夏季东海微表层与下层海水营养盐的分布特征研究❋
2017-01-06王绍为吴冠伟杨桂朋
孙 毅, 于 娟, 王绍为, 吴冠伟, 杨桂朋❋❋
(1.中国海洋大学化学化工学院,山东 青岛 266100; 2.山东省青岛第一中学,山东 青岛 266002)
研究简报
夏季东海微表层与下层海水营养盐的分布特征研究❋
孙 毅1, 于 娟1, 王绍为2, 吴冠伟1, 杨桂朋1❋❋
(1.中国海洋大学化学化工学院,山东 青岛 266100; 2.山东省青岛第一中学,山东 青岛 266002)
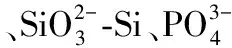
海洋微表层; 微表层营养盐; 富集因子; 东海
东海位于中国大陆以东,南起台湾海峡南端,北至长江北岸启东角与韩国济州岛的连线,东达冲绳海槽以西的琉球群岛,面积约为77×104km2。东海有2/3处于世界上最宽广的黄东海陆架上[1-3],是当前海洋研究的关键地区,也是世界上高生产力的区域之一[4]。海洋生态系统的主要生源物质—营养盐,是影响该区海洋初级生产力的重要因素,其输送、循环与更新是构成再生生命资源的物质与环境基础[5]。
海洋微表层是海洋一大气之间相互作用的重要界面,其厚度一般为50~200μm[6]。海洋微表层内含细菌、浮游生物、有机物、无机物、营养盐及多种污染物等。研究海洋微表层对海气通量计算、能量及物质在海洋界面的传输等具有十分重要的作用。另外,微表层是有机物和微生物富集的微环境[7],在此环境中可发生特殊的化学和微生物过程。这些过程产物或留在微表层中,或输入大气和表层水中,对促成海洋环境中天然物质和污染物的迁移将起到重要的作用。
目前,一些学者已对东海营养盐的空间分布进行了调查[8-10],但对东海海域微表层营养盐的相关研究相对不足。国内已经对黄渤海、大亚湾、胶州湾等部分海域微表层进行了初步研究[11-13],研究结果表明微表层作为独特的物理、化学、生物性质的薄膜有着不同于次表层物质分布的特点,且有富集效应。本文针对以往的研究不足,对东海微表层和表层海水中N、P、Si营养盐的时空分布进行了调查,并分析了微表层中各种营养盐的富集状况,为进一步了解营养盐在海-气界面的生物地球化学循环提供了科学依据。
1 采样及分析方法
1.1 采样站位
于2014年5月15日—6月13日随中国海洋大学“东方红2号”海洋科学考察船对营养盐进行现场采集样品,调查海区共设计7个断面25个调查站位(见图1),其中包含垂直断面2个,第一个垂直断面(DH1-3、DH1-5、DH1-7),为一条自西向东方向伸展的断面。第二个垂直断面(DH4-1、DH4-2、DH4-4、DH4-5)为一条自西北向东南方向伸展的断面。另外,我们还研究分析了DH2-1站营养盐的周日变化。从6月9日下午18:00开始,每隔3h取一次表层海水样进行分析,对DH2-1站位进行了24h的连续观测。
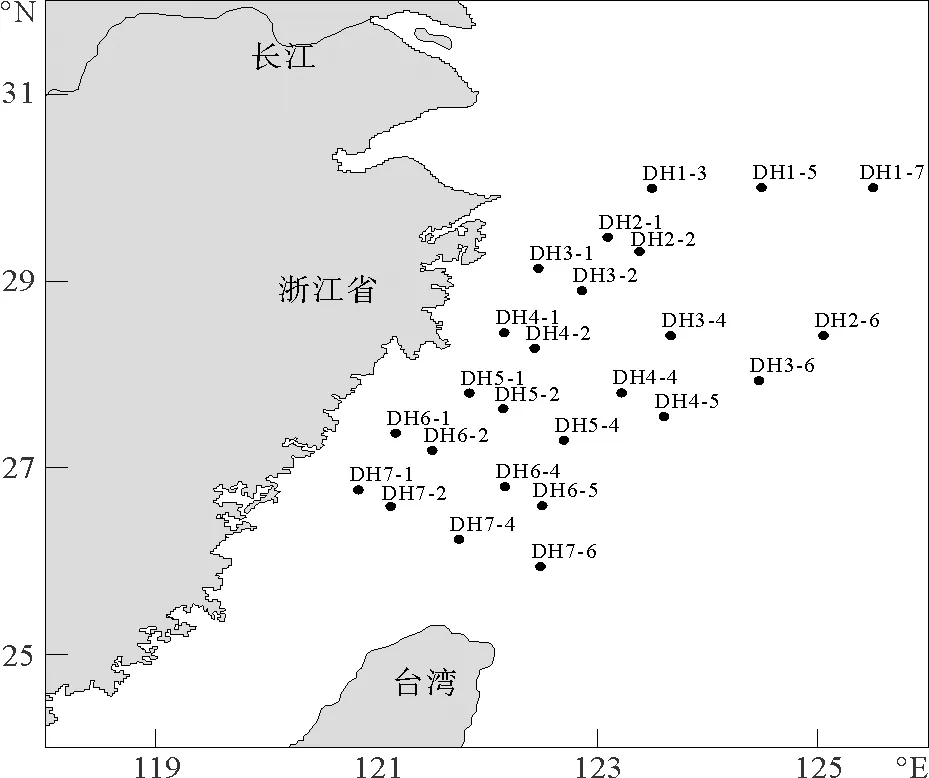
图1 东海采样站位图
1.2 调查方法
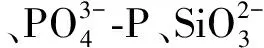
1.3 富集因子
微表层富集系数为微表层营养盐浓度与表层营养盐浓度的比值,微表层富集概率为富集系数大于1.0的样品数占总样品数的百分率。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 表层海水中温度、盐度的水平分布
温度和盐度的等值线基本都与海岸线平行,在调查区域的北端由于受陆源冲淡水的冲击,盐度等值线呈现东南方向水舌特征(见图2)。
2.2 微表层和表层海水中营养盐的水平分布
舟山群岛海域周围微表层和表层均具有较高浓度的DIN,分别在DH2-1、DH3-1站位其浓度达到最大值(微表层:32μmol/L;表层:54μmol/L),可能是长江、钱塘江等陆地径流携带大量营养盐流入杭州湾周边海域导致营养盐浓度偏高。图2显示低温、低盐的陆地径流呈水舌状分布流入东海。浙江沿岸海域微表层和次表层的DIN浓度相对偏低,可能是浮游植物大量生长摄取吸收营养盐导致DIN浓度偏低。东海东南部海域的微表层和表层中DIN浓度相差不大,且显著高于北部无陆源径流影响区,图2显示黑潮向陆架海入侵的一个高盐水舌,富含营养盐的黑潮次表层水涌升[15-16]可能是造成东南部DIN偏高的主要原因。
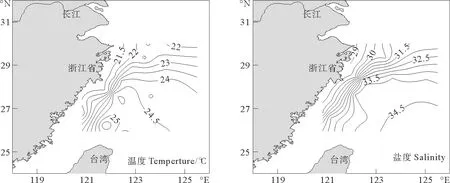
图2 表层海水温度、盐度的水平分布
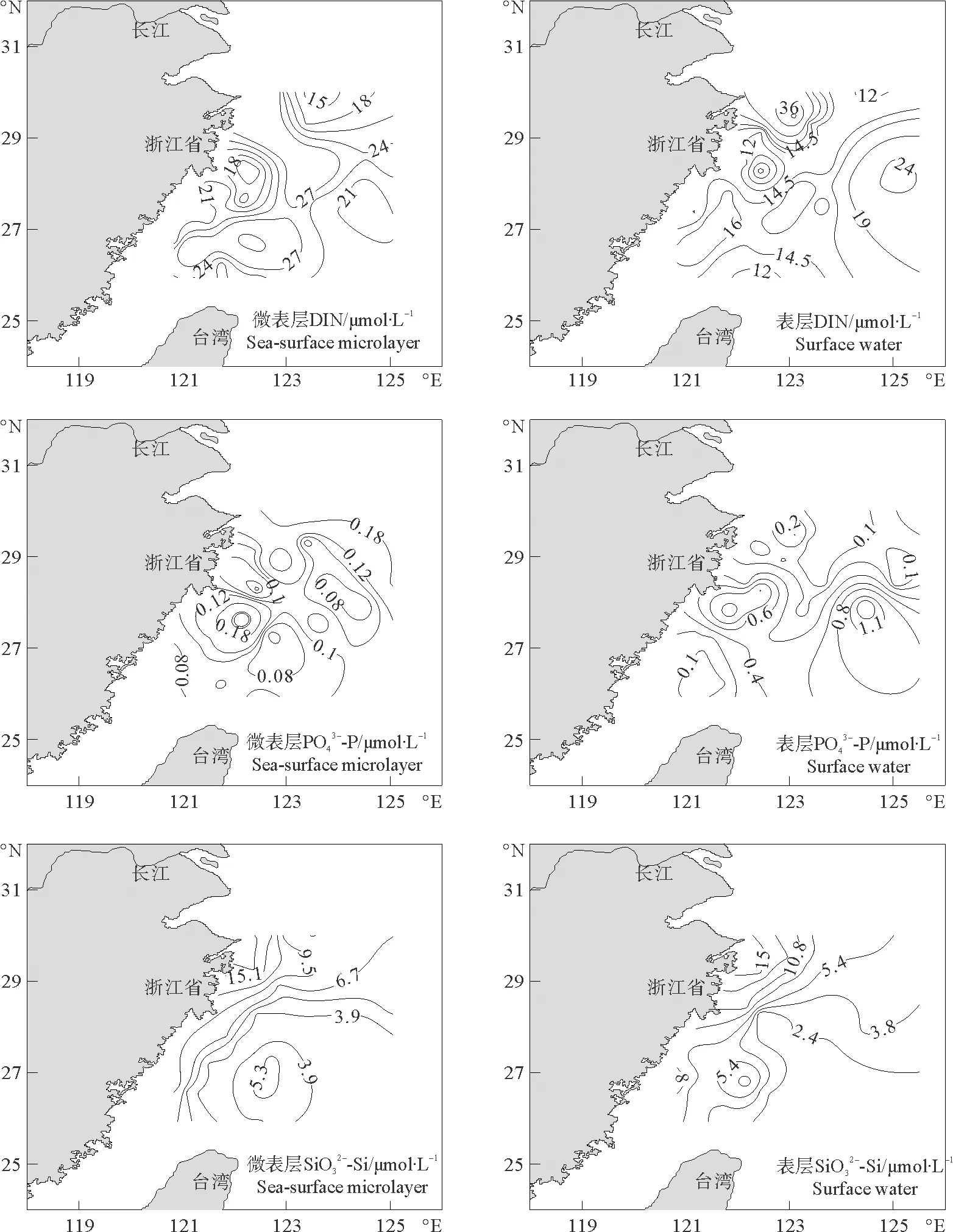
图3 东海微表层和表层中的水平分布
2.3 东海营养盐的断面垂直分布

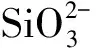
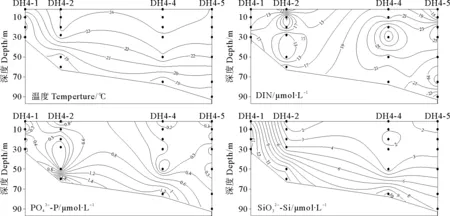
图4 东海中部断面温度和营养盐的垂直分布

2.4 微表层海水对营养盐的富集作用
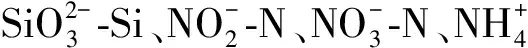

图5 长江口断面温度和营养盐的垂直分布
2.5 海水表层营养盐的周日变化
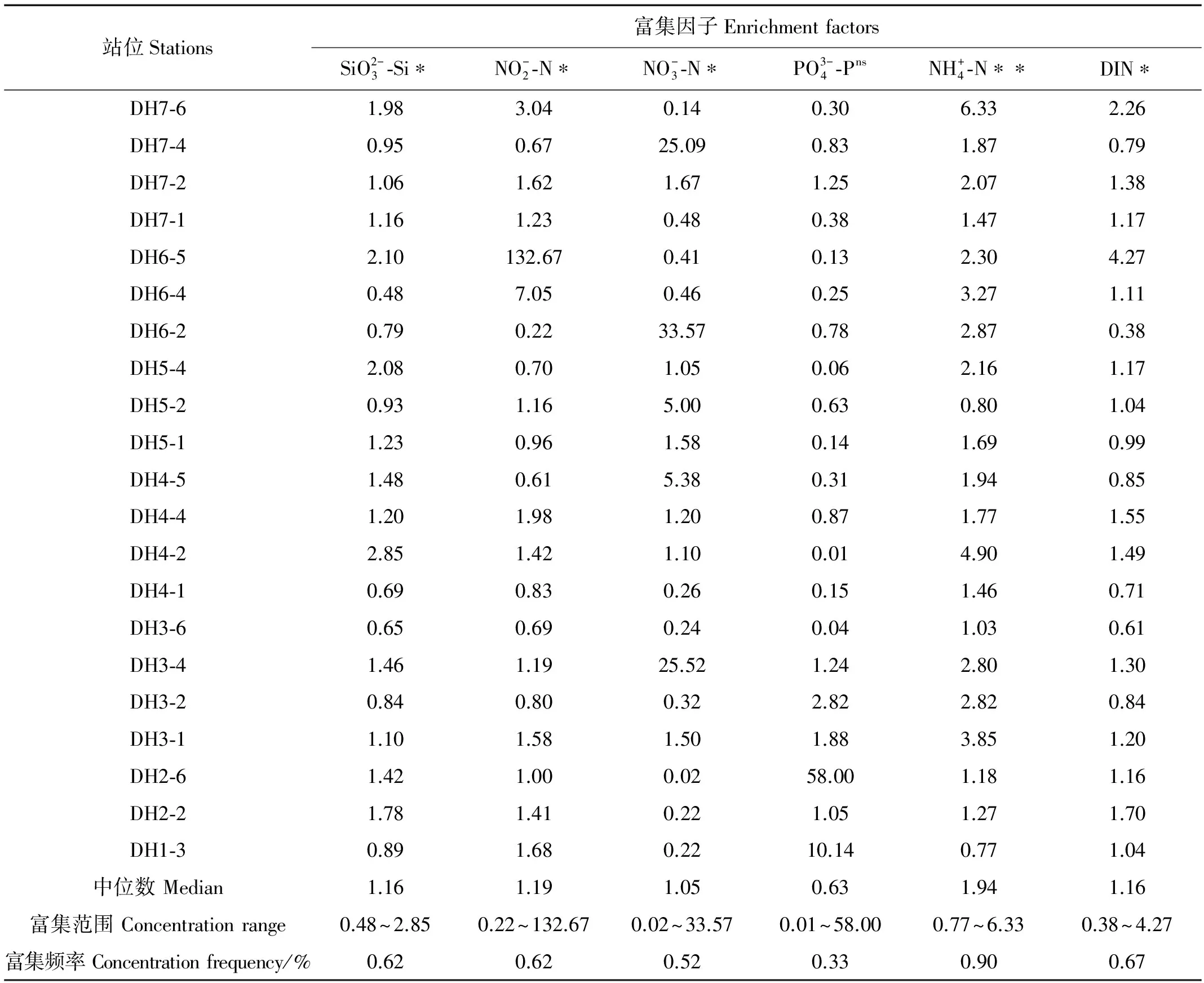
表1 营养盐在微表层中的富集因子
注:*Sig<0.05; **Sig<0.01; ns:Sig>0.05.

图6 DH2-1站位表层海水营养盐周日变化
3 结论

(2)东海中部断面及长江口断面由于温跃层影响呈现层化现象,长江口断面表层由于受到陆地径流影响营养盐浓度自西向东递减,底层由于受到生物分解及沉积物溶解影响,营养盐浓度较高。
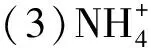
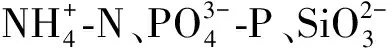
[1] Chu Peter, Chen Yu-chun, Akira Kuninaka. Seasonal variability of the Yellow sea/East China Sea surface fluxes and thermohaline structure[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2005, 22(1): 1-20.
[2] Yanagi T, Takahashi S. Seasonal variation of circulations in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 1993, 49(5): 503-520.
[3] 王颖. 中国海洋地理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996. Wang Ying. China OceanGeography[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996.
[4] Tadanori Arakaki, Yukiko Dokiya, Yukio Kodama, et al. Chemical characterization of sediments from the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea[J]. Geochemical Journal, 1994, 28: 31-46.
[5] 唐启升, 苏纪兰, 孙松, 等. 中国近海生态系统动力学研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2005, 20(12): 1288-1299. Tang Qisheng, Su Jilan, Sun Song, et al. Researchprogress of China coastal ecosystems dynamics[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2005, 20(12): 1288-1299.
[6] 张正斌. 海洋微表层的“物理—生物—化学”研究[M]. [s.l.]: 面向21世纪的科技进步与社会经济发展(上册), 1999. Zhang Zhengbin. “Physics-Biology-Chemistry” StudyoftheSea-surface Microlayer[M]. [s.l.]: Technological Progress and Socio-economic Development in the 21st Century (the first volume), 1999.
[7] Carlson D J. A field evaluation of plate and screen microlayer sampling techniques[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1982, 11(3): 189-208.
[8] 王保栋. 黄海和东海营养盐分布及其对浮游植物的限制[J]. 应用生态学报, 2003, 14(7): 1122-1126. Wang Baodong. Nutrients’distributions and their limitation on phytoplankton[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2003, 14(7): 1122-1126.
[9] 米铁柱, 姚庆祯, 孟佳, 等. 2011年春、夏季黄海、东海营养盐分布特征研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(3): 23-32. MiTiezhu, Yao Qingzhen, MengJia, et al. Study of nutrients’ distribution in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea in spring and summer[J]. Ocean and Limnology, 2012, 43(3): 23-32.
[10] 王修林, 孙霞, 韩秀荣, 等. 2002年春、夏季东海赤潮高发区营养盐结构及分布特征的比较[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2004, 35(4): 323-331. Wang Xiulin, Sun Xia, Han Xiurong, et al. Comparison of the structure and distribution of nutrient of the East China Seain the high incidence of red tide in summer[J]. Ocean and Limnology, 2004, 35(4): 323-331.
[11] 王文涛, 杨桂朋, 于娟, 等. 夏季黄海和渤海微表层和次表层海水中营养盐的分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(8): 2983-2991. Wang Wentao, Yang Guipeng, Yu Juan, et al. The distribution of nutrient of the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea in the sea surface microlayer and subsurface layer in summer[J]. Environmental Sciences, 2013, 34(8): 2983-2991.
[12] 陈晨, 杨桂朋, 高先池, 等. 胶州湾微表层和次表层海水中营养盐的分布特征及富营养化研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2012, 32(8): 1856-1865. Chen Chen, Yang Guipeng, Gao Xianchi, et al. Study of the distribution of nutrients and eutrophication in the sea surface microlayer and subsurface layer of JiaozhouBay[J]. Environmental Sciences, 2012, 32 (8): 1856-1865.
[13] 彭云辉, 王肇鼎, 孙丽华, 等. 大亚湾微表层和次表层海水营养盐的研究[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2002, 21(3): 310-316. Peng Yunhui, Wang Zhaoding, Sun Lihua, et al. The study of nutrients of the sea surface microlayer and subsurface layer in DayaBay[J]. Journal of Application Oceanography, 2002, 21(3): 310-316.
[14] Garrett W D. Collection of slick-forming materials from the sea surface[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1965, 10: 602-605.
[15] 郑锡建. 东海南部黑潮流域溶解磷酸盐的分布特征. 黑潮调查研究论文选(五)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1993: 372-379. Zheng Xijian. The distribution characteristics of dissolved phosphate in Kuroshio Basin of south of the East China Sea[M]. SelectedPapersof KuroshioSurvey Research(V). Beijing: Ocean Press, 1993: 372-379.
[16] 项有堂, 辛士河, 王东衬, 等. 东海黑潮区海水无机氮的分布特征及其成因探讨. 黑潮调查研究论文文选(五)[JM]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1993: 363-370 . Xiang Youtang, Xin Shihe, Wang Dongchen, et al. Discussion of the distribution and the causes of inorganic nitrogen in Kuroshio region of the East China Sea. Kuroshio survey research papers(V)[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 1993: 363-370.
[17] Harvey H W. The Chemistry and Fertility of Seawaters[M]. [s.l.]: Cambridge University Press, 1955, 224.
[18] Conway H L. Interactions of inorganic nitrogen in the uptake and assimilation by marine phytoplankton[J]. Mar. Biol., 1977, 39: 221-232.
[19] Carpenter E J, Dunham S. Nitrogenous Nutrient Uptake, Primary Production, and Species CompositionofPhytoplankton in Carmans River estuary LongIsland[J]. LimnoOceanogr, 1985, 30(3): 513-526.
[20] 沈志良, 陆家平, 刘兴俊, 等. 长江口区营养盐的分布特征及三峡工程对其影响[J]. 海洋科学集刊, 1992, 33; 107-129. Shen Zhiliang, Lu Jiaping, Liu Xingjun, et al. The distribution of nutrients in Changjiang Estuary and the impact on Three Gorges Project[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1992, 33; 107-129.
[21] 王保栋, 战闰, 藏家业. 长江口及其邻近海域营养盐的分布特征和输送途径[J]. 海洋学报, 2002, 24(1): 53-58. Wang Baodong, Zhan Run, ZangJiaye, et al. The distribution and transportation of Yangtze River Estuary and its adjacent waters[J]. Journal of Ocean, 2002, 24(1): 53-58.
[22] 赵骞, 田纪伟, 赵仕兰, 等. 渤海冬夏季营养盐和叶绿素a的分布特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2004, 28(4): 34-39. Zhao Qian, Tian Jiwei, Zhao Shilan, et al. The distribution characteristics of nutrients and chlorophyll a in summer and winter in BohaiSea[J]. Marine Science, 2004, 28(4): 34-39.
[23] Zhang J, Chen S Z, Yu Z G, et al. Factors influencing changes in rainwater composition from urban versus remote regions of the Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 1999, 104(D1): 1631-1644.
[24] 陈立奇, 杨旭林, 杨荣坤, 等. 黑潮海域上空气溶胶化学特征. 黑潮调查研究文选(四)[M]. [s.l.]: [s.n.], 1992, 195-307. Chen Liqi, Yang Xulin, Yang Rongkun, et al. The Chemical Characteristics of the Aerosol Over the Kuroshio Waters. Kuroshio Investigation Anthology(VI)[M]. [s.l.]: [s.n.], 1992, 195-307.
[25] 刘素美. 黄、渤海沉积物-水界面营养盐的交换及其质量平衡[D]. 青岛: 青岛海洋大学, 2000. Liu Sumei. Mass Balance and Exchange of Nutrients in Sediment-Water Interface of theYellow Sea and BohaiSea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of Qingdao, 2000.
[26] 戚晓红, 刘素美, 张经, 等. 东海赤潮高发区沉积物中营养盐再生速率的研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 2003, 14(7): 1112-1116. Qi Xiaohong, Liu Sumei, Zhang Jing, et al. Study of nutrients regeneration rate in high incidence of red tide in East China Sea[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2003, 14(7): 1112-1116.
[27] 王修林, 辛宇, 石峰, 等. 溶解无机态营养盐在渤海沉积物-海水界面交换通量研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 37(5): 795-800. Wang Xiulin, Xin Yu, Shi Feng, et al. Study of nutrient exchange fluxes in the sediments-water interfaceinBohaiSea[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2007, 37(5): 795-800.
[28] 吴志坚, 李军, 丁海兵, 等. 海洋微表层中物质富集机理[J]. 海洋科学, 1998, 8(1): 21-22. Wu Zhijian, Li Jun, Dinghai Bing, et al. The enrichment mechanism of matter in marine micro-surface layer[J]. Marine Science, 1998, 8 (1): 21-22.
[29] Horrigan S G, Carlucci A F, Williams P M. Light inhibition of nitrification in sea-surface films [J]. Journal of Marine Research, 1981, 39: 557-595.
[30] Zhang Z, Liu L, Liu C, et al. Studies on the sea surface microlayer: II. The layer of sudden change of physical and chemical properties[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2003, 264(1): 148-159.
[31] 潘明祥, 张正斌, 王肇鼎, 等. 大亚湾海水微表层生物-化学研究Ⅱ. (二)生物-化学特性的周日变化规律[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2000, 19(2): 57-77. Pan Mingxiang, Zhang Zhengbin. The bio-chemical research of the sea-surface microlayer of Daya Bay: Ⅱ. Diurnal variation of bio-chemical feature[J]. Law of Tropical Oceanography, 2000, 19(2): 57-77.
[32] 王朝晖, 杨宇峰, 宋淑华, 等. 大亚湾海域营养盐的季节变化及微表层对营养盐的富集作用[J]. 环境科学学报, 2011, 31(2): 307-315. Wang Zhaohui, Yang Yufeng, Song Shuhua, et al. Enrichment of nutrients of seasonal changes in the sea-surface microlayer of Daya Bay[J]. Environmental Sciences, 2011, 31(2): 307-315.
[33] 王文涛, 杨桂朋, 于娟, 等. 夏季黄海和渤海微表层和次表层海水中营养盐的分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(8): 2983-2991. Wang Wentao, Yang Guipeng, Yu Juan, et al. Distribution of nutrients in sea surface microlayer and subsurface layer of the Yellow Sea and BohaiSea[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34 (8): 2983-2991.
[34] 冯士笮, 李凤岐, 李少菁主编. 海洋科学导论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1999. Feng Shizhen, Li Fengqi, Li Shaojing. Introduction of Marine Science[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1999.
责任编辑 徐 环
Distribution of Nutrients in the Sea-Surface Microlayer and the Buck Water of the East China Sea in Summer
SUN Yi1, YU Juan1, WANG Shao-Wei2, WU Guan-Wei1, YANG Gui-Peng1
(1.College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China; 2.Qingdao No.1 High School, Qingdao 266002, China)
sea-surface microlayer; subsurface; nutrients; enrichment factor; the East China Sea
2014青岛世界园艺博览会植物馆海洋展陈项目资助国家自然科学基金项目(41320104008);教育部“长江学者”奖励计划项目;山东省“泰山学者”建设工程专项资助 Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (41320104008); Ministry of Education “Cheung Kong Scholar” Award Projects; Shandong Province “Taishan Scholar” Construction Projects
2015-08-16;
2015-12-07
孙 毅(1990-),男,硕士生。E-mail:972120704@qq.com
❋❋ 通讯作者:E-mail: gpyang@ouc.edu.cn
P734.4+4
A
1672-5174(2017)01-052-09
10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20150285
孙毅, 于娟, 王绍为, 等. 夏季东海微表层与下层海水营养盐的分布特征研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 47(1): 52-60.
SUN Yi, YU Juan, WANG Shao-Wei, et al. Distribution of nutrients in the sea-surface microlayer and the Bulk Water of the East China Sea in summer[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(1): 52-60.
