复合材料层合圆柱壳的振动特性
2017-08-27谭安全刘敬喜李天匀朱翔
谭安全,刘敬喜,李天匀,朱翔
(1.中国船级社重庆分社,重庆401121;2.华中科技大学船舶与海洋工程学院,武汉430074)
复合材料层合圆柱壳的振动特性
谭安全1,刘敬喜2,李天匀2,朱翔2
(1.中国船级社重庆分社,重庆401121;2.华中科技大学船舶与海洋工程学院,武汉430074)
文章基于Love壳体理论,对复合材料层合圆柱壳的振动特性进行了研究。通过比较,文中计算方法所得的结果与文献比较吻合。运用该方法,讨论了简支、固支和自由等边界条件,轴向模态和铺层角度对圆柱壳振动特性的影响。分析表明,在低阶周向模态时,边界条件和轴向模态的影响更大。
复合材料圆柱壳;振动;边界条件;周向模态
0 引言
复合材料因其自身的高比强度、比刚度和减振性能好等优点,现已广泛应用于各工程领域中。由于复合材料结构的各向异性,其振动特性必然不同于各向同性结构,因此对复合材料圆柱壳的振动特性进行研究很有必要。针对各向同性梁、板和壳的振动特性研究[1-5]已很成熟,但对于复合材料层合圆柱壳的振动特性研究则较少。陈辉[6]利用最小势能原理给出了复合材料圆柱壳的自振频率的计算方法。Chen[7]则基于三维弹性理论考察了层合板的自由振动。Aydogdu[8]运用瑞利—里兹法研究了不同边界条件下层合梁的振动特性。本文基于Love壳体理论导出了任意铺层复合材料圆柱壳的自由振动方程,考虑耦合效应的影响,对不同铺层数的复合材料层合圆柱壳的振动特性进行了研究。
1 理论分析
分析一有限长弹性薄壁复合材料层合圆柱壳,坐标系及周向模态如图1所示。x、θ和r分别表示圆柱壳的轴向、周向和径向坐标,u、v和w分别表示圆柱壳中面的轴向位移、周向位移和径向位移。壳厚为h,中面半径为R,纵向弹性模量为E1、横向弹性模量为E2、主泊松比为μ1、次泊松比为μ2、壳体密度为ρ、面内剪切模量为G、壳体长度X和铺层数L。
由Love壳体理论[9]得:
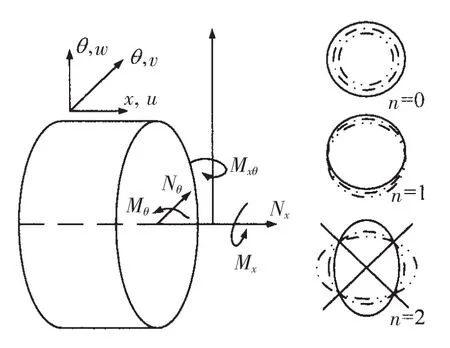
图1 圆柱壳坐标系及周向模态示意图Fig.1 Coordinate system and circumferential modes

式中:圆柱壳的内力可以表示为:

对于薄壳,(2)式中的应力可以用广义胡克定律写成:

方程(3)中的应变部分用Love壳体理论表示为厚度z的函数

式中:ex、eθ和γxθ为距离参考面z处的轴向、周向和剪切应变,e1、e2和γ分别为参考面应变,k1、k2和τ为参考面曲率。参考面的应变和曲率可以表示为:
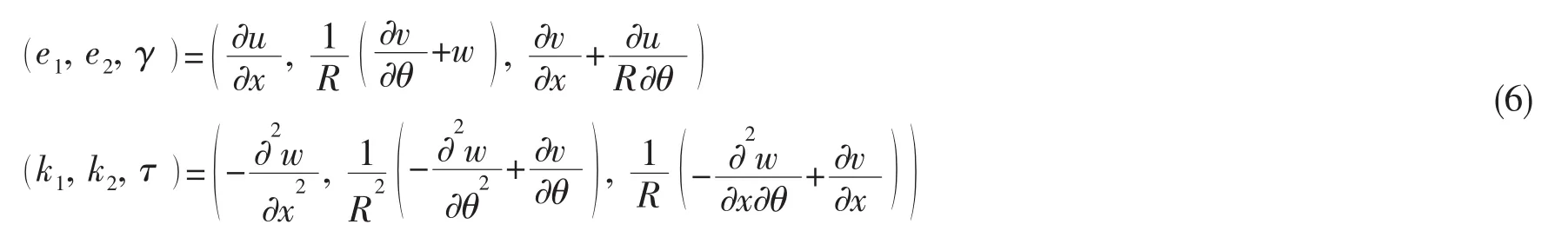
将(5)式和(6)式代入(3)式中,然后将结果代入(2)式中,圆柱壳的内力最终可以表示为如下矩阵形式:

式中:Aij、Bij和Dij分别表示拉伸刚度、耦合刚度和弯曲刚度。蔡氏不变量:

令V1=cos2θi,V2=cos4θi,V3=sin2θi,V4=sin4θi,θi表示复合材料层合圆柱壳各层的铺层角度,则有:
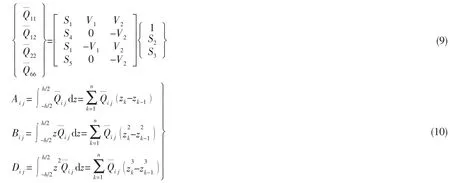
壳体振动时周向取驻波形式的解,考虑到振动波沿壳体轴向的传播,因此用波传播方法将壳体中面位移表示为:

式中:Um、Vm和Wm是x、θ和r方向的振幅,km为轴向波数,m和n分别是轴向和周向模态阶数,ω是圆频率(rad/s)。
将(7)、(10)式和(11)式代入到(1)式中,得到圆柱壳的自由振动微分方程,将其表示为如下矩阵形式:

由(12)式可得:

通过(13)式,可以获得有限长复合材料层合圆柱壳的固有频率,因此,可将(13)式转换为:

上式是关于ω2的三阶代数方程,对于每一个km和n有3对不同的频率,3个正根,3个负根。其中,3个正根分别代表复合材料层合圆柱壳的轴向、周向和径向环频率,最小的根代表弯曲振动,其它两个则为平面振动。
根据Zhang[1]提出的不同边界条件下所对应的波数,如表1所示(F:自由,C:固支,S:简支)。
2 计算与讨论
为了验证本文分析的正确性,将所得结果与Lam[10]和Zhang[11]进行了对比。表2给出的复合材料层合圆柱壳铺层数为3层,铺层角度为90/0/90,两端简支时的自由振动频率,无量纲频率。

表1 各边界条件下的波数Tab.1 Wave numbers of all kinds of boundary conditions
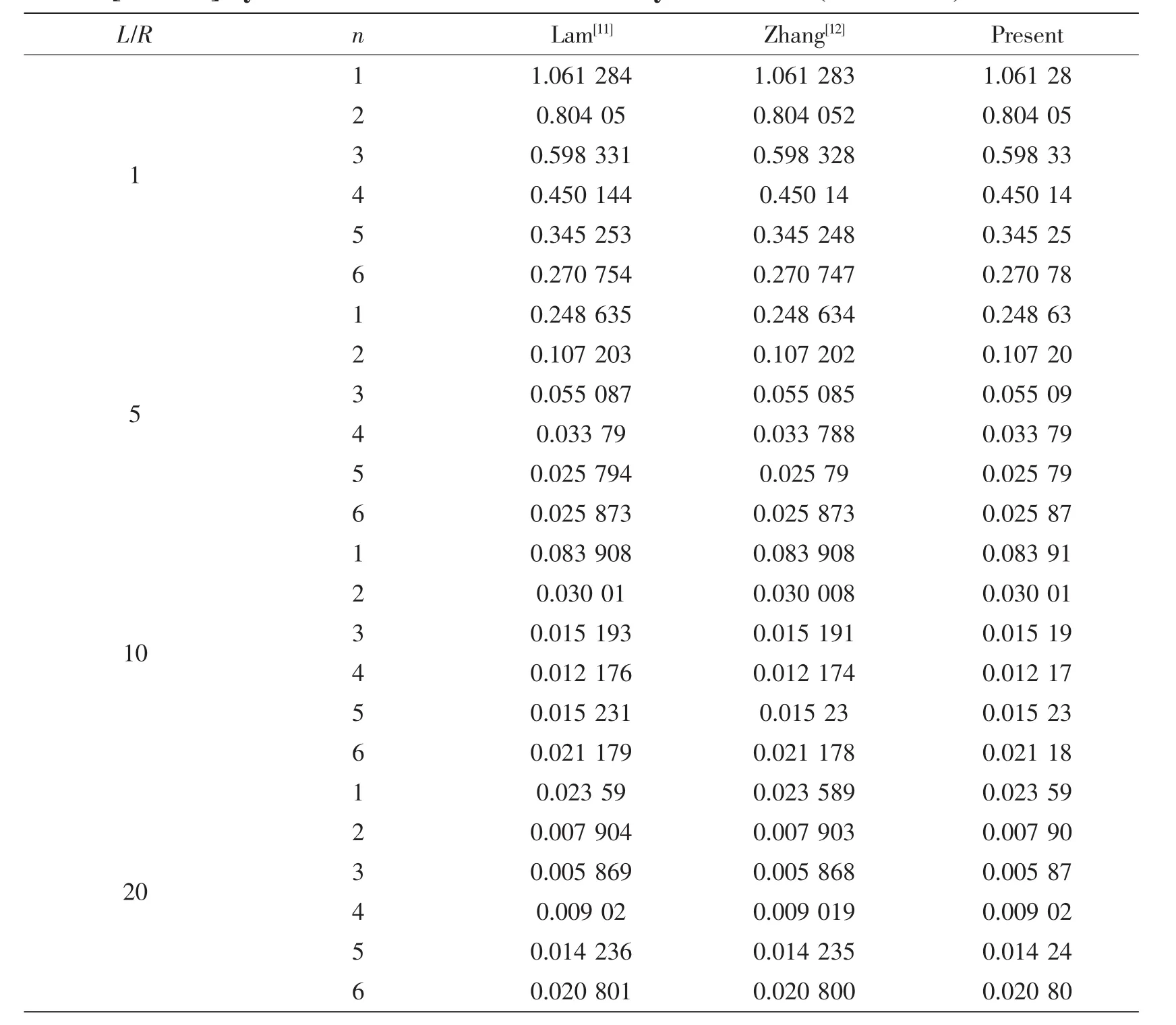
表2 两端简支时铺层角度为[90/0/90]的圆柱壳自由振动频率比较(h/R=0.002)Tab.2 Comparison of the natural frequencies parameters for a three-layered,cross-ply [90/0/90]cylindrical shell with SS boundary conditions(h/R=0.002)
通过比较发现结果吻合很好,表明本文的推导和计算程序是正确、可靠的。
本文计算了对称铺层数分别为4、6和8层的有限长复合材料层合圆柱壳的振动特性。参数如下:壳体厚径比h/R=0.002,横向弹性模量E2=8.0 GN/m2,纵向弹性模量E1=2E2,泊松比μ1=0.25,壳体密度ρ=1 640 kg/m3,壳体长径比X/R=10,铺层角度分别为(0/90)S、(0/60/-60)S和(0/45/90/-45)S。
图2(a)-(c)给出了不同铺层数的复合材料层合圆柱壳在两端固支(C-C)、两端简支(S-S)、一端固支一端简支(C-S)和一端固支一端自由(C-F)四种边界条件下,频率随周向模态的变化曲线。当壳体在低阶模态时,不同的边界条件对壳体的自由振动影响很大,频率从高到低依次为:C-C、C-S、S-S和C-F。随着周向模态n的增大,不同边界条件对壳体振动的影响逐渐减小,最终趋于一致。

图2 各边界条件对壳体振动频率的影响(m=1)Fig.2 Influences of boundary conditions on vibration frequence for cylindrical shells
通过计算,四种边界条件对不同铺层数壳体自由振动频率的影响趋于一致。为便于说明,图3只给出了两端固支(C-C)边界时,铺层角度为(0/90)S、(0/60/-60)S和(0/45/90/-45)S的壳体振动频率随周向模态的变化曲线。随着周向模态的增大,边界条件对不同铺层数壳体振动的影响逐步由无到有,从小到大。壳体频率由高到低依次为(0/45/90/-45)S、(0/90)S和(0/60/-60)S的铺层角度。
图4给出了铺层角度为(0/60/-60)S,两端简支的壳体在不同轴向模态时,周向模态对壳体自由振动的影响曲线。当周向模态较低时,不同轴向模态数对壳体自由振动影响较大,并随着周向模态的增大而减小,最终趋于一致。对于某一周向模态n,轴向模态m越大,壳体的振动频率越高。
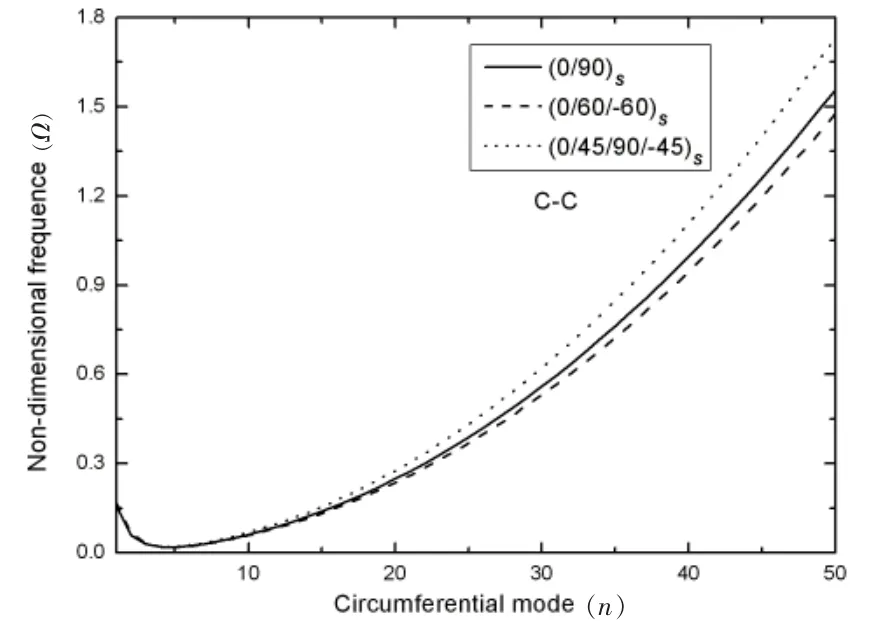
图3 固支边界条件对不同铺层数壳体振动频率的影响(m=1)Fig.3 Influences of CC conditions on vibration frequence for cylindrical shells with different layers(m=1)

图4 简支边界条件对壳体振动频率的影响Fig.4 Influences of SS conditions on vibration frequence for cylindrical shells
3 结论
基于Love壳体理论,针对不同铺层角度的复合材料层合圆柱壳在各边界条件下的振动特性进行了研究,并将所得结果与相关文献进行了比较,结果吻合得很好。从中可以得到以下结论:
(1)各边界条件对壳体自由振动的影响在周向模态较小时较大,随着n的增大,影响逐渐较小,对于某一周向模态C-C时壳体频率最大,依次为C-S、S-S和C-F。
(2)各边界条件对不同铺层角度壳体的自由振动的影响,随着周向模态的增大而逐渐增大。铺层角度为(0/45/90/-45)S的壳体振动频率最高,(0/90)S次之。
(3)轴向模态对壳体自由振动的影响也是在n较小时出现,并且轴向模态m越大,壳体的振动频率越高。
[1]Zhang X M,Liu G R,Lam K Y.Frequency analysis of cylindrical panels using a wave propagation approach[J].Applied Acoustics,2001,62(3):527-543.
[2]Zhang X M,Liu G R,Lam K Y.Vibration analysis of thin cylindrical shells using wave propagation approach[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,2001,239(3):397-403.
[3]Zhang X M,Liu G R,Lam K Y.Coupled vibration analysis of fluid-filled cylindrical shells using the wave propagation approach[J].Applied Acoustics,2001,62(4):229-243.
[4]Yan J,Li F Ch,Li T Y.Vibrational power flow analysis of a submerged viscoelastic cylindrical shell with wave propagation approach[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,2007,303(1-2):264-276.
[5]Zhang X M.Frequency analysis of submerged cylindrical shells with the wave propagation approach[J].International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2002,44(7):1259-1273.
[6]陈辉.复合材料圆柱壳的振动频率分析[J].纤维复合材料,1989,3(12):12-21. Chen H.Analysis of vibration frequency on laminated composite cylindrical shell[J].Fiber Composites,1989,3(12):12-21.
[7]Chen W Q,Lu C F.3D free vibration analysis of cross-ply laminated plates with one pair of opposite edges simply supported[J].Composite Structures,2005,69(1):77-87.
[8]Aydogdu M.Vibration analysis of cross-ply laminated beams with general boundary conditions by Ritz method[J].International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2005,47(11):1740-1755.
[9]Love A E H.A treatise on the mathematical theory of elasticity[M].Cambridge:Cambridge University,1952:242-260.
[10]Lam KY,Loy C T.Analysis of rotating laminated cylindrical shells by different thin shell theories[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,1995,186(1):23-35.
[11]Zhang X M.Vibration analysis of cross-ply laminated composite cylindrical shells using the wave propagation approach [J].Applied Acoustics,2001,62(11):1221-1228.
[12]Sarmila Sahoo.Free vibration of laminated composite stiffened hyperbolic paraboloid shell panel with cutout[J].Journal of Physics:Conference Series,2016(1):52-63.
[13]Viswanathan K K,Lee Sang-Kwon.Free vibration of laminated cross-ply plates including shear deformation by spline method[J].International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2007,49(3):352-363.
[14]Sarmila Sahoo.Free vibration behavior of laminated composite stiffened elliptic parabolic shell panel with cutout[J].Curved and Layered Structures,2015(1):162-182.
[15]Lam K Y,Qian Wu.Free vibration of symmetric angle-ply thick laminated composite cylindrical shells[J].Composites Part B:Engineering,2000,31(4):345-354.
[16]Sarmila Sahoo.Laminated composite stiffened cylindrical shell panels with cutouts under free vibration[J].International Journal of Manufacturing,Materials,and Mechanical Engineering(IJMMME),2015(3):37-63.
[17]Dey Tanish,Ramachandra L S.Non-Linear vibration analysis of laminated composite circular cylindrical shells[J].Composite Structures,2016(6):135-148.
[18]蔡四维.复合材料结构力学[M].北京:人民交通出版社,1987:7-38.
Vibrational characteristics of laminated composite cylindrical shell
TAN An-quan1,LIU Jing-xi2,LI Tian-yun2,ZHU Xiang2
(1.China Classification Society Chongqing Branch,Chongqing 401121,China;2.College of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering,Huazhong University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430074,China)
Based on the Love theory,the vibrational characteristics of laminated composite cylindrical shell are studied.The obtained results were evaluated with those in the literature and both are in agreement.With this method,the influences of boundary conditions,axial modes and fiber angles on the vibrational characteristics of cylindrical shell are investigated.It is concluded that the influences of boundary conditions and axial modes can be seen to be more significant at small circumferential modes than at large circumferential modes.
composite cylindrical shell;vibration;boundary condition;circumferential mode
O343
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2017.08.013
1007-7294(2017)08-1035-06
2016-12-14
国家自然科学基金资助项目(40976058)
谭安全(1986-),男,工程师,E-mail:tananquan@126.com;刘敬喜(1975-),男,副教授。
