determinations
The single crystals of both complexes 1 and 2 were mounted onto thin glass fibers by epoxy glue in air for data collection.And the diffraction data for complexes 1 and 2 were collected on a Bruker Apex 2 CCD with Mo Kα radiation(λ=0.071 073 nm)using ω-2θscan method at 298 K.An empirical absorption correction was applied.All the non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically.The hydrogen atoms of organic molecule were refined in calculated positions,assigned isotropic thermal parameters,and allowed to ride their parent atoms,while the H atoms for water are located from different map.All calculations were performed using the SHELX-97 program package[20].In complex 1,the sulfate oxygen atoms(O1,O2,O4 and O6,O7,O8)split to two parts with the occupation of 0.66(2)and 0.34(2),0.59(3)and 0.41(3),respectively.Details of the crystal parameters,data collections and refinements for 1 and 2 are summarized in Table 1.Selected bond lengths and angles,and hydrogen bonds for 1 and 2 are listed in Table 2 and Table 3,respectively.
CCDC:808063,1;808067,2.

Table 1 Crystal data and structural refinement of complexes 1 and 2

Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and angles(°)for complexes 1 and 2
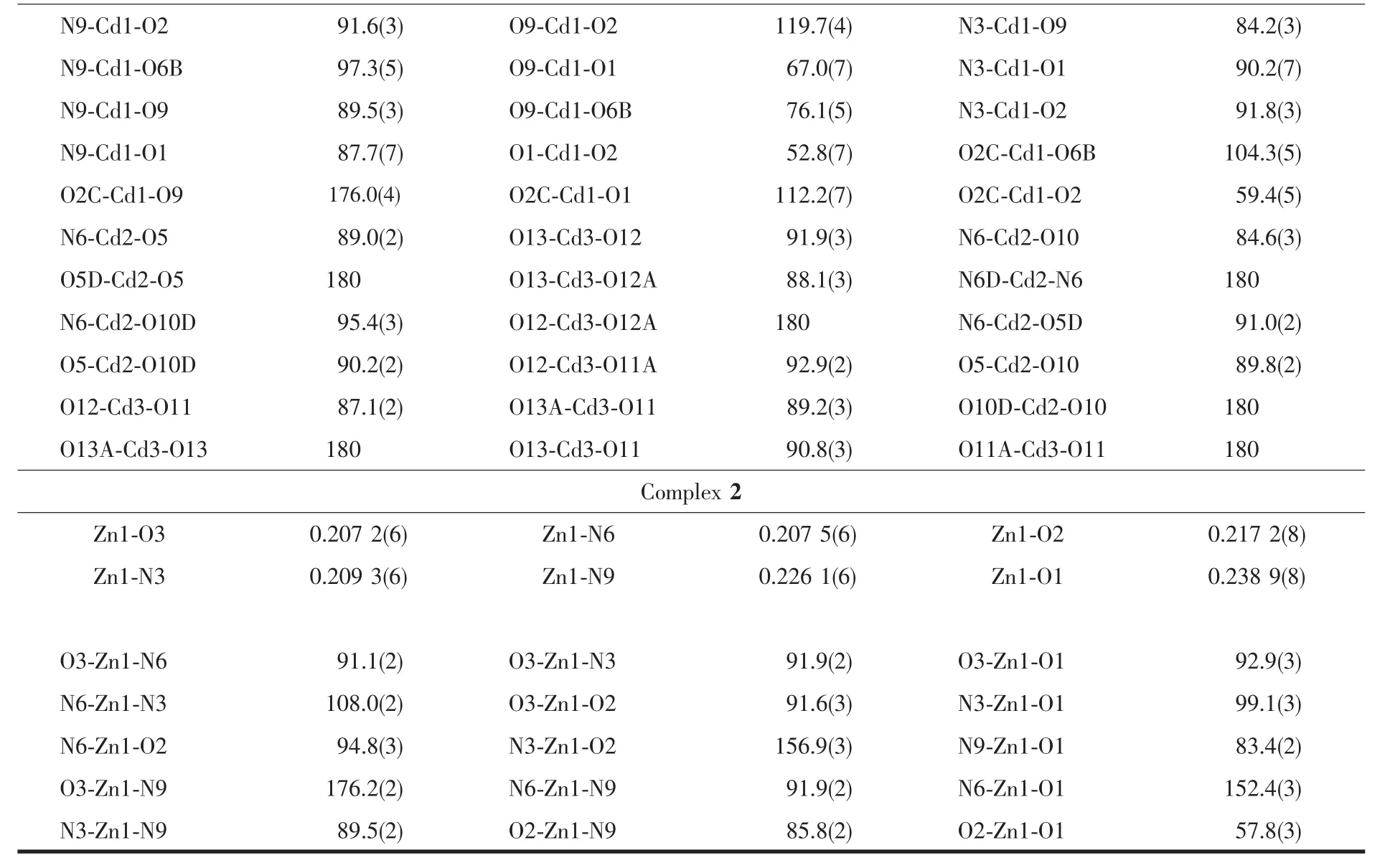
Continued Table 1
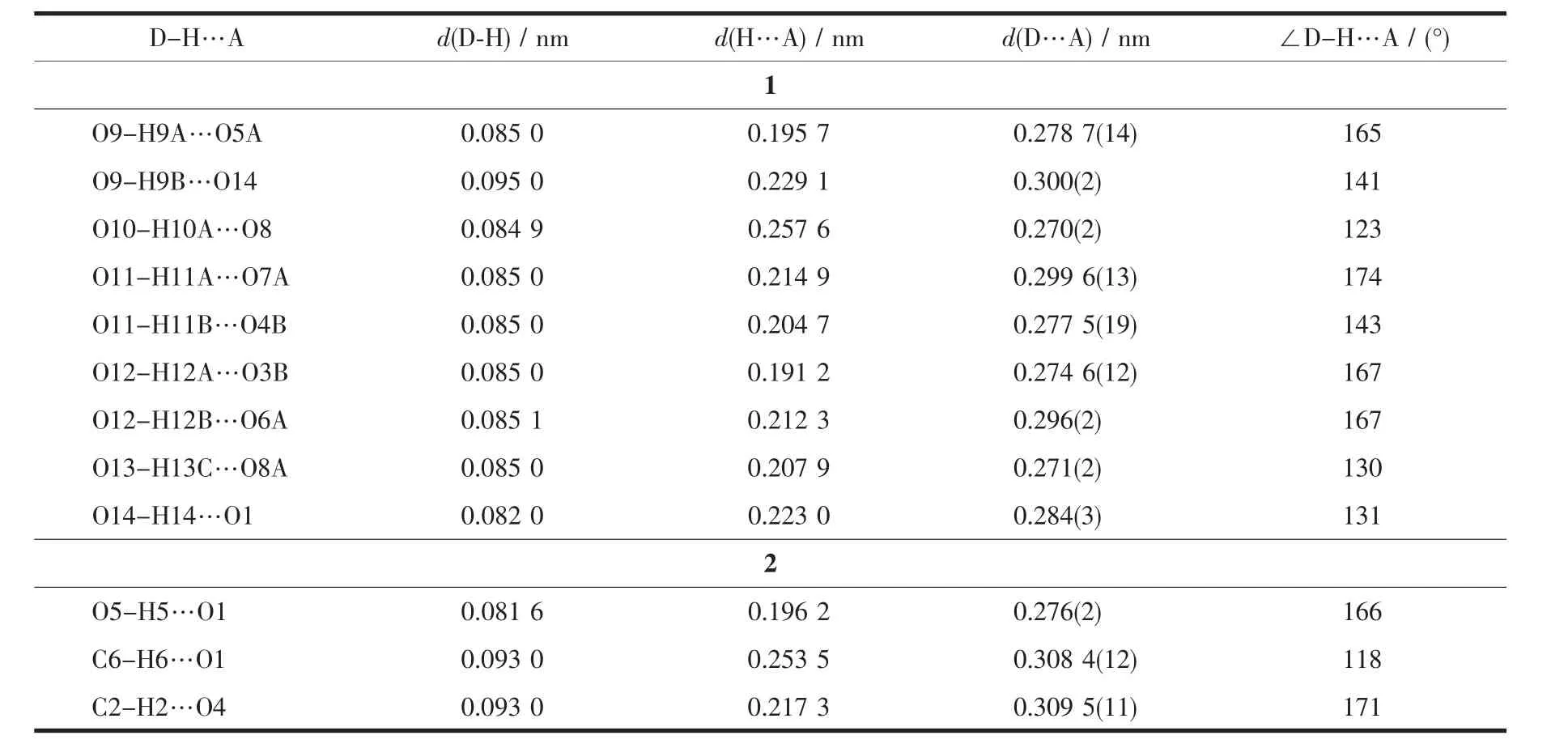
Table 3 Hydrogen bond lengths(nm)and angles(°)for complexes 1~2
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Crystal structure of complex 1
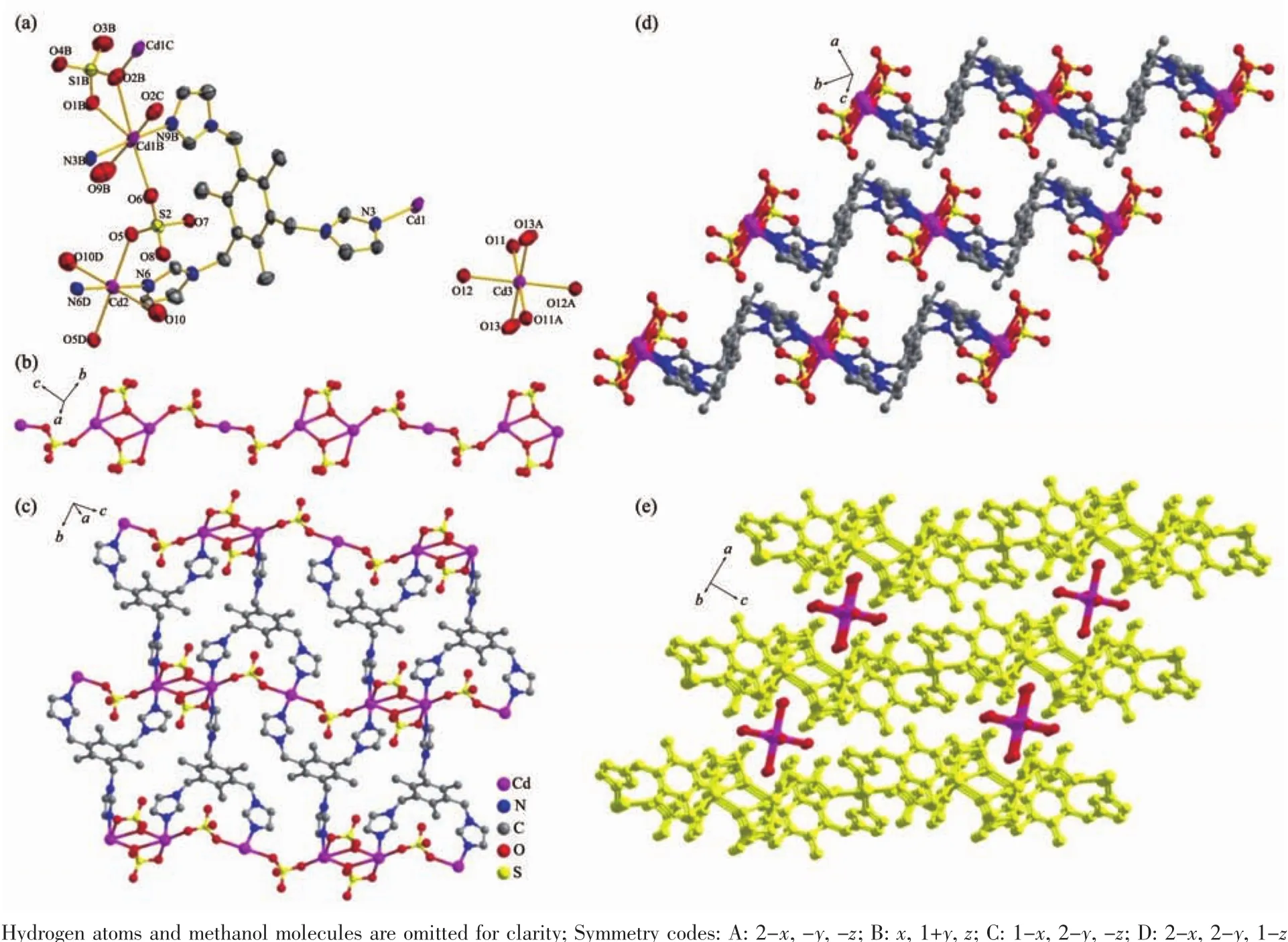
Fig.1 (a)View of ORTEPdrawing of complex 1 with 30%ellipsoid;(b)One dimensional inorganic chain formed by bridging sulfate anion and Cd;(c)Two dimensional network constructed by TITMB ligands with 1D inorganic chain;(d)AAA stacking modes in complex 1;(e)Cd(H2O)6 units located between the 2D networks further extending the 2D network to 3D framework through hydrogen bonds
Single crystal X-ray diffraction reveals that complex 1 crystallizes in the triclinic P1 space group.There are two independent units in complex 1:[Cd3(SO4)4(TITMB)2(H2O)4]2-and[Cd(H2O)6]2+.In complex 1,three crystallographic distinct Cdions exist(Fig.1):one seven coordinated Cd1 with bipyramidal geometry and two six coordinated Cd2 and Cd3 with distorted octahedral geometry(Fig.1a).Each Cd1 is coordinated by two nitrogen atoms (N9B and N3B)from imidazole rings,four oxygen atoms (O1B,O2B,O2C and O6)from three distinct sulfate anions and one terminated water molecule (O9B).Each Cd2 sitting at symmetric center is coordinated by two nitrogen atoms(N6 and N6D)from two imidazole rings,two oxygen atoms (O5 and O5D)from two different sulfate anions and two terminal water molecules(O10 and O10D).Each Cd3 was coordinated by six water molecules and independently located in complex 1.The average bond length of Cd-N and Cd-O is comparable to previously reported[21].
Each sulfate anion in complex 1 coordinates two Cdions through adopting two different bridging modes(η1-η1-η0-η0-and η1-η2-η0-η0-coordination mode for the four oxygen atoms,respectively),which extends to one dimensional(1D)inorganic chain(Fig.1b).The 1D chains are further linked by the TITMB ligand with cis,cis,trans-configuration to two dimensional(2D)network(Fig.1c),where each TITMB ligand coordinates to three Cdcenters.The 2D networks stack in an AAA sequence along the b axis(Fig.1d),where the[Cd(H2O)6]2+units locate in the cavity between two adjacent 2D layers by hydrogen bonds to neutralize the charge (Fig.1e).The strong O-H…O hydrogen bonds between the Cd(H2O)6units and the sulfate anions facilitated the formation of the 3D structure of complex 1,where the distance between the donor oxygen atom to the acceptor oxygen atom was in the range of 0.270(2)~0.300(2)nm(Table 3).
2.2 Crystal structure of complex 2
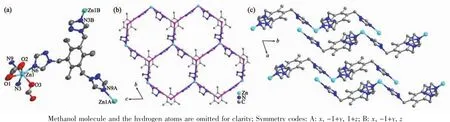
Fig.2 (a)View of ORTEPof complex 2 with 30%ellipsoid;(b)Two dimensional honeycomb 63 network built by TTTMB ligand with Zncenters;(c)ABAB packing mode of 2D layers along a axis in complex 2
As shown in Fig.2,the asymmetric unit of complex 2 contains one zinc,one TTTMB ligand and two methanoic acid,and one methanol molecular.Single crystal X-ray crystallographic analyses reveal that each zincis six-coordinated with a distorted octahedral geometry by three nitrogen atoms(N3,N6 and N9)from three different TTTMB ligands and three oxygen atoms(O1,O2,O3)from two methanoic acid(Fig.2a).Two methanoic acids present two different coordination modes,chelate and monodentate,respectively[17].The Zn-Obond distances vary from 0.207 2(6)to 0.238 9(8)nm,and the Zn-N distances are in the range of 0.207 5(6)~0.226 1(6)nm.
A typical 632D topological network is found in complex 2,where each TTTMB ligand coordinates to three Zncenters and is considered as a 3-connected nodes.The 2D networks stack in an ABAB packing sequence and further extend to a 3D structure by hydrogen bonds between the methanoic acid and methanol molecules(Table 3).
2.3 Thermal stability analyses
Thermogravimetric analyses were performed on grounded samples of 1 and 2 to evaluate their thermal robustness and decomposition behavior and the results areshown in Fig.3a.Up to 350℃,complex 1 undergoes continuous weight loss of 13.1%due to the release of two free methanol and ten coordinated water molecules(Calcd.13.6%).Obvious rapid weight loss is observed after heating over 350℃,which suggests the structure decomposition of complex 1.For complex 2,the first weight loss(11.1%)under 90℃may be assigned to the loss of methanol molecule (5.8%)and partially release of methanoic acid,and the structure could maintained up to 250℃.
2.4 Photoluminescence property
Thephotoluminescenceof ligands TITMB,TTTMB,complexes 1 and 2 was studied in the solid state at room temperature.The excitation wavelength for TITMB and 1,TTTMB and 2 is 330 and 280 nm,respectively.The results were depicted in Fig.3b and 3c.
Complex 1 shows a weak emission band at 400 nm and a strong peak at 450 nm upon the excitation(Fig.3b).Since free ligand TITMB displays an emission band at 402 nm upon the excitation,the emission band of complex 1 at 400 nm should be due to the ligand-to-ligand (π-π*)charge transfer(LLCT)[22-24].The 450 nm band should be ascribed to the ligand-to-metal charge transfer(LMCT)[25-27].Complex 2 exhibits very similar emission band at 498 nm comparing to the free TTTMB ligand(Fig.3c).Thus,the emission of complex 2 is assigned to be ligand-based(LLCT)[28-29].
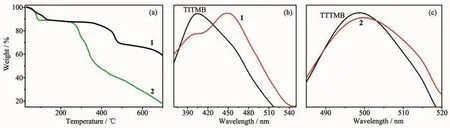
Fig.3 TGA curves of complexes 1 and 2(a),solid state photoluminescence emission spectra of ligand TITMB and complex 1 with 330 nm excitation(b),ligand TTTMB and complexes 2 with 280 nm excitation(c),respectively
3 Conclusions
Two new 2D coordination polymers based on flexible tripodal ligands of TITMB and TTTMB have been synthesized and characterized.In both complexes,the TITMB and TTTMB adopt cis,cis,trans-configuration.The counter anions play an important role in the construction of coordination polymer in consideration of their different coordination ability,size and so on.In this work,sulfate anions participate in the coordination of the resulted structure of complex 1 as the bridging ligand,while in complex 2,act as terminal coordination ligand only.In addition,complexes 1 and 2 display blue fluorescent emissions in the solid state at room temperature.
[1]Feng D W,Jiang H L,Chen Y P,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2013,52:12661-12667
[2]Zhou H C,Long JR,Yaghi OM.Chem.Rev.,2012,112:673-674
[3]Liu J,Thallapally PK,McGrail B P,et al.Chem.Soc.Rev.,2012,41:2308-2322
[4]Liu H K,Tan H Y,Liao S,et al.Chem.Commun.,2001:1008-1009
[5]Feng D W,Gu Z Y,Li J R,et al.Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.,2012,51:10307-10310
[6]Jiang H L,Feng D W,Wang K C,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2013,135:13934-13938
[7]Chen Y,Lykourinou V,Carissa V,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2012,134:13188-13191
[8]Wiester M J,Ulmann P A,Mirkin C A.Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.,2011,50:114-137
[9]Chen Y,Lykourinou V,Hoang T,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2012,51:9156-9158
[10]Liu H K,Sun WY,Zhu H L,et al.Inorg.Chim.Acta,1999,295:129-135
[11]XU Zhou-Qing(徐周庆),HE Ya-Ling(何亚玲),LI Hui-Jun(李慧军),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(无机化学学报),2017,33(5):897-904
[12]Hiroyasu F,Felipe G,Zhang Y B,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2014,136:4369-4381
[13]Reinsch H,Marszalek B,Wack J,et al.Chem.Commun.,2012,48:9486-9488
[14]Yin X J,Zhou X H,Gu Z G,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun.,2009,12:548-551
[15]Henninger SK,Jeremias F,Kummer H,et al.Eur.J.Inorg.Chem.,2012,16:2625-2634
[16]Fan J,Zhu H F,Okamura T,et al.Chem.Eur.J.,2003,9:4724-4731
[17]Fan J,Zhu H F,Okamura T,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2003,42:158-162
[18]Yan W,Han L J,Jia H L,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2016,55:8816-8821
[19]Nguyen JG,Cohen SM.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2010,132:4560-4561
[20]Sheldrick G M.SHELXS-97,Program for X-ray Crystal Structure Solution and Refinement,University of Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[21]ZHAO Lun(赵仑),CHEN Rui-Zhan(陈瑞战),WANG Zi-Chen(王子忱).Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(无机化学学报),2016,32(7):1190-1198
[22]ZHAO Yue(赵越),ZHAI Lin-Lin(翟玲玲),SUN Wei-Yin(孙为银).Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(无机化学学报),2014,30(1):18-22
[23]Hu T P,Xue Z J,Zheng B H,et al.CrystEngComm,2016,18:5386-5392
[24]Khatua S,Kang J,Huh JO,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2010,10:327-334
[25]Bach S,Panthöfer M,Bienert R,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2016,16:4232-4239
[26]Dong W W,Xia L,Peng Z,et al.J.Solid State Chem.,2016,238:170-174
[27]Wang J,Zhang X,Wei Q L,et al.Nano Energy,2016,19:222-233
[28]Sun D R,Sun F X,Deng X Y,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2015,54:8639-8643
[29]Sun D R,Ye L,Sun F X,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2017,56:5203-5209
Syntheses,Crystal Structures and Fluorescence of Cadmiumand ZincComplexes Based on Flexible Tripodal Ligands
Two new coordination polymers,{[Cd3(SO4)4(TITMB)2(H2O)4][Cd(H2O)6]·2CH3OH}n(1)and{[Zn(TTTMB)(HCOO)2]·CH3OH}n(2),based on the flexible tripodal ligands1,3,5-tris(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylbenzene(TITMB)and 1,3,5-tris(triazol-1-ylmethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylbenzene(TTTMB),have been synthesized and characterized by single-crystal XRD analyses,IR spectra,solid state photoluminescence studies,thermogravimetric analyses,and elemental analyses.Single-crystal X-ray diffraction reveals that both complexes 1 and 2 are twodimensional layers,and extended to three-dimensional structure by hydrogen bonds.In complex 1,inorganic chains constructed by SO42-and Cdare linked by ligand TITMBto the 2Dnetworks,where the[Cd(H2O)6]2+units locate in the cavity between two adjacent 2D layers by hydrogen bonds to neutralize the charge.Complex 2 owns typical 632D topological networks.The thermal stability and photoluminescence property were also studied.Both complexes show high thermal stabilities and display blue fluorescent emissions in the solid state at room temperature.CCDC:808063,1;808067,2.
flexible tripodal ligand;coordination polymers;luminescence property
O614.24+2;O614.24+1
A
1001-4861(2017)10-1889-07
10.11862/CJIC.2017.196
WU Qi1SU Zhi1WANG Hong-Yan1DONG Yi-Li1HU Jiong-Sheng1LIU Dong-Ju1WU Chang1XU Yun1YING Ao1FANG Min*,1LIU Hong-Ke*,1,2
(1College of Chemistry and Materials Science,Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Biofunctional Materials,Nanjing Normal University,Nanjing 210023,China)
(2State Key Laboratory of Coordination Chemistry,Nanjing University,Nanjing 210023,China)
2017-05-02。收修改稿日期:2017-06-08。
国家自然科学基金国际合作重点项目(No.21420102002)和国家自然科学基金(No.21601088,21401105)资助。*
。 E-mail:liuhongke@njnu.edu.cn,fangmin@njnu.edu.cn
