新型农村合作医疗卫生政策对农村卫生费用的影响研究
2017-09-14范忭斐李丽清刘巧艳
范忭斐,李丽清,*,刘巧艳
·卫生经济与管理研究·
新型农村合作医疗卫生政策对农村卫生费用的影响研究
范忭斐1,李丽清1,2*,刘巧艳2
目的探讨新型农村合作医疗(新农合)卫生政策对农村卫生费用的影响,为新农合卫生政策的稳步推进提供建议。方法收集卫生总费用、农村卫生费用、农村人均卫生总费用、参合率、村卫生室数、乡村医生和卫生员数、需住院而未住院比例、农民人均医疗保健支出及占比、农民个人现金卫生支出及占比等指标数据,通过比较新农合卫生政策实施前后农村卫生费用的变化,探讨新农合卫生政策对农村卫生费用的影响。结果农村卫生费用从2001年的2 248.70亿元增至2013年的11 026.97亿元,增加8 778.27亿元,增幅为390.37%。农村人均卫生总费用从2001年的246.49元增至2013年的1 717.01元,增加1 470.52元,增幅为596.58%。参合率在2004年为75.2%,2014年为98.9%,增幅为31.52%,参合率稳步提高。乡镇卫生院的病床使用率由2003年的36.2%增加到2014年的60.5%,增幅为67.13%。农村需住院而未住院比例由2003年的30.3%下降至2013年的16.7%,下降了13.6个百分点。农村居民的人均医疗保健支出由2001年的96.61元增加至2014年的753.90元,增加了657.29元,增幅为680.35%,占人均纯收入比例、占人均生活消费支出比例也呈增高趋势。农村居民的个人现金卫生支出由2001年的1 491.60亿元增加至2014年的3 883.90亿元,增幅为160.38%;而个人现金卫生支出占卫生总费用的比例由2001年的29.68%下降至2014年的11.00%,下降了18.68个百分点。结论新农合卫生政策的实施造成农村卫生费用上升,农村的人均卫生总费用、参合率、人均医疗保健支出大幅增加,需住院而未住院的比例、个人现金卫生支出占比明显下降。新农合卫生政策的落实,需要卫生费用的大力支持,国家需提供更多的医疗补助,加大宏观层面的卫生费用投入,降低微观个体的医疗负担。应继续着力推进新农合卫生政策,提高卫生服务的公平性。
新型农村合作医疗;卫生政策;农村卫生;卫生费用
范忭斐,李丽清,刘巧艳.新型农村合作医疗卫生政策对农村卫生费用的影响研究[J].中国全科医学,2017,20(25):3158-3162.[www.chinagp.net]
FAN B F,LI L Q,LIU Q Y.Effect of the implementation of the new rural cooperative medical scheme on the rural residents′ health expenditure in China[J].Chinese General Practice,2017,20(25):3158-3162.
卫生费用是在一定时期内社会卫生事业为提供卫生保健服务所耗费的经济资源,主要由政府、社会及个人卫生支出三部分构成。国内外学者关于卫生费用的研究步步深入,包括从宏观到微观、从经济到社会人口结构的研究分析,也有学者从城镇化进程的角度剖析其对卫生费用的影响及作用机制[1]。影响卫生费用的因素众多繁杂,包括国家层面的国内生产总值(GDP)、政府卫生支出、人口老龄化程度等[2-4];个人层面的家庭人均收入、文化程度、个人卫生现金支出等;卫生层面的医疗机构、基层卫生人员、医生专业能力及医德等[5-6]。卫生政策的实施反映了国家对卫生事业的支持力度,因此也会影响到同期卫生费用的改变。当前关于新型农村合作医疗(新农合)卫生政策的论证主要有以下两方面:一方面是新农合实施后的效果评价分析[7-9];另一方面是新农合实施对灾难性卫生支出的影响[10-12],但是新农合卫生政策对农村卫生费用的影响却少有研究。本研究探讨了新农合卫生政策对农村卫生费用的影响,以期为新农合的稳步推进提供借鉴,更好地实现新农合惠民利民的初衷。
1 研究方法
根据研究目的,本研究选取卫生总费用、农村卫生费用、农村人均卫生总费用、参合率、村卫生室数、乡村医生和卫生员数、需住院而未住院比例、农民人均医疗保健支出及占比、农民个人现金卫生支出及占比等指标。以上指标数据均来源于2001—2015年《中国统计年鉴》、2001—2015年《中国卫生(和计划生育)统计年鉴》及2014—2015年《中国卫生总费用研究报告》。通过比较新农合卫生政策实施前后农村卫生费用的变化,探讨新农合卫生政策对农村卫生费用的影响。
2 结果
2.1 我国农村卫生费用分析 我国卫生总费用由2001年的5 025.93亿元增至2014年的35 312.40亿元,增加30 286.47亿元;对GDP的占比从2001年的4.56%上升至2014年的5.55%,呈逐年上升趋势。农村卫生费用从2001年的2 248.70亿元增至2013年的11 026.97亿元,增加8 778.27亿元,增幅为390.37%。农村人均卫生总费用从2001年的246.49元增至1 717.01元,增加1 470.52元,增幅为596.58%,较同期农村卫生费用的增幅高。农村卫生费用与农村人均卫生总费用在2008年之后增速显著提高,增长态势明显(见表1)。
2.2 农村居民的医疗服务利用情况
2.2.1 参合率 参合率在2004年为75.2%,2014年为98.9%,增幅为31.52%。2004—2014年参合率稳步提高,2008年之后参合率高达90.0%以上。自2003年新农合试点以来,开展新农合的县市数量在2004—2008年增加明显,但是2008—2013年出现下降的趋势(见表2)。
2.2.2 农村医疗设施、医疗人员数及病床使用率 2003—2014年,村卫生室、乡村医生和卫生员数、乡镇卫生院的病床使用率呈平稳上升态势。村卫生室数由2003年的514 920个增加到2014年的645 470个,增幅为25.35%;乡村医生和卫生员数由2003年的867 778人增加到2014年的1 058 182人,增幅为21.94%;乡镇卫生院的病床使用率由2003年的36.2%增加到2014年的60.5%,增幅为67.13%(见表3)。
2.2.3 需住院而未住院比例 全国需住院而未住院比例由2003年的29.6%下降至2013年的17.1%,下降了12.5个百分点;农村需住院而未住院比例由2003年的30.3%下降至2013年的16.7%,下降了13.6个百分点(见表4)。
2.3 农村居民的卫生费用
2.3.1 农村居民的人均医疗保健支出 农村居民的人均医疗保健支出由2001年的96.61元增加至2014年的753.90元,增加了657.29元,增幅为680.35%,占人均纯收入比例、占人均生活消费支出比例也呈增高趋势(见表5)。
2.3.2 农村居民的个人现金卫生支出 农村居民的个人现金卫生支出由2001年的1 491.60亿元增加至2014年的3 883.90亿元,增幅为160.38%;而个人现金卫生支出占卫生总费用的比例由2001年的29.68%下降至2014年的11.00%,下降了18.68个百分点(见表6)。
表1 全国卫生总费用、农村卫生费用及农村人均卫生总费用的变化情况
Table1 China′s total national health expenditure in 2001—2014,and total health expenditure and total health expenditure per capita for rural residents in 2001—2013

年度 卫生总费用(名义值)费用(亿元) 增速(%) 占GDP比例(%)农村卫生费用费用(亿元) 增速(%)农村人均卫生总费用费用(元) 增速(%)2001年5025.93 9.58 4.562248.7014.59246.4914.832002年5790.0315.204.792426.207.89268.689.002003年6584.1013.714.822594.056.92292.768.962004年7590.2915.284.722946.2813.58335.1914.492005年8659.9114.094.662813.494.51377.4312.602006年9843.3413.674.523262.0215.94442.3617.202007年11573.9717.584.323558.409.09489.1310.572008年14535.4025.594.594493.7526.29622.9627.362009年17541.9220.685.085758.9428.15807.8429.682010年19980.3913.904.896492.3312.73967.3719.752011年24345.9121.855.038395.6429.321278.7332.192012年28119.0015.505.269632.6614.731499.9017.302013年31668.9512.625.3911026.9714.471717.0114.472014年35312.4011.505.55----
注:GDP=国内生产总值;-表示数据缺失
表2 新型农村合作医疗(新农合)的参合情况
Table2 Status of rural residents enrolling the NRCMS in China in 2004—2014
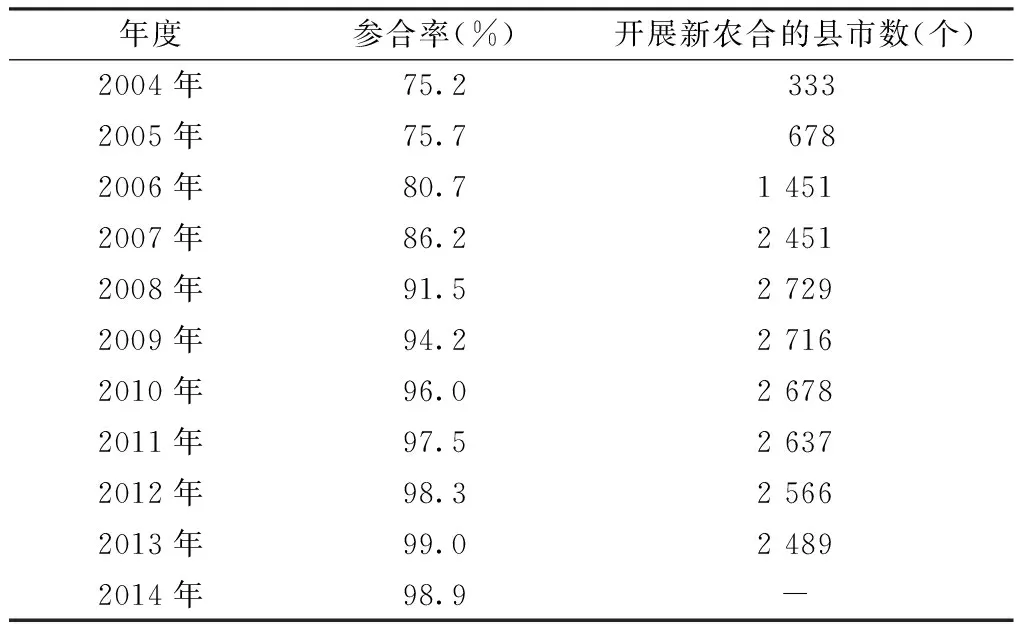
年度参合率(%)开展新农合的县市数(个)2004年75.2 3332005年75.7 6782006年80.714512007年86.224512008年91.527292009年94.227162010年96.026782011年97.526372012年98.325662013年99.024892014年98.9-
注:新农合自2003年开始试点,数据不能获取,故以2004年为起点;-表示数据缺失
表3 农村医疗设施、医疗人员数及病床使用率
Table3 Number of village clinics and rural physicians and utilization rate of beds in township hospitals in China in 2003—2014

年度村卫生室数(个)乡村医生和卫生员数(人)乡镇卫生院的病床使用率(%)2003年514920 86777836.22004年551600 88307537.12005年583209 91653237.72006年609128 95745939.42007年613855 93176148.42008年613143 93831355.82009年632770105099160.72010年648424109186359.02011年662894112644358.12012年653419109441962.12013年648619108106362.82014年645470105818260.5
表4 需住院而未住院比例(%)
Table4 Proportion of residents who need hospitalized treatment but do not receive it in China in 2003,2008 and 2013
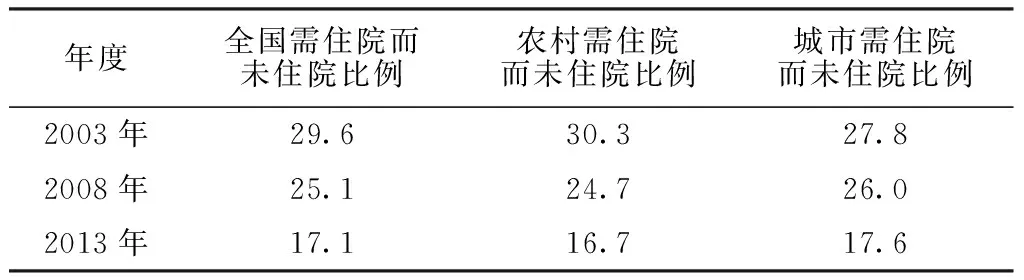
年度全国需住院而未住院比例农村需住院而未住院比例城市需住院而未住院比例2003年29.630.327.82008年25.124.726.02013年17.116.717.6
表5 农村居民的人均医疗保健支出
Table5 Status of healthcare expenditure per capita for rural residents in China in 2001—2014
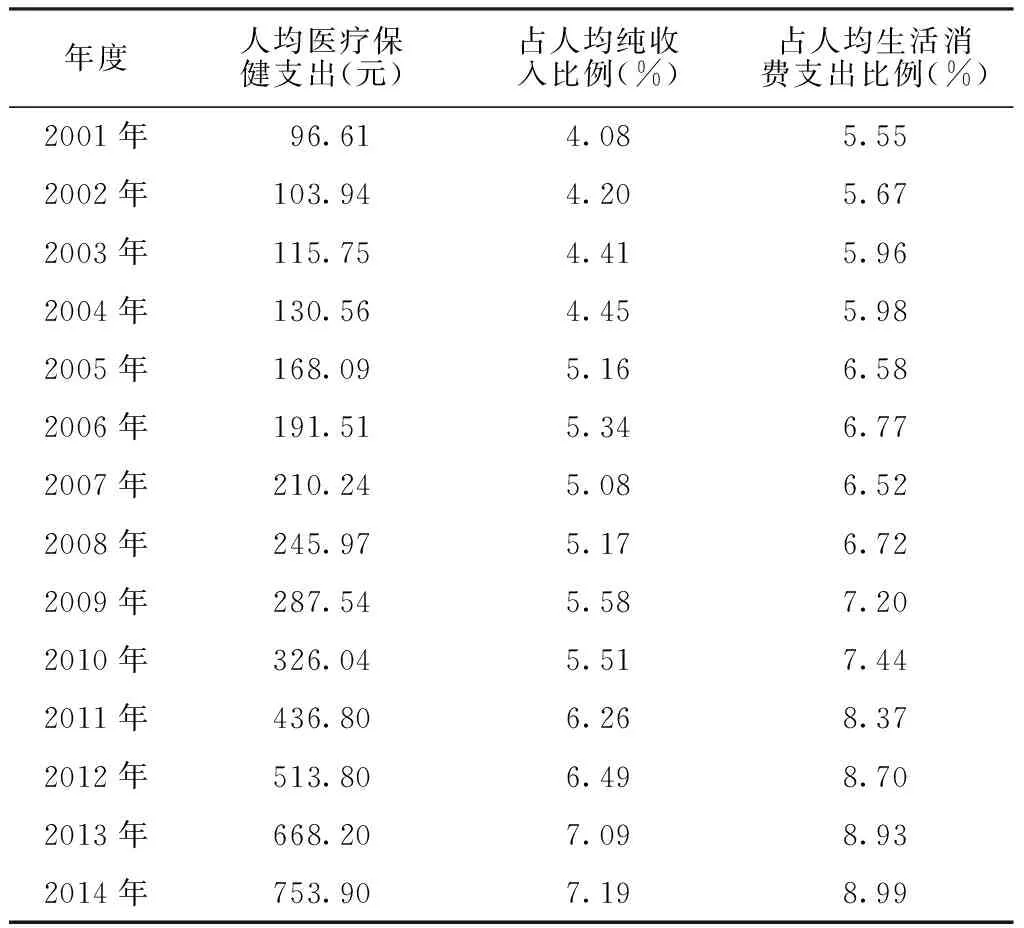
年度人均医疗保健支出(元)占人均纯收入比例(%)占人均生活消费支出比例(%)2001年 96.61 4.085.552002年103.944.205.672003年115.754.415.962004年130.564.455.982005年168.095.166.582006年191.515.346.772007年210.245.086.522008年245.975.176.722009年287.545.587.202010年326.045.517.442011年436.806.268.372012年513.806.498.702013年668.207.098.932014年753.907.198.99
表6 农村居民的个人现金卫生支出及占卫生总费用的比例
Table6 Total national amount of cash paid personally for healthcare services and its percent accounted of the total health expenditure in rural residents in China in 2001—2014

年度个人现金卫生支出(亿元)占卫生总费用的比例(%)2001年1491.6029.682002年1559.3026.932003年1670.1225.372004年1830.6124.122005年1599.6718.472006年1768.3117.962007年1529.5013.212008年1774.3012.212009年2049.8211.692010年2188.1510.952011年2867.8511.782012年3299.7311.732013年3865.1812.202014年3883.9011.00
3 讨论
随着社会医疗保障制度的日益健全,其在卫生费用筹资中发挥着主体作用,新农合作为其中的一部分,对卫生费用的增加起到助推作用[13]。新农合的实施与卫生费用之间的正相关关系已被大多学者所认可[14-15]。
本研究结果显示,新农合政策实施之后,政府重视卫生费用的支出,农村卫生费用从2003年的2 594.05亿元增加至2013年的11 026.97亿元,增幅为325.09%。新农合工作的逐步推进,不仅表现在农村卫生费用的增加,更多的是农民对医疗服务与设施的利用度。本研究以参合率、医疗设施利用率、需住院而未住院的比例来反映农村医疗工作的现状,考察新农合政策的实施对医疗条件和医疗服务利用率是否起到促进作用。研究结果显示,随着新农合覆盖面的推广,参加新农合的县市数与参合率不断上升;村卫生室、乡村医生和卫生员数、乡镇卫生院的病床使用率呈平稳上升态势;需住院而未住院的比例高于全国的降幅,说明新农合提高了健康服务的公平性和可及性,有效保障了农村居民就医的权利。本研究以农村居民人均医疗保健支出、个人现金卫生支出及占比来反映农村卫生费用的现状,来考察新农合政策的实施对农村卫生费用的影响。研究结果显示,人均医疗保健支出作为人均卫生费用的重要组成部分呈上升态势,从2001年的96.61元增加至2014年的753.90元,增加了657.29元,其占人均纯收入与人均生活消费支出的比例不断上升,特别是2003年新农合试点之后增速明显。个人现金卫生支出是导致人均卫生总费用增长的直接原因,农村人均卫生总费用从2001年的246.49元增加至2013年的1 717.01元,增加了1 470.52元,增幅为596.58%,这说明农村人均卫生总费用快速增加。而农民个人现金卫生支出占卫生总费用的比例从2001年的29.68%下降至2014年的11.00%,下降了18.68个百分点,说明政府与社会负担了卫生费用的大部分,农村居民的医疗卫生服务经济负担有所减轻。
新农合政策影响农村卫生费用上升的同时,更多的是促进医疗卫生工作有序开展,因此,针对如何继续有效推进新农合的实施工作,提出以下建议:(1)政府应积极制定合理的新农合监管激励机制,合理分配有限的卫生资源。针对不同级别的医院制定不同的用药标准与补偿标准,减少小病大治大养现象,缓解当前卫生资源相对匮乏的现状,提高医疗资源利用率,为实现新农合的公平性提供保障,使农民病有所治、病有所医。(2)充分利用大众传媒等社会宣传设施,加大对新农合的宣传,提升新农合的知晓度,使其深入人心。尤其要提升农村干部及医疗人员对新农合的系统性认识,设置固定的健康教育宣传栏,逐步消除农民对新农合的质疑和不认可的态度,使其充分认识并享有新农合的福利。(3)作为新农合的目标群体即我国农村居民应当强化自身医疗保健意识,关注自身健康问题的同时培养合理的就医习惯,端正就医的意图,不盲目就医,也不为私利骗取医疗补偿款,在医疗服务可及性的基础上提高看病就医的效用。
作者贡献:范忭斐负责论文的撰写,研究过程的实施,研究数据的获取与分析,得出结论;李丽清负责把握全文的研究命题,负责文章结构的完善,提供学术性建议;刘巧燕负责数据的整理,文献的提供。
本文无利益冲突。
[1]李丽清,杜福贻,刘巧艳,等.我国人口城镇化对卫生费用的影响[J].中国卫生经济,2016,35(4):51-53.DOI:10.7664/CHE20160414. LI L Q,DU F Y,LIU Q Y,et al.The impact of population urbanization on health expenditure in China[J].Chinese Health Economics,2016,35(4):51-53.DOI:10.7664/CHE20160414.
[2]颜梦欢,俞雯雅,马海燕.2000—2011年中国卫生总费用发展变化趋势分析[J].卫生软科学,2014,28(10):636-639.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-2800.2014.10.006. YAN M H,YU W Y,MA H Y.Analysis on development trend of Chinese total health expenditure from 2000 to 2011[J].Soft Science of Health,2014,28(10):636-639.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-2800.2014.10.006.
[3]王超群.老龄化是卫生费用增长的决定性因素吗?[J].人口与经济,2014,35(3):23-30.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-4149.2014.03.003. WANG C Q.Is aging the determinant of health expenditure growth or not?[J].Population & Economics,2014,35(3):23-30.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-4149.2014.03.003.
[4]文捷,杜福贻,李丽清,等.我国卫生总费用影响因素及实证研究[J].中国全科医学,2016,19(7):824-827.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2016.07.018. WEN J,DU F Y,LI L Q,et al.Influencing factors and empirical research of total expenditure on health in China[J].Chinese General Practice,2016,19(7):824-827.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2016.07.018.
[5]李丽清,杜福贻,卢祖洵,等.我国居民收入变化对卫生费用的影响及作用机理分析[J].中国卫生经济,2016,35(4):54-56.DOI:10.7664/CHE20160415. LI L Q,DU F Y,LU Z X,et al.Analysis on the impact of resident income changes on the health expenditure and its functional mechanism in China[J].Chinese Health Economics,2016,35(4):54-56.DOI:10.7664/CHE20160415.
[6]李丽清,卢祖洵,邬丹,等.社区卫生服务未来发展趋势的建模与仿真研究[J].中国全科医学,2016,19(1):12-18.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2016.01.003. LI L X,LU Z X,WU D,et al.Model building and simulation of the development trend of community health services in China[J].Chinese General Practice,2016,19(1):12-18.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2016.01.003.
[7]李扬.新型农村合作医疗试点地区卫生服务公平性研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2006. LI Y.Study on equity of health service in pilot areas of new rural cooperative medical service[D].Taiyuan:Shanxi Medical University,2006.
[8]葛智馨,陈英耀.我国农村基层医疗机构卫生服务质量管理问题研究[J].中国卫生质量管理,2013,20(3):5-8.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7515.2013.03.002. GE Z X,CHEN Y Y.Management of health services quality in rural primary medical agency in China[J].Chinese Health Quality Management,2013,20(3):5-8.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7515.2013.03.002.
[9]刘中正.吉林省新型农村合作医疗制度成效分析及未来展望研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2014. LIU Z Z.The effectiveness analysis and future research of new rural cooperative medical care system in Jilin Province[D].Changchun:Jilin University,2014.
[10]闫菊娥,闫永亮,郝妮娜,等.三种基本医疗保障制度改善灾难性卫生支出效果实证研究[J].中国卫生经济,2012,31(1):1-3.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-0743.2012.01.008. YAN J E,YAN Y L,HAO N N,et al.Empirical study on the relief effect of catastrophic health expenditure under three basic medical schemes[J].Chinese Health Economics,2012,31(1):1-3.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-0743.2012.01.008.
[11]李昱,孟庆跃.医改前后农村老年家庭灾难性卫生支出状况分析[J].中国卫生经济,2015,34(1):45-47.DOI:10.7664/CHE20150113. LI Y,MENG Q Y.Analysis on catastrophic health expenditure on rural elderly families before and after medical reform[J].Chinese Health Economics,2015,34(1):45-47.DOI:10.7664/CHE20150113.
[12]朱大伟,郭娜,王健,等.新型农村合作医疗补偿政策对灾难性卫生支出的影响分析[J].中国初级卫生保健,2016,30(1):10-12.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-568X.2016.01.0004. ZHU D W,GUO N,WANG J,et al.Analysis on the impact of new rural cooperative medical scheme on catastrophic health expenditure[J].Chinese Primary Health Care,2016,30(1):10-12.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-568X.2016.01.0004.
[13]王昕.社会基本医疗保障与卫生总费用的动态关系分析[J].中国卫生统计,2013,30(1):77-82.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-3674.2013.30.001. WANG X.Social basic medical insurance and the dynamic relationship between the total healthexpenses analysis[J].Chinese Journal of Health Statistics,2013,30(1):77-82.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-3674.2013.30.001.
[14]何平平.我国医疗支出增长因素研究[D].北京:北京邮电大学,2007. HE P P.Study on the growth factors of medical expenditure in China[D].Beijing:Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications,2007.
[15]周武.浅谈如何控制卫生总费用的过快增长[J].中国医疗前沿,2012,7(16):94.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5552.2012.16.0069. ZHOU W.Talking about how to control the excessive growth of the total health expenditure[J].National Medical Frontiers of China,2012,7(16):94.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5552.2012.16.0069.
(本文编辑:闫行敏)
EffectoftheImplementationoftheNewRuralCooperativeMedicalSchemeontheRuralResidents′HealthExpenditureinChina
FANBian-fei1,LILi-qing1,2*,LIUQiao-yan2
1.SchoolofEconomicsandManagement,JiangxiScience&TechnologyNormalUniversity,Nanchang330013,China2.TongjiMedicalCollege,HuazhongUniversityofScienceandTechnology,Wuhan430030,China
*Correspondingauthor:LILi-qing,Associateprofessor,Mastersupervisor;E-mail:1009160869@qq.com
ObjectiveTo investigate the effect of implementation of New Rural Cooperative Medical Scheme (NRCMS) on the rural residents′ health expenditure in China,so as to offer advices for the steady operation of NRCMS.MethodsWe collected the data of China′s total national health expenditure in 2001—2014,total health expenditure for rural residents in 2001—2013,total health expenditure per capita for rural residents in 2001—2013,rate of rural residents enrolling the NRCMS in 2004—2014,number of village clinics in 2003—2014,number of rural physicians in 2003—2014,proportion of residents who need hospitalized treatment but do not receive it in 2003,2008 and 2013,healthcare expenditure per capita for rural residents and the percent it accounted for of the net income per capita and living cost per capita in 2001—2014.We investigated the effect of implementation of NRCMS on the rural residents′ health expenditure by comparing the above data before and after the implementation of NRCMS.ResultsThe implementation of NRCMS caused the rise of rural residents′ total health expenditure,specifically,it increased to 1 102.697 billion yuan in 2013 from 224.870 billion yuan in 2001 with a growth rate of 390.37%;the health expenditure per capita for rural residents was 1 717.01 yuan in 2013,up by 1 470.52 yuan compared with 246.49 yuan in 2001 with a growth rate of 596.58%.The rate of rural residents enrolling the NRCMS presented a steady increase trend from 2004 to 2014.It increased to 98.9% in 2014 from 75.2% in 2004 with a growth rate of 31.52%.The utilization rate of beds in township hospitals increased from 36.2% in 2003 to 60.5% in 2014,with an increased rate of 67.13%.The proportion of rural residents who need hospitalized treatment but do not receive it reduced to 16.7% in 2013 from 30.3% in 2003,with a decreased rate of 13.6%.The healthcare expenditure per capita for rural residents was 753.90 yuan in 2014,up by 657.29 yuan compared with 96.61 yuan in 2001,with an increased rate of 680.35%.And the percent it accounted for of the net income per capita and living cost per capita showed upward trends from 2001 to 2014.The total national amount of cash paid personally for healthcare services in rural residents increased to 388.390 billion yuan from 149.160 billion yuan in 2001 with an increased rate of 160.38%,but its percent accounted for of the total health expenditure decreased to 11.00% in 2014 from 29.68% in 2001,with a decreased rate of 18.68%.ConclusionAfter the implementation of NRCMS,the total health expenditure for rural residents has increased,the total health expenditure per capita for rural residents,rate of rural residents enrolling the NRCMS,and healthcare expenditure per capita for rural residents have enhanced greatly,while the proportion of rural residents who need hospitalized treatment but do not receive it and the percent that the amount of cash paid personally for healthcare services accounted for of the total health expenditure have decreased significantly.The implementation of NRCMS needs the financial support,so it is suggested that in order to reduce the personal healthcare expenditure burden,more government subsidies should be funded as the reimbursement at the macro level.Furthermore,the equity of access to healthcare services should be improved so as to enhance the operation of the NRCMS.
New rural cooperative medical scheme;Health policy;Rural health;Health care costs
国家自然科学基金资助项目(71473110);中国博士后特别资助基金项目(2015T80811)
R 197
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2017.25.020
2016-12-10;
2017-05-10)
1.330013 江西省南昌市,江西科技师范大学经济管理学院
2.430030 湖北省武汉市,华中科技大学同济医学院
*通信作者:李丽清,副教授,硕士生导师;E-mail:1009160869@qq.com
