电控玉米排种系统设计与试验
2017-03-02张春岭陈黎卿
张春岭 吴 荣 陈黎卿
(1.安徽农业大学工学院, 合肥 230036; 2.华中农业大学工学院, 武汉 430070)
电控玉米排种系统设计与试验
张春岭1,2吴 荣1陈黎卿1
(1.安徽农业大学工学院, 合肥 230036; 2.华中农业大学工学院, 武汉 430070)
传统精量玉米播种机作业时,排种器的动力由地轮提供,针对由于田间作业工况复杂导致地轮打滑而造成漏播率增加等问题,设计了电控玉米排种系统。该系统在田间播种作业时,由雷达测速仪采集播种作业速度,结合所需粒距得到排种器理论转速;通过编码器采集排种器实时转速,利用控制器控制策略,进行转速的最优控制,从而得到目标排种转速,提高排种精度。田间试验结果表明:应用该电控排种系统进行田间玉米播种作业时,排种合格指数平均值为92.40%,与传统排种相比提高3.63个百分点;漏播指数平均值为4.82%,与传统排种相比降低2.04个百分点;不同播种作业工况下粒距变异系数均小于4.20%,播种效果好。
精量玉米播种机; 电控; 排种系统
引言
目前,玉米精量播种作业中多采用机械式排种器[1],但其动力常由地轮提供,由于田间作业工况复杂,地表不平整等易造成地轮打滑,从而增加漏播率[2-5]。国内外对机械式玉米排种器的研究主要集中于结构设计和性能参数优化[6-9],并未从根本上解决由地轮打滑带来的漏播率增加问题。气力式排种器虽然对种子损伤小、充填效果好,但其适宜于大豆等圆形类种子的播种,在播种玉米时漏播率和动力消耗都较大,特别是在地头时由于风机转速不够、气压不足,漏播现象更严重;而且其结构复杂,价格昂贵,使其推广使用受到限制[10-12]。
近些年,农业机械控制系统的控制策略主要依据PID控制算法[13-15],但大部分都集中于精准施肥控制器上,且模糊算法使用居多,而在精准排种器上的研究较少[16-23]。
针对以上问题,本文设计一款电控排种系统。该系统应用雷达测速仪采集播种作业速度,采用无刷直流电动机作为排种器的动力源,基于遗传算法整定PID参数,使得排种器旋转速度与播种作业速度保持同步,从而提高排种精度,并实现精准排种的最优控制。
1 电控排种系统作业原理
电控排种系统作业原理框图如图1所示。排种作业时,由雷达测速仪检测播种实时作业速度,将其与输入株距联合计算得到排种器理论转速;同时,由旋转编码器检测排种器实时转速。控制决策系统将排种器理论转速和排种器实时转速作为输入量,通过遗传算法对PID参数进行整定,得到排种器目标转速,然后调节控制器输出相应的PWM占空比,进而调节施加在电动机电枢两端的平均电压,达到调节电动机转速、实现精密排种的目的。

图1 电控排种系统作业原理框图Fig.1 Schematic of electronic control seeding system
2 电动机调速系统数学模型
2.1 播种作业速度与排种器转速的关系
选择玉米勺轮式排种器为研究对象,设有m个种勺,则相邻2粒种子的落地时间差为
(1)
式中 Δt——相邻2粒种子落地时间差,sn——排种盘转速,r/min
株距为
(2)
式中Z——玉米株距,mmv——拖拉机行走速度,km/h
本次设计中m=18,代入式(2)可得
(3)
2.2 电动机调速系统传递函数
电控排种系统主要是实现电动机转速的控制,实际上也是一个无刷直流电动机的控制系统。假设电动机在理想状态下进行工作,由电动机学理论可得无刷直流电动机的微分方程式为[24-26]
(4)
式中Td——电磁时间常数Tm——机电时间常数n1——电动机转速Ce——电动机反电动势系数U0——电枢电压
对式(4)进行拉氏变换,得电动机的传递函数为
(5)
选用80系列无刷直流电动机,其主要参数为:Tm=0.9 s,Td=8.1 ms,Ce=11.7 V/(r/min),代入式(5)后可得
(6)
3 控制器控制策略
3.1 基于Ziegler-Nichols阶跃响应法的PID参数整定
控制系统的设计关键是实现对电动机的控制,所以电动机的传递函数即系统的传递函数。通过Matlab中的Ziegler-Nichols程序得到系统传递函数的根轨迹图形,如图2所示。

图2 电动机调速系统传递函数根轨迹图形Fig.2 Root locus graph of motor speed system transfer function
由图2可得开环增益Zm=21.057 dB,穿越频率Wm=84.96 Hz。根据PID整定公式得
(7)
式中KP——比例系数KI——积分系数KD——微分系数
将式(7)的3个参数分别输入系统PID控制器的Simulink模型中,得仿真结果如图3所示。

图4 控制系统Simulink模型Fig.4 Simulink model of control system

图3 由Ziegler-Nichols阶跃响应法整定PID参数的仿真结果Fig.3 Simulation results of PID parameters by Zieglor-Nichols step response method
由仿真结果可以看出,应用Ziegler-Nichols阶跃响应法整定的PID参数虽然能使控制系统趋于稳定,但超调量大,所以仍需对PID参数进行优化整定。遗传算法可以在初始条件选择不当的情况下,仍能寻求合适的参数,而且避免了大量的专家经验和知识库整理工作,因此本文应用遗传算法对PID参数进行优化。
3.2 遗传算法的PID参数优化整定
由Ziegler-Nichols阶跃响应法整定的PID参数确定遗传算法中PID参数KP、KI、KD的取值范围分别为[0,20]、[0,350]、[0,1],采用二进制编码方式对3个参数进行编码。为了避免超调,采用了惩罚功能,最优指标函数选为
(8)
式中w1、w2、w3、w4——权值,且w4≫w1e(t)——系统误差u(t)——控制器输出ey(t)——两次采样时间间隔系统输出误差
tu——上升时间
建立控制系统的Simulink模型如图4所示。本次设计中,遗传算法各参数取值为:w1=0.999,w2=0.001,w3=1,w4=100,种群规模N=30,交叉概率Pc=0.9,变异概率随机且小于0.5。
经过100代进化后,代价函数J-1的优化过程如图5所示。优化后可得各参数如下:J-1=5.046 2,KP=1.289 4,KI=0.769 2,KD=0.002。将优化后的PID参数代入Simulink模型中进行仿真,得到由遗传算法整定的PID参数的仿真曲线如图6所示。由仿真结果可得,将遗传算法整定的PID参数应用于电控排种器控制,系统无超调,通过软件中的坐标标识可得调节时间为0.25 s。

图5 代价函数J-1的优化过程Fig.5 Cost function J-1 optimization process

图6 遗传算法整定的PID参数仿真结果Fig.6 Simulation results of PID parameters based onLJ optimal algorithm
4 控制系统设计
4.1 硬件设计
控制系统主要由硬件和软件组成,其中硬件主要由电源模块、信号采集模块、控制模块、电动机驱动模块、排种执行模块和人机交互模块组成。其中电源模块在田间试验时采用逆变器将拖拉机自带电源的12 V转换为48 V供控制系统使用;电动机驱动模块中,由于电动机转速过高,设计时根据排种器作业转速限制选用速比为40的减速器;为便于排种器、电动机、减速器和编码器的安装,设计时对排种轴进行了改进,安装方式如图7所示;信号采集模块中,应用雷达测速仪的多普勒效应,通过采集发射与接收的频率差来检测播种作业速度,其安装方式如图8所示。硬件配置表和控制系统电路图分别如表1和图9所示。

图7 排种执行模块Fig.7 Metering executable module

图8 雷达测速仪安装方式Fig.8 Installation mode of radar speed device

设备名称规格型号雷达测速仪美国帝强RadarIII编码器38T8G524E1000BL1T2m电动机驱动器直流无刷驱动器ZM6615显示屏TFTLCDILI9341在线调试器STLINKV2电压转换模块XW36481260W开关式直流稳压器电平信号转换器HCPL2630双通道逻辑输出光电耦合器
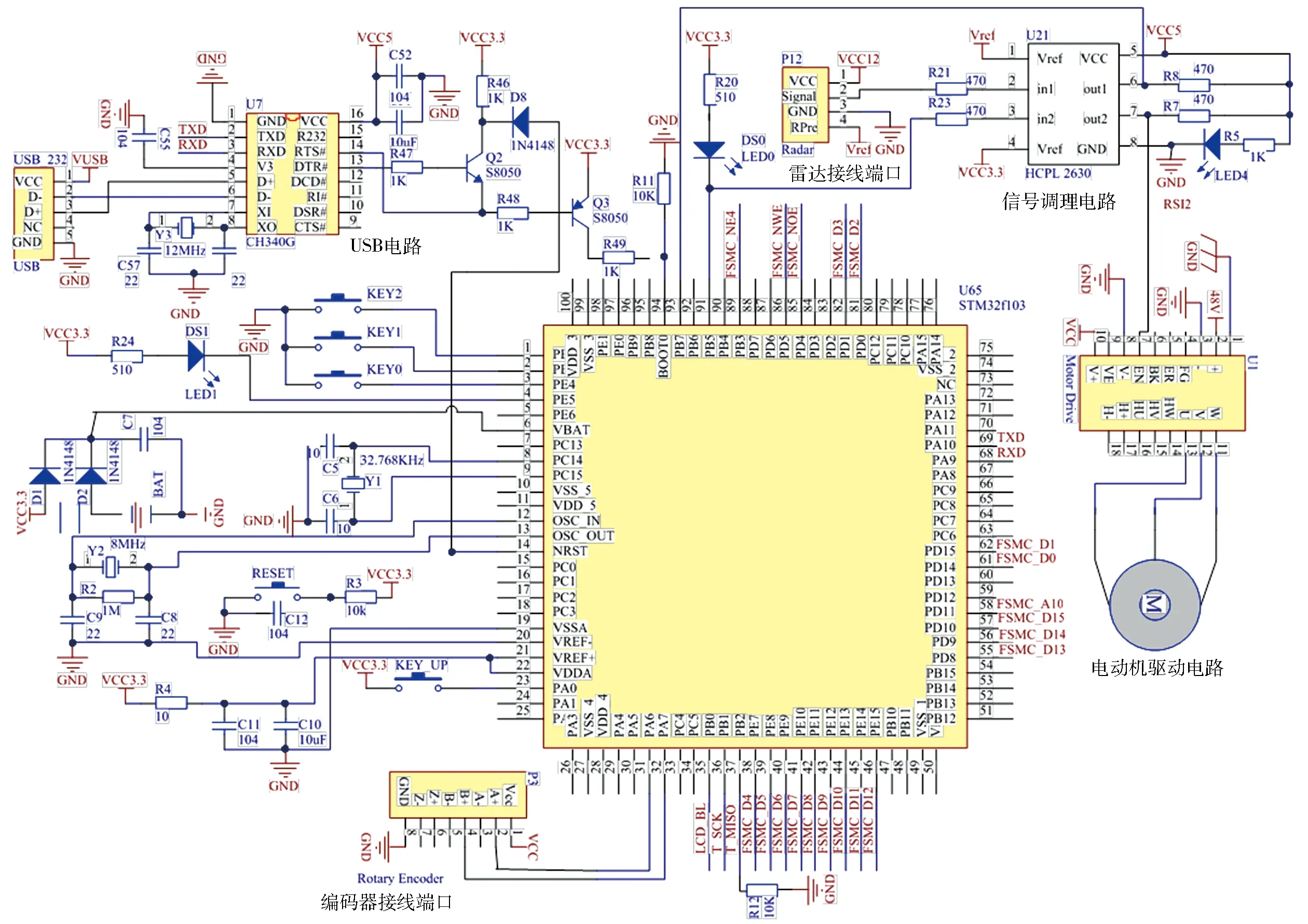
图9 控制系统电路图Fig.9 Circuit diagram of control system
4.2 软件设计
控制系统软件设计选用Keil μ Vision 5作为开发环境,应用C语言进行编程,系统控制流程图如图10所示。
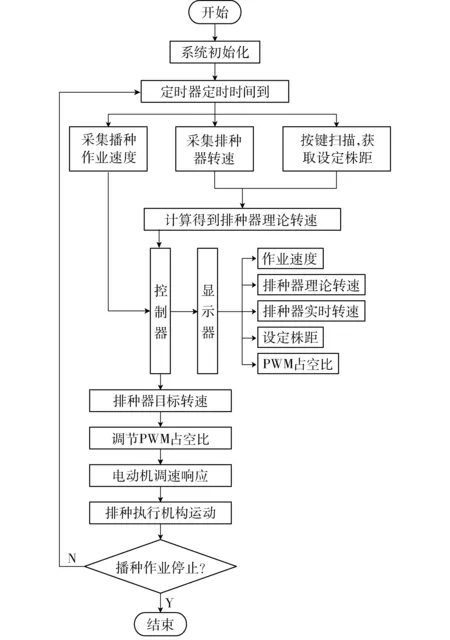
图10 控制系统流程图Fig.10 Flow chart of control system

图11 田间试验Fig.11 Field experiment
5 试验与结果分析
5.1 控制精度性能试验
试验材料选用中单909玉米杂交种,试验在安徽农业大学工学院试验田进行,整机实物图和田间试验如图11所示。试验地块长20 m,每次试验采集平稳作业后的60个数据,重复3次,结果取平均值。以不同作业工况下的排种器理论转速和实时转速为检测对象,比较两者之间的差值大小,作为控制精度。试验结果如图12所示。
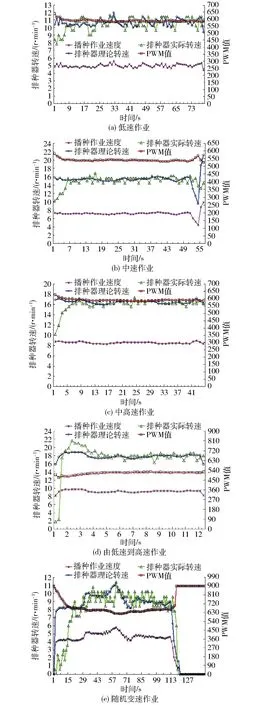
图12 不同作业工况下机具部分运动参数变化曲线Fig.12 Variation curves of machine’s some motion parameters in different driving cycles
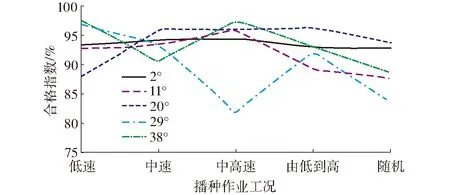
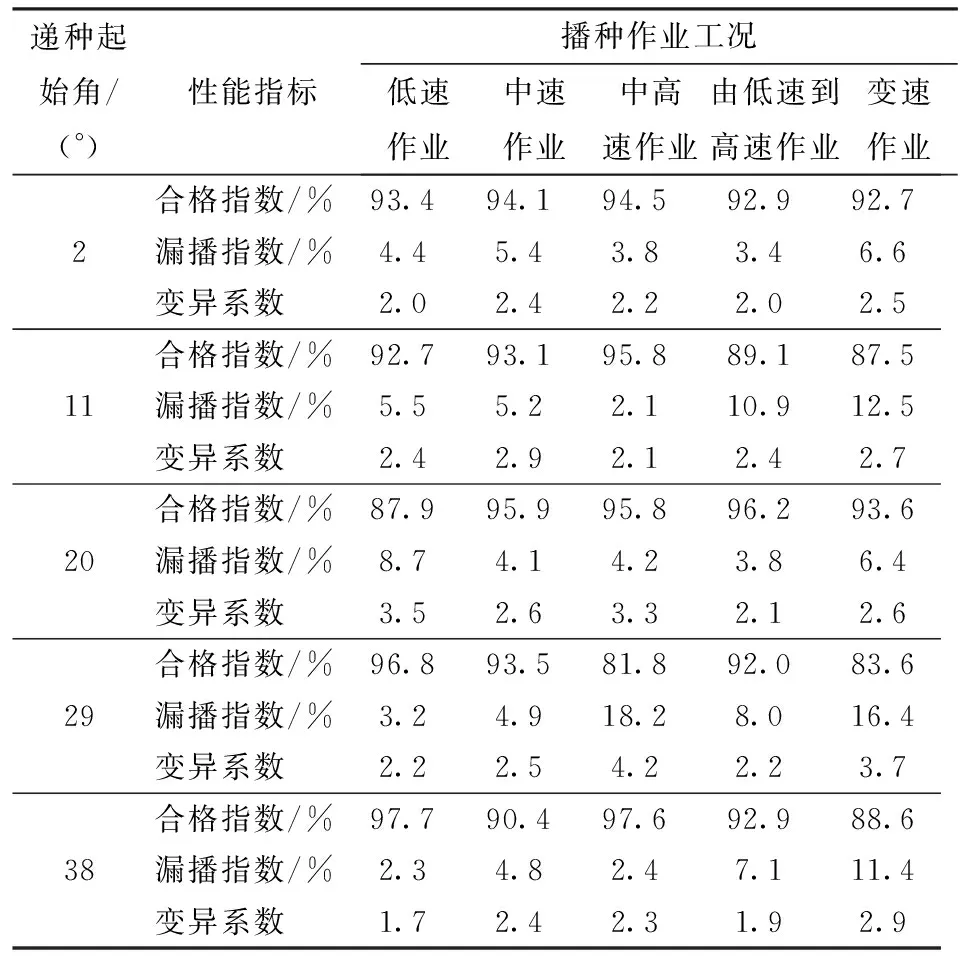
图12中的PWM值表示在0~900范围内调节细分数从而实现调节占空比由0~1的变化。以排种器理论转速和实时转速为分析对象,分析结果见表2。由图13和表2可以看出,在播种作业开始和停止阶段,排种器理论转速和实时转速偏差较大;当播种作业于稳定阶段时,平均误差的最大值为8.02%,最小值为2.32%,控制精度高;各播种作业工况中,以中高速行驶(8 km/h 表2 不同作业工况下排种器理论转速和实际转速误差Tab.2 Analysis of theoretical speed and actual speed of metering device in different driving cycles 图13 电控播种和传统播种在不同作业工况下的合格指数平均值对比Fig.13 Comparison of average qualified index under different working conditions by electronic control and traditional sowing 5.2 排种性能试验 试验参照GB/T 6973—2005《单粒(精密)播种机试验方法》,选择合格指数、重播指数、漏播指数和粒距变异系数为排种性能指标。试验统计结果如表3所示。 由图13和图14可以看出,应用该电控排种系统进行田间玉米播种作业时,排种合格指数平均值为92.40%,与作者前期对传统排种研究的合格指数88.77%相比提高3.63个百分点[27];漏播指数平均值为4.82%(除去个别由田间复杂工况出现的突变情况外),与作者前期对传统排种研究的漏播指数6.86%降低2.04个百分点。 由图15和图16可以看出,当递种起始角为29°时,应用该电控排种控制系统在中高速播种作业下效果较其它作业工况差;但所有播种作业工况下粒距变异系数均小于4.2%,播种效果好。 表3 不同作业工况和不同递种起始角下的排种性能统计结果Tab.3 Statistic results of seed performance under different working conditions and different start delivery angles 图14 电控播种和传统播种在不同作业工况下的漏播指数平均值对比Fig.14 Comparison of average miss index under different working conditions by electronic control and traditional sowing (1)针对现有播种控制系统设计时存在的速度采集误操作问题和精准农业要求,设计了一款电控排种器,建立了相应的传递函数与Simulink模型,并基于遗传算法进行了PID参数的整定和控制器设计,提高了控制精度。 图15 不同递种起始角与不同播种作业工况下的排种合格指数Fig.15 Sowing qualified index under different working conditions and different start delivery angles 图16 不同递种起始角与不同作业工况下的粒距变异系数Fig.16 Maize distance variation coefficient under different working conditions and different start delivery angles (2)试验结果表明,应用该电控排种系统进行田间玉米播种作业时,排种合格指数平均值为92.40%,与传统排种相比提高3.63个百分点;漏播指数平均值为4.82%,与传统排种相比降低2.04个百分点;不同播种作业工况下的粒距变异系数均小于4.20%,播种效果好。 1 杨丽,史嵩,崔涛,等.气吸与机械辅助附种结合式玉米精量排种器[J/OL].农业机械学报,2012,43(增刊):48-53. http:∥www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=2012s10&journal_id=jcsam. DOI:10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2012.S0.010. YANG Li,SHI Song,CUI Tao,et al.Air-suction corn precision metering device with mechanical supporting plate to assist carrying seed[J/OL].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2012,43(Supp.):48-53. (in Chinese) 2 王庆杰,李洪文,何进,等.凹形圆盘式玉米垄作免耕播种机的设计与试验[J].农业工程学报,2011,27(7):117-122. WANG Qingjie,LI Hongwen,HE Jin,et al.Design and experiment on concave disc type maize ridge-till and no-till planter[J].Transactions of the CSAE,2011,27(7):117-122. (in Chinese) 3 戴飞,赵武云,唐学鹏,等.旱地玉米全膜覆盖双垄沟精量播种机工作参数优化[J/OL].农业机械学报,2013,44(增刊1):39-45. http:∥www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=2013s108&journal_id=jcsam. DOI:10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2013.S1.008. DAI Fei, ZHAO Wuyun,TANG Xuepeng,et al.Parameters optimization of precision seeder with corn whole plastic-film mulching on double ridges in dry land[J/OL].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2013,44(Supp.1):39-45. (in Chinese) 4 张喜瑞,何进,李洪文,等.水平拨草轮式玉米免耕播种机设计和试验[J].农业机械学报,2010,41(12):39-43. ZHANG Xirui,HE Jin,LI Hongwen,et al.Design and experiment on no-till planter in horizontal residue-throwing finger-wheel type for maize[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2010,41(12):39-43. (in Chinese) 5 李复辉,杜瑞成,刁培松,等.舵轮式玉米免耕精量施肥播种机设计与试验[J/OL].农业机械学报,2013,44(增刊1):33-38. http:∥www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=2013s107&journal_id=jcsam. DOI:10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2013.S1.007. LI Fuhui,DU Ruicheng,DIAO Peisong,et al.Design and experiment of helm-shaped no-tillage precision fertilization planter for corn[J/OL].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2013,44(Supp.1):33-38. (in Chinese) 6 耿端阳,李玉环,孟鹏祥,等.玉米伸缩指夹式排种器设计与试验[J/OL].农业机械学报,2016,47(5):38-45. http:∥www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20160506&journal_id=jcsam. DOI:10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2016.05.006. GENG Duanyang,LI Yuhuan,MENG Pengxiang,et al.Design and test on telescopic clip finger type of metering device[J/OL].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016,47(5):38-45. (in Chinese) 7 王应彪,赵学观,徐丽明,等.基于电磁振动的玉米种子定向排序输送技术[J/OL].农业机械学报,2015,45(1):79-88. http:∥www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20150112&journal_id=jcsam. DOI:10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2015.01.012. WANG Yingbiao,ZHAO Xueguan,XU Liming,et al.Experiment and directional movement technology of corn seed based on electromagnetic vibration[J/OL].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2015,45(1):79-88. (in Chinese) 8 刘佳,崔涛,张东兴,等.机械气力组合式玉米精密排种器[J/OL].农业机械学报,2012,43(2):43-47. http:∥www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20120209&journal_id=jcsam. DOI:10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2012.02.009. LIU Jia,CUI Tao,ZHANG Dongxing,et al.Mechanical-pneumatic combined corn precision seed-metering device[J/OL].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2012,43(2):43-47. (in Chinese) 9 van LIEDEKERKE P,TIJSKENS E,DINTWA E,et al.DEM simulations of the particle flow on a centrifugal fertilizer spreader[J].Powder Technology,2009,190(3):348-360. 10 赵学观,徐丽明,王应彪,等.基于Fluent与高速摄影的玉米种子定向吸附研究[J/OL].农业机械学报,2014,45(10):103-109. http:∥www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20141017&journal_id=jcsam. DOI:10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2014.10.017. ZHAO Xueguan,XU Liming,WANG Yingbiao,et al.Directional adsorption characteristics of corn seed based on fluent and high-speed photography[J/OL].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2014,45(10):103-109. (in Chinese) 11 史嵩,张东兴,杨丽,等.气压组合孔式玉米精量排种器设计与试验[J].农业工程学报,2014,30(5):10-18. SHI Song,ZHANG Dongxing,YANG Li,et al.Design and experiment of pneumatic maize precision seed-metering device with combined holes[J].Transactions of the CSAE,2014,30(5):10-18. (in Chinese) 12 YAZGI A,DEGIRMENCIOGLU A.Optimisation of the seed spacing uniformity performance of a vacuum-type precision seeder using response surface methodology[J].Biosystems Engineering,2007,97(3):347-356. 13 郭娜,胡静涛.插秧机行驶速度变论域自适应模糊PID控制[J/OL].农业机械学报,2013,44(12):245-251. http:∥www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20141017&journal_id=jcsam. DOI:10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2014.10.017. GUO Na,HU Jingtao.Variable universe adaptive fuzzy-PID control of traveling speed for rice transplanter[J/OL].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2013,44(12):245-251. (in Chinese) 14 张辉,李树君,张小超,等.变量施肥电液比例控制系统的设计与实现[J].农业工程学报,2010,26(增刊2):218-222. ZHANG Hui,LI Shujun,ZHANG Xiaochao,et al.Development and performance of electro-hydraulic proportion control system of variable rate fertilizer[J].Transactions of the CSAE,2010,26(Supp.2):218-222. (in Chinese) 15 梁春英,衣淑娟,王熙.变量施肥控制系统PID控制策略[J].农业机械学报,2010,41(7):157-162. LIANG Chunying,YI Shujuan,WANG Xi.PID control strategy of the variable rate fertilization control system[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2010,41(7):157-162. (in Chinese) 16 陈满,鲁伟,汪小旵,等.基于模糊PID的冬小麦变量追肥优化控制系统设计与试验[J/OL].农业机械学报,2016,47(2):71-76. http:∥www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20160210&journal_id=jcsam. DOI:10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2016.02.010. CHEN Man,LU Wei,WANG Xiaochan,et al.Design and experiment of optimization control system for variable fertilization in winter wheat field based on fuzzy PID[J/OL].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2016,47(2):71-76. (in Chinese) 17 苗中华,李闯,韩科立,等.基于模糊PID的采棉机作业速度最优控制算法与试验[J/OL].农业机械学报,2015,46(4):9-14. http:∥www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20150402&journal_id=jcsam. DOI:10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2015.04.002. MIAO Zhonghua,LI Chuang,HAN Keli,et al.Optimal control algorithm and experiment of working speed of cotton-picking machine based on fuzzy PID[J/OL].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2015,46(4):9-14. (in Chinese) 18 梁春英,吕鹏,纪建伟,等.基于遗传算法的电液变量施肥控制系统PID参数优化[J/OL].农业机械学报,2013,44(增刊1):89-93. http:∥www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=2013s117&journal_id=jcsam. DOI:10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2013.S1.017. LIANG Chunying,LÜ Peng,JI Jianwei,et al.Optimization of PID parameters for electro-hydraulic variable rate fertilization system based on genetic algorithm[J/OL].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2013,44(Supp.1):89-93. (in Chinese) 19 BACK S W,YU S H, KIM Y J,et al. An image-based application rate measurement system for a granular fertilizer application[J].Transactions of the ASABE,2014,57(2):679-687. 20 DONG Fuhong,PETZOLD Olaf, HEINEMANN Wolfgang,et al.Time-optimal guidance control for an agriculture robot with orientation constraints[J].Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,2013,99:124-131. 21 HUAN J, LIU X Q, CHONG Q F, et al.Design of an aquaculture monitoring system based on android and gprs[J].Applied Engineering in Agriculture,2014,30(4):681-687. 22 陈满,施印炎,汪小旵,等.冬小麦精准追肥机专家决策系统[J/OL].农业机械学报,2015,46(7):64-70. http:∥www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20150505&journal_id=jcsam. DOI:10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2015.05.005. CHEN Man,SHI Yinyan,WANG Xiaochan,et al.Expert decision system of variable nitrogen application in winter wheat[J/OL].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2015,46(7):64-70. (in Chinese) 23 古玉雪,苑进,刘成良.基于模糊系统的开度转速双变量施肥控制序列生成方法[J].农业工程学报,2011,27(11):134-139. GU Yuxue,YUAN Jin,LIU Chengliang.FIS-based method to generate bivariate control parameters regulation sequence for fertilization[J].Transactions of the CSAE,2011,27(11):134-139. (in Chinese) 24 杜荣华,朱昭,舒雄,等.无刷直流电动机自适应模糊PID控制及仿真[J].长沙理工大学学报,2014,11(2):60-66. DU Ronghua,ZHU Zhao,SHU Xiong,et al.Brushless DC motor self-adaptive fuzzy PID control and simulation[J].Journal of Changsha University of Science and Technology:Natural Science,2014,11(2):60-66. (in Chinese) 25 傅晓云,方旭,杨钢,等.基于遗传算法的PID控制器设计与仿真[J].华中科技大学学报:自然科学版,2012,40(5):1-5. FU Xiaoyun,FANG Xu,YANG Gang,et al.Design and simulation of GA-based PID controller[J].Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology: Natural Science Edition,2012,40(5):1-5. (in Chinese) 26 刘成颖,刘龙飞,孟凡伟,等.基于遗传算法的永磁直线同步电动机伺服系统参数设计[J].清华大学学报:自然科学版,2012,52(12):1751-1757. LIU Chengying,LIU Longfei,MENG Fanwei,et al.Genetic algorithm based parameter selection of permanent magnet linear synchronous motor servo system design[J].Journal of Tsinghua University: Science and Technology,2012,52(12):1751-1757. (in Chinese) 27 张春岭,陈黎卿,吴荣.基于离散元法的勺轮式排种器性能仿真分析[J/OL].安徽农业大学学报,2016,43(5): 848-852. http:∥www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1162.S.20160929.1029.052.html.DOI:10.13160/j.cnki.1672-352x.20160929.026. ZHANG Chunling, CHEN Liqing, WU Rong. Simulation analysis for seeding performance of spoon-wheel seed metering device based on discrete element method[J/OL]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2016,43(5): 848-852. (in Chinese) Design and Test of Electronic Control Seeding System for Maize ZHANG Chunling1,2WU Rong1CHEN Liqing1 (1.SchoolofEngineering,AnhuiAgriculturalUniversity,Hefei230036,China2.CollegeofEngineering,HuazhongAgriculturalUniversity,Wuhan430070,China) When the traditional maize seeder works in the field, the power of seed metering device comes from ground steel. Aiming at the problem that the field conditions are so complicated that the ground steel will skid easily, then the miss index will be increased, an electronic maize sowing control system was designed. The police traffic radar collected the sowing operation speed when the sowing was started, then the control system will calculate the seed metering device rotational speed combined with the theoretical particle distance. The rotary encoder collected the seed metering device rotational speed, then the controller would process speed based on control strategy and obtained the last speed. The optimal process of control strategy can improve the accuracy. The results of the field test showed that when the electronic control seed metering device was working in the field, the average qualified index was 92.40%, which was increased by 3.63 percentage points compared with the traditional sowing. The average miss index was 4.82% and it was reduced by 2.04 percentage points compared with the traditional sowing. The variability of seed-spaces was less than 4.20% and the sowing effects were much more than the national standard. When the speed of sowing was more than 10km/h, the effects was worse than other cases, therefore some improvement on the structure to improve the accuracy. The design of the electronic control maize seed metering device provided some definite reference for study of sowing control system. precision maize planter; electronic control; seeding system 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2017.02.007 2016-06-29 2016-10-08 农业部公益性行业专项(201503136)和安徽省科技攻关项目(1501031104) 张春岭(1989—),男,助教,华中农业大学博士生,主要从事精细农业理论技术与装备研究,E-mail: ZCL158967592@163.com 陈黎卿(1979—),男,教授,博士,主要从事玉米播种和秸秆处理类机械设计研究,E-mail: lqchen@ahau.edu.cn S223.2 A 1000-1298(2017)02-0051-09


6 结论