延迟退休年龄对劳动力市场的影响
2017-09-03黄健元
黄健元 凌 巧 王 欢
(1.河海大学人口研究所,江苏南京 211100; 2.河海大学理学院,江苏南京 211100)
延迟退休年龄对劳动力市场的影响
黄健元1凌 巧2王 欢1
(1.河海大学人口研究所,江苏南京 211100; 2.河海大学理学院,江苏南京 211100)
人口老龄化程度不断加深,劳动力市场供求关系将面临反转的局面,延迟退休年龄是大势所趋。为探究延迟退休年龄对劳动力市场供需产生的具体影响,通过设定3种延迟退休年龄方案,对江苏省劳动力市场供需进行预测。结果表明,延迟退休年龄有助于推迟劳动力市场首次出现供需缺口的时间,降低劳动力供需缺口规模,但难以扭转劳动力由供大于需转向供小于需的趋势。此外,延迟退休年龄对劳动力市场供需平衡的影响效果还与延迟退休的起始人群、速度、目标年龄以及经济增长速度等密切相关。
退休年龄;劳动力;供给;需求;预测
一、引 言
自实行计划生育政策以来,我国用不到30年的时间便完成了发达国家需要上百年才能完成的向现代人口增长模式(低生育率、低死亡率、低自然增长率)的转变[1]。计划生育政策在控制人口总量增长的同时也使得我国人口老龄化问题日益严峻。据联合国人口司统计数据,2011—2050年间我国60岁及以上人口占比将提高21个百分点,到2050年60岁及以上人口占比将达到34%,届时中国将是全球人口老龄化速度最快的国家之一[2]。在人口年龄结构快速老化的同时,我国也面临劳动力资源加速萎缩的问题,在此背景下,为提高人口出生率,缓解人口老龄化问题,我国先后实施了“单独二孩”政策和“全面二孩”政策,但“单独二孩”政策实施后遭遇普遍“遇冷”,全面二孩政策实施后新生人口也并未如预期般出现“井喷式”增长,加上在短期内新生儿也无法以新增劳动力的身份进入就业市场,因而生育政策的实施短期内无法解决劳动力市场供给量减少的问题。
劳动力市场的供需关系对我国经济社会的稳定发展至关重要,无论是劳动力的过剩还是短缺都将会带来重大影响,所以必须引起高度关注[3]。此外,当前我国经济迈入“新常态”,存在就业形式异常严峻:就业岗位减少、劳动力市场竞争加剧、产业结构与就业结构不匹配等问题。而与经济新常态相伴而生的是我国今后较长时间内面临的劳动力结构性短缺的人口新常态,两者相互交织使就业形势更加复杂。面对劳动力市场有可能出现的供需不平衡,一些学者提出了延迟退休年龄这一对策[4-5]:一方面延迟退休年龄能够有效增加劳动力供给数量,尤其是增加那些具有丰富工作经验、劳动技术人员的贡献时间,满足经济社会发展对人力资本发挥的需求;另一方面,延迟退休年龄还可以提高老年人的就业需求,进而带动经济增长,创造出新的就业机会。
为应对人口老龄化及劳动力市场供给不足的问题,西方先进国家纷纷采取延迟退休年龄的政策。2005年芬兰将退休年龄由60岁提高到63岁,身体健康且愿意继续工作的可延长至68岁。据芬兰统计中心数据,2012年底,芬兰65岁以上的工作人数为23 135人,比1990年增加了5倍[6]。2013年韩国将退休年龄由60岁提高到61岁,之后每5年提高1岁,直至退休年龄达到65岁。英国从2010—2020年计划将女性退休年龄由60岁逐步延长到65岁。而国内的研究主要集中于以下几个方面:一是是否应该延迟退休年龄。虽然这个问题存在一定争论,但以目前形势来看,延迟退休只是时间早晚的问题。谭远发从人均预期寿命、健康工作寿命的角度出发,通过研究认为我国可适当延迟退休年龄[7]。而唐钧认为延迟退休年龄解决不了劳动力老化的问题,相反只会使得劳动力的年龄结构更加偏大[8]。二是延迟退休年龄改革的方式。杨馥提出了稳步推行延迟退休年龄政策、延迟退休与弹性退休相结合、实施差异化退休等构想[9]。十八届三中全会《决定》提出,“研究制定渐进式延迟退休年龄政策”。三是延迟退休年龄的思路与方案设计。郑功成认为理性的延迟退休年龄方案是“小步渐进、先女后男、兼顾特殊”[10]。杨燕绥等在“清华方案”中指出通过提高领取养老金年龄引领国民推迟退休,具体计划和实施步骤如下:从2015年开始,1965年出生的女性职工和居民应当推迟1年领取养老金,1966年出生的推迟2年,以此类推,到2030年实现女性65岁领取养老金;从2020年开始,1960年出生的男性职工和居民推迟6个月领取养老金,以此类推,到2030年实现男性职工和居民65岁领取养老金。艰苦岗位的男女职工可以提前10年领取养老金[11]。
除了延迟退休年龄方面的研究,关于劳动力市场供需,学界也有不少研究成果。张车伟利用脱离教育人数法,预测得到“十三五”时期,新增劳动力供给规模稳中略降,劳动需求增加也比较平稳,劳动力供求呈现基本平衡的格局[12]。但也有学者认为未来劳动力供给必将持续减少,且劳动力年龄结构老化趋势十分明显[13]。蔡昉认为在经济新常态下,保持劳动力市场的持续供给,促进就业势头的持续强劲,开发人口红利已十分迫切与必要[14]。除了单方面对延迟退休年龄、劳动力市场进行研究以外,还有学者专门针对两者之间的关系作了研究。薛继亮提出延迟退休年龄能够增加劳动力供给的观点[15]。然而不少学者对此持不同意见,认为当前我国仍面临劳动力总量过剩的矛盾,劳动力资源丰富,并且当前面临着沉重的就业和失业压力,没有必要通过延迟退休年龄来解决劳动力资源不足的问题[16]。
纵观已有文献,对于延迟退休年龄及劳动力市场供需的研究多集中于单方面,关于两者之间关系的研究较少,且对两者之间的关系多停留在定性分析上,而对于延迟退休年龄在多大程度上能影响劳动力市场供需关系的论点,仍缺乏相关实证研究的支撑。本文基于现行退休年龄政策,结合人口转变、经济社会发展等因素,提出了3种延迟退休年龄方案,在分析延迟退休年龄对劳动力市场供需影响的基础上,对现行退休年龄及延迟退休年龄方案下的劳动力市场供需分别进行预测,并对预测结果展开比较分析。
二、延迟退休年龄方案设定
在实证分析延迟退休年龄对劳动力市场的供需影响之前,需对延迟退休年龄方案进行设定。国际上,已有不少西方先进国家实施了延迟退休年龄改革。法国将退休年龄从60岁提高到62岁,从2011年开始,每年延长4个月,到2018年完成,另外针对一些特殊群体还实施了弹性政策。德国从2012年到2029年,利用18年的时间将法定退休年龄逐步从65岁提高至67岁,退休年龄从2012年开始每年提高一个月,从2024年开始每年提高两个月。对于如何延迟退休年龄,国内学者也对此表达了自己的看法。中央财经大学教授褚福灵表示,延迟退休年龄应该是渐进的过程,即用几十年时间把男女退休年龄提高到一个适中的水平,如用50年时间提高5岁,大概10年提高一岁,一年也就提高一两个月[17]。中国社科院建议从2017年完成制度并轨时,首先将女职工的退休年龄提高到55岁,且在一定时间段内,女工人仍然可以选择50岁退休;2018年开始,女性退休年龄每3年延迟1岁,男性退休年龄每6年延迟1岁,直至2045年同时达到65岁[18]。“十三五”规划建议出台渐进式延迟退休年龄政策,按照人社部的计划,2017年或将出台延迟退休方案,2022年将正式实施。
通过借鉴上述国内外的经验,本文提出两种延迟退休的思路,思路一:“先女、后男女同步”,思路二:“男女同时”。思路一的提出是因为在现行政策下,女性退休时间早于男性约5~10年,所以在制定延迟退休年龄方案时应进一步缩小男、女退休年龄差距。而思路二的提出是为了有效避免男女之间可能出现的攀比心理。在思路一下,首先统一女性退休年龄到60岁,随后男女同时延迟到65岁退休;思路二下男女同时延迟,只是各个人群延迟退休年龄的速度不一样,其中女职工最快,女干部次之,男职工最慢。另外由于延迟退休年龄方案一、方案二目标年龄相同,但是延迟退休的起始人群、速度等均不尽相同,难以比较政策实施的具体效果,因而本文在思路一下添加了目标退休年龄为62岁的延迟退休年龄方案三,假设上述3种方案均于2021年开始实施(表1)。
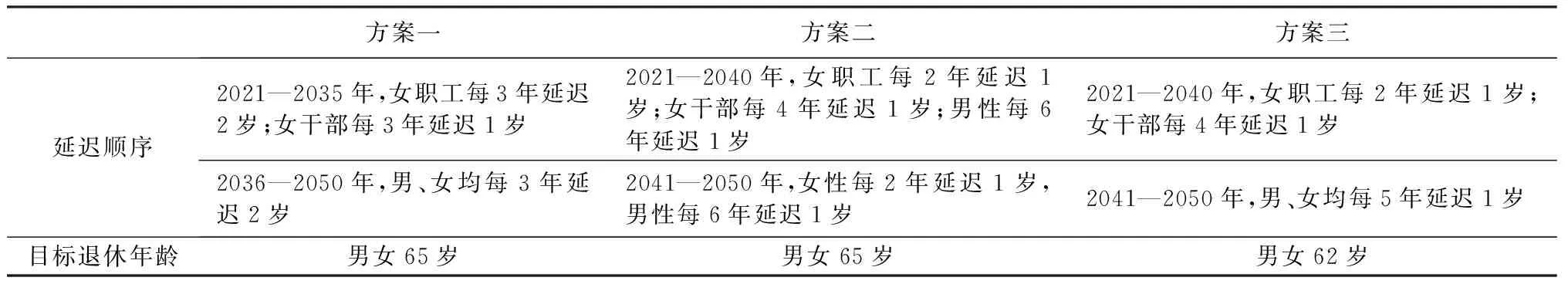
表1 延迟退休年龄方案
三、延迟退休年龄对劳动力市场供需平衡影响的实证分析
1.劳动力供需现状
由表2给出的数据可知,2011—2015年,江苏省劳动力供给数量持续下降,且下降幅度不断扩大,但劳动需求总量除了2014—2015年有所下降外,其他年份均在增加。这就导致剩余劳动力由2010年的305.76万人下降至2015年的212.26万人,降低了93.50万人。
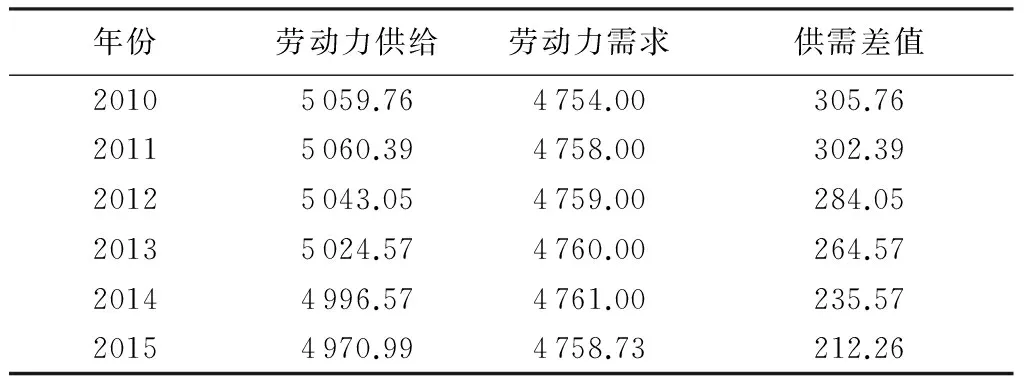
表2 2010—2015年江苏省劳动力供需状况 万人
数据来源:2010—2014数据来源于《江苏统计年鉴》,2015年数据来源于江苏省1%的人口抽样调查公报
2.延迟退休年龄对劳动力供给的影响
在现行的退休年龄政策下,有很大一部分人被强制退休[5],而如果延迟退休年龄,这部分被强制退休的人口将能够加大劳动力供给总量。据此,我们以2010年江苏省人口普查数据为基期数据,利用灰色预测法得到未来劳动参与率,在对未来死亡率、生育率等因素作出合理假定的基础上,利用队列要素法分别得到2015—2050年现行政策及延迟退休年龄方案下江苏省劳动力供给总量(表3)。
从表3可看出,3种延迟退休年龄方案均能有效增加劳动力供给。假设2021年延迟退休年龄方案一开始实施,每年劳动力供给均有所增加,且增加规模不断扩大。延迟退休年龄方案一预设到2050年达到目标退休年龄65岁,2050年新增劳动力供给量达到峰值752.62万人。

表3 现行政策与延迟退休年龄方案下江苏省劳动力供给总量 万人
注:表中增量是指同一年份相对于现行政策,延迟退休年龄方案新增的劳动力供给总量

图1 现行政策与延迟退休年龄方案下劳动力供给总量
延迟退休年龄方案二下,劳动力供给量增长情形与延迟退休年龄方案一类似。且由于两种方案实施的目标年龄均为65岁,延迟退休年龄方案二新增劳动力供给同样在2050年达到峰值752.62万人,劳动力供给的增加值先增大后减小,总体趋势与延迟退休年龄方案一一致,只在个别年份有所区别,这是由于不同的实施速度所导致的。在延迟退休年龄方案三中,新增劳动力供给在2050年达到峰值435.84万人,小于延迟退休年龄方案一、方案二在2050年时达到的峰值,这是由于延迟退休年龄方案三实施的目标年龄相比于延迟退休年龄方案一、方案二要低。
3.劳动力需求趋势分析
影响劳动力需求的因素包括经济增长、产业结构等。近几年我国经济增速降低,进入经济新常态的发展阶段,且根据一些先进国家及地区的经验,未来我国经济增速仍会进一步减慢。而从产业结构来看,三次产业对就业的影响效果有所差别,即就业弹性各不相同。通常情况下,第一产业的就业弹性最低,甚至是负值;第二产业与第三产业的就业弹性均为正值,第三产业的就业弹性最高[3]。
为进一步研究产业结构和就业结构之间的关系,本文就1978—2016年三次产业增加值(Gi,i=1,2,3)与三次产业就业人数(Li,i=1,2,3)的对数值(分别记为lnGi、lnLi,i=1,2,3)之间的关系建立了计量经济模型。通过ADF单位根检验与Johansen协整关系检验,得到第二产业增加值、第三产业增加值与相应就业人数之间存在长期协整关系,故可建立如下协整方程:
lnL2= 5.537 4+0.249 2lnG2
(1)
t值: (55.997 4) (17.353 5)R2=0.903 9
lnL3= 4.416 3+0.386 1lnG3
(2)
t值: (48.980 6) (27.448 9)R2=0.959 3
第一产业增加值与第一产业就业人数之间不存在长期协整关系,这主要是因为第一产业增加值与就业之间不具有长期的均衡比例关系,即第一产业增加值增加并不会相应的促进第一产业的就业人数,这是由第一产业的劳动生产率低,现代化程度不高所引起的[19]。但考虑到现阶段第一产业所占的比重及其对就业的影响,本文通过引入残差的自回归形式对第一产业增加值与产业就业人数相关关系进行修正,得到如下回归方程:
lnL1=10.647 3-0.584 9lnG1+0.784 9AR(1)
(3)
t值:(17.438 6) (-5.504 0) (9.331 4)
从上述得到的方程可看出,第二产业增加值与第三产业增加值对就业具有拉动作用,第二产业、第三产业增加值每增加1%,将分别促进0.249 2%、0.386 1%的就业量;而第一产业增加值对就业具有反向的挤出效应,其产业增加值每增加1%,就业量相应减少0.584 9%。
为预测未来劳动力需求总量,本文对一些参数进行假定。2016年江苏省GDP增速为7.8%,三次产业增加值增长率分别为0.7%、7.1%、9.2%,考虑到未来经济社会的转型以及经济增长模式的转变,GDP增长速度将会进一步下降。因此,本文以2016年GDP增速作为中方案下的经济增速,设定出三次产业增加值增长率低、中、高方案(表4)。
2015年江苏省第一产业、第二产业及第三产业的就业弹性分别为-0.49、0.006及0.23。考虑到就业弹性下降空间有限,因此本文假设未来三次产业的就业弹性维持现值不变。此外,随着经济社会的发展,人均受教育年限越来越长,有研究表明,教育年限的增加会降低就业增长率。在此,我们用教育指数修正就业岗位需求量[20],得到不同经济增长方案下劳动力需求的预测结果(表5)。
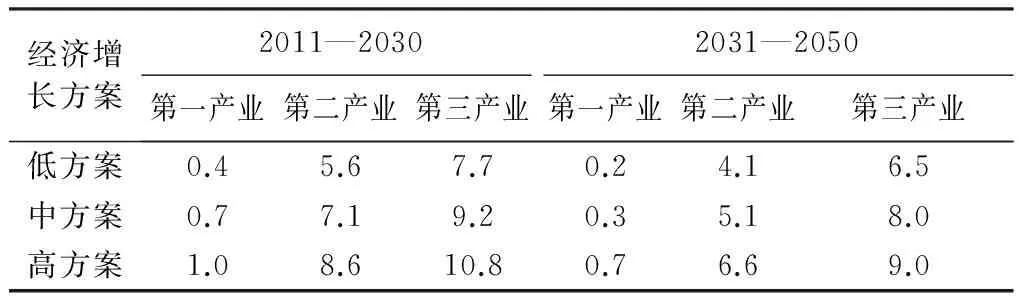
表4 2011—2050年三次产业增加值增长率方案 %

表5 2011—2050年劳动力需求预测 万人
从表5可看出,在经济增长低、中、高3种方案下,江苏省劳动力需求总体呈不断上升趋势,但上升速度不断减小。经济增长低方案下,劳动力需求量最低,经济增长中方案下的劳动力需求量次之,经济增长高方案下劳动力需求量最高,即经济增速越快,劳动力需求量越大。比较三类产业就业人数,可发现第一产业的就业需求人数在减少,第二、三产业的就业需求人数在增加,且第三产业就业需求的增加幅度要大于第二产业,符合三次产业发展的一般规律。
4.劳动力供需平衡趋势
将表5与劳动力供给方案进行比较,得到不同经济增长方案下现行政策与延迟退休年龄方案下的劳动力供需差额。如表6所示,在经济增长低、中、高方案下,若维持现行退休年龄政策,江苏省将在2024年前后出现劳动力供需逆转。其中,在经济增长低方案与经济增长中方案下,劳动力市场均于2024年首次出现供需缺口,且缺口值分别为61.47万人与85.41万人;在经济增长高方案下,劳动力市场将在2023年开始出现供需缺口,缺口值为18.93万人。

表6 现行政策与延迟退休年龄方案下劳动力供需差额 万人

图2 现行政策与延迟退休年龄方案下劳动力供需差额
经济增长低方案下,延迟退休年龄方案一在2034年开始出现供需缺口,缺口值为15.80万人;延迟退休年龄方案二出现供需缺口的时间较延迟退休年龄方案一要晚2年,这是由于在延迟退休年龄方案二中,人数占比最多的男性职工最初就加入了改革行列;延迟退休年龄方案三开始出现缺口的时间为2029年,缺口值为1.09万人,因为延迟退休年龄方案三实行的是“先女后男”的思路,且延迟退休的目标年龄仅为62岁。经济增长中方案情形,延迟退休方案一首次出现缺口的时间为2031年,缺口值为11.64万人;延迟退休年龄方案二开始出现缺口的时间较延迟退休年龄方案一晚1年,且缺口值为2.23万人;延迟退休年龄方案三出现缺口时间为2026年,缺口值为3.37万人。而在经济增长高方案中,延迟退休年龄方案一、方案二及方案三出现供需缺口的时间分别为2028年、2029年和2024年。
5.延迟退休年龄的效应分析
实证研究结果表明,经济增长低方案、中方案及高方案下,3种延迟退休年龄方案均能在不同程度上推迟劳动力市场首次出现供需缺口的时间,降低劳动力供需缺口规模。以经济增长中方案为例,在现行退休年龄政策下,劳动力市场首次出现供需缺口的时间为2024年,缺口值为85.41万人,而延迟退休年龄方案一将劳动力市场首次出现供需缺口的时间推迟到了2031年,晚了7年。延迟退休年龄方案二则将供需缺口出现的时间推迟到了2032年,延迟退休年龄方案三将其推迟到2026年。另外,以首次出现供需缺口的年份为例,在3种延迟退休年龄方案下,劳动力市场出现的供需缺口值均小于同一年份现行退休年龄政策下劳动力市场出现的供需缺口值。
此外,延迟退休年龄对劳动力市场供需的影响效果,还与延迟退休年龄的起始人群、延迟速度、目标年龄及宏观经济增长速度有关。
(1)起始人群。若延迟退休政策从数量最多的人群开始,则促进劳动力市场供需平衡的效果越显著。方案一与方案三均采取的是“先女,后男女同步”思路,方案二采取的是“男女同时”的思路,由于男性职工的人数最多,女职工次之,女干部的人数最少,因此,在延迟退休年龄方案实施初期,方案二在促进劳动力市场供需平衡方面的效果要优于方案一与方案三。
(2)延迟速度。延迟退休方案设定的速度越快,越能够促进劳动力市场供需平衡。方案一与方案三采取的均是“先女,后男女同步”的思路,但在政策实施初期的延迟速度快慢有别,导致两种方案对于促进劳动力市场供需平衡也有一定区别。实证分析结果表明,在延迟退休年龄政策的起始时间、起始人群均一致的情况下,延迟退休年龄的速度越快,越能够促进劳动力市场供需平衡。
(3)目标年龄。较高的目标退休年龄,更能够促进劳动力市场供需平衡。方案一、方案二延迟退休的目标年龄均为65岁,而方案三为62岁。由于3种方案均是利用30年时间来完成,因此,不同的目标退休年龄就会导致不同的延迟退休速度,对于促进劳动力市场供需平衡的效果也会不一样。
(4)宏观经济增长速度。经济增长速度越低,劳动力市场首次出现供需缺口的时间越靠后,缺口值越小。由表6可知,在经济增长低、中、高方案下,同一种延迟退休年龄方案对促进劳动力市场供需平衡的效果也会有所区别。在经济增长低方案下,延迟退休年龄方案对于促进劳动力市场供需平衡效果最明显,经济增长中方案次之,高方案效果最差。
四、结论与讨论
本文基于江苏省2010年第六次全国人口普查数据,对江苏省2011—2050年劳动力供需进行了预测,并对三次产业增加值增长率、经济增速以及就业弹性等因素在2050年前的变动趋势做出了相关假设,设置了低、中、高3种经济增长方案。围绕“先女、后男女同步”“男女同时”两种思路设定了3种延迟退休年龄方案,并结合现行政策展开实证分析。
结果表明,延迟退休年龄能够有效推迟劳动力供需缺口出现的时间,降低缺口值。如果仅维持现行政策,在经济增长低、中、高方案下,剩余劳动力数量不仅将逐渐减少,还会在2024年前后出现供不应求的情形。延迟退休年龄不仅能够推迟劳动力市场首次出现供需缺口的时间,还能有效降低缺口值。当然,除着力于推行延迟退休年龄政策,我们还能通过深化改革户籍制度,逐渐打破劳动力市场的制度壁垒,加强人力资本投资,提高劳动力素质,加快转变经济发展方式与产业结构升级等措施,进一步激发劳动力市场的灵活性和竞争性。
本文研究过程中采取了中长期的预测技术。需要说明的是,这一跨期预测的目的在于对未来劳动力市场供需关系的变动趋势做出预判并起到警示性作用,建议政府相关部门及社会各方提早采取应对措施以规避潜在风险的发生,而不至于让预测得到的缺口值成为现实。
另外,本文预测过程中涉及延迟退休年龄3种方案设计和三次产业增加值增长率、人口死亡率、出生率等参数设定,方案和参数的变动均会影响到预测结果;全面二孩政策的实施、人口政策的进一步调整都会对劳动力市场产生深刻的影响,相关问题仍需持续跟踪研究。
[1] 胡翠,许召元.人口老龄化对储蓄率影响的实证研究——来自中国家庭的数据[J].经济学(季刊),2014(4):1345-1364.
[2] United Nations Population Division.World population prospects: the 2010 revision[R].NY: UN Population Division,2011:41-43.
[3] 王欢,黄健元,王薇.人口结构转变、产业及就业结构调整背景下劳动力供求关系分析[J].人口与经济,2014(2):96-105.
[4] 金刚.中国退休年龄的现状、问题及实施延迟退休的必要性分析[J].社会保障研究,2010(2):32-38.
[5] 张雄.退休年龄对劳动参与率的影响[J].西北人口,2009(6):23-26.
[6] 李骥志,徐谦.芬兰推动延迟退休和养老金制度改革取得成效[N].经济参考报,2014-12-05(5).
[7] 谭远发,朱明姣,周葵.平均预期寿命、健康工作寿命与延迟退休年龄[J].人口学刊,2016(1):26-34.
[8] 唐钧.别让“延迟退休”吓坏老百姓[J].中国经济周刊,2014(6):16-17.
[9] 杨馥.我国退休年龄改革的探讨[J].宁夏社会科学,2013(2):58-63.
[10] 郑功成. 对延迟退休年龄的基本认识[N]. 光明日报,2012-09-12(14).
[11] 杨燕绥,胡乃军,刘广君.清华方案:中国养老金顶层设计[N].第一财经日报,2013-08-12(5).
[12] 张车伟,蔡翼飞.中国“十三五”时期劳动供给和需求预测及缺口分析[J].人口研究,2016(1):38-56.
[13] 王金营,顾瑶.中国劳动力供求关系形势及未来变化趋势研究——兼对中国劳动市场刘易斯拐点的认识和判断[J].人口学刊,2011(3):3-13.
[14] 蔡昉.劳动人口负增长下的改革突破[J].改革论坛,2014(2):82-84.
[15] 薛继亮.延迟退休和放开二胎对劳动力市场的影响研究[J].东北财经大学学报,2014(2):74-79.
[16] 赵艳芳.论法定退休年龄的合理改革[J].劳动保障世界(理论版),2011(11):25-27.
[17] 吴成良,裴广江,张杰.延迟退休 多数国家采用渐进式[N].人民日报,2012-09-13(4).
[18] 蔡昉,张车伟.人口与劳动绿皮书:中国人口与劳动问题报告NO.17[M].北京:社会科学文献出版社,2016.
[19] 李玉凤,高长元.产业结构与就业结构的协整分析[J].统计与决策,2008 (4):84-86.
[20] 罗亚萍.就业与受教育程度的相关性研究——以中国城镇就业量为基础[J].西安交通大学学报(社会科学版),2010(5):84-89.
(责任编辑:吴 玲)
Mao Zedong’s Thoughts of Nurturing the Marxist Belief during the Revolutionary Period and Contemporary Inspiration/FAN Meixiang,et al(School of Marxism, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China)
Abstract: Mao Zedong’s thoughts of nurturing the Marxist belief during the revolutionary period are an essential part of Maoism. Mao Zedong points out the importance of nurturing the Marist belief and argues that Marxism guides the direction of Chinese revolution, which is the “weapon of thoughts” and “spiritual pillar” for the victory of the revolution. Marxism can arouse the double “awakening” consciousness of the communists and common people. Mao Zedong holds that the basic components of nurturing the Marxist belief are the cosmology of dialectical materialists and historical materialists, the “two definite aims” of the new democratic revolution and the cause of socialism and communism, and the value aim and the moral pursuit of the thought that “people are the God”. Then, Mao Zedong explicates the approaches of nurturing the Marxist belief by means of stressing the importance of theoretical education, people’s benefits, and the Communist Party’s discipline, it is of great significance to review Mao Zedong’s thoughts of nurturing the Marist belief during the revolutionary period to strengthen Marxism and run the Party strictly in the new century.
Key words: MAO Zedong; Marxist belief; ideals and conviction;contemporary inspiration
The October Revolution and the First Dream Construction of the Chinese Communist Party/Liu Fusheng(School of Maxism of Chongqing Technology and Business University,Chongqing 400067, China)
Abstract: The October Revolution turned out to be a significant event, which exercised a great influence on the world history. The Chinese Communist Party has taken its own endless struggle as a new move in terms of the October Revolution. Clarification on the misreading of historical idealism and Historical Nihilism would be, both theoretically and practically, of great importance in cultivation of people’s ideals and beliefs. Therefore, to learn from the October Revolution and draw on its experience concerned, and to advance along the road to socialism as well as adhere to communism, would be all the kernel implications of “beginner’s mind” for the Chinese Communist Party.
Key words: the October Revolution; the World Significance; Chinese Communist Party; the First Dream Construction
Challenges in Innovation and Implementation of Harmonious Core Value and Countermeasures/GE Chunyu,et al(School of Marxism, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China)
Abstract: Harmony, as one of the core values at national level, highly summarizes the objects of social and ecological construction in the five-in-one overall arrangement. In spite of its connection with the harmony in harmonious society or social harmony, but they are different. Provided that it is deemed as value at social level, it cannot fully reflect the objective requirements of the socialist market economy. Harmonious core value mirrors the theme of the times, peace and development, acts as the inheritance and transcendence of essential traditional Chinese philosophy that “man is an integral part of nature”, and represents the Marxism related to substitutive characteristics of socialist society. Harmony, as the value goal in the relationship between man and nature, is faced with the challenge of destroying the ecological environment for the development of economy. So it is necessary to establish the concept of green development and the strictest ecological and environmental protection system. Harmony, as the value goal in the interpersonal relationships, is also faced with the challenge of widening gap between the rich and the poor. Work is needed to be done to implement the concept of shared development in policy. Moreover, harmony, as the value goal in the physical and spiritual health development of citizens, is faced with the challenge of human alienation. Therefore, right world view and reasonable value should be established.
Key words: harmony; core values; significance; challenge
The Subject of Network Ideological and Political Education and Its Collaborative Relationship/Chen Zongzhang,et al(Department of Philosophy, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093,China)
Abstract: The space transfer from social space to cyberspace which provides a new spacial condition for ideological and political education.In the face of fragmentation, decentralization and formalization of the subject of network ideological and political education, We have to face the problem of identity fracture.In order to play a good system function of network ideological and political education,and maintain a good cyberspace ecology, various subjects have to get the identity.In addition, the subject of network ideological and political education should construct the benign interaction by establishing and perfecting comprehensive coordination mechanism.And then the subject of network ideological and political education will reconstruct its value in cyberspace,and build an organic and open ideological and political education community.
Key words: network ideological and political education; subject; space transfer; collaborative relationship
The Flexible Features of International Cooperation in International Rivers Water Resources and China/ZHOU Haiwei,et al(Business School, Hohai University, Nanjing 211100, China)
Abstract: Based on flexible strategic management framework, the paper takes international cooperation protocols related to water from Trans-boundary Freshwater Disputes Database (TFDD) for example and analyzes the number of cooperation governance issues, the amount of management layers and regulators’ agencies in cooperation organization and the categories of income (cost) distribution (allocation) mode. The research demonstrates that there are some flexible features of international rivers water resources cooperation governance: riparian countries may select relative diversification governance strategies related to water, tend to construct a flexible cooperation organization featured with moderate hierarchies and simplified administrations, and adopt selective inducement modes with more flexibility to respect “joint and several liability”.
Key words: international river;cooperation governance;flexibility;water—oriented international cooperation treaties
Strategic Thinking on the Adaptive Construction of Water Ecological Civilization in Jiangsu Province/QIU Lei,et al(Management Science Institute, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China)
Abstract: Water is the most active controlling factor in the ecological environment. Water ecosystem is an important carrier and material basis for the survival and development of the mankind. Water ecological civilization is an important component and core element of ecological civilization. The paper analyzes the existing problems in the construction of ecological civilization in Jiangsu province and summarizes the international advanced experience of adaptive management. Under the guidance of ecological idea of “the new harmony between human and nature”, it puts forward the strategic thinking and the adaptive construction of ecological civilization. Based on the natural endowments and humanities of Jiangsu province, it proposes the specific strategic paths: planning the overall layout of water ecological civilization construction with “Water Chain” plan, carrying out the water sensitive urban construction and the red line control in Jiangsu province.
Key words: water ecological civilization; adaptive construction; “Water Chain” plan; water sensitive urban construction
A Study of Area Difference and Threshold Effect of Total Factor Productivity of Farmland Water Conservancy in China/SONG Min,et al(Business School, Hohai University, Nanjing 211100, China)
Abstract: Irrigation and water conservancy is an important part of agricultural infrastructure investment,which has important impact on agricultural economic growth and farmers’ income increase. This paper uses DEA-Malmquist method to estimate the irrigation and water conservancy efficiency of 31 provinces based on the data from 2001 to 2015. Result shows that the efficiency of farmland water conservancy is different between those areas: the efficiency of northeast is higher than that of east China and central China. Such areas have more agricultural provinces. Irrigation and water conservancy efficiency does not completely match the regional economic development level mainly because of the nonlinear of irrigation and water conservancy efficiency and its influential factors. On the basis of provincial differences of water conservancy efficiency, the paper uses the estimating method of threshold panel estimation to checkout the threshold factors which have impact on the efficiency of farmland water conservancy. The results show that rural economic development level has a significant convergence threshold effect on water conservancy efficiency and mechanical power input has obvious threshold effect on the acceleration of water conservancy efficiency.
Key words: farmland water conservancy; total factor productivity; threshold effect; DEA-Malmquist productivity index approach
Research into the Impact of the Development of Shadow Banking System on Monetary Policy from the Perspective of Credit Rationing/PAN Haiying,et al(Business School, Hohai University, Nanjing 211100, China)
Abstract: Based on the theory of equilibrium credit rationing and the shadow banking system, the paper theoretically analyzes the impact of the shadow banking system on the implementation of monetary policy. The paper uses the structural vector autoregressive (SVAR) model and verifies the impacts on account of monthly data of China from 2007 to 2015. The results show that the liquidity supply of different types of shadow banking weakens the credit rationing which is dominated by commercial banks in different degree. When the central bank adopts an easy monetary policy,the shadow banking system has a positive effect on the economy and plays a positive role in promoting the implementation of easy monetary policy. Moreover, the shadow banking system has a significant stimulus effect on the economy under tight monetary policy and significantly inhibits the implementation of tight monetary policy to the economy. Compared to easy monetary policy, the shadow banking system makes a higher contribution to the economy under tight monetary policy and has more significant impact on the implementation of tight monetary policy.
Key words: credit rationing; shadow banking; monetary policy; SVAR model
An Analysis of Innovation Effect of Negative List Management Mode of China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone/SHEN Yuan,et al(College of Applied Mathematics, Nanjing University of Finance and Economics,Nanjing 210046,China)
Abstract: Since 2010, China’s economy has entered a new normal state. Under the pressure of dual economic transformation and development both at home and abroad, China needs to find a new economic model that can cope with the increasingly fierce international competitive environment and effectively promote international development. The innovation of the “Negative List” management system of China (Shanghai) Free Trade Area has had a great impact on the economy of China and the world. Therefore, this paper uses the theoretical framework of the new institutional economics to account for the market effect produced by the negative inventory management system and studies the innovative mechanism and effect of management system of China’s free trade area from the perspective of market space focusing effect.
Key words: Shanghai free trade zone; institutional innovation;negative list; effect analysis
The Action Logic, Social Causes and Governance Mechanism of Industrial Water Pollution/XU Genhong(Law School, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China)
Abstract: The industrial water pollution in China’s urbanization process is both an ecological technology issue and a social governance problem. Based on sociological dimension,it is found that there is an explicit social fact that formal rules and the practice norms are separated in industrial water pollution field. The formation of social fact is related with certain action logic: local policies surpass formal regulations, local governments are coerced by polluters, implicit violation actions appear from backstage to the front and violation actions change from endogenous ones to exogenous. The main social causes of such action logic lie in evaluation mechanism in the context of imbalanced institutional structure, supervision mechanism in the context of imbalanced power structure and the limited internalized regulation drive. Therefore, the governance mechanism of industrial water pollution chiefly includes main structure optimization, regulation culture reproduction and effective social supervision.
Key words: industrial water pollution; action logic; social causes; governance mechanism.
Study of Influential Factors of Chinese NIMBY Movement Outcomes: A Multi-Value Set Qualitative Comparative Analysis of 22 NIMBY Cases/GAO Xinyu,et al(School of Finance and Public Administration,Anhui University of Finance and Economics,Bengbu 233030,China)
Abstract: This paper systematically compares 22 Not In My Back Yard (NIMBY) movement cases from 2003 to 2015, using the method of multi-value set qualitative comparative analysis. Based upon the characteristics of Chinese contentious politics, the study proposes an exploratory analytical framework to explain the success of social protests. The results show that with regard to the theory of resource-mobilization, the theory of political opportunity explains NIMBY movement in a good way. The analysis demonstrates that risk perception, eastern region, internet mobilization, citizen participation and the favorable coverage of central media contribute to a successful outcome. Differing from the previous study, it is found that the intervention of the environmental protection organizations may result in the failure of NIMBY movement. In addition, this research broadens the methodological implications for the future research on NIMBY protest outcomes.
Key words: NIMBY movement; political opportunity; resource mobilization
A Functional Review of the Middle Class in the View of NIMBY Movements:Taking the “Nuclear NIMBY Movements” in R City for Example/WANG Gang,et al(School of Law & Politics, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China)
Abstract: In recent years, with the increasing of the NIMBY movements caused by urban middle class. Traditional Chinese academia usually regards the “middle class” as a “stable and buffer” device of social politics. It seems to be in accord with China’s social fabric, but in reality, it ignores the complexity and transition of Chinese political and social situations during the transition period. Based on a case study of “nuclear NIMBY movement” in R City, it is found that the social political functions of the middle class of the city may change at a particular time, or even appear two opposite states of “stabilizer” and “turbulence”. The internal mediation mechanism includes hierarchical class features and the rising-to-power elite and, the external intermediary mechanism includes “the production of resentment” and “divergences within the government”, which is the deep mechanism of evolution of social and political function of the middle class. In addition, it is worth noting that, due to the “dual identity limit” and “system limit”, the social political function of the middle class often does not evolve into a “subversive dissimilation”.
Key words: NIMBY movement; middle class; stable-buffer; conflict-turmoil
The Influence of the Delay Retirement Age on the Labor Market/HUANG Jianyuan, et al(Institute of population studies, Hohai University,Nanjing 211100, China)
Abstract: The aging of the population is deepening, and the supply and demand of the labor market will face a reversal. The retirement age is a general trend. In order to explore the impact of the retirement age on the supply and demand of the labor market, this paper forecasts the supply and demand of the labor market in Jiangsu by setting up 3 deferred retirement age schemes. The results show that the retirement age will for the first time to postpone the time gap between supply and demand of labor market, to reduce the gap between labor supply and demand scale, But it is still difficult to reverse the trend of labor supply from supply to demand. In addition, the effect of the delayed retirement age on the labor market is closely related to the starting population, speed, target age, and economic growth rate of the late retirement.
Key words: retirement age; labor force; supply; demand; forecast
Ecological Implication of Marx’s Labor Thought/WU Xuedong(School of Marxism, West Anhui University, Luan 237012, China)
Marx’s ecological thought is the logical extension of his labor thought. Ecological problem is a problem of the relationship between human and nature and labor is an interrelated link between human and nature. As a result, Marx takes labor as a logical starting point to deduce his ecological thought. Labor is not only material transformation mediation between human and nature and is the means of material transformation to adjust and control relationship between man and nature. When the function of labor about adjustment and control lose efficacy, material transformation cracks may appear and lead to ecological crisis. Marx’s research on ecological problem has a ingenious point which reveals the social root of ecology crisis by means of the alienation relationship between capital and labor through ecological problem. Then, based on the exploration, it is possible to find reality path to deal with ecological crisis through labor liberation.
Marx; labor; labor thoughts; ecological thought
10.3876/j.issn.1671-4970.2017.04.014
2017-03-10
江苏高校哲学社会科学研究重点项目(2015ZDIXM010);河海大学中央高校基本科研业务费项目(2015B13514;2016B32714)
黄健元(1964—),男,江苏溧阳人,教授,从事人口和社会保障研究。
F061.2;C913
A
1671-4970(2017)04-0083-06
