经皮肾镜碎石取石术后尿脓毒血症的相关因素
2017-05-31邓月云李秀宁
邓月云+李秀宁

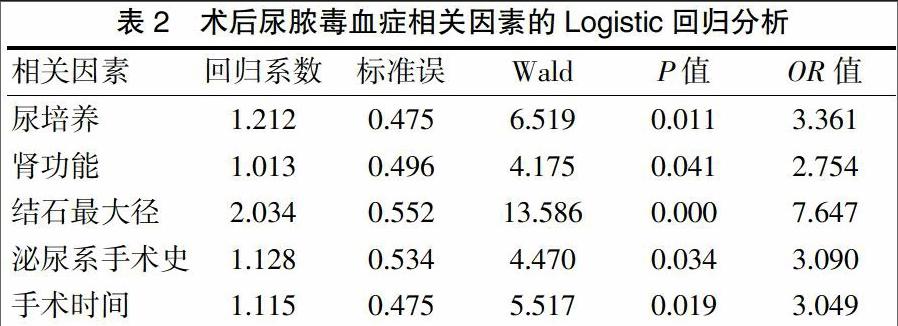
[摘要]目的 探讨经皮肾镜碎石取石术(PCNL)后尿膿毒血症的相关因素。方法 收集2013年3月~2016年4月云浮市人民医院456例行PCNL的患者,术后出现尿脓毒血症28例,对这些病例的年龄、性别、尿白细胞、血白细胞、术前尿培养、肾功能、结石大小、肾积液、手术史、出血量及手术时间等因素进行分组比较,并对其中有统计学差异的因素进行Logistic回归分析,得到PCNL术后尿脓毒血症的相关因素。结果 尿白细胞、术前尿培养、肾功能、结石大小、肾积液、手术史、术中出血量及手术时间的不同分组比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。回归分析发现尿培养、肾功能、结石大小、手术史及手术时间与PCNL术后尿脓毒血症相关。结论 术前针对尿培养阳性、肾功能损害、结石较大、有泌尿系手术史及估计手术时间长的这些因素进行处理和评估,有望预防和降低术后尿脓毒血症的发生。
[关键词]经皮肾镜碎石取石术;尿脓毒血症;相关因素
[中图分类号] R699 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-4721(2016)12(c)-0051-03
Related factor of urinary sepsis after percutaneous nephrolithotomy
DENG Yue-yun LI Xiu-ning
Department of Urology,People′s Hospital of Yunfu City in Guangdong Province,Yunfu 527300,China
[Abstract]Objective To explore related factor of urinary sepsis after percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL).Methods 45 patients who conducted PCNL in People′s Hospital of Yunfu City from March 2013 to April 2016 were collected.Postoperative urinary sepsis in 28 cases,factors of age,sex,urine white blood cell,blood white blood cells,preoperative urine culture,renal function,renal stone size,renal effusion,surgery history,bleeding volume and operation time were group compared,and Logistic regression analysis was performed on the factors which were statistically different to get related factors of urinary sepsis after PCNL.Results Comparison different groups of urine white blood cell,preoperative urine culture,renal function,renal stone size,renal effusion,surgery history,intraoperative bleeding volume and operation time,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).Logistic regression analysis found that urine culture,renal function,renal stone size,operation history and operation time were related to urinary sepsis after PCNL.Conclusion Aim at processing and evaluation the factors of positive urine culture,renal injury,larger renal stones,surgery history of urinary tract,ecaluation of longer operation time before operation are expected to prevent and reduce occurrence rate of urinary sepsis after PCNL.
[Key words]Percutaneous nephrolithotomy;Urinary sepsis;Related factor
经皮肾镜碎石取石术(percutaneous nephrolithotomy,PCNL)在处理上尿路结石具有明显优势,特别是>2 cm的结石,以创伤小、术后恢复快使其成为该类型结石的主要术式[1-2]。但该术式也有一定的并发症,如肾实质出血、肾周脏器损伤、尿路感染和肾功能损害等[3]。术后尿路感染可进展为尿脓毒血症,虽然发生率不高,但可引起严重后果,处理较为棘手[4]。因此,笔者分析与PCNL术后尿脓毒血症的相关因素,有的放矢地预防,以期降低与手术相关的尿脓毒血症的发生率。
1资料与方法
1.1一般资料
收集2013年3月~2016年4月云浮市人民医院行B超引导下PCNL的病例,均有完整的病历资料可查,由同一术者主刀。共纳入病例456例次,右肾169例次,左肾287例次,双侧32例;2次手术的有22例;年龄24~78岁,平均49岁;平均手术出血量(72.36±35.48)ml;平均手术时间(93.59±20.08)min。术后共有28例出现尿脓毒血症。对研究中涉及的因素进行分组:年龄根据均值分组;性别分男、女两组;尿白细胞分为>2+组和≤2+组;血白细胞分为>10×109/L组和≤10×109/L组;术前尿培养分为阳性组和阴性组;肾功能根据肌酐值分为升高组和正常组;结石大小根据直径分为>2 cm和≤2 cm组;肾积液中,分为无积液和轻度积液、中重度积液两组;根据术前有无泌尿系手术史分两组;术中出血量和手术时间根据均值分组。
