双系统离子色谱法同时测定湖水中的氨氮和过硫酸根
2017-08-02戚荣平周晓红孟琪桑娴商晓春郭伟强
戚荣平, 周晓红, 孟琪, 桑娴, 商晓春, 郭伟强
(1. 浙江大学 化学系, 浙江 杭州 310027; 2. 杭州市下城区疾病预防控制中心, 浙江 杭州 310003)
双系统离子色谱法同时测定湖水中的氨氮和过硫酸根
戚荣平1,2, 周晓红2, 孟琪2, 桑娴2, 商晓春2, 郭伟强1
(1. 浙江大学 化学系, 浙江 杭州 310027; 2. 杭州市下城区疾病预防控制中心, 浙江 杭州 310003)
研究过硫酸盐降解水体中氨氮等含氮化合物的能力,必须掌握能够同时监测水体中以氨氮为代表的含氮化合物以及过硫酸根含量的分析方法.建立了一种同时测定湖水中氨氮和过硫酸根的双系统离子色谱法.过硫酸根在一定的光、热、过渡金属离子条件下可分解水体中的氨氮.通过双系统离子色谱,分别以甲烷磺酸和氢氧化钾为淋洗液,抑制电导检测.结果表明:该方法氨氮检出限为0.005 mg·L-1,过硫酸根检出限为0.009 mg·L-1,相对标准偏差均小于1.78%,加标回收率为98.2%~103.5%,为环境实时监测提供了方便、快捷、有效的分析方法.
双系统离子色谱;氨氮;过硫酸根;同时测定
0 引 言

目前,氨氮的测定方法主要有分光光度法[6-9]、蒸馏-中和滴定法[8]以及离子色谱法[1-2,10-11]等.过硫酸根的仪器分析方法主要有光谱法[12-13]和色谱法[14-16].若分开测定氨氮和过硫酸根,耗时耗力,操作繁琐.虽然,离子色谱法对氨氮和过硫酸根都能进行较为灵敏的有效检测,但在同一样品中同时测定氨氮和过硫酸根的方法则鲜有报道.本研究采用离子色谱双系统同时测定湖水中的氨氮和过硫酸根,灵敏度高,选择性好,检出限低,可为环境实时监测提供方便、快捷、有效的分析方法.
1 实验部分
1.1 实验与试剂
美国赛默飞(Thermofisher)公司ICS-3000 型离子色谱仪,EG40(EGC-MSA)淋洗液发生器,EG40(EGC-KOH)淋洗液发生器,CSRS 300(4 mm)阳离子抑制器,ASRS 300 (4 mm) 阴离子抑制器,电导检测器,Chromeleon 6.8 色谱工作站,IonPac CG12A (50 mm×4.0 mm) 保护柱,IonPac CS12A (250 mm×4.0 mm) 分析柱,IonPac AG11 (50 mm×4.0 mm) 保护柱,IonPac AS11 (250 mm×4.0 mm) 分析柱.SPE C-18短柱(天津富集科技有限公司).
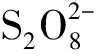
地表水样品从杭州西湖中采集.取样后通过离心除去悬浮物,24 h内测定.
1.2 样品处理
水样中加入适量的过硫酸根,水浴加热至70 ℃,反应0~4 h后,放冷取样经孔径0.22 μm滤膜过滤、SPE C18短柱后直接进样.
1.3 色谱条件
阳离子系统:淋洗液为18 mmol·L-1甲烷磺酸,流速为1.0 mL·min-1,抑制电流为50 mA,进样量为25 μL.
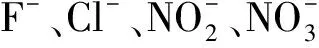
2 结果与讨论
2.1 色谱柱的选择
用于测定常规阳离子的色谱柱主要有IonPac CS12A、 CS16以及CS17.其亲水性IonPac CS17最弱,适合分析有机胺类,IonPac CS16 最强,IonPac CS12A次之.由于水体中的阳离子主要为1价和2价阳离子,而IonPac CS16 对2价阳离子的分析时间较长,效率低.综合考虑,采用IonPac CS12A作为分析柱.
用于测定阴离子的色谱柱种类很多,有强疏水性的、高柱容量的.由于过硫酸根的强保留性,且其他常规阴离子可以采用赛默飞世尔科技公司大多数的色谱柱,因此本系统适合采用低阴离子交换量的色谱柱,即采用IonPac AS11色谱柱作为阴离子分析柱.
2.2 色谱条件的选择
对于常规阳离子分析,等度的甲烷磺酸即可得到较好的分离度.因此,本方法选择18 mmol·L-1的甲烷磺酸作为流动相,在20 min内即可完成分析.
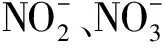
2.3 标准曲线的绘制
准确吸取铵根标准储备液逐级稀释,配制成浓度分别为0.05,0.1,0.5,1.0,2.5,5.0 mg·L-1的标准溶液,在1.3节色谱分析条件下进样分析,以峰面积y(μS·min)对氨氮的质量浓度x(mg·L-1)进行线性回归,线性方程为y=0.897 4x+0.103 3,线性相关系数为0.999 5.与此同时,准确吸取过硫酸根标准储备液逐级稀释,配制成浓度分别为0.05,0.1,0.5,1.0,5.0,10.0 mg·L-1的标准溶液,在1.3节色谱分析条件下进样分析,以峰面积y(μS·min)对过硫酸根的质量浓度x(mg·L-1)进行线性回归,线性方程为y=0.206 8x+0.034 7,相关系数为0.999 7.
2.4 方法的检出限
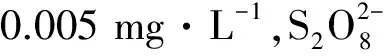
2.5 精密度实验
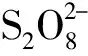
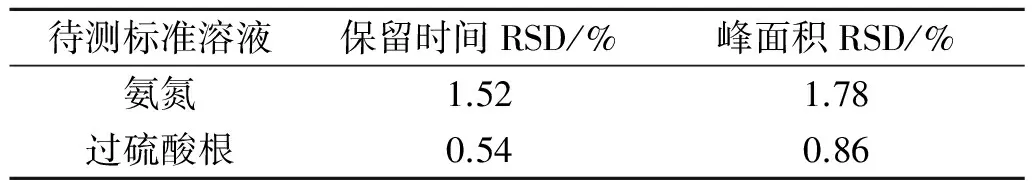
表1 精密度实验结果(n=6)
2.6 样品测定及加标回收实验
实验的水样取自杭州西湖.在水样中加入10 mg·L-1过硫酸根,经过样品处理后在优化的色谱条件下测定,采用外标法定量.实验测定结果见表2,图谱见图1和图2.参照GB 3838-2002《地表水环境质量标准》,将地表水分为Ⅰ~Ⅴ 类,对应的氨氮质量分数逐步升高,分别为0.15,0.5,1.0,1.5,2.0 mg·L-1.一般景观要求水域限值为2.0 mg·L-1.取样的湖水均符合标准.
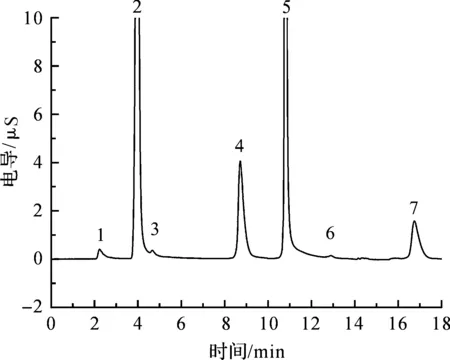
图1 加入过硫酸根的水样I的阴离子色谱图Fig.1 Analysis anions in lake water I with peroxydisulfate introduced by the IC system色谱峰:(1)氟离子(F-);(2)氯离子(Cl-);(3)亚硝酸根;(4)硝酸根;(5)硫酸根;(6)磷酸根;(7)过硫酸根).).
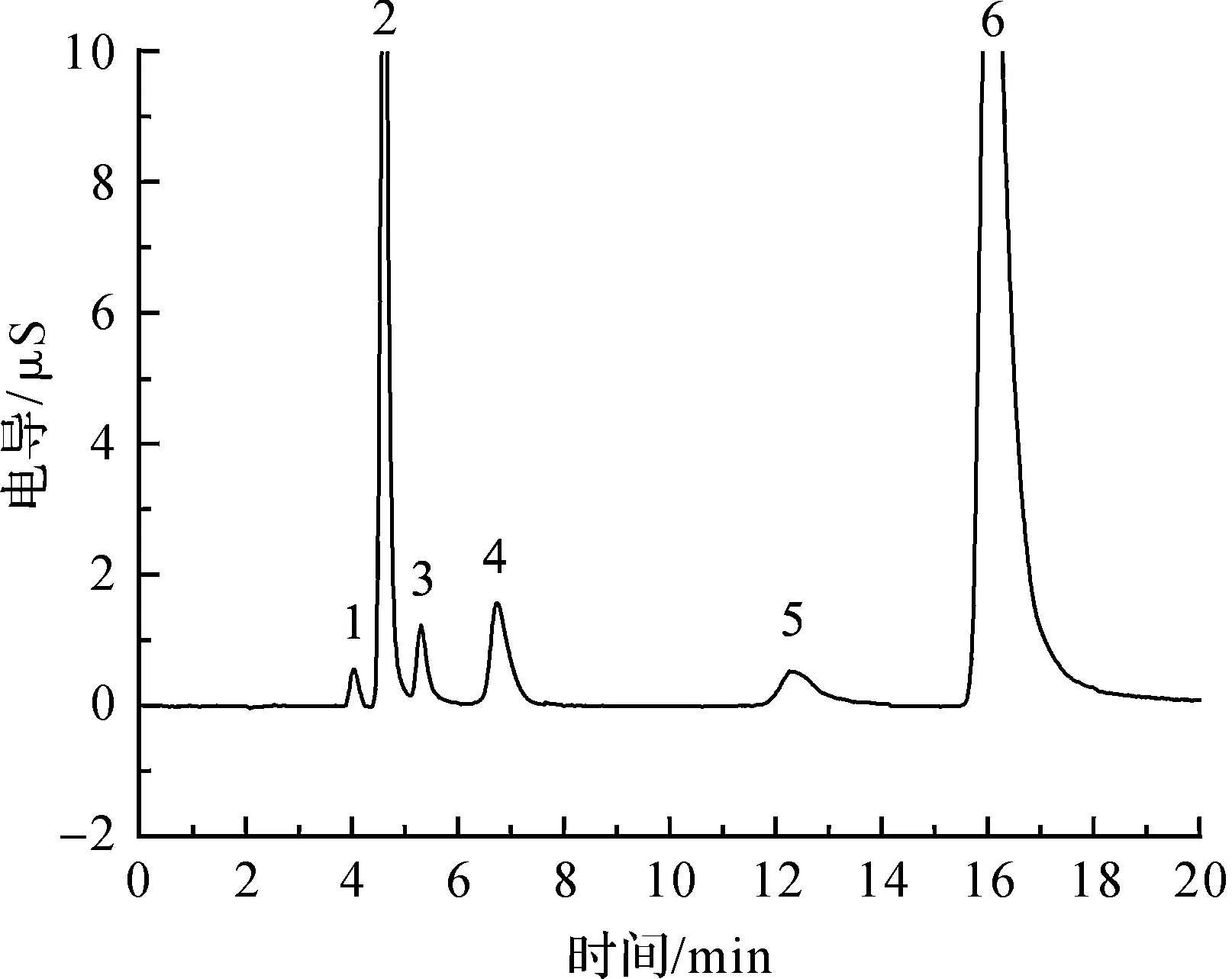
图2 加入过硫酸根的水样I的阳离子色谱图Fig.2 Analysis cations in lake water I with peroxydisulfate introduced by the IC system 色谱峰:(1)锂离子(Li+);(2)钠离子(Na+);(3)铵根离子;(4)钾离子(K+);(5)镁离子(Mg2+);(6)钙离子(Ca2+).Peaks: (1)Lithium(Li+);(2)Sodium(Na+);;(4)potassium(K+);(5)magnesium(Mg2+);(6)calcium(Ca2+).
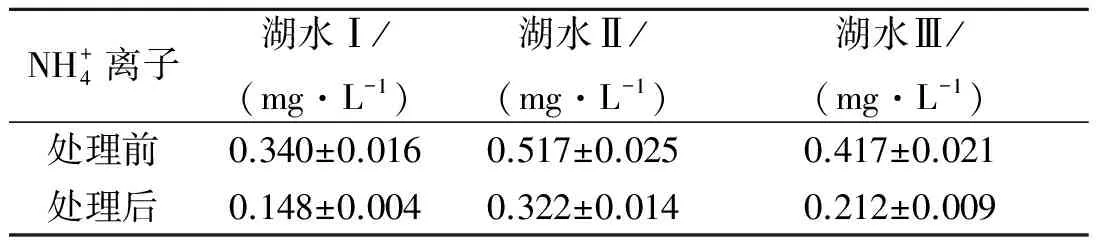
NH+4离子湖水Ⅰ/(mg·L-1)湖水Ⅱ/(mg·L-1)湖水Ⅲ/(mg·L-1)处理前0.340±0.0160.517±0.0250.417±0.021处理后0.148±0.0040.322±0.0140.212±0.009
由表2可知,通过过硫酸盐降解处理后的西湖水质已经达到国家水源水质的要求(2005年6月1日开始实施的《城市供水水质标准》(CJ/T206-2005)规定城市供水中氨氮含量不得超过0.5 mg·L-1),该治理方法具有明显的效果.
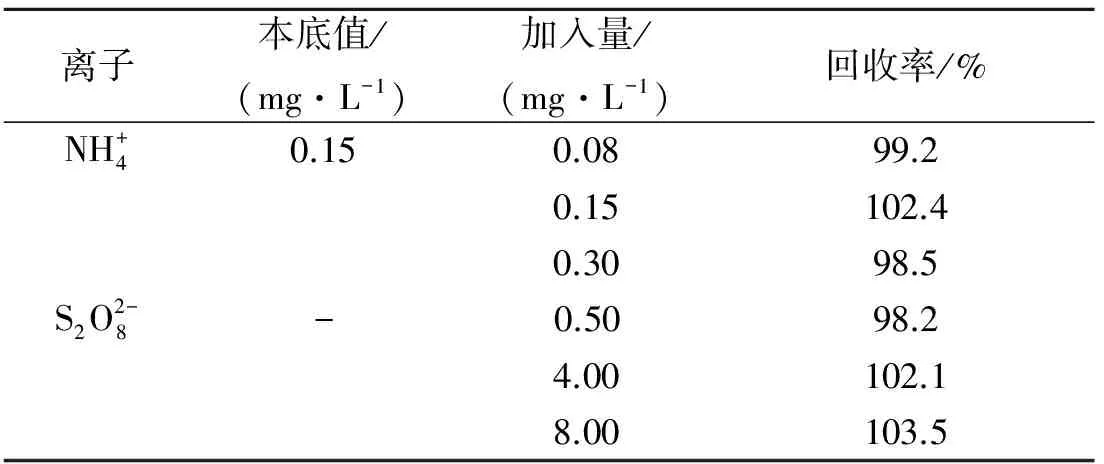
表3 过硫酸根和氨氮的加标回收率
2.7 过硫酸根消耗情况
过硫酸盐在加热条件下可活化成硫酸根自由基,通过电子转移、氢提取等方式氧化降解水体中的大多数有机物[17].图3表示的是不同时间段过硫酸根消耗量的趋势图.纵坐标表示的是实时过硫酸根量/最初过硫酸根量的对数值,横坐标表示反应时间.从图3可以看出,在给定实验条件下,水样中的过硫酸根消耗是时间的一阶函数,同时证明该方法可以实时监测过硫酸根的浓度.
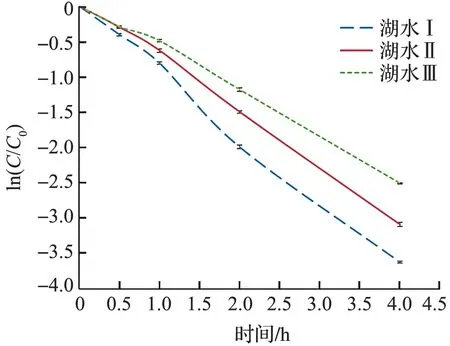
图3 过硫酸根在 70 ℃ 和 pH=7条件下的降解情况(n=6)Fig.3 The decomposition of peroxydisulfate at 70 ℃ and pH=7(n=6)
3 结 论
建立了离子色谱双系统法同时检测水体中的氨氮和过硫酸根,阳离子检测系统以甲烷磺酸溶液进行等度淋洗,阴离子检测系统选择氢氧化钾溶液进行梯度淋洗,2种检测系统中各待测离子均分离良好.实验结果表明,通过阳离子分析可以监控氨氮浓度,证实过硫酸盐水处理的有效性.通过检测过硫酸根含量,发现随着水处理时间的延长,过硫酸根含量逐渐减少,表明对过硫酸根有降解作用.本方法实用、方便、准确,精密度高,适用于环境领域水处理的实时监测.
[1] 袁明浩,张喜凤,张文丽.离子色谱法测定工业废水中的氨氮[J].河南科学,2014,32(10):2117-2119. YUAN M H, ZHANG X F, ZHANG W L. Determination of ammonia nitrogen in industrial wastewater by ion chromatography[J]. Henan Science,2014,32(10):2117-2119.
[2] 马云云,谭金峰,王斌之.离子色谱测定环境水样中的氨氮[J].环境科学与管理,2011,36(3):92-93. MA Y Y,TAN J F,WANG B Z. NH3-N monitoring in water by IC method[J]. Environmental Science and Management,2011,36(3):92-93.
[3] 李丽,刘占孟,聂发挥.过硫酸盐活化高级氧化技术在污水处理中的应用[J].华东交通大学学报,2014,31(6):114-117. LI L, LIU Z M, NIE F H. Research of activating persulfate oxidation technology in sewage disposal[J]. Journal of East China Jiaotong University,2014,31(6):114-117.
[4] TSITONAKI A, PETRI B, CRIMI M, et al. In situ chemical oxidation of contaminated soil and groundwater using persulfate: A review[J]. Critica Reviews Environmental Science and Technology,2010,40:55-91.
[5] 杨世迎,陈友媛,胥慧真,等.过硫酸盐活化高级氧化新技术[J].化学进展,2008,20(9):1433-1438. YANG S Y, CHEN Y Y, XU H Z, et al. A novel advanced oxidation technology based on activated persulfate[J]. Progress in Chemistry,2008,20(9):1433-1438.
[6] 国家环境保护部.水质氨氮的测定纳氏试剂分光光度法HJ535-2009[S].北京:中国环境科学出版社,2009-12-31[2010-04-01]. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Water quality-determination of ammonia nitrogen-Nseeler’s reagent spectrophotometry HJ535-2009[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press,2009-12-31[2010-04-01].
[7] 万霞,冯洁频,冯佳和,等.流动注射-分光光度法测定环境水样中的氨氮[J].绿色科技,2011(11):108-109. WAN X, FENG J P, FENG J H, et al. The flow injection-spectrophotometry determination of ammonia in water[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology,2011(11):108-109.
[8] 杨铠齐.氨氮的测定蒸馏中和滴定法与纳氏试剂分光光度法的比较[J].汕头科技,2011(4):48-50. YANG K Q. The comparison of distillation neutralized titration with nesslers reagent spectrophotometry in determination of ammonia nitrogen[J]. Shantou Science and Technology,2011(4):48-50.
[9] 尚玲伟,张剑平,张红丽,等.离子色谱法纳氏试剂光度法测定地表水中氨氮的比较试验[J].环境科学与管理,2009,34(3):143-147. SHANG L W,ZHANG J P,ZHANG H L, et al. Comparison of ion chromatography with Nessler’s reagent spectrophotometry in detecting the concentrations of NH4-N in surface water samples[J].Environmental Science and Management,2009,34(3):143-147.
[10] 章骅,宋文华,赵婷.双系统离子色谱同时测定河流中的氨氮、亚硝酸盐和硝酸盐的含量[J].环境污染与防治,2013,35(9): 75-81. ZHANG H, SONG W H, ZHAO T. Determination of ammonia nitrogen,nitrate and nitrite in river by dual system ion chromatography[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control,2013,35(9):75-81.
[11] 甄玉静,程俊峰,梅清科.地表水中氨氮测定方法的研究[J].内蒙古石油化工,2014(9):5-7. ZHEN Y J, CHENG J F, MEI Q K. Study on determination of ammonia in surface water[J]. Inner Mongolia Petrochemical Industry,2014(9):5-7.
[12] LIANG C J, HUANG C F, MOHANTY N, et al. A rapid spectrophotometric determination of persulfate anion in ISCO[J]. Chemosphere,2008,73:1540-1543.
[13] SHIUNDU P M, WADE A P, JONNALAGADDA S B. Spectrophotometric determination of peroxydisulphate with o-dianisidine by flow injection[J]. Canadian Journal of Chemistry,1990,68:1750-1756.
[14] WEIDENAUER M, HOFFMANN P, LIESER K H. Separation of inorganic sulphur-anions with ion-exchange and ion-pair chromatography[J]. Analytical Chemistry,1988,331:372-375.
[15] KHAN N E, ADEWUYI Y G. A new method of analysis of peroxydisulfate using ion chromatography and its application to the simultaneous determination of peroxydisulfate and other common inorganic ions in a peroxydisulfate matrix[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2011,1218(3):392-397.
[16] HUANG Z P, NI C Z, WANG F L, et al. Simultaneous determination of peroxydisulfate and conventional inorganic anions by ion chromatography with the column-switching technique[J]. Journal of Separation Science,2014,37:198-203.
[17] 王兵,李娟,莫正平,等.基于硫酸自由基的高级氧化技术研究及应用进展[J].环境工程,2012,30(4):53-57. WANG B, LI J, MO Z P, et al. Progress advanced oxidation processes based on sulfate radical[J]. Environmental Engineering,2012,30(4):53-57.
Simultaneous determination of ammonia nitrogen and peroxydisulfate in lake water by dual system ion chromatography.
QI Rongping1,2, ZHOU Xiaohong2, MENG Qi2, SANG Xian2, SHANG Xiaochun2, GUO Weiqiang1
(1.DepartmentofChemistry,ZhejiangUniversity,Hangzhou310027,China; 2.CenterforDiseaseControlandPreventionofXiachengDistrict,Hangzhou310003,China)
In order to study the ability of peroxydisulfate in degrading ammonia nitrogen and other nitrogen compounds in water, it is necessary to analyze the content of nitrogen compounds and peroxydisulfate in the water. Simultaneous determination of ammonia nitrogen and peroxydisulfate in lake water by dual system ion chromatography was proposed. Ammonia nitrogen could be decomposited by peroxydisulfate under the proper condition of light, heat and transition metal ions. KOH and MSA were used as eluent, and suppression conductivity detector was used for detection. The detection limits (LODs) of ammonia nitrogen and peroxydisulfate were 0.005 mg·L-1and 0.009 mg·L-1, respectively, based on the signal-to-noise ratio of 3 (S/N=3) and the 25 μL injection volume. Relative standard deviations (RSDs) for retention time and peak area were all less than 1.78%. The easy and fast method was performed with satisfactory recoveries between 98.2% to 103.5% for all ions. It provides a convenient, rapid and effective analysis method for environmental monitoring.
dual system ion chromatography;ammonia nitrogen; peroxydisulfate;simultaneous determination

2016-10-27.
戚荣平(1977-),ORCID: http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3581-1466,男,学士,主任技师,主要从事理化检验研究,E-mail:363748275@qq.com.
10.3785/j.issn.1008-9497.2017.04.014
O 657.7
A
1008-9497(2017)04-480-05
Journal of Zhejiang University(Science Edition), 2017,44(4):480-484
