Time-dependent Expression of MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA in the Contused Skeletal Muscle of Rats
2017-03-28FANHaoliangLIUShufangSUNJunhongWANGYingyuan
FAN Hao-liang,LIU Shu-fang,SUN Jun-hong,WANG Ying-yuan
(1.School of Forensic Medicine,Shanxi Medical University,Taiyuan 030001,China;2.Department of Forensic Medicine,Hainan Medical University,Haikou 571199,China;3.Yuzhong Branch of Chongqing Public Security Bureau,Chongqing 400021,China)
Time-dependent Expression of MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA in the Contused Skeletal Muscle of Rats
FAN Hao-liang1,2,LIU Shu-fang1,3,SUN Jun-hong1,WANG Ying-yuan1
(1.School of Forensic Medicine,Shanxi Medical University,Taiyuan 030001,China;2.Department of Forensic Medicine,Hainan Medical University,Haikou 571199,China;3.Yuzhong Branch of Chongqing Public Security Bureau,Chongqing 400021,China)
ObjectiveTo investigate the time-dependent expression of metallothionein(MT)1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA in contused skeletal muscle of rats.MethodsA total of 54 Sprague-Dawley rats were used in this study.The rats were divided into two parts:control group(n=6)and contusion groups(0.5, 1,6,12,18,24,30,and 36 h after contusion,n=6).Total RNA was extracted from skeletal muscle. The expression levels of MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA were detected by SYBR Green I real-time PCR.ResultsThe expression trends of the two potential marker genes were related to wound age.In addition to 0.5 h,there were significant contrasts between the control group and contused group(P<0.05), about the expression levels of MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA in different phases.As the extension of wound age,the relative expression of MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA at 1h,6h,12h and 18h after contusion demonstrated upgrade tendency until its expression levels in 18 h peak with 239.41±15.20 and 717.42±50.76,respectively.When time extends to 24 h after injury,the expression of above two marks decreased,respectively.The MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA expression levels increased at 30 h and then decreased.ConclusionDetermination of MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA levels by real-time PCR may be useful for the estimation of wound age.
forensic pathology;muscles;contusions;metallothionein;wound age estimation
Introduction
Wound age estimation is one of the main topics of the forensic pathology.Typically,macroscopic and microscopic methods are used to detect the expression of proteins and nucleic acids for wound age determination,and most of these molecules participate in the inflammatory responses,such as free ofhistamine,5-hydroxytryptamine(5-HT),catecholamine,prostaglandins,D-dimer and electrolyte[1]. In recent years,real-time PCR(RT-qPCR)is explored to detect the expression levels of mRNA for wound age estimation in some studies[2,3],and the results indicated that using real-time PCR to detect the expression levels of mRNA is more suitable forthe age estimation of early wounds.
Metallothionein(MT)exists in organism widely,participating in storage,transport and metabolism of trace elements and heavy metals detoxification, antagonism of ionizing radiation,removing hydroxyl oxygen free radicals and lipid peroxidation[4].In addition,MT is involved in the development and the regulation of cell apoptosis process,and strengthen the body's response to various stresses[5].Sun et al.[6,7]demonstrated that MTs reduced cardiac myopathy in response to an oxidative stress stimulus using a MT-overexpressing transgenic mouse model.There is,however,little evidence supporting this role in skeletal muscle.Penkowa et al.[8]have documented increased expression of MT1 protein and MT2 protein in response to acute exercise,a stimulus known to increase oxidative stress.They suggested that the upregulationofMTsrepresentedaresponseto counter oxidative stress-induced damage to muscle fibers,but there were no data provided to substantiatethissuggestion.Althoughclearlymorework needs to be done to define a protective antioxidant role for MTs in skeletal muscle,the accumulating evidence would suggest that,if at all,they perform a minor function in this capacity.
In this study,the expression of MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA were conducted by RT-qPCR at various phases during the wound healing of contused skeletal muscle in rats.We also assessed whether MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA could be possible markers for the estimation of the wound age.
Materials and methods
Experimental skeletal muscle contusion
Totally,54 Sprague-Dawley rats,sex unlimited, approximately 10 to 12 weeks old,weighed 250-300 g,were used in this study.All rats were randomly divided into two parts:control group(n=6)and contusion groups(containing 0.5,1,6,12,18, 24,30,and 36h after contusion,n=6).
Animals were kept under a per 12 h light/dark cycle environment with free access to food and water.After the rats were anesthetized with ethyl ether and the right posterior limb was shaved,a depilatory agent(Nair:Carter-Wallace,New York,NY,USA)was applied to remove residual hair.Subsequently, the rats were put on a foam bed,and a 250 g cylindrical counterpoise was raised and fallen 150 cm freely through a clear Lucite guide tube onto the right posterior limb of rats(The impact interface between the counterpoise and the rats was about 3 cm2). After the rats were injured,they were recovered from the anesthetic naturally and were stayed in a cage and fed commercial rat food and tap waterad libitum.
Tissue preparation
At 0.5,1,6,12,18,24,30,and 36 h after contusion,the rats were sacrificed with alethal dose of pentobarbital(350 mg/kg body weight,intraperitoneal injection).Around 100mg muscle sample was dissected from the right posterior limb,cut into two parts,and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen.
Total RNA preparation
Total RNA was extracted from muscle specimens(about 50mg weight)using the SV Total RNA Isolation System(Promega,Madison,WI,USA)following thekit's instructions.Theconcentration(mg/mL)of total RNA was quantitated using a UV/visible spectrophotometer(Ultrospec 4300 pro: Biochrom,Cambridge,UK).RNA integrity was accessed using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer(Agilent Technologies,Santa Clara,CA,USA)by loading samples onto the Eukaryote total RNA nano-chip.
RT-qPCR
Primers were designed based on sequences obtained from GenBank.The sequences were imported into AlleleID 6 software(Primer Biosoft International),which is designed to generate paired primers suitable for RT-qPCR.In order to get a high efficiency,thedesignedsequencesofthepaired primers were validated on BLAST.Primers were obtainedfromInvitrogenTradingCo.Ribosomal protein L13(RPL13)was used as reference gene[9](Table 1).

Table 1Details of primers used for RT-qPCR
The first-strand cDNA was synthesized using the Prime Script RT-PCR Kit(Takara Biotechnology,Dalian,China)according to a standard protocol. To conduct reverse transcription,0.4 mg of total RNA was used in a reaction volume of 10mL.
RT-qPCRamplificationwasperformedina25 mL reaction mixture,which included 12.5 mL SYBRPremixExTaq,9.5 mLdH2O,0.5 mL(10 mmol/L)of each primer,and 2 mL cDNA according to the manufacturer's protocol provided with SYBRPremix Ex Taq(Takara Biotechnology Co. Ltd.,Dalian,China).Amplification was performed with one round of pre-denaturation at 95℃for 10 s, step-cycle mode for 40 s round of denaturation at 95℃for 5 s and annealing and extension at 60℃for 30 s.The last was performed with a round of 95℃for 30 s,55℃for 30 s,95℃for 30 s.The fluorescence signal was detected at the end of each cycle.All reactions were performed using a Mx3000P real-time PCR System(Stratagene,La Jolla,CA, USA).The results were normalized to the expression level of RPL13,which has been confirmed as the most stably expressed gene in contused skeletal muscle[9].Fluorescence curves of PCR products were evaluated using Strategene MxPro(Stratagene,La Jolla,CA)to yield the expression data of MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA relative to RPL13 mRNA. Relative gene expression were calculated using the Strategene MxPro Software.
The synthesized cDNAs were serially diluted(1,1∶101,1∶102,1∶103and 1∶104)in EASY Dilution solution(Takara Biotechnology Co.Ltd.,Dalian, China),and 2 mL of each dilution were used for amplification in a reaction volume of 25 mL.Sterile purified water was used as the negative control.
Statistical analysis
One-wayanalysisofvariancewasusedto compare the survival time after muscle contusion. Thettest was used to assess statistical significance. When thePvalue was less than 0.05,significant difference was concluded.
Results
Integrity of total RNA
All samples were performed on Agilent 2100 BioanalyzerusingtheRNA6000LabChipsKit. Approximately 0.1-0.4mg of total RNA was extracted from each milligram wet muscle using the SV Total RNA Isolation System.And only those RNA with a RNA integrity number(RIN)above 7.5 and clearly visible 28/18s peaks were used for RT-qPCR.
Calculationoftheamplificationefficiencyof MT1A,MT2A and RPL13 genes
The dissociation curves of MT1A,MT2A and RPL13 genes showed signal cusps,and the dissociation temperature were 89℃,88℃and 83℃,respectively(Fig.1).The results could be explained by that there were no other PCR productions besides our target genes,and there was no primer dimmer.The standard curves of the three genes were studied at a threshold fluorescence of 600[Fu]. The amplification efficiency of MT1A and RPL13 genes was respectively 105.7%and 106.0%.And the amplification efficiency of the MT2A and RPL13 was 87.0%and 89.4%,respectively.The results indicatedthattheMT1A,MT2A andRPL13had similar PCR efficiency in the same experiment environment.
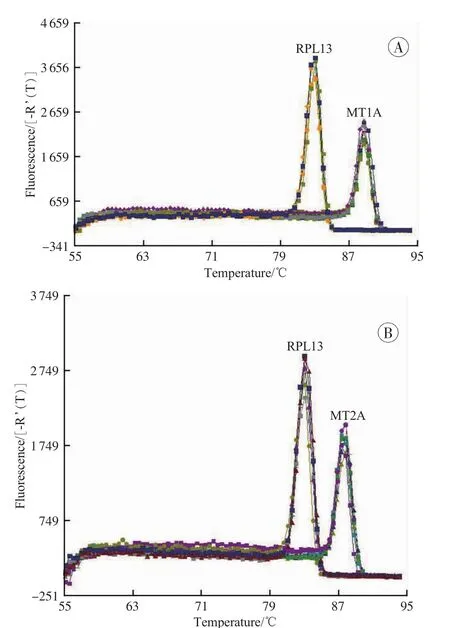
Fig.1Dissociation curves of MT1A and RPL13(A),MT2A and RPL13(B)
Expression of MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA
In the present study,the expression of MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA showed that there was a similar expression trend.At 1 h after contusion,an obvious increase in the expression levels of MT1A and MT2A and reached the peak at 18 h after contusion,but it decreased sharply at 24 h,and the second peak appeared at 30h after contusion.There were significant differences in the expression levels of MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA between the control group and contusion groups when normalized to RPL13 mRNA(P<0.05).Compared to the control group,there were significantly increased expression levels of MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA up to 36 h after contusion(P<0.05).However,there were no significant changes in the expression levels of MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA both at the phase of 0.5h(P>0.05)after contusion when normalized to the levels of RPL13 expression(Table 2).
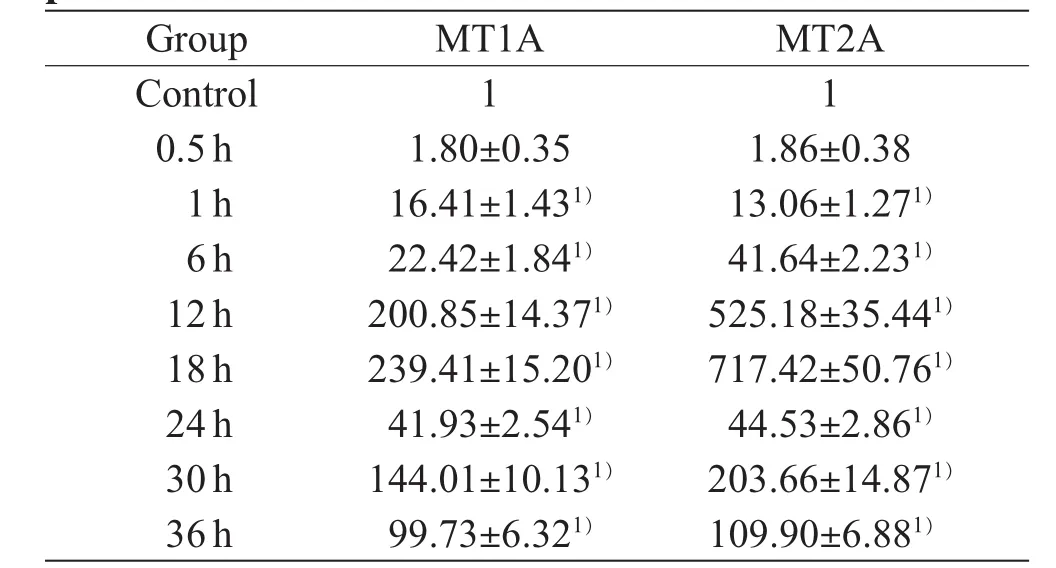
Table 2The mRNA relation expression and statistical analyses of MT1A and MT2A at different phases
Discussion
Skeletal muscle wound healing is an organized, continuous and complex process to keep the integrity of the tissues,which consists of three overlapping phases:inflammation,proliferative and maturation.There are a variety of inflammatory cells,cytokinesandcellcomponentsparticipatinginthe healing process,in order to remove the necrotic tissues and invaded pathogens and rebuild the damaged tissue[10,11].
MT is a small cysteine-rich molecular protein and has genetic polymorphism[12].It is widely expressed in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells and part of prokaryotic cells,and can be released into the extracellular environment under the condition of stress,etc.MT is highly conserved in evolution,all the isomers extracted from different mammalian tissues,is consistent with the basic molecular size and shape[13].Although that there are four isomers of MT(MT1,MT2,MT3,MT4),MT1 and MT2 as the main forms of MT were expressed in a variety of organizations of the body.Through the hydrosulphonyls,MT combines and releases the metal to adjust the metal concentration[14].
In the present study,the expression of MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA showed that there was a similar expression trends.At 1 h after contusion,an obvious increase in the expression levels of MT1A and MT2A and reached the peak at 18 h after contusion,but it decreased sharply at 24 h,and the second peak appeared at 30 h after contusion.Sogawaet al.[15]studied MT expression of rat dental pulp by Cd induced and Carmel[16]who studied the expression of MT after spinal cord ischemia injury reported that there are differences in the expression levels of MT1A mRNA and MT2A mRNA,but the trends of the expression levels are in much the same.Our results are consistent with those reports.
MT can not only provide the protective effect at the period of acute inflammation,but also be regarded as an important factor to promote the repair and regeneration after contusion.It attenuates inflammation action which leading to apoptosis by reducing the expression of TNF-α and IL,on the other hand,MT promotes tissue proliferation through regulating the expression of the apoptosis-associated proteins,for example,caspase,p53 and NF-κB[17]. Underthephysiologicalconditions,MTactivates capase-3 which involves in the process of apoptosis by preventing the release of cytochrome-c,but at the exist of pro-apoptosis factors,MT inhibits apoptosis by guiding the release of cytochrome-c and reducing the activation of caspase-3.MT also can suppress the expression of p53 directly to inhibit apoptosis[18].Overall,MT plays a significant role in repairing and reconstructing the skeletal muscle after contusion.
The reason why the significant down-regulation expressionlevelsofMT1AmRNAandMT2A mRNA at 24 h after contusion is possibly that MT proteins synthesis vastly by adjusting the inhibition of transcription;or a lack of Zn,which can combine with MT that results in the declining concentration of Zn in the cells,leads to the decreasing levelofMTmRNA;anotherpossibilityisthe degradation of MT in quantity after demetalization. The expression trend indicates that the speed of generation and metabolism of MT in the body is quickly,MT plays a significant role in the function of detoxifying rapidly and antioxidant[14,19].
Conclusion
Although the data obtained from animal models might be different than human tissues,investigation ofthetime-dependentexpressionofMT1Aand MT2A mRNA could help in determining the age of early wounds.To enable our results apply to the forensic,the comparison of MT1A and MT2A mRNA expressionbetweenthecontusedskeletalmuscle and the normal muscle is needed to contrast the differences.
Acknowledgment
This study was financially supportedby the National Science Foundation of China(grant No. 81571852)and the Research Project Supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council of China(grant No. 2015-052).
[1]Takamiya M,Saigusa K,Kumagai R,et al.Studies on mRNA expression of tissue-type plasminogen activator in bruises for wound age estimation[J].Int J Legal Med,2005,119(1):16-21.
[2]Singh R,Recinos RF,Agresti M,et al.Real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction:an improvement in detecting mRNA levels in mousecraninal tissue[J].Plast Reconstr Surg,2006,117(7): 2227-2234.
[3]Wickert L,Steinkruger S,Abiaka M,et al.Quantitative monitoring of the mRNA expression pattern of the TGF-β-isoforms(βl,β2,β3)during transdifferentiation of hepatic stellate cells using a newly developed real-time SYBR Green PCR[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2002,295(2): 330-335.
[4]Rigby KE,Stillman MJ.Structural studies of metal-free metallothionein[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2004,325(4):1271-1278.
[5]Vasák M.Advances in metallothionein structure and functions[J].Trace Elem Med Biol,2005,19(1):13-17.
[6]Sun X,Kang YJ.Prior increase in metallthionein levels is required to prevent doxorubicin cardiotoxicity[J].Exp Biol Med(Maywood),2002,227(8):652-657.
[7]Maret W.Fluorescent probes for the structure and function of metallothionein[J].Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci,2009,877(28):3378-3383.
[8]Penkowa M,Caceres M,Borup R,et al.Novel roles for metallthionein-I+II(MT-I+II)in defense responses,neurogenesis,and tissue restoration after traumatic brain injury:insights from global gene expression profiling in wild-type and MT-I+II knockout mice[J]. J Neurosci Res,2006,84(7):1452-1474.
[9]Sun JH,Nan LH,Gao CR,et al.Validation of reference genes for estimating wound age in contused rat skeletal muscle by quantitative real-time PCR[J].Int J Legal Med,2012,126(1):113-120.
[10]Giralt M,Carrasco J,PenkowaM,et al.Astrocyte-targeted expression of interleukin-3 and interferon-α causes region-specific changes in metallothionein expression in the brain[J].Exp Neurol,2001,168:334-346. [11]Chen QM,Alexander D,Sun H,et al.Corticosteroids inhibit cell death induced by doxorubicin in cardiomyocytes:inductionofantiapoptosis,antioxidant,and detoxification genes[J].Mol Pharmacol, 2005,67(6):1861-1873.
[12]Inoue K,Takano H,Shimada A,et al.Metallothionein as an anti-inflammatory mediator[J].Mediators Inflamm,2009:101659.
[13]Liu J,Cheng ML,Yang Q,et al.Blood metallothionein transcript as a biomarker for metal sensitivity: low blood metallothionein transcripts in arsenicosis patients from Guizhou,China[J].Environ Health Perspect,2007,115(7):1101-1106.
[14]Frederickson CJ,Maret W,Cuajungco MP.Zinc and excitotoxic brain injury:a new model[J].Neuroscientist,2004,10(1):18-25.
[15]Sogawa CA,Sogawa N,Yamamoto T,et al.Localization of metallothionein(MT)and expression of MT isoforms induced by cadmium in rat dental pulp[J]. Jpn J Pharmacol,2001,86(1):65-72.
[16]Carmel JB,Kakinohana O,Mestril R,et al.Mediators of ischemic preconditioning identified bymicroarray analysis of rat spinal cord[J].Exp Neurol,2004, 185(1):81-96.
[17]Liu Y,Liu J,Habeebu SM,et al.Metallothionein-I/II null mice are sensitive to chronic oral cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity[J].Toxicol Sci,2000,57(1): 167-176.
[18]West AK,Hidalgo J,Eddins D,et al.Metallothionein in the central nervous system:Roles in protection, regeneration and cognition[J].Neurotoxicology,2008, 29(3):489-503.
[19]Helal GK.Systemic administration of Zn2+during the reperfusion phase of transient cerebral ischaemia protects rat hippocampus against iron-catalysed postischaemic injury[J].Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol,2008, 35(7):775-781.
(Received date:2016-04-14)
(Editor:HUANG Ping)
金属硫蛋白1A和2A的mRNA时序性表达(英文)
范浩亮1,2,刘淑芳1,3,孙俊红1,王英元1
(1.山西医科大学法医学院,山西太原 030001;2.海南医学院法医学教研室,海南海口 571199;3.重庆公安局渝中分局,重庆400021)
目的研究大鼠肌肉挫伤后金属硫蛋白(metallothionein,MT)1A mRNA、MT2A mRNA的时序性表达。方法54只SD大鼠被分成挫伤组(挫伤后0.5、1、6、12、18、24、30和36h组各6只)和对照组(6只)。所有总RNA均取自大鼠的骨骼肌。利用SYBR GreenⅠ法进行RT-qPCR检测大鼠挫伤骨骼肌中MT1A mRNA、MT2A mRNA的相对表达量。结果MT1A mRNA、MT2A mRNA在损伤后的变化趋势与损伤时间具有一定的相关性。除了挫伤后0.5h组外,其余各组MT1A mRNA、MT2A mRNA的表达量与对照组相比差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。损伤后1h、6h、12h、18h MT1A mRNA和MT2A mRNA的相对表达量呈现逐渐上升的趋势,在18 h时达到了峰值,分别为对照组的(239.41±15.20)倍和(717.42±50.76)倍;损伤后24h时两者的表达量均明显减少;损伤后30h再次上升,随后下降。结论MT1A mRNA、MT2A mRNA可能对损伤时间推断有一定的意义。
法医病理学;肌;挫伤;金属硫蛋白;损伤时间推断
DF795.1
A
1004-5619(2017)01-0006-05
Author:FAN Hao-liang(1989—),postgraduate,major in forensic pathology;E-mail:fanhaoliang198931@163.com
WANG Ying-yuan,professor,major in forensic pathology;E-mail:wyy580218@163.com
Corresponding Author:SUN Jun-hong,associate professor, major in forensic pathology;E-mail:sunjunhong146@163.com
10.3969/j.issn.1004-5619.2017.01.002
