耙齿式垄作花生残膜回收机设计及参数优化
2017-02-17施丽莉胡志超顾峰玮吴朋来
施丽莉,胡志超,顾峰玮,吴 峰,吴朋来
耙齿式垄作花生残膜回收机设计及参数优化
施丽莉,胡志超※,顾峰玮,吴 峰,吴朋来
(农业部南京农业机械化研究所,南京 210014)
为解决垄作花生收获后残膜回收问题,针对耙齿式残膜回收机进行试验研究及参数优化使其适用于垄作花生残膜回收。针对主要工作部件进行研究,确定整机结构参数。前、中、后耙齿直径分别为10、8、8 mm;耙齿材料为65号锰钢;耙齿入土角度范围为10°~35°;3排齿的齿间距分别为120、100、80 mm;对机具前进速度,耙齿入土深度,耙齿曲率半径进行试验且做了MATLAB四维切片和响应面分析,可知3个因素对残膜回收率均有显著影响,影响程度依次为:机具前进速度>耙齿入土深度>耙齿曲率半径。应用Design expert寻优功能进行优化,优化后机具前进速度1.2 m/s,耙齿入土深度11 mm,耙齿曲率半径222 mm,残膜回收率为93%。经田间试验验证,证明了该优化方案的可行性,将为相关设备的改进提供理论依据。
农业机械;塑料薄膜;优化;垄作花生残膜;响应面
0 引 言
地膜覆盖栽培技术是一种可改善和优化栽培条件,具有保温、保墒、抑制杂草生长等优点的先进农业栽培技术。但此技术广泛使用导致的“白色污染”问题却日益严重[1-2]。采用机械方式回收残膜能提高生产效率、降低劳动成本,研发改进适用的残膜回收机已成为农业机械化发展的迫切任务[3-5]。据中国统计年鉴(2015)统计2014年我国花生种植面积460.6万hm2(约占全球种植面积的17.9%),全国花生产量1 648.17万t(约占全球总产量的38.9%)。但田间残膜会破坏土地结构,导致土壤结板失去供养能力,影响花生产量和农业机械的使用顺畅性。所以,解决垄作花生残膜污染问题难度高且意义重大[6-9]。
现有残膜回收机主要分为滚筒式、铲链式、铲筛式、耙齿式等[10]。但却少有针对垄作花生残膜回收的机具。耙齿式残膜回收机回收残膜效果较好,结构简单且工作效率高,对其进行研究并试验优化,使其满足垄作花生残膜回收的使用效果是目前解决垄作花生残膜污染行之有效的方法之一[11-13]。
1 垄作花生残膜回收机总体设计
1.1 垄作花生种植模式与残膜分布特点
花生种植方式分为平作,垄作,畦作,其中尤以垄作使用最为广泛。垄作是将花生播种在垄上,垄作分为双行垄作和单行垄作。如图1所示为花生种植形式示意图。起垄播种可方便排灌,防止田间积水和烂果;改善种植地土壤团粒结构,提高地温和昼夜温差,在丘陵地上起垄种植还可相应加厚土层,扩大根系吸收范围,有利于花生荚果发育[14-16]。
不同主产区花生的种植模式并不相同,以河北、山东为例。依据播种机具、土壤肥力的不同,河北地区花生垄距85~90 cm,垄面宽55~60 cm,垄沟宽约30 cm,垄上窄行距25~30 cm。山东地区,垄距75~90 cm,垄面宽55~60 cm,垄上窄行距25~35 cm。
花生覆膜有薄膜、厚膜,收获作物动土或不动土时,残膜的破坏程度不一,有长条整膜、短条碎膜等多种形态。垄作与平作相比残膜残留情况有差异,主要为地面高低不平、残膜碎片多、埋膜深、断枝断秧多、秧膜易混合等。
花生垄作残膜回收的难点是:垄作花生收获后,地表不平整,残膜分布于垄面上及垄沟内,且收获后残膜碎片多、埋膜深、断枝断秧多、秧膜易混合。所以,必须通过试验进行结构和运动参数的优化,使耙齿式残膜回收机适应垄作花生残膜回收[17-19]。
1.2 整机结构简介与作业原理
图2为残膜回收机结构示意图。耙齿式残膜回收机由牵引架1、耙齿3等装置组成。机架2与牵引架1相连。作业时,机具以悬挂方式与拖拉机相连。作业时,耙齿与土壤及残膜接触,机具3点悬挂于四轮拖拉机尾部,拖拉机驱动残膜回收机前进,并带动耙齿入土收膜。由于地表不平整,埋在两边的边膜略微低于垄表面,要选择弹性较大的耙齿进行残膜回收作业并确保其入土深度,使其可以回收垄沟内以及垄面较深残膜。工作时,前、中、后3排搂膜耙齿依次进行搂膜,3排耙齿间距不等且交错排列。前排耙齿最先进行搂膜,主要对大块残膜进行收集;中排耙齿对前排耙齿的漏膜以及较小的残膜进行收集;前、中排耙齿的漏膜以及小块的残膜均由后排耙齿进行收集。
本文重点研究的影响机具性能的因素为:耙齿曲率半径、耙齿直径、耙齿材料、耙齿入土角度、耙齿间距排列、机具前进速度、耙齿入土深度。
2 关键部件结构与参数设计
2.1 耙齿静态强度分析
花生收获后,田间的残膜、石块及前茬作物残留,都会对残膜回收机工作性能产生影响,所以耙齿设计要点之一就是在收膜的基础上满足田间工作强度要求。
机具前进为动态过程,设计时若耙齿在最大极限载荷条件下满足强度要求,则其他情况就符合受力要求,本文选取耙齿在入土时的最深极限载荷条件进行计算,通过静强度分析,可得知耙齿的最大受力位置,分析其强度以及对耙齿材料及各种参数进行确定。如图3所示为耙齿在土壤中变形示意图,为变形量,本文要求≤10 cm。
根据分析,耙齿有垂直方向的入土阻力F,水平方向受到的土壤阻力′以及摩擦力1
式中为载荷系数,其取值与耙齿的齿面参数、残膜回收机机具前进速度、土壤情况等有关,因为4.9~9.8 N/cm2,根据实际情况取最大值9.8 N/cm2[20]。为作用面积,F=500~1 000 N,取500 N
式中为土壤与钢的摩擦系数,tan15°~tan40°。
水平方向的牵引阻力F为
垂直方向的阻力在耙齿根部产生弯矩M1为
耙齿受到的合力作用合为
水平方向的阻力在耙齿根部产生弯矩M2为
静态强度校核的检验条件是
式(4)-(9)中F为水平方向的牵引阻力;M2为水平方向的阻力在耙齿根部产生弯矩,N·M;为应力值;W为抗弯截面系数;为耙齿的曲率半径,mm;[]是材料的许用应力,MPa;max是实际计算的最大应力,MPa;是材料的安全系数,取=2(=1.2~2.5)。公式计算可得,F'=9.8×3.14×0.25=7.7 N,1=f×F=tan30°×500= 288 N,F=288+7.7=295.7 N,并根据公式(5)可计算580 N。所以M1=500×0.073=36.5 N·M,M2=295.7× 0.163=48.2 N·M,=374.4 MPa。
计算可知,耙齿的最大应力出现在耙齿根部,而影响耙齿根部强度最重要的因素为耙齿曲率半径、直径、材料。锰钢强度高,主要用于需承受冲击、挤压、物料磨损等恶劣工况条件,是典型的抗磨钢,其中65号锰钢钢板强度、硬度、弹性和淬透性均较好且经济性好,故将材料定为65号锰钢。
经试验可知,耙齿直径超过12 mm其弹性会降低不利于收膜,耙齿直径小于8 mm其强度不足会导致耙齿变形失效,所以耙齿适宜的直径范围为8~12 mm。根据机具作业原理,前排耙齿在收膜过程中遇到的阻力最大最易变形,所以前排耙齿的直径要稍大于后两排。
鉴于上述情况,本研究设计2种直径排列方式,前、中、后排耙齿直径排列分别为:12、10、10 mm;10、8、8 mm两种形式。具体选择应根据花生产地的实际土壤硬度等情况。
2.2 耙齿入土角度及形状分析
耙齿的角度也是影响其工作性能的重要因素之一。耙齿在进行受力分析时,不同的入土深度受力是不同的,即耙齿入土前和入土后耙齿的入土角不同,如图4所示为耙齿前进过程中的受力图(即入土之后的受力分析),耙齿受到前进过程中的工作阻力、土壤的反作用力、摩擦力,以及缠绕在耙齿上残膜及土壤的重力对耙齿均有影响。根据受力平衡方程可以确定耙齿入土角度的理论值为
式中为耙齿前进过程中所受工作阻力,N;为耙齿受到的土壤及残膜对其反作用力,N;为耙齿上缠绕的残膜和土壤的重力,N;为耙齿前进过程中对土壤及残膜的摩擦力,N,其中,,将公式(10)和(11)进行合并和化简,可得(12)
耙齿的入土角度与入土深度、本身结构参数等多种情况有关,入土角度过大或过小都不利于残膜回收[21-25]。综合理论分析及田间试验的实际情况,耙齿入土角度=10°~35°时残膜回收效果好。
注:为耙齿与地面之间的夹角;为耙齿前进过程中所受工作阻力;为耙齿受到的土壤及残膜对其反作用力;为耙齿上缠绕的残膜和土壤的重力;为耙齿前进过程中对土壤及残膜的摩擦力。
Note:is the angle of the collecting film teeth and ground;is the working resistance when the machine is working;is the opposite reaction of the plastic and the soil;is the gravity of plastic and soil on the collecting film teeth;is the friction of soil and plastic when the machine is working.
图4 耙齿受力分析
Fig.4 Force analysis of collecting film teeth
2.3 耙齿排列设计试验及分析
耙齿作为回收残膜的重要部件,其形状尺寸及其排列都会对残膜回收效果起到重要影响。图5为耙齿排列示意图。
本研究中,耙齿均采用弧形齿且有一定的入土角度,利于残膜堆积上升,耙齿的排列与间距采用试验的方法来确定。耙齿的间距排列设计遵循3个原则:第一,齿的间距过大会造成漏膜,间距过小会壅土,所以间距要在合理的范围之内;第二,采用3排齿进行收膜,3排齿交错排列保证收膜效果,且齿的排列为均分,使每一个齿都能起到收膜的作用;第三,齿的有效收膜幅宽要跟作物的幅宽相匹配以保证收膜效果。
根据分析,3排耙齿间隙不同且交错排列。前两排耙齿密度较小,可收集大块残膜,最后且能防止物料堆积,最后一排耙齿密度较大,可收集小块残膜防止漏膜。现对耙齿的每一排调整不同间隙单独进行试验,挑选出最优的间隙。
评价收膜部件的指标为残膜回收率高且壅土高度低。现设定,总分为100分,残膜回收率权重为60,壅土高度权重为40。将耙齿的间隙设为不同值,测出其残膜回收率1(%)、壅土高度1(mm)。为保持量纲的一致性,定义2为壅土高度占耙齿总离地高度的百分比。采用加权综合评分法进行评价,为综合评分。
1、2为2个衡量指标,1越大越好,2则越小越好,为方便使用加权综合评分法,现定义值3,3值=1−2。两者都是越大越好,可以使用加权综合评分法进行评价。
加权综合评分指标可用式(13)来计算
式中Z为第号试验所得计算值(加权评分指标),=1,2,3…,6;W为第个指标的“权”值,=1,2,其中160,240;Y为第个试验中第个指标;Ymax为所有试验中,第个指标的最大值。
通过分析可知,间距与残膜回收率1和壅土高度占耙齿总离地高度的百分比2满足方程(14)、(15)
加权综合评分结果如表1所示,加权综合评分的结果最大的结果分别为90.31、87.87、87.78,最大值分别对应的间隙为100、120、80 mm,所以选择的最优的耙齿间隙从小到大依次即为80、100、120 mm。
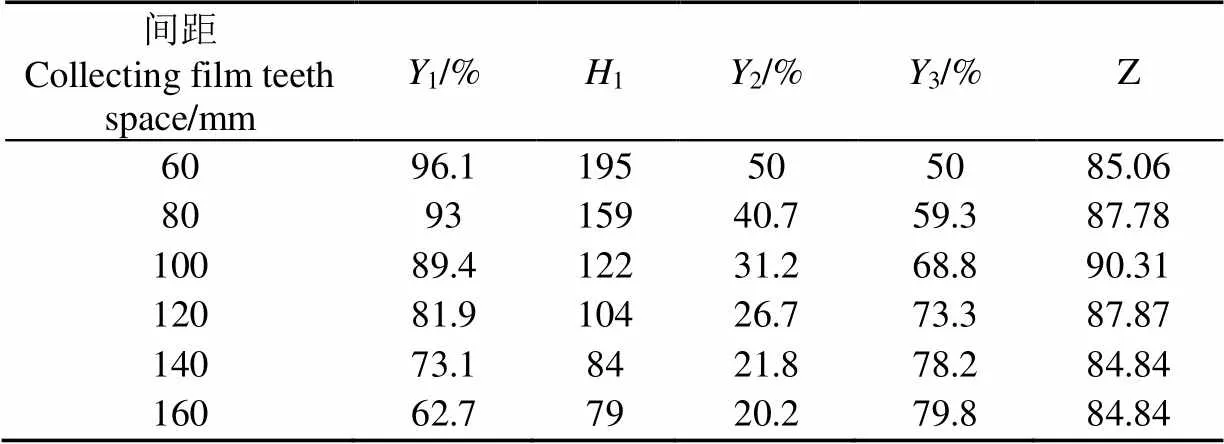
表1 加权综合评分结果
注:1为残膜回收率,1为壅土高度,2为壅土高度占耙齿总离地高度的百分比,3=1-2,为综合评分。
Note:1is residual film recovery rate,1is soil height,2is soil height divided by total height,3=1-2,is comprehensive scoring.
分析可知,3排齿排列时,密度应依次加大,既可以防止壅土也可以确保拾膜效果。即3排齿的齿间距分别为:120、100、80 mm。如图6所示。
3 田间试验及参数优化
通过上述分析,可确定部分影响残膜机具作业的参数取值和范围。根据试验地的实际情况,设计前、中、后耙齿的直径分别为10、8、8 mm;耙齿材料为65号锰钢;耙齿入土角度的范围为10°~35°;3排齿的齿间距分别为:120、100、80 mm;耙齿入土深度亦可通过机具前端安装的限深轮进行调节。
影响残膜回收效果的另外3个主要因素:机具前进速度、耙齿入土深度、耙齿曲率半径则通过试验的方式进行分析优化,并进行验证试验以确定最优的结构和参数组合,使耙齿式垄作花生残膜回收机的机具工作性能达到最佳。
3.1 试验设计
3.1.1 试验条件及指标
本试验地点为锦州,前茬作物为花生,花生收获后进行收膜试验。花生种植方式为垄作,一垄双行,垄高100 mm;土壤类型为沙土,表层含水率约为10%(0~100 mm)。地膜宽度68 mm,厚度0.010 mm。收获前垄宽90 mm,覆膜宽度68 mm,收获后垄高11 mm。试验时,连续工作长度对保证工作效率有影响,长度过长导致残膜堆积、长度过短导致试验结果不够准确,故本试验设定连续工作长度为100 m。具体工作及机具主要指标如表2所示。
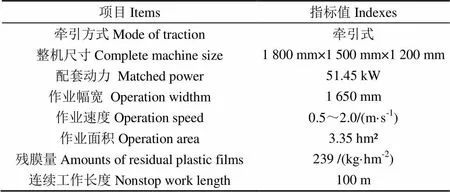
表2 机具主要指标
收膜性能良好且不壅土是残膜回收机能够连续作业的必要条件,残膜回收率直接反应了机具的工作效果,其值可用式(16)[26-27]表示
式中为残膜回收率,%;0为试验地所铺地膜的总重量,kg;1为使用残膜回收机回收残膜的质量,kg。
3.1.2 试验过程与结果
在收膜过程中存在很多影响残膜回收率的非线性因素,通常需要选用2次或者更高次的模型来逼近响应,模型可采用响应面法来建立[28-30]。机具前进速度、耙齿入土深度、耙齿曲率半径和残膜回收率分别用1、2、3、表示。
通过分析和试验可知:机具前进速度过慢会导致作业效率低下及壅土严重,速度过快会导致漏膜,所以试验时机具前进速度选择应在合理范围,即分别选为0.5、1.0、1.5 m/s;耙齿入土深度过浅会降低收膜率,影响机具收膜效果;过深会导致壅土严重和耙齿的剧烈变形,所以试验时耙齿的入土深度分别为5、10、15 mm;耙齿曲率半径过小会影响整体机架的高度进而导致壅土,过大会影响耙齿强度和收膜效果,所以试验时耙齿的曲率半径分别为195、225、255 mm。表3为试验因素水平,表4为田间试验结果。
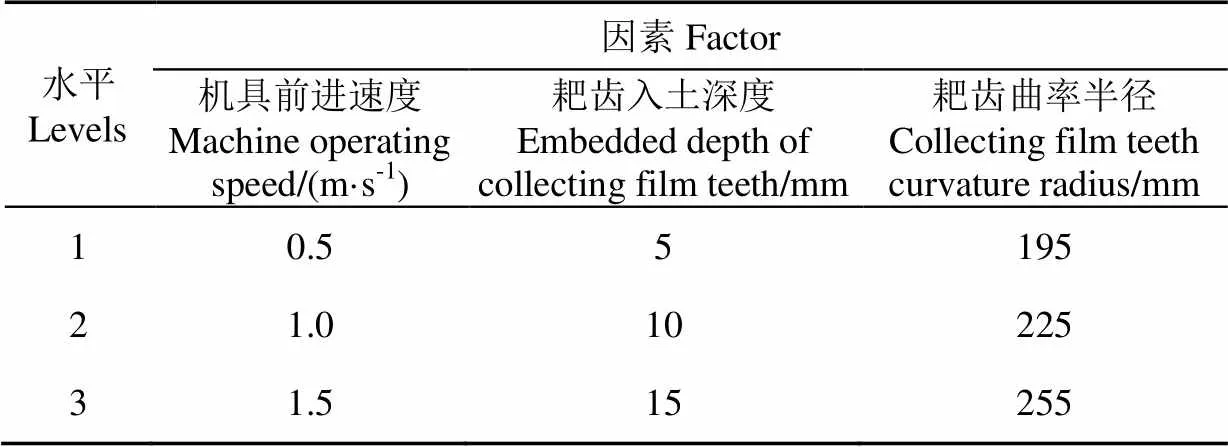
表3 试验因素水平

表4 田间试验结果
3.1.3 结果分析
应用软件Design expert对表3中数据拟合并进行方差分析,可得回归系数及其显著性检验如表5所示。
残膜回收机收膜率编码后的回归方程为式(17)
如表5所示,模型的显著性检验=85.79,<0.0001,说明二次回归方程的检验达到高度显著;且失拟性检验=2.5,>0.1为不显著,说明在试验范围内模型的拟合性非常好,可以用此模型对3个因素的影响效果进行分析和预测。
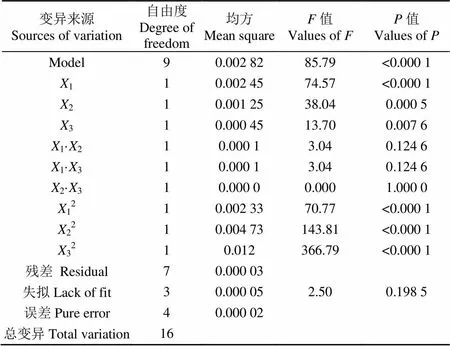
表5 模型显著性检验
根据残膜回收机收膜率编码后的回归方程为式(17),为了更直观地了解、分析残膜回收机机械性能与机具前进速度、耙齿入土深度、耙齿曲率半径之间的关系,借助MATLAB软件的图形设计技术,编辑代码可绘制直观、形象的残膜回收率与3个因素的四维切片图。由图7可知各影响因素的取值范围及变化。
3.2 影响因素分析及参数优化
3.2.1 影响因素分析
通过分析可知,机具前进速度、耙齿入土深度、耙齿曲率半径对残膜回收率均有显著性影响,且影响强弱次序为:机具前进速度>耙齿入土深度>耙齿曲率半径。1·2、1·3、2·3均为显著。如图8所示为残膜回收率的响应曲面3D效果。
a. 入土深度和前进速度对残膜回收率的影响
a. Influence of depth of collecting film teeth and machine operating speed on film recycling rate
b. 耙齿曲率半径和入土深度对残膜回收率的影响
b. Influence of film teeth curvature radius and the embedded depth of film teeth on film recycling rate
3.2.2 参数优化
残膜回收率是反应机具残膜回收效果的重要指标,在试验范围内要求其值越大越好。应用Design expert的寻优功能对其进行优化,可得各参数的优化结果如表5所示。如表5可知,预测的最佳试验条件为:机具前进速度1.2 m/s,耙齿入土深度11.09 mm,耙齿曲率半径222.33 mm,预测残膜回收率为91%。

表5 优化结果与实际值对比
3.3 验证试验
为了验证优化结果的可行性,现按预测的数值进行试验,为方便机具的加工,现设定机具前进速度为1.2 m/s,耙齿入土深度11 mm,耙齿曲率半径为222.5 mm。试验进行三次取平均值,最后得试验残膜回收率为93%,与预测值的相对误差为2%。试验结果与预测值很接近,验证了所建模型的准确性,优化后的残膜回收装置性能得到改善,完全符合残膜回收作业的要求。
4 结 论
1)耙齿的直径、材料、入土角度、齿间距均会对耙齿式垄作花生残膜回收机的工作性能产生影响;设计前、中、后耙齿的直径分别为10、8、8 mm;耙齿材料为65号锰钢;耙齿入土角度的范围为10°~35°;三排齿的齿间距分别为120、100、80 mm时机具收膜效果好。
2)机具前进速度、耙齿入土深度和耙齿曲率半径3个因素对残膜回收效果均有显著性影响,且影响强弱次序为:机具前进速度>耙齿入土深度>耙齿曲率半径。应用Design expert的寻优功能对其进行优化,优化后机具前进速度为1.2 m/s,耙齿入土深度11 mm,耙齿曲率半径222 mm,残膜回收率为93%。
优化后的耙齿式残膜回收机能基本满足垄作花生残膜的回收,但目前制约耙齿式残膜回收机大面积推广使用的是缺少有效的自动卸膜装置,应进一步研究并开发其自动卸膜装置。
[1] 严昌荣,梅旭荣,何文清,等. 农用地膜残留污染的现状与防治[J]. 农业工程学报,2006,22(11):269-272.
Yan Changrong, Mei Xurong, He Wenqing, et al. Present situation of residue pollution of mulching plastic film and controlling measures[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2006, 22(11): 269-272. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 杜晓明,徐刚,许端平,等. 中国北方典型地区农用地膜污染现状调查及其防治对策[J]. 农业工程学报,2005,21(增刊1):225-227.
Du Xiaoming, Xu Gang, Xu Duanping, et al. Mulch film residue contamination in typical areas of North China and counter measures[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2005, 21(Supp.1): 225-227. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 张丹,胡万里,刘宏斌,等. 华北地区地膜残留及典型覆膜作物残膜系数[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(3):1-5.
Zhang Dan, Hu Wanli, Liu Hongbin, et al. Characteristics of residual mulching film and residual coefficient of typical crops in North China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(3): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 马树庆,王琪,郭建平,等. 东北地区玉米地膜覆盖增温增产效应的地域变化规律[J]. 农业工程学报,2007,23(8):66-71.
Ma Shuqing, Wang Qi, Guo Jianping, et al. Geographical change law of effects of corn plastic mulching on increasing temperature and production in Northeast China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2007, 23(8): 66-71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 那明君,董欣,侯书林,等. 残膜回收机主要工作部件的研究[J]. 农业工程学报,1999,15(2):112-115.
Na Mingjun, Dong Xin, Hou Shulin, et al. Research on main components of the machine for retrieving the used plastic film after harvesting[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 1999, 15(2): 112-115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 侯书林,胡三媛,孔建铭,等. 国内残膜回收机研究的现状[J]. 农业工程学报,2002,18(3):186-190.
Hou Shulin, Hu Sanyuan, Kong Jianming, et al. Present situation of Research on plastic film residue collector in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2002, 18(3): 186-190. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李斌,王吉奎,蒋蓓. 新疆棉区残膜污染及其治理技术[J].农机化研究,2012,34(5):228-232.
Li Bin, Wang Jikui, Jiang Bei. The plastic film pollution and treatment technology in Xinjiang cotton area[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2012(5): 228-232. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 游兆延,顾峰玮,吴峰,等. 垄作花生残膜回收技术研究[J]. 农机化研究,2016(1):207-211.
You Zhaoyan, Gu Fengwei, Wu Feng, et al. Research on ridged peanut residue plastic film recycling technology[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016(1): 207-211. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 中华人民共和国国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴2015[J]. 北京:中国统计出版社.
[10] 徐弘博,胡志超,吴峰,等. 残膜回收收膜部件研析[J]. 农机化研究,2016,38(8):242-249.
Xu Hongbo, Hu Zhichao, Wu Feng, et al. Study on the collecting component of plastic film residue collector[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016, 38(8): 242-249. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 陈发,史建新,王学农,等. 弧型齿残膜捡拾滚筒捡膜的机理[J]. 农业机械学报,2006,37(6):36-41.
Chen Fa, Shi Jianxin, Wang Xuenong, et al. Study on collecting principle of arc-type tooth roller for collecting plastic residue[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2006, 37(6): 36-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 王吉奎,付威,王卫兵,等. SMS-1500型秸秆粉碎与残膜回收机的设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,27(7):168-172.
Wang Jikui, Fu Wei, Wang Weibing, et al. Design of SMS-1500 type straw chopping and plastic film residue collecting machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(7): 168-172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 胡志超,王海鸥,彭宝良,等. 4HLB-2型花生联合收获机起秧装置性能分析与试验[J[. 农业工程学报,2012,28(6):26-31.
Hu Zhichao, Wang Haiou, Peng Baoliang, et al. Performance analysis and experiment on operation process of plant lifting device in 4HLB-2 type peanut combine harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(6): 26-31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 陈有庆,王海鸥,胡志超. 半喂入花生联合收获损失致因与控制对策研析[J]. 中国农机化,2011(1):72-77.
Chen Youqing, Wang Haiou, Hu Zhichao. Research and analysis on harvest loss causes and control strategies of half-feeding peanut combine harvester[J]. Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2011(1): 72-77. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 胡志超,彭宝良,尹文庆,等. 4LH2型半喂入自走式花生联合收获机的研制[J]. 农业工程学报,2008,24(3):148-153.
Hu Zhichao, Peng Baoliang, Yin Wenqing, et al. Design of 4LH2 type half-feed and self-propelled peanut combine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2008, 24(3): 148-153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 胡志超,王海鸥,王建楠,等. 4HLB-2型半喂入花生联合收获机试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2010,41(4):79-84.
Hu Zhichao, Wang Haiou, Wang Jiannan, et al. Experiment on 4HLB-2 type half feed peanut combine harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2010, 41(4): 79-84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 侯书林,张淑敏,孔建铭,等. 弹齿式收膜机的主要结构设计[J]. 中国农业大学学报,2004,9(2):18-22.
Hou Shulin, Zhang Shumin, Kong Jianming, et al. Development of spring-tooth plastic fi1m collecting machine[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2004, 9(2): 18-22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 卢博友,杨青,薛少平,等. 圆弧形弹齿滚筒式残膜捡拾
机构设计及捡膜性能分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2000,16(6):68-71.
Lu Boyou, Yang Qing, Xue Shaoping, et al. Design of arc spring-tooth type collector for collecting mulching plastic film the collecting property analysis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2000, 16(6): 68-71.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 毕继业,王秀芬,朱道林. 地膜覆盖对农作物产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2008,24(11):172-175.
Bi Jiye, Wang Xiufen, Zhu Daolin. Effect of plastic-film mulch on crop yield[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2008, 24(11): 172-175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 聂理君. 残膜回收机弧形挑膜齿的应用研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆大学,2006:26-27.
Nie Lijun. Researching the Application of the arc Spring-finger in Plastic Film Residue Collector[D]. Urumqi:Xinjiang University, 2006: 26-27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 胡凯,王吉奎,李斌,等. 棉秆粉碎还田与残膜回收联合作业机研制与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(19):24-32.
Hu Kai, Wang Jikui, Li Bin, et al. Development and experiment of combined operation machine for cotton straw chopping and plastic film collecting[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(19): 24-32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 李明洋. 分区式残膜回收机的设计与试验研究[D]. 新疆阿拉尔:塔里木大学,2015:17-30.
Li Yangming. Design and Experiment Study on Zoning of Residual Film Recycling Machine[D]. Aral City, Xinjiang: TARIM University, 2015: 17-30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 张佳. 驱动耙残膜回收联合作业机的设计及试验研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆农业大学,2013:11-20.
Zhang Jia. Design and Experiment Study on Driving Target and Plastic Film Collecting Operation Machine[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2013: 11-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 谢建华,侯书林,付宇,等. 残膜回收机弹齿式拾膜机构运动分析与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2013,44(1):94-99.
Xie Jianhua, Hou Shulin, Fu Yu, et al. Motion analysis and experiment on spring-tooth mulching plastic film collector[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(1): 94-99. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 张东兴. 残膜回收机的设计[J]. 中国农业大学学报,1999(6):41-43.
Zhang Dongxing. Research and design on collector of used plastic film on farm field[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 1999(6): 41-43. (in Chinesewith English abstract)
[26] 李斌,王吉奎,胡凯,等. 残膜回收机顺向脱膜机理分析 与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(21):23-28.
Li Bin, Wang Jikui, Hu Kai, et al. Analysis and test of forward film removing mechanism for polythene film collector[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(21): 23-28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 李文龙,冯江,尹金东. 卷绕式拾膜机集膜轮的运动及力学分析[J]. 农机化研究,2010,32(11):74-77.
Li Wenlong, Feng Jiang, Yin Jindong. Kinematic analysis on the lifter’s winding component of mulch removal[J]. Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2010, 32(11): 74-77. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 张泽志,韩春亮,李成未. 响应面法在试验设计与优化中的应用[J]. 河南教育学院学报:自然科学版,2011,20(4):34-37.
Zhang Zezhi, Han Chunliang, Li Chengwei. Applicationof response surface method in experimenta and optimization[J]. Journal of Henan Institute of Education: Natural Science Edition, 2011, 20(4): 34-37. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 任露泉. 试验优化设计与分析[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社,2003:11-16.
[30] 陈魁. 试验设计与分析[M]. 北京:清华大学出版社,1996:22-26.
Design and parameter optimization on teeth residue plastic film collector of ridged peanut
Shi Lili, Hu Zhichao※, Gu Fengwei, Wu Feng, Wu Penglai
(,210014,)
With the increasing use of agricultural plastic film, the pollution it bringing is becoming more and more serious. It has become a problem which needs to be solved urgently. In China, the plant areas of peanut were expanded to 460.6 hm2in 2014, which accounted for about 17.9% of the global area of peanut crops. And its output reached to 16.481 7 million tons in the same year, which accounted for about 38.9 % of the global production of peanut yields. Therefore, design and experiment on plastic film collector of ridged peanut means a great deal to us. The collecting film teeth residue plastic film collector of ridged peanut was designed, and the whole structure and working mechanism of the machine were introduced. Therefore, the main operation components of it were designed and the structure parameters were determined at last. To solve the problem of residual film recycling after peanuts harvest, we designed the plastic film residue collector, and then optimized its parameters. The key structural parameters were determined by mechanism analysis and tests. The collecting film teeth diameter of the first row, the second row, and the third row were set as 10, 8 and 8 mm, respectively. The harrowing tooth was made of No.65 manganese steel, and the harrowing tooth’s lug angle ranges from 10° to 35°. The collecting film teeth space on the first row, the second row, and the third row were 120, 100 and 80 mm, respectively.The four-dimensional slice of MATLAB and response surface analysis was done on the machine speed, the harrowing tooth’s lug depth and its radius of curvature. The quadratic regression model between film removing ratio and machine operating speed,the embedded depth of the rake, tooth curvature radius was built. The optimal structure parameters of plastic film residue collector were obtained by response surface analysis. The response surface analysis of the model was optimized, and the effect of 3 factors on the recovery of the residual membrane was significant. The order of strength is: machine operating speed> embedded depth of the collecting film teeth > collecting film teeth curvature radius. The machine was optimized by parameter optimization. The machine operating speed, depth of collecting film teeth, tooth’s radius of curvature of machine was 1.2 m/s, 11mm, and 222 mm, respectively. And film recycling rate was about 93% through the field test. Its relative error was 2% compared with the predictive value. In conclusion, the optimization scheme was feasible. This paper could provide theoretical basis for optimization of related machines. With the preliminary experiment, the collecting film teeth residue plastic film collector of ridged peanut has good film quality, which meets the design requirements of plastic recycling machine. Removing mechanism on the collecting film teeth residue plastic film collector of ridged peanut is the further research.
agricultural machinery; plastic films; optimization; ridged peanut residue Plastic Film; response surface method
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.02.002
S223.5
A
1002-6819(2017)-02-0008-08
2016-05-31
2016-12-28
公益性行业(农业)科研专项“残膜污染农田综合治理技术方案”(201503105_08);中国农业科学院创新工程土下果实收获机械。
施丽莉,助理研究员,主要从事农机化装备研发。南京 农业部南京农业机械化研究所,210014。Email:1301706961@qq.com
胡志超,博士,研究员,博士生导师,主要从事农作物收获及产后加工技术与装备研究。南京 农业部南京农业机械化研究所,210014。Email:nfzhongzi@163.com
施丽莉,胡志超,顾峰玮,吴 峰,吴朋来. 耙齿式垄作花生残膜回收机设计及参数优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(2):8-15. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.02.002 http://www.tcsae.org
Shi Lili, Hu Zhichao, Gu Fengwei, Wu Feng, Wu Penglai. Design and parameter optimization on teeth residue plastic film collector of ridged peanut[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(2): 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.02.002 http://www.tcsae.org
