RNA干扰Livin基因对甲状腺乳头状癌的增殖及侵袭抑制作用及其分子机制
2017-06-08薛栋靳继海夏修良王建强王雯成丕
薛栋 靳继海 夏修良 王建强 王雯 成丕光 李新军 巩本刚
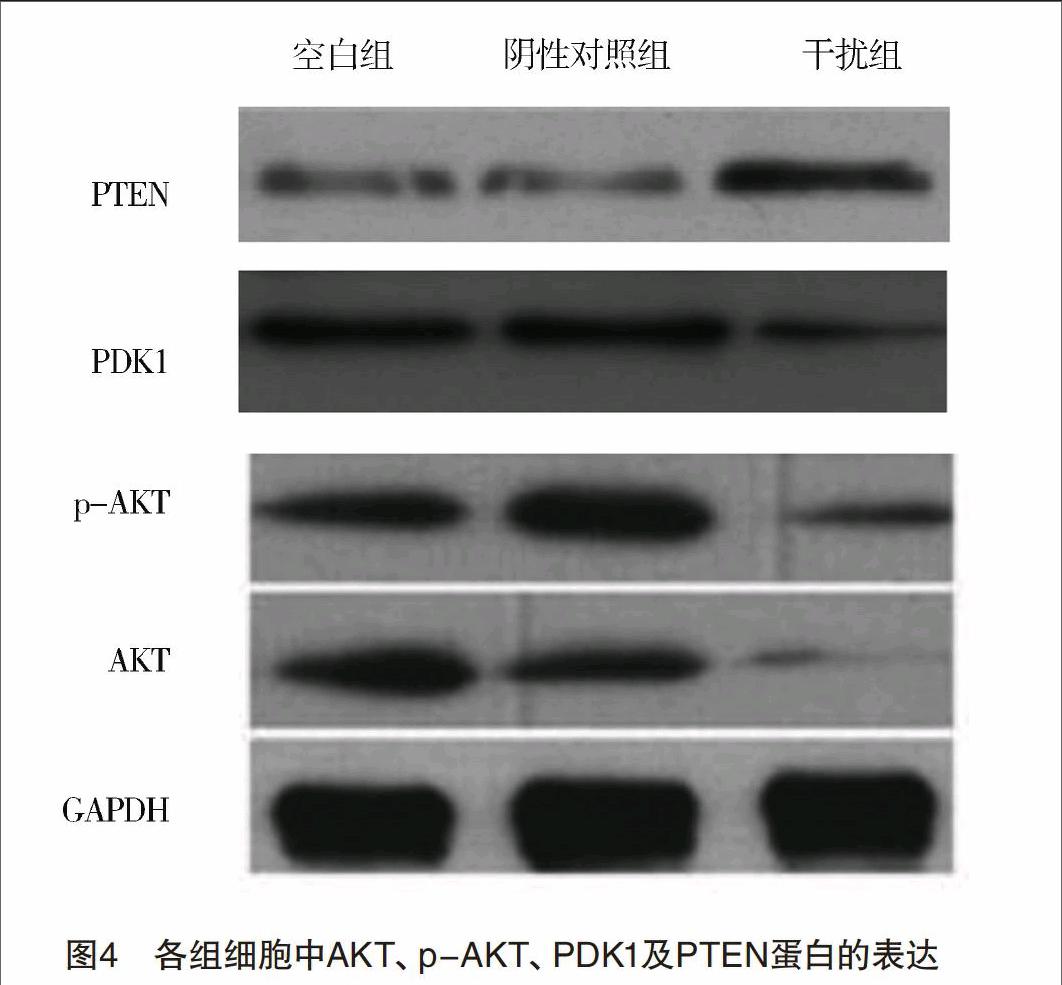
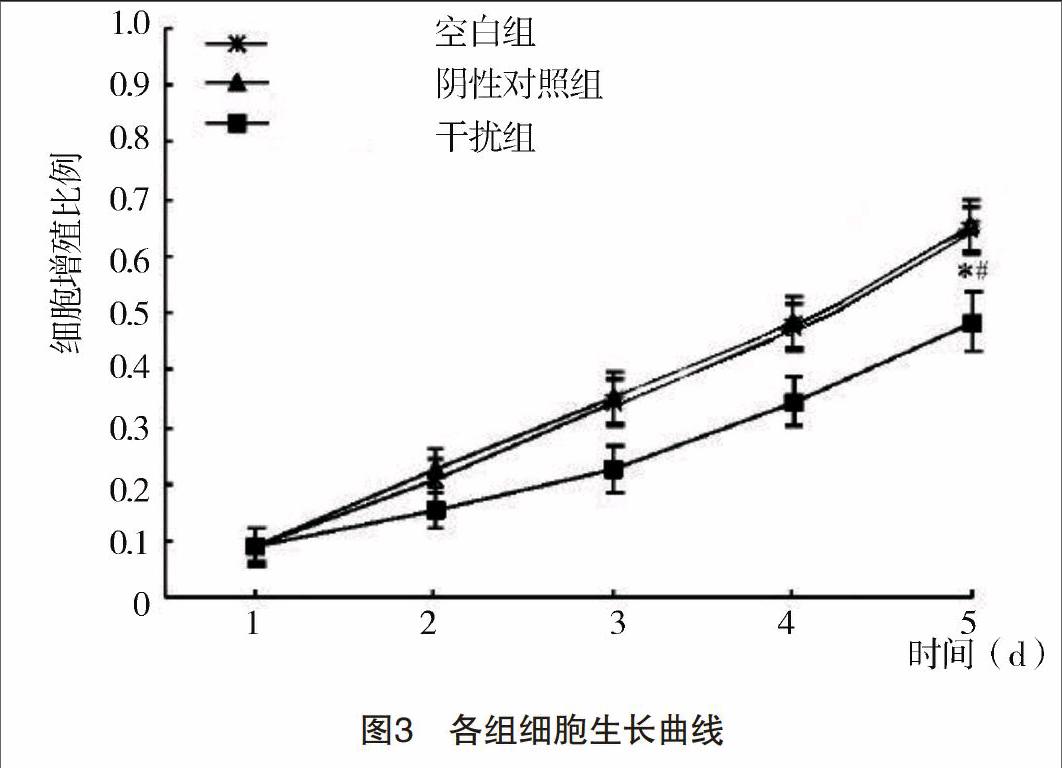
【摘要】 目的:探討Livin对甲状腺乳头状癌TPC-1细胞增殖、凋亡及侵袭的影响以及可能的调控分子机制。方法:构建靶向Livin基因的慢病毒shRNA载体,转染甲状腺乳头状癌细胞株TPC-1,实验分为干扰组、阴性对照组和空白组。应用RT-PCR和Western印迹检测转染Livin-shRNA后细胞Livin mRNA和蛋白表达水平的变化。应用MTT、流式细胞仪、Western印迹与Transwell侵袭实验检测Livin对甲状腺乳头状癌细胞增殖、凋亡及侵袭的影响。并接种于裸鼠模型中,进一步确定Livin在体内对甲状腺乳头状癌细胞的影响。结果:慢病毒Livin-shRNA载体成功抑制TPC-1细胞中Livin mRNA和蛋白的表达;转染Livin-shRNA后TPC-1细胞的增殖能力受到明显抑制(P<0.01),转染Livin-shRNA组、阴性对照组和空白组的凋亡率分别为(15.72±0.21)%,(4.54±0.13)%和(4.87±0.22)%,三组比较差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01)。干扰组穿膜细胞数明显少于阴性对照组和空白组(P<0.05)。与空白组和阴性对照组相比,干扰组细胞AKT、p-AKT及PDK1蛋白表达量均下调(P<0.05),而PTEN蛋白明显上调(P<0.05)。甲状腺乳头状癌裸鼠模型结果表明干扰组肿瘤的生长速度、肿瘤质量[(1.11±0.08)g]明显小于空白组[(1.90±0.15)g]和阴性对照组[(2.10±0.12)g]。结论:沉默Livin基因能抑制甲状腺乳头状癌细胞的增殖、侵袭及体内生长,促使甲状腺乳头状癌细胞凋亡的发生,可能是通过抑制PI3K-AKT信号转导通路来发挥作用。
【关键词】 甲状腺肿瘤; Livin; RNA干扰; 侵袭; 迁移; 动物模型
Inhibition on Proliferation and Invasion of Human Thyroid Papillary Cancer Cells by RNA Interference Livin Gene Expression and Its Possible Molecular Mechanism/XUE Dong,JIN Ji-hai,XIA Xiu-liang,et al.//Medical Innovation of China,2017,14(14):004-008
【Abstract】 Objective:To investigate the effect of Livin on the proliferation,apoptosis and invasion of human thyroid papillary cancer cell line TPC-1,and its possible molecular mechanism.Method:Livin was silenced by using RNA interference.In this experiment,three groups were designed:the experimental group,the negative control group and the blank control group.The expression of Livin at mRNA and protein levels were detected by reverse transcription PCR and Western blot respectively.MTT,FCM,transwell and Western blot were utilized to analyze the result and specific molecular mechanism of Livin on TPC-1 cancer cells by transfected.The expressions of AKT,p-AKT,PDK1 and PTEN in TPC-1 cells were detected after transfection.Nude mice models inoculated TPC-1 cells were used to further clarify the effect of Livin on thyroid papillary cancer cells in vivo.Result:The stable Livin silencing cells line was successfully established.The expression of Livin at mRNA and protein levels was reduced significantly(P<0.05),leading to the inhibition of cell proliferation in the experimental group compared with the negative control group and the blank control group(P<0.05).The apoptosis index of tumor cells in the above three groups were (15.72±0.21)%,(4.54±0.13)% and (4.87±0.22)%,respectively.Compared to the negative control group and the blank control group,the experimental group was significantly increased(P<0.01).The transwell chamber assay showed that transmembrane cells of the experimental group were less than the negative control group and the blank control group after incubation 48 hours.Meanwhile,western blot analysis revealed that cells with stably knock-down of Livin showed decreased expression levels of AKT,p-AKT and PDK1 compared to the negative control group and the blank control group,but PTEN was highly expressed(P<0.05).Nude mice models indicated that the growth and weight (1.11±0.08)g of the experimental group were significantly lower than (1.90±0.15)g of the blank control group and (2.10±0.12)g of the negative control group(P<0.05).Conclusion:Scilencing the expression of Livin can inhibit the proliferation of thyroid papillary cancer cell and growth in vivo,and then accelerate the apoptosis of TPC-1 cancer cells by cutting down the activity of PI3K-AKT signal pathway.
【Key words】 Thyroid neoplasm; Livin; RNA interference; Invasion; Migration; Animal model
First-authors address:The Peoples Hospital of Binzhou,Binzhou 256610,China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2017.14.002
甲状腺乳头状癌的发病率正逐年上升。Livin与肿瘤的发生、恶性侵袭和转移具有密切相关性[1-2]。笔者前期研究结果已发现Livin在甲状腺乳头状癌组织中呈高表达状态,并且Livin与肿瘤的临床分期、淋巴结转移都明显有关[3]。磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(PI3K/AKT)信号转导通路在肿瘤细胞的侵袭转移过程之中发挥着重要的作用,3-磷酸肌醇依赖性蛋白激酶1(PDK1)及第10号染色体缺失的磷酸酶及张力蛋白同源的基因(PTEN)是该信号通路的重要基因[4]。新近的研究结果表明,Livin還能够明显促进肺癌及口腔鳞癌细胞的增殖、局部侵袭和转移[5-6]。
本研究通过构建慢病毒载体介导的shRNA沉默甲状腺乳头状癌细胞中Livin基因,观察Livin对甲状腺乳头状癌TPC-1细胞的生物学行为的影响,构建裸鼠成瘤模型,分析Livin促进甲状腺乳头状癌细胞生长及侵袭转移的作用机理。现报道如下。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料 人甲状腺乳头状癌TPC-1细胞。慢病毒载体携带质粒pGCSIL-GFP、Livin-shRNA和构建的阴性对照(scramble)序列等。反转录试剂盒、Taq DNA聚合酶、Trizol试剂等。BALB/C雌性裸鼠,4~6周龄,体质量在15~21 g。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 细胞培养 TPC-1细胞株在DMEM细胞培养液中培养,在温度为37 ℃、5%CO2孵箱中进行培养。
1.2.2 慢病毒Livin-shRNA转染,构建稳定转染Livin-shRNA的甲状腺乳头状癌TPC-1细胞选用生长较好的TPC-1细胞按照4×104个/孔的密度接种于6孔板之中,当细胞融合率能达到60%~80%的时候,选用含有沉默Livin效果最好的靶点序列(5-GGAAGAGACTTTGTCCACA-3)及其阴性对照(scramble)序列,制备成稳定感染Livin-shRNA的TPC-1细胞干扰组及阴性对照组;无任何处理的TPC-1细胞设为空白组。
1.2.3 RT-PCR实验检测Livin mRNA的表达 在细胞转染48 h后,分别收集各组的TPC-1细胞,利用Trizol RNA提取肿瘤细胞的总RNA,放置在-80 ℃冰箱暂时保存或者直接进行反转录。反转录成cDNA,在PCR扩增仪上进行扩增。将目的基因产物与内对照β-actin密度比值计算。
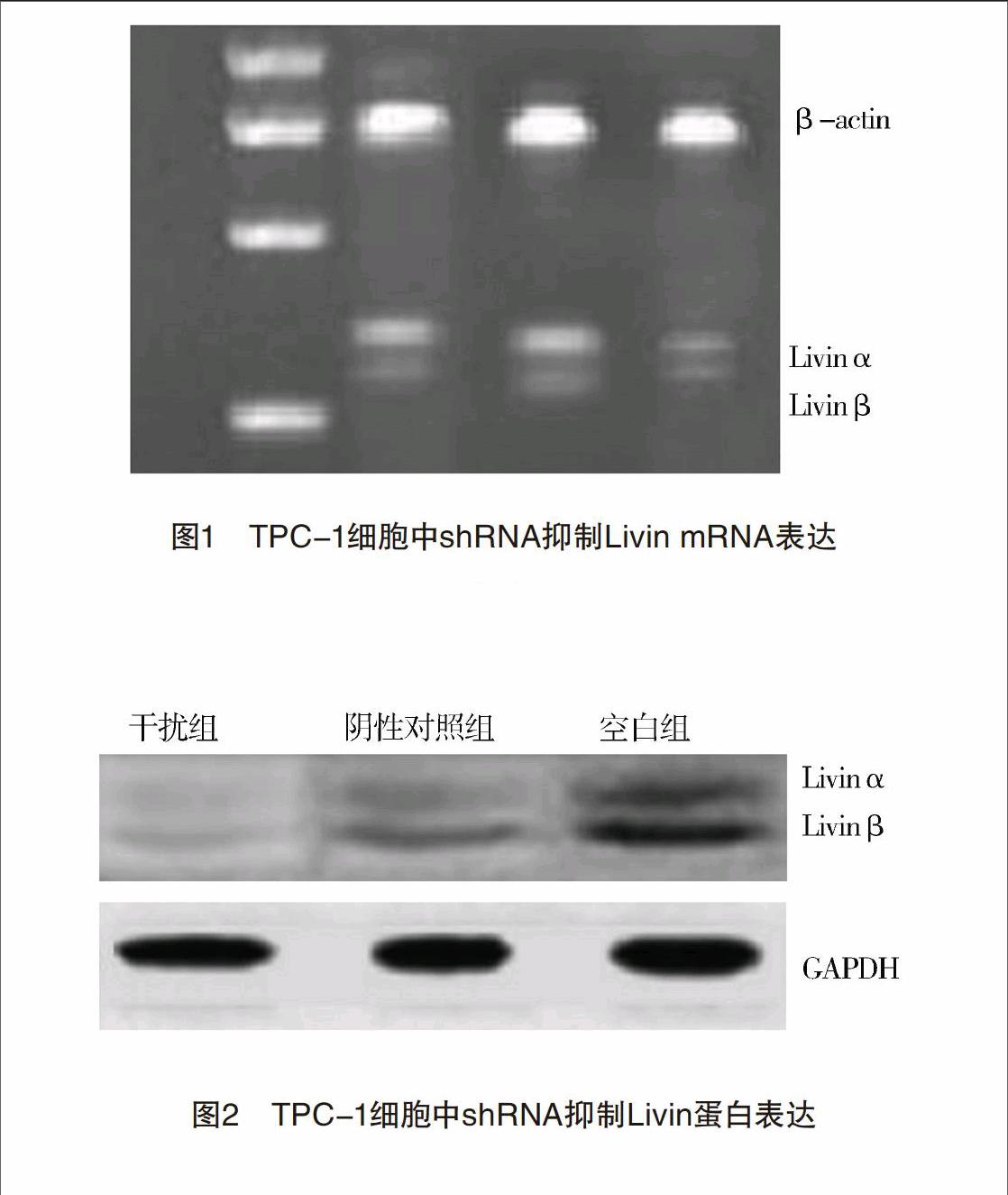
1.2.4 Western印迹实验检测转染之后Livin蛋白表达 在细胞转染48 h后,分别收集各组TPC-1细胞,然后裂解细胞并提取总蛋白。蛋白上样、PVDF转膜,脱脂奶粉封闭,加入兔抗人Livin抗体,内参选用GAPDH,以目标蛋白电泳条带的灰度值与GAPDH灰度值之比表示相对的表达量。
1.2.5 MTT实验检测细胞生长 分别收集处于对数生长期的各组细胞,然后调整细胞悬液的浓度并接种于96孔板之中,每组设定有5个复孔,加入MTT溶液和DMSO,在酶联免疫检测仪用490 nm波长测各孔吸光度(A)值,并绘制肿瘤细胞生长曲线。
1.2.6 流式细胞术检测转染后TPC-1细胞周期变化 收集转染48 h后的TPC-1细胞,离心后75%乙醇固定,重悬细胞再加入PI染色剂和RNase A,流式细胞仪检测细胞周期变化。
1.2.7 流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡 收集转染48 h 的TPC-1细胞,制成单细胞悬液。置入5 mL流式管中,分别加入AnnexinⅤ/FITC和碘化丙锭,混合均匀。用流式细胞仪检测,结果用随机软件进行分析。
1.2.8 Transwell小室实验检测各组细胞的侵袭能力 应用Transwell小室侵袭模型,无血清细胞培养基使Matrigel稀释成2倍,然后加入Transwell上室,将细胞密度调整至4×105个/mL,在6孔板下室中加入无血清DMEM培养基,在上室内加入单细胞悬液,固定后并染色,计算出每个视野的平均值。
1.2.9 Western印迹检测各组细胞AKT、p-AKT、PDK1及PTEN蛋白表达 分别收集沉默48 h后的各组细胞,提取肿瘤细胞的总蛋白,实验的步骤同前,分别孵育一抗(AKT、p-AKT、PDK1和PTEN),洗膜后孵育二抗等。计算时以目的基因的蛋白凝胶电泳条带灰度值与对应的GAPDH灰度值之比来表示相对的表达量。
1.3 建立裸鼠甲状腺乳头状癌模型 取BALB/c雌性裸小鼠30只,随机分成空白组、阴性对照组和干扰组(各10只),制成细胞悬液,接种于裸鼠的颈背皮下处。在种植后的第1、7、14、21、28天分别测量肿瘤的最长径a和最短径b,根据公式来计算肿瘤的体积V,计算公式V(mm3)=πab2/6。然后绘制出裸鼠的瘤体体积-时间曲线,在第28天处死所有的裸鼠,最后测量种植瘤的质量。
1.4 统计学处理 采用SPSS 13.0软件对所得数据进行统计分析,计量资料用(x±s)表示,计数资料以率(%)表示,比较采用 字2检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 靶向shRNA能够明显降低TPC-1细胞中Livin mRNA的表达 RT-PCR的结果表明:干扰组、阴性对照组及空白组的Livin mRNA相对表达量分别为(0.15±0.04)、(0.72±0.11)和(0.76±0.13);干扰组中的Livin mRNA的表达量均明显低于阴性对照组和空白组(P<0.05),Livin mRNA的表达量在阴性对照组和空白组之中无明显差异,见图1。
