杜仲化学成分及药理作用研究进展
2017-06-08张帅男李煦照
张帅男++李煦照


【摘要】对杜仲的化学成分和药理作用进行综述。在体内和体外实验中,杜仲的药理作用主要表现在抗高血压、高血糖、糖尿病、肥胖、骨质疏松症、阿尔兹海默症、衰老和性功能低下等。目前发现的杜仲化学成分共有70种化合物,包括27种木质素、6种环烯醚萜、13种酚类、9种甾体和萜类、8种黄酮和7种其他化合物。但这些化合物的潜在活性和潜在毒性以及作用机制尚未明晰,仍需通过系统生物学和系统毒理学方法对其进行挖掘和筛选。
【关键词】杜仲;化学成分;药理作用
【中图分类号】R2855【文献标志码】 A【文章编号】1007-8517(2017)10-0056-06
The Research Review of the Components and Pharmacological Action of the Bark of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.
ZHANG ShuainanLI Xuzhao*
Pharmacy Schoolof Guiyang University of Chinese Medicine, Guiyang 550025,China
Abstract:This article reviewed the components and pharmacological action of the bark of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.(EO). In modern pharmacological studies, in vivo and in vitro, Eucommia ulmoides has showed treatment effect on hypertension, hyperglycemia, diabetes, obesity, osteoporosis, Alzheimer's disease, aging, and sexual dysfunction and so on. There are 70 components have been isolated and identified from EO bark, including 27 lignans, 6 iridoids, 13 phenolics, 6 steroids, 3 terpenoids, 8 flavonoids and 7 other compounds. However, the potential activities and toxicity of these compounds and mechanism are not been clarified and need to be developed and screened by system biology and system toxicology research method.
Keywords:Bark of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.;Compounds; Pharmacological Action
杜仲(Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.)是杜仲科杜仲屬多年生落叶乔木,其药材是杜仲树的干燥树皮。杜仲具有补肝肾、强筋骨、安胎的功效,用于肝肾不足、腰膝酸痛、筋骨无力、头晕目眩、妊娠漏血、胎动不安[1]。杜仲单独用药或组方用药能够治疗阳痿、遗精、早泄、健忘、骨质疏松症、更年期综合征、高血压、类风湿性关节炎、腰痛、坐骨神经痛、膝盖痛、肾脏缺乏性疼痛、骨折和关节疾病等。药理学研究发现,杜仲化学成分对高血压、高血糖、糖尿病、肥胖、骨质疏松症、阿尔兹海默症、衰老和性功能低下等均有药理活性[2]。现将杜仲的化学成分和药理作用,综述如下。
1杜仲的化学成分
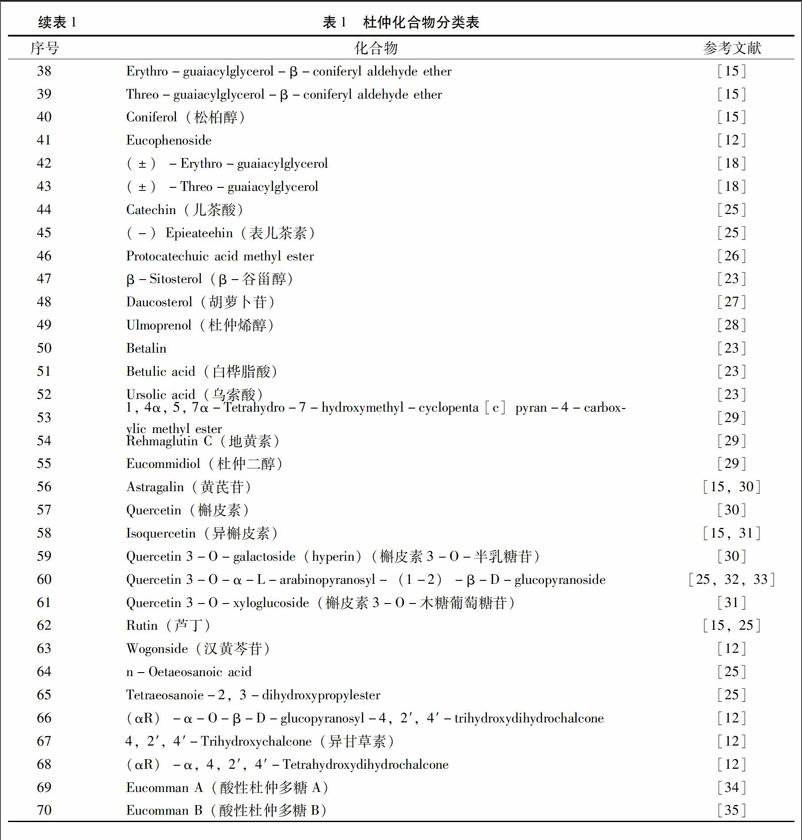
目前相关研究已从杜仲中分离得到了70种化合物,包括27种木质素、6种环烯醚萜、13种酚类、9种甾体和萜类、8种黄酮和7种其他化合物。见表1。
11木脂素类木脂素及其衍生物是杜仲的主要成分。据统计,从杜仲中已分离出27种木脂素,包括双环氧木脂素(1-15)、单环氧木脂素(16-20)、新木脂素(21-25)、倍半木脂素(26-27)。
12环烯醚萜类杜仲的另一种主要成分是环烯醚萜类。目前已有6种环烯醚萜类成分从杜仲中提取并鉴定出来。在这些化学成分中京尼平苷酸在体内和体外实验中已经证实其具有多种生物活性[2-7]。
13酚类酚类成分具有抗氧化、抗突变、抗炎和抗癌活性。据统计,从杜仲中已分离并鉴定出13种酚类成分(34-46)。在这些成分中,绿原酸具有保护神经的作用[2],也是评价杜仲提取物和制剂质量的重要指标。
14甾体和萜类在杜仲中仅发现并纯化了9种甾体(47-52)和萜类(53-55)。目前,在杜仲中已分离出β-谷甾醇、胡萝卜苷、杜仲丙烯醇、betalin、白桦脂酸、杜仲二醇、地黄酸C、1, 4α, 5, 7α-tetrahydro-7-hydroxymethylcyclopenta [c] pyran-4-carboxylic methyl ester[8]。
15黄酮类黄酮类成分是自然界中非常普遍的次生代谢产物。目前,从杜仲中已经提鉴定出了山槲皮素、芦丁、槲皮素3-O-半乳糖苷、quercetin 3-O-α-L-arabino-pyranosyl-(1-2)-β-D-glucopyranoside、异槲皮素等。
16其他成分杜仲中还含有多糖、氨基酸、脂肪酸、Cutta-percha、微量元素等。如杜仲多糖A和杜仲多糖B,Ethylglucopyranoside、noetaeosanoic acid、tetraeosanoie-2, 3-dihydroxy-propylester、(αR)-α-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-4,2′,4′-trihydroxy-dihydrochalcone、4,2′,4′-trihy-droxychalcone、(αR)-α,4,2′,4′-tetrahydroxy-dihydrochalcone[9-12]
2药理作用
杜仲具有多种药理作用,可用于治疗阳痿、高血压、高血脂、糖尿病、肥胖、关节炎、阿尔茨海默病等。
21抗高血压通过体内和体外药理实验发现,杜仲中的木脂素和提取物具有抗高血压的作用。其机制是通过抑制cAMP、钙离子内流、调控NO含量、肾上腺素-血管紧张素系统、舒张血管、增加冠脉血流量来产生降压作用。杜仲中槲皮素、芦丁、山柰酚等化学成分作用于 C3、BDKR B2、CA1 疾病靶点可产生对高血压的治疗、调节、预防作用。通过构建整体网络,发现杜仲抗高血压的3条主要途径是通过抑制血管重塑过程改善高血压的恶化病情、影响与原发性高血压发病有关的多态性遗传基因的活性、抑制碳酸酐酶活性维持机体渗透压[36]。槲皮素是杜仲中主要的降压成分。槲皮素根据浓度高低的不同,其降压机制也不同。在低浓度时,槲皮素的舒张血管作用具有内皮依赖性,通过促进内皮细胞释放NO从而舒张血管;在高浓度时,槲皮素通过抑制血管平滑肌细胞的Ca2+通道等途径舒张血管。罗丽芳等[37]研究发现,杜仲木脂素可以显著降低血浆一氧化氮水平,降低血浆中肾上腺素活性和血管紧张素水平,快速松弛肠系膜动脉,从而降低自发性高血压小鼠的血压。
22降血脂杜仲中绿原酸是降血脂的主要成分。王建辉等[39]发现杜仲绿原酸可以显著降低小鼠血清TC、TG、LDL-C水平、动脉硬化指数和冠心指数,肝脏TC、TG含量显著降低,血清和肝脏中MDA下调、抗氧化酶活性增加。
23抗糖尿病研究发现杜仲多糖对四氧嘧啶所致的糖尿病小鼠有一定的治疗作用。刘国荣等[40]发现,杜仲多糖能有效降低四氧嘧啶致糖尿病小鼠的血糖,相对于模型组,杜仲多糖组的血糖明显降低,胸腺指数和脾脏指数明显增高,MDA和NO降低,SOD和NOS升高。金玲[41]研究发现,杜仲中的提取物能够显著地增加脂肪细胞中葡萄糖的转运情况和消耗情况,在脂肪细胞的作用过程中有很强的降糖作用。
24抗骨质疏松杜仲可以防治大鼠去势和维甲酸引起的骨质疏松症[42]。杜仲总黄酮可以促进骨钙素、骨保护素mRNA和护骨素蛋白的表达、但不能显著地促进成骨细胞合成I型胶原蛋白[43-45]。杜仲木脂素能显著促进大鼠原代成骨细胞骨细胞素的表达,抑制核因子κB受体激活因子配体的表达,从而调节破骨细胞功能,抑制骨吸收,促进骨形成[46]。
25抗炎和抗菌杜仲皮提取物具有抑制COX-2(IC50=992μg/mL)的作用。杜仲提取物(01和05mg/mL)可抑制LPS诱导的炎症大鼠的胸腺巨噬细胞中TNF-α、IL-6、COX-2、PGE和NO的表达[47]。杜仲的95%乙醇提取物(01mg/mL和1mg/mL)具有抗鲍氏不动杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌和真菌(烟曲霉菌)的作用[48]。
26神经保护杜仲提取物具有治疗神经退行性病变的潜在治疗作用,比如阿尔茨海默氏症。杜仲水提物对Aβ(25-35)诱导的学习和记忆障碍小鼠有神经保护作用。在体内实验中,杜仲水提物可以改善记忆缺陷小鼠在Y迷宫中的行为和避暗实验中的分步延时时间。另外,杜仲水提物减少了认知缺陷小鼠在Morris水迷宫中的逃避潜伏期。杜仲水提物(20mg/kg)具有明显抑制海马区和前额叶中AChE的活性,并呈现剂量依赖性[49]。
27抗氧化杜仲水提物具有降低对细胞的氧化损伤和增加细胞存活率的作用,并具有剂量依赖性。另外,杜仲水提物具有明显降低H2O2诱导的MC3T3E1细胞中caspases 3、6、7和9的表达。实验表明,杜仲水提取物对多种细胞具有抗氧化保护作用[50]。在Ⅱ型糖尿病中,杜仲水提物体现出了明显的抗氧化活性,可增强红细胞超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶的活性,可降低红细胞、肝、肾中过氧化氢和脂类过氧化物的含量[51]。
28其他药理作用有研究对糖尿病大鼠进行连续四周灌胃杜仲提取物(剂量400mg/kg)后发现,阴茎中nNOS表达明显增加,勃起功能发生了明显的改善[52]。在体外实验中发现,用70%的杜仲乙醇提取物(浓度150μg/mL)孵育人早幼粒淋巴HL-60细胞系24h后,可通过增强caspase-3的活性导致其死亡[53]。通过Bacille-Calmette-Guerin和脂多糖对小鼠进行免疫性肝损伤后,采用杜仲乙醇提取物(4095、8190、16380mg/kg)灌胃给药,每天1次,连续给药10d。发现其显著降低了小鼠血清中ALT和AST的水平,并且提高了SOD和GSH的活性[54]。杜仲多糖口服剂量50、100、200mg/kg,可以使环磷酰胺导致的体重、胸腺指数、腹腔巨噬细胞吞噬率和吞噬细胞指数下降速度减慢。杜仲多糖可以提高免疫抑制小鼠模型的胸腺指数和增加腹腔巨噬细胞吞噬率和吞噬指数[55,56]。杜仲多糖对兔心肌缺血再灌注模型有良好的保护作用。通过实验发现,心肌缺血再灌注組家兔 SOD 活性降低、MDA 的量增高明显,说明体内脂质过氧化反应比较强烈,细胞膜、线粒体膜和磷脂膜等受到严重损伤,器宫损害程度较重,而杜仲多糖有抗氧化及对网状内皮系统有活化作用,增强机体非特异免疫功能[57]。
3小结与展望
杜仲是我国传统的名贵中药,具有抗高血压、高血糖、糖尿病、肥胖、骨质疏松症、阿尔兹海默症、衰老和性功能低下等多种药理作用[1]。杜仲的化学成分中,已发现了70种化合物,包括27种木质素、6种环烯醚萜、13种酚类、9种甾体和萜类、8种黄酮和7种其他化合物。但是,目前的药理作用研究大部分是基于杜仲提取物,其药效成分和作用机制尚未完全明确。且其具有的潜在活性和潜在毒性的成分尚未明晰,今后仍需通过系统生物学和系统毒理学的研究进行进一步的挖掘和筛选。
参考文献
[1]国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典[M].一部.北京:中国医药科技出版社,2015:165.
[2]He XR, Wang JH, Li MX, et al. Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.:Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of an important traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2014(151):78-92.
[3]Li Y, Sato T, Metori K, et al. The promoting effects of geniposidic acid and aucubin in Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. leaves on collagen synthesis [J]. Biol. Pharm. Bull, 1998(21):1306-1310.
[4]Bermejo BP. Effects of some iridoids from plant origin on arachidonic acid metabolism in cellular systems [J]. Planta Med, 2000(66):324-328.
[5]Takeshi D, Sanei N, Yoshihisa N. Constituents and pharmacological effects of Eucommia and Siberian ginseng [J]. Acta Pharmacol. Sin, 2001(22):1057-1070.
[6]Ho JN, Lee YH, Lee YD, et al. Inhibitory effect of aucubin isolated from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. against UVB-induced matrix metalloproteinase-1 production in human skin fibroblasts [J]. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,2005(69):2227-2231.
[7]Hirata T, Kobayashi T, Wada A, et al. Anti-obesity compounds in green leaves of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Bioorg [J]. Med. Chem. Lett, 2011(21):1786-1791.
[8]Hua HM, Yin HQ, Li BQ, et al. Study on the constituents of the bark of Eucommia ulmoides [J]. Mol. Plant Breed, 2003(1):801-803.
[9]Tomoda M, Gonda R, Shimizu N. A reticuloendothelial system-activating glycan from the barks of Eucommia ulmoides [J]. Phytochemistry, 1990(29):3091-3094.
[10]Cheng J, Zhao YY, Cui YX, et al. Studies on flavonoids from leaves of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv [J]. China J. Chin. Mater. Med, 2000(25):284-286.
[11]Sun YR, Zong JX, Wu SG. Studies on chemical constituents from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv [J]. J. Chin. Med. Mater, 2004(27):33-35.
[12]Yao LN. Studies on the Chemical Constituents of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv[D]. TianJin University, 2010.
[13]Deyama T. The constituents of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. I. Isolation of(+)-Medioresinol di-O-β-D-glucopyraLnoside [J]. Chem. Pharm. Bull, 1983(31):2993-2997.
[14]Deyama T, Ikawa T, Nishibe S. The Constituents of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. II. Isolation and structures of three new lignan glycosides [J]. Chem. Pharm. Bull, 1985(33):3651-3657.
[15]Deyama T, Ikawa T, Kitagawa S, et al. The Constituents of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. V. Isolation of dihydroxydehydrodiconiferyl alcohol isomers and phenolic compounds [J]. Chem. Pharm. Bull, 1987(35):1785-1789.
[16]Shi SY, Peng MJ, Zhang YP, et al. Combination of preparative HPLC and HSCCC methods to separate phosphodiesterase inhibitors from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. bark guided by ultrafiltration-based ligand screening [J]. Anal. Bioanal. Chem, 2013(405):4213-4223.
[17]Sih CJ, Ravikumar PR, Huang FC, et al, Whitelock H.(+)-Pinor esinol di-O-β-D-glucopyranoside was reported to be the majior antihypertensive principle of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv [J]. J. Am. Chem, 1976, Soc. 98:5412-5413.
[18]Deyama T, Ikawa T, Kitagawa S, et al. The Constituents of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. III. Isolation and structure of a new lignan glycoside [J]. Chem. Pharm. Bull, 1986(34):523-527.
[19]Deyama T, Ikawa T, Kitagawa S. The constituents of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. IV. isolation of a new sesquilignan glycoside and iridoids [J]. Chem. Pharm. Bull, 1986(34):4933-4938.
[20]Shimoyamo A, Yamadaki M, Nakazawa Y. Constituents of the leaf of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv [J]. Shoyakugzku Zasshi, 1993(47):56.
[21]Deyama T, Ikawa T, Kitagawa S, et al. The constituents of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. VI. Isolation of a new sesquilignan and neolignan glycosides [J]. Chem. Pharm. Bull, 1987(35):1803-1807.
[22]Takamura C, Hirata T, Yamaguchi Y, et al. Studies on the chemical constituents of green leaves of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv [J]. J. Nat. Med, 2007(61):220-221.
[23]Li D, Wang HL, Chen JM. The chemical constituents of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv [J]. Chin. Bull. Botany,1986(28):528-534.
[24]Zhang Y, Peng M, Liu L, et al. Screening, identification, and potential interaction of active compounds from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. leaves binding with bovine serum albumin [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem, 2012(60):3119-3125.
[25]Sun YR, Zong JX, Wu SG. Studies on chemical constituents from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv [J]. J. Chin. Med. Mater, 2004(27):33-35.
[26]Chen CJ, Shen S, Xiao TS, et al. Chemical constituents from the bark of Eucommia ulmoides [J]. Asia-Pac. Tradit Med., 2012(8):25-26.
[27]Xu JW, Li D, Zhao P. The constituents of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv [J]. Bull. Boanty, 1989(31):132.
[28]Horri Z, Ozaki Y, Nagao K. Ulmoprenol, a new type C30-Polyprenoid from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv [J]. Tetrahedron Lett, 1978(50):5015.
[29]Hua HM, Yin HQ, Li BQ. Pei YH. Study on the constituents of the bark of Eucommia ulmoides [J]. Mol. Plant Breed, 2003(1):801-803.
[30]Wang JX, Hao XH, Lei HM,et al. Study on the constituents of the bark of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv [J]. Northwest Pharm. J, 1996(S1):13-15.
[31]Si CL, Deng XJ, Wang D, et al. Study on chemical compositions of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. inner bark and its extractives [J]. Chem. Ind. For. Prod, 2008(28):7-10.
[32]Kim BH, Park KS, Chang IM. Elucidation of anti-inflammatory potencies of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. bark and Plantago asiatica seeds [J]. J. Med. Food, 2009(12):764-769.
[33]Kim HY, Moon BH, Lee HJ,et al. Flavonol glycosides from the leaves of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. with glycation inhibitory activity [J]. J. Ethnopharmacol, 2004(93):227-230.
[34]Gonda R, Masashi T, Noriko S,et al. An acidic polysaccharide having activity on the reticuloendothelial system from the bark of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv [J]. Chem. Pharm. Bull.,1990(38):1966-1969.
[35]Tomoda M, Gonda R, Shimizu N. A reticuloendothelial system-activating glycan from the barks of Eucommia ulmoides [J]. Phytochemistry, 1990(29):3091-3094.
[36]葉小彤, 张百霞, 王慧慧, 等. 基于“中药作用机理辅助解析系统”的杜仲抗高血压作用机制研究 [J].中国中药杂志,2015,40(19):3718-3722.
[37]罗丽芳, 吴卫华, 欧阳冬生, 等. 杜仲的降压成分及降压机制 [J]. 中草药, 2006, 37( 1) :150-152.
[38]Li Y, Metori K, Koike K,et al. Improvement in the turnover rate of the stratumcorneum in false aged model rats by the administration rats by the administration of geniposidic acid in Eucommia ulmoides Oliver Leafy[J].Biol Pharm Bull.,1999, 22(6):582-585.
[39]王建辉, 刘永乐, 李赤翎, 等. 杜仲绿原酸对高脂模型小鼠降血脂作用研究 [J]. 食品工业科技,2012, 33(15):360-362, 375.
[40]刘国荣, 邱立朋, 周延萌, 等. 杜仲多糖对糖尿病小鼠降血糖作用及其机制研究 [J]. 泰山医学院学报, 2010, 31(9):659-661.
[41]金玲. 杜仲提取物对脂肪细胞糖代谢的影响分析[J]. 中国保健营养, 2012, 16(9):3512-3513.
[42]潘亚磊, 翟远坤, 牛银波, 等. 杜仲防治骨质疏松症的研究进展 [J]. 化学与生物工程, 2013, 30(7):6-9.
[43]李三华, 何志全, 陈全利, 等. 杜仲总黄酮对成骨细胞增殖及I型胶原蛋白表达的影响[J].西北药学杂志, 2011, 26(4):272-274.
[44]李三华, 刘坤祥, 莫宁萍,等. RT-PCR法检测杜仲总黄酮对大鼠成骨细胞骨钙素表达的影响 [J].遵义医学院学报, 2011, 34(3):223-225.
[45]李三华, 陈全利, 何志全, 等. 杜仲总黄酮对大鼠成骨细胞护骨素表达的影响 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2011, 39(25):15279-15280, 15282.
[46]张蓉.杜仲防治绝经后骨质疏松及其机理研究 [D].西安:第四军医大学, 2008.
[47]Kim MC, Kim DS, Kim SJ, et al. Eucommiae cortex inhibits TNF-α and IL-6 through the suppression of caspase-1 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated mouse peritoneal macrophages [J]. Am. J. Chin. Med, 2012(40):135-149.
[48]Zhang L, Ravipati AS, Koyyalamudi SR, et al. Anti-fungal and anti-bacterial activities of ethanol extracts of selected traditional Chinese medicinal herbs [J]. Asian Pacific J. Trop. Med, 2013(7):673-681.
[49]Kwon SH, Kim MJ, Ma SX, et al. Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. bark protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced neuronal cell death in SH-SY5Y cells [J]. J. Ethnopharmacol, 2012, 13(142):337-345.
[50]Lin J, Fan YJ, Mehl C, et al. Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. antagonizes H2O2-induced rat osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 apoptosis by inhibiting expressions of caspases 3, 6, 7, and 9 [J]. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci, 2011(12):47-54.
[51]Park SA, Choi MS, Jung UJ, et al. Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. leaf extract increases endogenous antioxidant activity in type 2 diabetic mice [J]. J. Med. Food, 2006(9):474-479.
[52]Zhang WH, Li G, Dong HS, et al. The effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. on catching action of diabetic rats and myelinated nerve fibers in penile tissues [J]. Nat. J. Androl, 2006(12): 466-469.
[53]Nishida S, Kikuichi S, Yoshioka S, et al. Induction of apoptosis in HL-60 cells treated with medicinal herbs [J]. Am. J. Chin. Med, 2003(1):551-562.
[54]Gao YH, Shi XL, Wang M, et al. Protective effects of the alcohol extract and the water extract from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. on immunological liver-injury [J]. J. North China Coal Med. Univ, 2011(13):141-143.
[55]Xin XM, Feng L, Wang H, et al. Study advancement about chemical composition and pharmacological actions of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv [J]. Med. Recapitulate , 2007(13):1507-1509.
[56]Xu XZ, Rao H, Cai XF, et al. Study on the extraction and immunoregulatory activity polysaccharides from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv [J]. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2013(24):541-542.
[57]鄔晓臣, 欧阳辉, 张近宝, 等. 杜仲多糖对兔心肌缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J]. 药物评价研究, 2014, 37(1):34-36.
(收稿日期:2017-03-23编辑:穆丽华)
