MecA、Nuc基因在耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌检测中的应用
2017-06-27郭建巍齐文峰郝秀红李文军陈昌国马志家陈秋圆赵强元
郭建巍,齐文峰,郝秀红,李文军,陈昌国,张 云,马志家,陈秋圆,赵强元
MecA、Nuc基因在耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌检测中的应用
郭建巍,齐文峰,郝秀红,李文军,陈昌国,张 云,马志家,陈秋圆,赵强元
目的 通过对180株金黄色葡萄球菌临床分离株MecA、Nuc基因的检测,以期选择出一种适合临床的并能简便、快速、准确检测耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌(methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus,MRSA)的方法。方法 细菌鉴定及药敏采用全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪。MecA、Nuc基因检测采用荧光定量聚合酶链反应(fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction,FQ-PCR)法。结果 FQ-PCR对180株金黄色葡萄球菌MecA、Nuc基因检出率为75.0%,全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪对180株金黄色葡萄球菌的MRSA检出率为72.8%,2种检测方法比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪对MRSA的检测正确率为94.8%。结论 FQ-PCR检测MRSA正确率高,只需要1~2 h即可完成。该方法快速、简便、准确,值得推广应用。
耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌;MecA基因;Nuc基因;荧光定量聚合酶链反应;全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪
金黄色葡萄球菌是医院感染和社区感染的重要病原菌,在金黄色葡萄球菌引起的临床感染中,耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌(methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus,MRSA)占到了60%~80%[1-4],并逐年增加。确定金黄色葡萄球菌是否为MRSA对指导临床合理使用抗生素以及制定防控措施具有重要意义。MecA基因是耐甲氧西林的决定性因素。本研究拟通过对金黄色葡萄球菌临床分离株MecA、Nuc基因检测与全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪结果进行比较,以期选择出一种简便、快速、准确检测MRSA的方法。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 菌株 180株金黄色葡萄球菌分离自2011年1月—2013年12月为临床送检的样本,样本类型有血液、尿液、胸腹水、痰液。质控菌金黄色葡萄球菌ATCC25923购自卫生部临床检验中心。
1.1.2 仪器 法国生物梅里埃公司全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪(VITEK COMPACT);荧光定量聚合酶链反应(fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction,FQ-PCR)分析仪(SLAN,上海宏石医疗科技有限公司);金黄色葡萄球菌MecA、Nuc基因检测试剂(上海之江生物科技有限公司,批号2014002)。
1.2 方法 细菌分离鉴定按第4版《全国临床检验操作规程》进行[5];FQ-PCR检测MRSA根据试剂盒操作说明书进行,扩增条件为94℃2 min、93℃2 min、62℃30 s,循环40次,在62℃上机荧光检测。
1.3 统计学处理 应用SPSS 18.0软件,计数资料用百分比表示,采用χ2检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 FQ-PCR荧光扩增曲线 耐甲氧西林MecA基因阳性,金黄色葡萄球菌特异性Nuc基因阳性,荧光曲线均为典型的S形(图1)。

图1 MRSA的MecA、Nuc基因双阳检测
耐甲氧西林MecA基因阴性,金黄色葡萄球菌特异性Nuc基因阳性,荧光曲线为典型的S形(图2)。
耐甲氧西林MecA基因阴性,金黄色葡萄球菌特异性Nuc基因阴性,均无特异性扩增曲线(图3)。
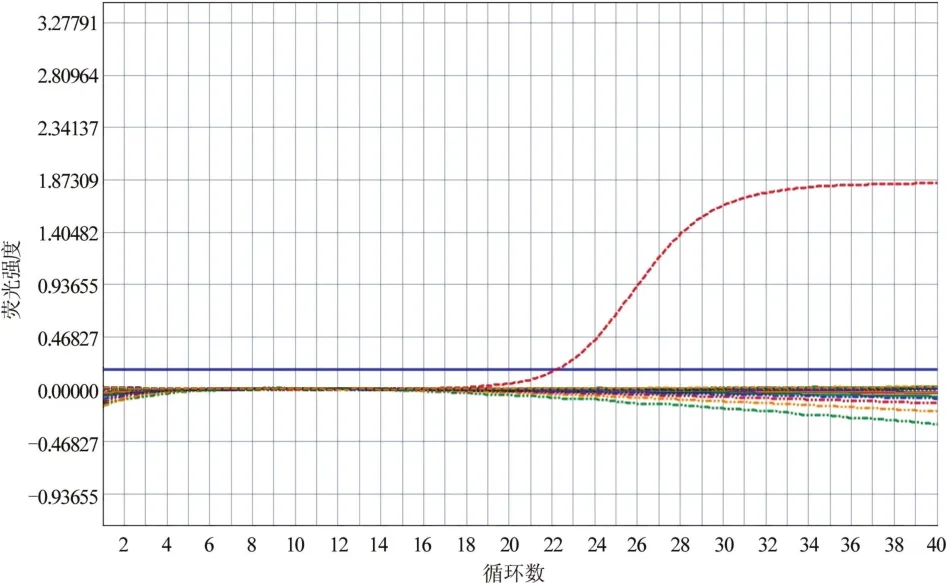
图2 MSSA的MecA基因阴性、Nuc基因阳性检测
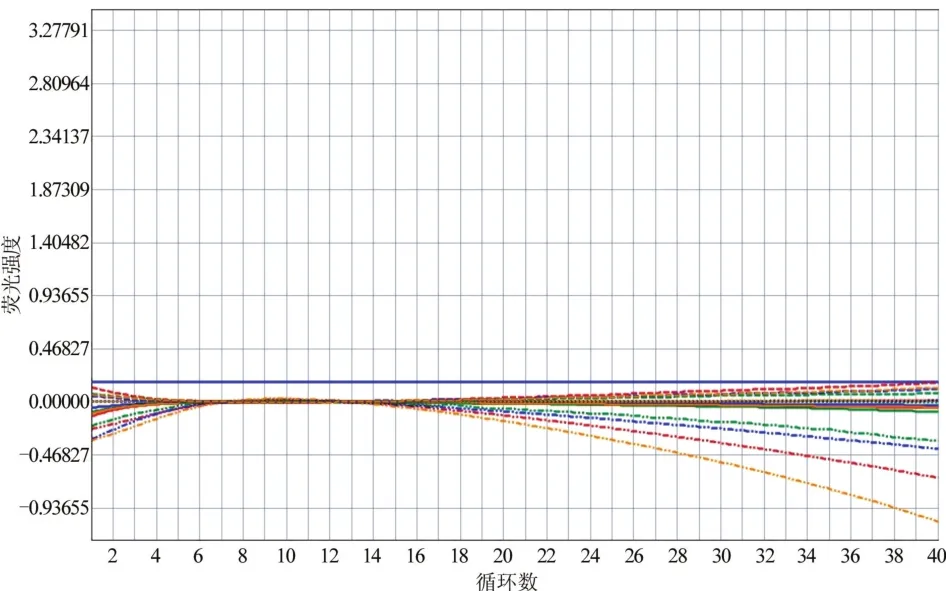
图3 MecA、Nuc基因双阴检测
2.2 细菌鉴定和药敏分析 180株样本中,全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪鉴定,有131株MRSA,检出率为72.8%;49株为甲氧西林敏感金黄色葡萄球菌(methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus,MSSA),检出率为27.2%。FQ-PCR对180株金黄色葡萄球菌MecA、Nuc基因进行检测,MecA、Nuc基因检出率为75.0%(均为阳性即MRSA)。两者比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。如以FQ-PCR法作为MRSA测定的“金标准”,有7株本是MRSA,全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪报成MSSA;3株本是MSSA,全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪报成MRSA。对错误菌株进行校正后全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪对180株金黄色葡萄球菌的MRSA检出率为71.1%,检测正确率为94.8%。
3 讨论
传统的MRSA检测方法有苯唑西林和头孢西丁纸片扩散法、琼脂稀释法、青霉素结合蛋白2a胶乳凝集筛选试验、微量肉汤稀释法等[6-7]。这些方法操作费时、费力、判读不客观,准确度有待验证。表型检测方法受遗传背景、诱导剂和培养条件等因素影响,使得同一菌株随培养条件和使用抗生素的不同抗药性有变化(即异质性)。随着全自动细菌鉴定仪的普遍使用,许多医院已经开始用其取代传统手工鉴定和药敏方法。全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪通常需要48~72 h才能向临床提供报告,但其对MRSA的确诊率是多少、方法的敏感性、特异性如何鲜见报道。
MRSA具有较强的外界适应能力、定植能力和对β-内酰胺类抗生素的耐受能力,其所致感染的流行病学逐渐从过去的院内获得型逐渐向社区获得型转化。目前认为MecA基因为MRSA耐药的决定基因,金黄色葡萄球菌一旦获得MecA基因,即表现为高度耐药和多重耐药。Nuc基因是编码金黄色葡萄球菌耐热核酸酶的基因,在不同菌株之间具有较高的保守性,是金黄色葡萄球菌特异性基因。用FQ-PCR法联合检测MecA、Nuc基因,既保证了金黄色葡萄球菌检测的特异性,又保证了MRSA检测的特异性。由于分子生物学方法具有特异、灵敏、快速的特点,与全自动微生物鉴定和药敏分析仪相比,从理论上更适用于临床或社区MRSA感染的快速检测[8-14]。
本研究使用的180株金黄色葡萄球菌,通过全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪确认,有131株MRSA、49株MSSA。进一步用FQ-PCR法进行确认后,有7株本是MRSA,全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪报成MSSA,MRSA的漏报很有可能造成其传播,从而引起严重院内感染的爆发;3株本是MSSA,全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪报成MRSA,MRSA的错报可能会导致临床抗生素的滥用。
FQ-PCR对180株金黄色葡萄球菌的MecA基因检出率为75.0%,全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪对180株金黄色葡萄球菌的MRSA检出率为72.8%;对全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪错误菌株进行校正后,全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪对180株金黄色葡萄球菌的MRSA检出率为71.1%,全自动细菌鉴定和药敏分析仪对MRSA的检测正确率为94.8%。
本研究表明,用FQ-PCR检测金黄色葡萄球菌的MRSA快速、敏感、准确,与国外的研究结果基本一致[15],可为临床提供及时的病原菌防控信息,为抗菌药物的合理使用、院内感染的预防指导提供科学依据。
[1]Hiramatsu K,Cui L,Kuroda M,et al.The emergence and evolution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Trends Microbiol,2001,9(10):486-493.
[2]Dumitrescu O,Dauwalder O,Boisset S,et al.Staphylococcus aureus resistance to antibiotics:key points in 2010[J]. Med Sci(Paris),2010,26(11):943-949.
[3]Cosgrove SE,Sakoulas G,Perencevich EN,et al.Comparison of mortality associated with methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia:a meta-analysis[J].Clin Infect Dis,2003,36(1):53-59.
[4]Cosgrove SE,Qi Y,Kaye KS,et al.The impact of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia on patient outcomes:mortality,length of stay,and hospital charges[J]. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol,2005,26(2):166-174.
[5]尚红,王毓三,申子瑜.全国临床检验操作规程[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2015.
[6]Louie L,Matsumura SO,Choi E,et al.Evaluation of three rapid methods for detection of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus[J].J Clin Microbiol,2000,38(6): 2170-2173.
[7]Pourmand MR,Hassanzadeh S,Mashhadi R,et al.Comparison of four diagnostic methods for detection of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus[J].Iran J Microbiol,2014,6(5):341-344.
[8]Liu Y,Zhang J,Ji Y.PCR-based approaches for the detection of clinical methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus [J].Open Microbiol J,2016,14(10):45-56.
[9]Huletsky A,Giroux R,Rossbach V,et al.New real-time PCR assay for rapid detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus directly from specimens containing a mixture of staphylococci[J].J Clin Microbiol,2004,42 (5):1875-1884.
[10]Cuny C,Witte W.PCR for the identification of methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA)strains using a single primer pair specific for SCCmec elements and the neighbouring chromosomeborne orfX[J].Clin Microbiol Infect,2005,11(10):834-837.
[11]Holfelder M,Eigner U,Turnwald AM,et al.Direct detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in clinical specimens by a nucleic acid-based hybridization assay [J].Clin Microbiol Infect,2006,12(12):1163-1167.
[12]Boyce JM,Havill NL.Comparison of BD GeneOhm methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA)PCR versus the CHROMagar MRSA assay for screening patients for the presence of MRSA strains[J].J Clin Microbiol,2008,46:350-351.
[13]Francois P,Bento M,Renzi G,et al.Evaluation of three molecular assays for rapid identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus[J].J Clin Microbiol,2007,45(6):2011-2013.
[14]Deplano A,Tassios PT,Glupczynski Y,et al.In vivo deletion of the methicillin resistance mec region from the chromosome of Staphylococcus aureus strains[J].J Antimicrob Chemother,2000,46(4):617-620.
[15]Sudhaharan S,Vanjari L,Mamidi N,et al.Evaluation of LAMP assay using phenotypic tests and conventional PCR for detection of nuc and mecA genes among clinical isolates of Staphylococcus spp[J].J Clin Diagn Res,2015,9(8): DC06-DC09.
Application of MecA and Nuc genes detection in clinical isolated methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus
GUO Jianwei,QI Wenfeng,HAO Xiuhong,LI Wenjun,CHEN Changguo,ZHANG Yun,MA Zhijia,CHEN Qiuyuan,ZHAO Qiangyuan
(Department of Clinical Laboratory,Navy General Hospital,Beijing 100048,China)
Objective In order to choose an easier performed rapid and accurate methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA)detection method.MecA and Nuc genes were detected from 180 strains clinical isolated Staphylococcus aureus.Methods Staphylococcus aureus were identified by automatic bacteria identification and drug sensitivity analyzer.MecA and Nuc genes were detected by fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction(FQ-PCR)analyzer.Results The expression rate of MecA and Nuc genes in 180 Staphylococcus aureus was 75.0%.MRSA positive rate of 180 Staphylococcus aureus identified by automatic bacteria identification and drug sensitivity analyzer was 72.8%.No difference between automatic bacteria identification and FQ-PCR.The accuracy rate of automatic bacteria identification and drug sensitivity analyzer was 94.8%.Conclusion Detection MRSA according to quantitation of MecA and Nuc genes expression by FQ-PCR has a high accurate rate.The whole experiments would be finished in 1—2 hours.This method is rapidly,easily performed and has a wide application.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA);MecA gene;Nuc gene;Fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction(FQ-PCR);Automatic bacteria identification and drug sensitivity analyzer
R446.5
B
2095-3097(2017)03-0157-03
10.3969/j.issn.2095-3097.2017.03.007
2016-04-11 本文编辑:张在文)
国家自然科学基金面上项目(30872394);北京市自然科学基金资助项目(面上项目)(7162188)
100048北京,海军总医院检验科(郭建巍,齐文峰,郝秀红,李文军,陈昌国,张 云,马志家,陈秋圆,赵强元)
[注 明]郭建巍,齐文峰:并列第一作者
