二氮化锇结构和弹性性质的第一性原理计算
2016-12-30詹国富莫玉梅
詹国富, 莫玉梅
(广东理工学院 工业自动化系,广东 肇庆 526100)
二氮化锇结构和弹性性质的第一性原理计算
詹国富, 莫玉梅
(广东理工学院 工业自动化系,广东 肇庆 526100)
研究了在莹石结构(C1),黄铁矿结构(C2)和白铁结构(C18)下二氮化锇的结构和弹性性质。通过密度泛函理论,计算了它不同的结构参数和体弹模量、剪切模量以及弹性常数。弹性常数的计算反应了OsN2具有很强的硬度。
密度泛函理论;结构参数;弹性性质
过渡金属的氮化物、氧化物、硼化物等因其优越的物理化学性质,诸如耐高温、半导体性质、超导性能等[1],因而在光学涂层、耐磨涂层、切割工具方面有着广泛地应用[2]。众多研究3d和4d金属化合物的工作已经做过了,而铂、铱、铑的氮化物在极端条件下相继被合成出来[3-7],相关的性质也有了一定的研究。作为过渡金属的二氮化锇,它的一些常温常压下的结构性质、电子结构等都有了一定的了解[8,9]。
1 理论计算方法
总能量计算是基于密度泛函理论,采用Perdew-Burke-Ernergof(PBE)交换关联泛函[10]和广义梯度近似(GGA)的交换关联势。整个计算过程用Spanish Initiative for Electronic Simulations with Thousands of Atoms (SIESTA)[11]计算完成。采用原子轨道线性组合方法来计算总能和原子间作用力。采用Sanky-niklewsky赝原子轨道[12](PAOs)形成赝势,电子与芯核之间的相互作用通过分离的Troullier-Martins[13]模守恒赝势来模拟。对于锇来说,其价电子为5d66s2,而对于氮来说价电子为2s22p3。为了达到一定要求的计算精度,所以原子弛豫到原子间作用力小于0.04eV/Å;莹石结构(C1)、黄铁矿结构(C2)、白铁矿结构(C18)的截断能分别为700eV、800eV和700eV;布里渊区积分采用Monkhorst-Pack形式的K点网格,分别取12×12×12、12×12×12、15×12×11,所有自洽计算最后能量的收敛精度都达到0.1meV/atom。
2 结果与讨论
通过对OsN2三种结构进行结构(C1莹石结构、C2黄铁矿结构、C18白铁矿结构)优化,在优化过种中允许对原胞参数和坐标进行弛豫,得到不同结构的能量—体积曲线后。通过Brich-Murnaghan状态方程[11,12]对能量-体积曲线进行拟合,得到零温零压三种结构的晶格参数、体积和体模量及其一阶导数和其它的理论实验结果,一起列在了表1中。从中可以看到,计算结果总体上来说与其它的计算结果、实验结果比较一致。
其次,计算了三个结构的弹性常数(C1莹石结构、C2黄铁矿结构、C18白铁矿结构),体弹模量,剪变模量以及杨氏模量,同时列出了其它的计算结果与相关的实验结果。从表2中可以看到,计算结论与相关理论计算结果及实验结果吻合的比较好。

表1 零温零压下二氮化锇的晶格参数(Å),平衡态体积(Å3),体弹模量(GPa)以及体弹模量一阶导数
aRef.[14],bRef.[10],cRef.[15]dRef.[16]eRef.[6]
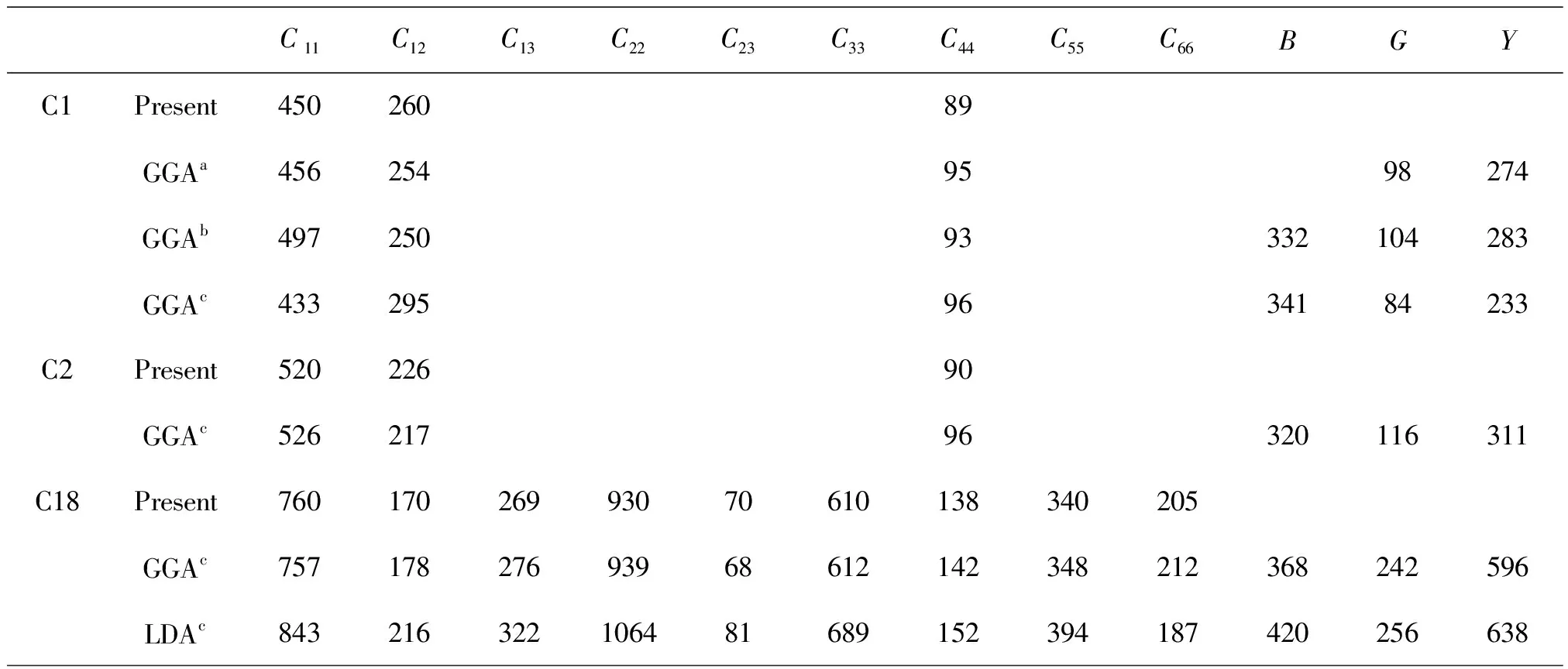
表2 零温零压下二氮化锇的弹性常数、体模量、切变模量及杨氏模量计算结果
aRef.[14],bRef.[10],cRef.[9]
3 总结
从晶体结构参数及相应的体弹模量的讨论可以发现,OsN2具有较高硬度,能够承受的压力非常大。不同结构的弹性常数显示其弹性性质各向异性。C1结构和C2结构各弹性常数比较接近,反映出其结构较相似;而C18结构的各弹性常数与C1、C2结构相差较大,反映其结构上的差异很大。
[1] WU Z, ZHAO E. Structural stability and electronic properties of Co2N, Rh2N and Ir2N[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2008, 69(11): 2723-2727.
[2] TOTH L E. Transition metal carbides and nitrides [M]. New York: Academic press, 1974.
[3] GREGORYANZ E, SANLOUP C, SOMAYAZULU M, et al. Synthesis and characterization of a binary noble metal nitride[J]. Nature materials, 2004, 3(5): 294-297.
[4] CROWHURST J C, GONCHAROV A F, SADIGH B, et al. Synthesis and characterization of the nitrides of platinum and iridium[J]. Science, 2006, 311: 1275-1278.
[5] JUN L, XIAO Y K, ZHEN H W, et al. Pressure-induced structural transition and thermodynamic properties of RhN2and the effect of metallic bonding on its hardness[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2012, 21(8): 086103-086107.
[6] YOUNG A F, SANLOUP C, GREGORYANZ E, et al. Synthesis of novel transition metal nitrides IrN2and OsN2[J]. Physical review letters, 2006, 96(15): 155501-155505.
[7] CROWHURST J C, GONCHAROV A F, SADIGH B, et al. Synthesis and characterization of nitrides of iridium and palladium[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2008, 23(1): 1-5.
[8] FAN C Z, ZENG S Y, LI L X, et al. Potential superhard osmium dinitride with fluorite and pyrite structure: First-principles calculations[J]. Phys. Rev. B. 2006, 74 (12):125118-125123.
[9] WU Z, HAO X, LIU X, et al. Structures and elastic properties of OsN2investigated via first-principles density functional calculations[J]. Physical Review B, 2007, 75(5): 054115-054119.
[10] PERDEW J P, BURKE K, ERNZERHOF M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple[J]. Physical review letters, 1996, 77(18): 3865-3869.
[11] ORCLEJON P, ARTACHO E,SOLER J M. Self-consistent order-N density-functional calculations for very large systems[J]. Phys. Rev. B (Rapid Commun). 1996, 53(16): 10441-10446.
[12] SOLER J M, ARTACHO E, GALE J D, et al. The SIESTA method for ab initio order-N materials simulation[J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2002, 14(11): 2745-2749.
[13] SANKEY O F, NIKLEWSKI D J. A initio multicenter tight-binding model for molecular-dynamics simulations and other applications in covalent systems[J]. Physical Review B, 1989, 40(6): 3979-3984.
[14] ZHANG M, WANG M, CUI T, et al. Electronic structure, phase stability, and hardness of the osmium borides, carbides, nitrides, and oxides: First-principles calculations[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2008, 69(8): 2096-2102.
[15] LIU C M, GE N N, FU Z J, et al. PHYSICS OF GASES, PLASMAS, AND ELECTRIC DISCHARGES: Structural and thermodynamic properties of OsN2from first-principles calculations[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2011, 20(4): 045101-045104.
[16] WU Z, HAO X, LIU X, et al. Structures and elastic properties of OsN2investigated via first-principles density functional calculations[J]. Physical Review B, 2007, 75(5): 054115- 054120.
Structure and Elastic Properties of OsN2from First-principles Study
ZHAN Guo-fu, MO Yu-mei
(Department of Industrial Automation, Guang Dong Polytechnic College, Zhaoqing Guangdong 526100, China)
We have studied the structure and elastic properties of OsN2in fluorite, pyrite and marcasite. The equilibrium lattice parameter, bulk modulus ,its pressure derivative and elastic modulus are calculated. The result of elastic modulus indicate the hardness of OsN2is high.
density functional theory; structure parameter; elastic properties
2016-09-29
冲压模具设计精品资源共享课(JPKC2015003)
詹国富(1988-),男,江西鄱阳人,硕士,主要从事原子分子结构与光谱结构分析,超硬材料的弹性和热力学性质计算。E-mail: qingkongyiye@163.com
O469
A
1004-2237(2016)06-0060-03
10.3969/j.issn.1004-2237.2016.06.013
